
The diverse landscape of India is mirrored not only in its culture, languages, and traditions but also in the distinctive health indicators that prevail across its various states. The country’s vast geographical expanse and socio-economic heterogeneity contribute to significant regional variations in health outcomes and indicators. From the bustling urban centers to the remote rural hinterlands, each Indian state exhibits unique patterns in terms of healthcare accessibility, disease prevalence, nutritional status, and overall well-being. Understanding these regional variations is crucial for policymakers and public health officials to tailor interventions and strategies that address the specific health challenges faced by different states. This complex tapestry of health indicators reflects the multifaceted nature of India’s public health landscape, underscoring the need for nuanced and region-specific approaches to promote overall well-being across the nation.
Contents
Answer
India exhibits significant regional variations in health indicators among its states, reflecting diverse socioeconomic and geographical factors.
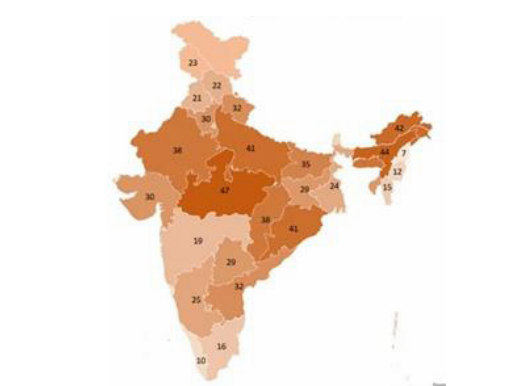
Regional variations in health indicators among the Indian States are as follows:
- Regional variations in Infant Mortality Rate (IMR)
- Northern states like Uttar Pradesh and Bihar often experience higher IMRs compared to southern states like Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
- In 2020, the IMR in Bihar was 51.9, while the IMR in Kerala was 9.1
- Factors such as female literacy (In Bihar, the female literacy rate is only 63%, while the female literacy rate in Kerala is 95%), child marriage (In Bihar, 34% of girls are married before the age of 18), other socio-economic indicators contribute to this disparity.
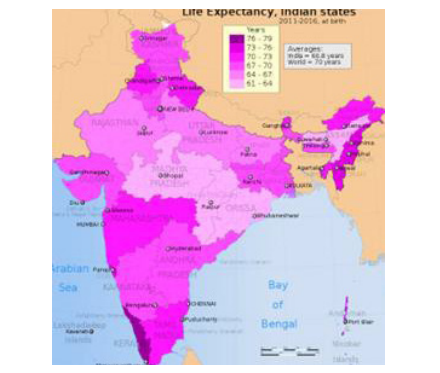
- Regional Variations in Life Expectancy
- Southern states generally boast higher life expectancies than northern states.
- As per the World Health Organization (WHO), the average life expectancy at birth in India is 68.3 years.
- However, there is a wide range of disparities, ranging from 61.5 years in Uttar Pradesh to 77.7 years in Kerala.
- Primary reasons for this are Socioeconomic status (Southern states tend to be wealthier than northern states), Lifestyle factors (People in southern states tend to have healthier lifestyles than people in northern states. They are more likely to be physically active and less likely to smoke or drink alcohol), Access to healthcare.

- Disease Prevalence
- Geographical features influence disease prevalence.
- For instance, states with tropical climates may face higher incidences of vector-borne diseases like malaria and dengue, impacting health indicators in those regions e.g., High prevalence of Dengue and other tropical infectious diseases in Bihar.
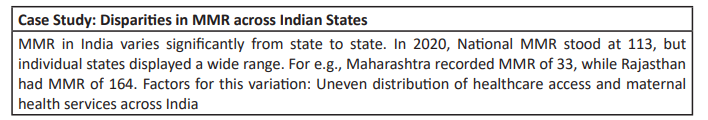
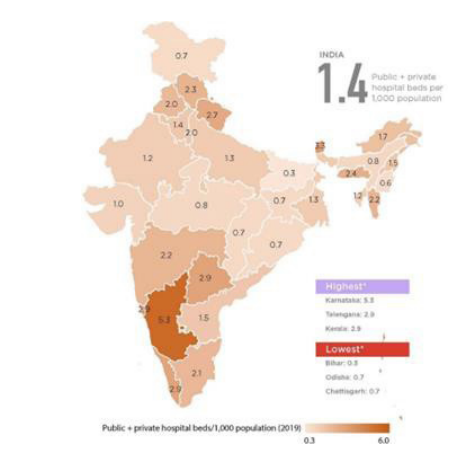
- Access to Healthcare Infrastructure
- Variations in access to healthcare infrastructure contribute to health disparities.
- States with better-developed healthcare systems, such as Maharashtra and Karnataka, often exhibit better health outcomes compared to states with limited infrastructure like UP and Northeastern states.
Regional variations in health indicators in India are influenced by a complex interplay of geographical, socioeconomic, and environmental factors. National Health Mission, Janani Suraksha Yojana, Anaemia Mukt Bharat Abhiyan, Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana are just a few of the many programs that the Government of India has implemented to reduce healthcare disparity in the country. These programs have made significant progress in improving access to healthcare services for poor and vulnerable populations.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

