
In recent years, the role of Indian Earth Observation Satellite (EOS) technology has become increasingly pivotal in revolutionizing weather forecasting and disaster management. India, with its robust space program led by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), has made significant strides in deploying advanced satellites equipped with state-of-the-art instruments designed to monitor and analyze Earth’s atmosphere, oceans, and landmasses. These satellites play a crucial role in gathering real-time data and providing invaluable insights into meteorological patterns, enabling more accurate and timely weather predictions. Additionally, the integration of Earth Observation Satellite data has proven instrumental in enhancing disaster management strategies, allowing for proactive measures in mitigating the impact of natural calamities such as cyclones, floods, and earthquakes. This paradigm shift towards space-based technologies underscores India’s commitment to leveraging innovation for the benefit of society, reinforcing the nation’s resilience in the face of environmental challenges.
Contents
Answer
India launched its 1st Earth Observing satellite in 1988 named IRS-1A. From then till now these satellites provided necessary data in a diversified spatial, spectral, and temporal resolution to cater to different requirements in the country and for global usage. The data from these satellites are used for several applications covering agriculture, water resources, urban planning, rural development, mineral prospecting, environment, forestry, ocean resources, and disaster management.
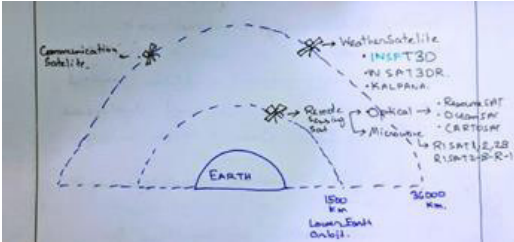

Effectiveness of Earth Observing Satellite:
- Continuation of Weather Forecasting.
- Real-time data prediction of Climatic Events like Cyclone tracking, intensity, predicting of landfall.
- All day and night weather forecasting is possible, due to the use of the microwave infrared spectrum.
- Efficiency of Weather Forecasting increases. due to. –
● Use of more modern standard equipment k imaging technique used.
● Weather forecasting is Not only by Cloud Cover – it considers 4 major parameters – Ocean temperature, wind direction, moisture content, air temperature, and pressure. - The NISAR satellite can examine land subsidence, landslide, and accounting damage in Himalayan disaster-prone areas using Radar Imaging Technology.
Major drawbacks still persistent in these technologies
- Climate & weather forecasting still uses empirical models rather than new big data-based analytical and AI&ML-based models.
- The INSAT satellite is not regularly replaced after its lifespan ends.
- Except for cyclones – other climate extreme disasters like cloudbursts, landslides, forest fires,
GLOF-related prediction and early singing systems are not efficient -resulting in huge loss of life and property majorly in the Himalayan and western Ghats region. Eg- The recent Teesta river flood and Chunthung Dam have washed away- due to heavy rain and the early warning system could not predict it enough.
Even if the drawbacks are present in less than half a century time India Satellite-based Weather Forecasting and Disaster Management Satellite are quite successful in their role. With rising extreme climate events majorly in south Asia the importance of this satellite technology increasing extremely, need for the advancement of these satellites similarly increasing.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

