
Information and Communication Technology (ICT) encompasses the utilization of digital tools and platforms for communication, information dissemination, and problem-solving.
It includes technologies such as the internet, mobile phones, computers, and software applications.
Contents
Economic Growth:
- ICT has propelled the growth of IT and outsourcing industries in cities like Bangalore, Hyderabad, and Pune.
- Example: Bengaluru, known as the Silicon Valley of India, hosts numerous IT companies and startups, contributing significantly to the city’s economic development.
Rural Development:
- Initiatives like Common Service Centers (CSCs) have extended government and private services to rural areas.
- Example: CSCs provide services like Aadhaar enrollment, utility bill payments, and banking services in remote villages, enhancing rural development.
Education:
- ICT initiatives like digital classrooms and online courses have improved educational access in remote areas.
- Example: The National Digital Library (NDL) offers free access to educational resources, benefiting students and teachers in underserved regions.
Healthcare:
- Telemedicine services enable remote consultations and specialist care access in rural areas.
- Example: Apollo TeleHealth Services connect patients in remote villages with doctors via video consultations, improving healthcare accessibility.
Infrastructure Development:
- Smart city projects leverage ICT for efficient urban planning and service delivery.
- Example: The Smart Cities Mission in cities like Jaipur and Pune integrates technology for better traffic management, waste disposal, and public safety.
Entrepreneurship:
- ICT facilitates entrepreneurship by providing digital platforms and access to markets.
- Example: Bengaluru’s startup ecosystem, supported by venture capital firms and incubators, fosters innovation and job creation.
Connectivity:
- BharatNet project enhances rural connectivity with broadband internet access.
- Example: Villages in Rajasthan and Tamil Nadu now have internet connectivity, enabling online communication, education, and commerce.
Concerns
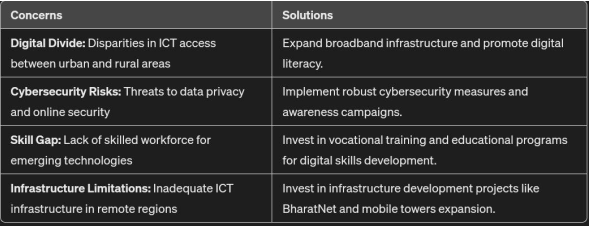
Conclusion:
However, addressing concerns like the digital divide, cybersecurity risks, and infrastructure limitations is crucial for ensuring inclusive development. By investing in infrastructure, promoting digital literacy, and fostering innovation, India can harness the full potential of ICT for sustainable and equitable growth in the future.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

