
Organic farming holds immense significance in the context of sustainable agricultural development in India, as it represents a holistic approach to cultivation that prioritizes environmental health, biodiversity conservation, and long-term viability. In a country where agriculture is a cornerstone of the economy and a livelihood for a significant portion of the population, the shift towards organic farming has the potential to address pressing issues such as soil degradation, water pollution, and the overuse of chemical inputs. Embracing organic practices not only promotes healthier ecosystems but also ensures the production of nutrient-rich, chemical-free crops, contributing to the well-being of both consumers and the environment. This discussion explores the multifaceted importance of organic farming in India, considering its role in fostering sustainability, enhancing food security, and creating a resilient agricultural system that can withstand the challenges posed by climate change and evolving global demands.
Contents
Answer
India is pre-eminently an agricultural country. The environment and people are impacted differently by modern agriculture and organic farming methods. Increased GHG emissions, land erosion, water pollution & human health are significant consequences of traditional agriculture. Organic farming reduces carbon emissions, improves soil health & reloads natural Eco systems.
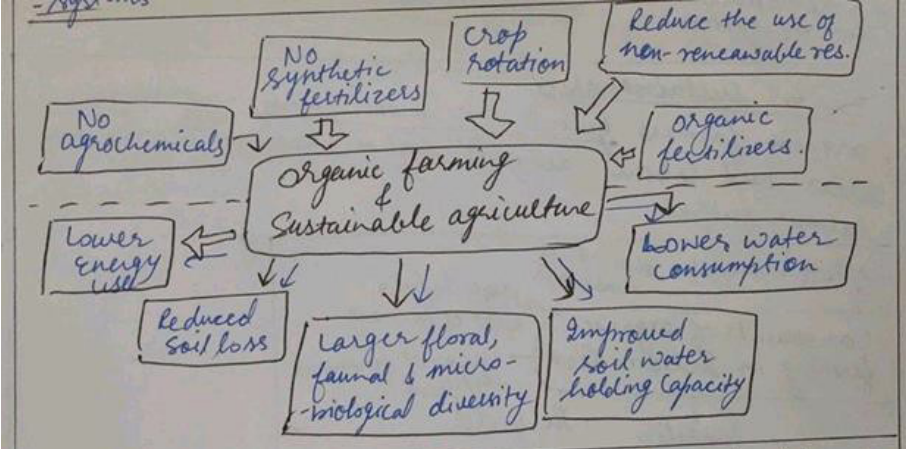
ORGANIC FARMING TOWARDS SUSTAINABLE AGRICULTURE DEVELOPMENT
Agriculture is at the heart of Goal 2 in the sustainability agenda, which strives to eliminate hunger. But to varying degrees agricultural sector is also involved in all SDGs. Sustainable agriculture integrates 3 main goals – environmental health, economic profitability, and social & economic equity.
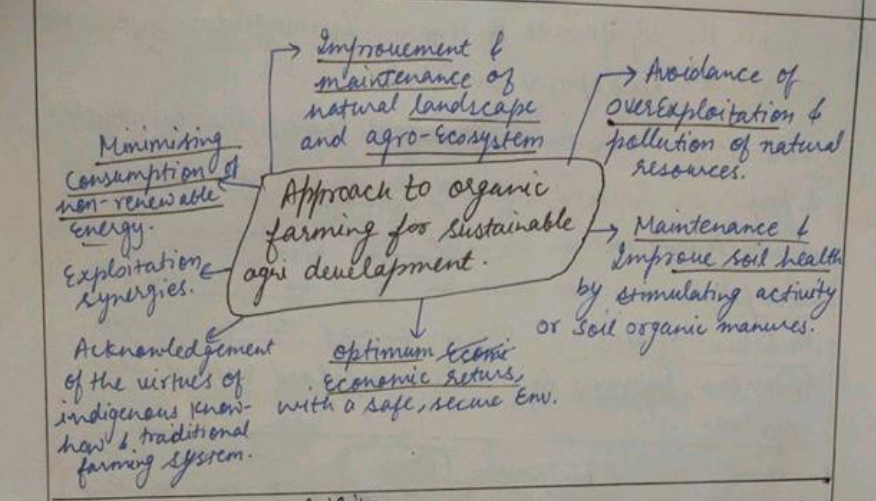
CONSTRAINTS OF ORGANIC FARMING IN INDIA IN THE PAST
- Lack of awareness
- Shortage of biomass
- Lack of financial support to farmers
- Low yield in initial days
- Inability to meet export demand
- High input cost of farming
Sustainable agriculture methods
- polyculture,
- Crop residue management (crm),
- biodynamic and organic farming,
- integration of livestock and crops,
- sustainable agriculture intercropping,
- mulching,
- Conservation tillage, using biofuels and zero-emissions transport, agroforestry,
- urban agriculture, etc.

Organic farmers generate 30% more employment in rural areas and labor achieves higher returns per unit of labor output.
Recently, the government of India has implemented no. Of schemes & programs for boosting organic farming for sustainable agricultural development.
- The paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana
- Mission for integrated development of horticulture
- National mission for sustainable agriculture
- Rashtriya krishi vikas yojana.
Zero budget natural farming (znbf): the practice of growing crops without the use of any external inputs such as pesticides & fertilisers.
Indian agriculture can become sustainable if more & more farmers successfully adopt organic & natural farming in with coordination of schemes of GOI. Lakshadweep groups of islands were declared as an organic agricultural area under the PGS of India. Sikkim became 1st 100% organic state in 2016.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

