In the ever-evolving world of geography and geospatial knowledge, staying updated with the latest developments is paramount. From geopolitical shifts to environmental transformations, students, researchers, and enthusiasts must have access to a reliable source of current affairs in the field of geography. “KOSMOS – Geography Current Affairs” by Edukemy is a beacon of knowledge, offering a comprehensive look at the most significant events and trends in geography. Whether you’re preparing for competitive exams, conducting research, or simply keen on expanding your geographical horizons, KOSMOS provides a curated collection of insights, analysis, and information that will keep you informed and engaged in the fascinating world of geography. In this edition of KOSMOS, we will journey through a fortnight of intriguing developments, exploring how geography impacts our world in numerous ways.
Contents
- 1 ROLE OF RURAL TOURISM
- 1.1 Why in the news?
- 1.2 Background:
- 1.3 WHY HAS RURAL TOURISM GROWN?
- 1.4 Factors responsible for the growth of rural tourism:
- 1.5 WHAT CAN RURAL TOURISM CONTRIBUTE TO RURAL DEVELOPMENT?
- 1.6 PROBLEMS OF RURAL TOURISM
- 1.7 CAN ALL RURAL AREAS SUCCESSFULLY DEVELOP RURAL TOURISM?
- 1.8 With Special focus on rural tourism in India, few highlights need to be noted down:
- 1.9 SUSTAINABLE TOURISM IN INDIA
- 1.10 WHAT IS MICE TOURISM IN GUJARAT?
- 1.11 STEPS TAKEN BY THE GOVERNMENT TO PROMOTE TOURISM IN INDIA
- 1.12 GOVERNMENT PROGRAMMES TO PROMOTE TOURISM IN INDIA
- 1.13 CONCLUSION:
- 1.14 Where to use?
- 2 EXTREME WEATHER EVENTS LEAD TO INCREASE IN CHILD MARRIAGES
- 3 FLOODPLAIN LOSS: BASINS OF IRRAWADDY, TAPI, INDUS, CAUVERY RIVERS FLOWING THROUGH INDIA ALTERED MOST DUE TO HUMAN ACTIVITIES
- 4 Key terms
- 5 Places in news:
- 6 CASE STUDY : AGRA’S DECENTRALISED GARBAGE PROCESSING PLANTS
- 7 FORTNIGHTLY KOSMOS MCQ PRACTICE
- 7.0.1 1. With reference to the Segur elephant corridor consider the following statements:
- 7.0.2 2. What are the main causes of dam failures?
- 7.0.3 3. Which region of the solar system, located beyond Neptune’s orbit, is known for containing numerous small icy bodies and is often considered the source of short-period comets?
- 7.0.4 4. What is the concept of tourism carrying capacity?
- 7.0.5 5. Consider the following statements regarding Deoxygenation:
- 7.0.6 6. Consider the following statements regarding World Ozone Day:
- 7.0.7 7. Which geological feature characterizes the Kermadec-Tonga subduction zone, where the Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai volcano is located?
- 7.0.8 8. Consider the following statements regarding the Narmada River:
- 7.0.9 9. Consider the following statements regarding “Storm Daniel”:
- 7.0.10 10. Consider the following statements regarding International Coastal Clean-up Day:
- 7.0.11 11. What is the typical climatic effect of El Niño in the western tropical Pacific region?
- 7.0.12 12. Which of the following factors contributes to land degradation?
- 7.0.13 13. With reference to ‘ fly ash’ produced by the power plants using coal as fuel, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- 7.0.14 14. What is the primary function of “Ionization technology” in the context of ambient air pollution reduction?
- 7.0.15 15. The term “Medicane” recently in news is related to
- 8 MCQ ANSWER with EXPLANATION
- 8.1 1. Answer: b. 2 and 3
- 8.2 2. Answer: c. 1, 3 and 4
- 8.3 Explanation:
- 8.4 3. Answer: c. Kuiper Belt
- 8.5 4. Answer: c. The threshold number of tourists that can visit a destination without harming its environment and culture.
- 8.6 5. Answer: b. Only 2
- 8.7 6. Answer: d. Neither 1 nor 2
- 8.8 7. Answer: c. A tectonic plate boundary
- 8.9 8. Answer: d. Neither 1 nor 2
- 8.10 9. Answer: c. Both are correct
- 8.11 10. Answer: a. Only 1
- 8.12 11. Answer: b. Decreased rainfall and warmer temperatures.
- 8.13 12. Answer: c. A, C, and D only
- 8.14 13. Answer: 1. 1 and 2
- 8.15 14. Answer: C. Releasing negatively charged ions to remove particulate matter and pollutants.
- 8.16 15. Answer: c. Mediterranean Hurricane
- 9 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
ROLE OF RURAL TOURISM
Why in the news?
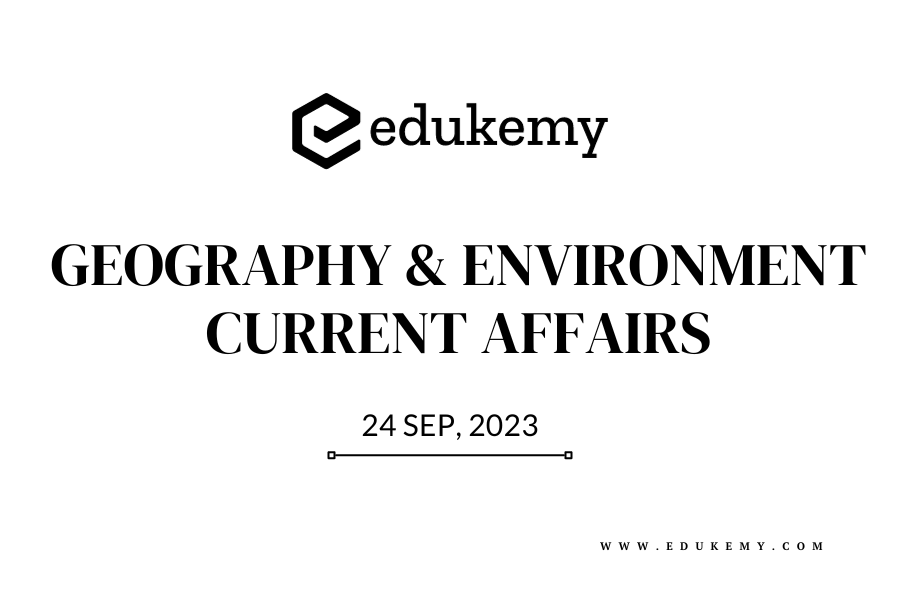
Tourism provides an opportunity for rural areas to reposition themselves.
Background:
Rural tourism, a thriving facet of the travel industry, takes tourists on an immersive journey into the heart of rural areas, providing them with an opportunity to experience the authentic culture, traditions, and natural beauty of these regions.
WHY HAS RURAL TOURISM GROWN?
- Rural tourism is not an accidental or temporary growth phenomenon. The forces behind the growth of rural tourism are more long-term in nature and linked to improvements in transport and communications and partly to the efforts of public agencies charged with assisting rural change.
Factors responsible for the growth of rural tourism:
- The growing interest in heritage: Increasing interest in both man-made and natural heritage has been attributed to fear of the future, better education, and better heritage presentation. Eg . Jaipur in Rajasthan.
- Green areas: Green areas or greenery play a pivotal role in promoting rural tourism as they offer a respite from the bustling urban life, and present an opportunity for tourists to connect with nature. Eg Coorg (also known as Scotland of India in Karnataka)
- Aging but active populations: Effective occupational pensions allow this active but aging population to travel widely: many choose rural holidays for health reasons and to discover new non-urban experiences. In 1995-96, only 83 percent of British males aged 60-64 were still working in full-time jobs. By 2010 it was reported that only 55 percent of men in that age group remained in full-time work.
- Individualism: Individualism is also a growth market, rejecting the mass activities of the past. Rural tourism, because of the fragmented and small-scale nature of the enterprises involved, is especially capable of exploiting this market trend, although high-quality selling and hospitality skills are needed. Eg The growth of individualism has been noted and acted upon by car manufacturers, by clothing manufacturers, and many other purveyors of consumer goods.
WHAT CAN RURAL TOURISM CONTRIBUTE TO RURAL DEVELOPMENT?
- Pluriactivity: It is the term used when an individual or family carries out more than one type of job to maintain their income. Eg. Sea fishermen may take tourist parties on angling trips, on whale-watching expeditions off the coast of Canada and the United States, or bird-watching excursions off the coast of Ireland or Scotland.
- Landscape conservation: Landscape is of crucial importance to rural tourism but, equally, visitor use is vital to the landscape conservation industry. Visitor use brings political benefits, and economic gains, and can provide jobs in maintaining and repairing traditional landscapes worn by recreational activities.
- Cultural provision: The festivals and other events have enabled rural areas to broaden their cultural provision, buying in artists and ensembles and supporting those purchases by ticket sales to visitors. Eg. Kalaripayattu martial art in rural areas of Kerala.
- Women Empowerment: Studies show that tourism enterprises have increased the power of women within both the family and the community. Experience in Spain, Greece, France, Britain, and Ireland has demonstrated how the flexible and open-minded approach of women towards new ideas and cooperative working has helped develop and lead successful rural tourism projects.
PROBLEMS OF RURAL TOURISM
- Environmental threat: Some of the most attractive tourism destinations have the most sensitive environments. These include sea, wetlands, and lake shorelines. Eg. Mandovi and Zuari rivers in Goa.
- Socio-cultural threat: The impact of “advanced” cultures on “traditional” cultures almost always brings change to the traditional culture and not in the other direction. Eg. Hippy culture in Goa has led to a surge in drugs, prostitution, and human trafficking.
- Housing problem: Some successful rural tourism areas – in the Canadian Rockies, in South-West England, in parts of the Alps – have found that success in the visitor market has brought accommodation problems for local people.
- Incoming entrepreneur: Surveys show that, in extreme cases, up to 80 percent of tourism-related businesses in small towns and villages are owned, managed, or controlled by incoming or non-local entrepreneurs. They have little loyalty to their new base of operations and often leave when trading conditions deteriorate.
| CASE STUDY: RURAL TOURISM IN DARJEELING Rural tourism in Darjeeling Hills has brought about rural and economic development. The two important destinations namely, Takdah and Mineral Spring have attracted a large number of tourists, opening doors of employment, conserving rural ecology, and minimizing the disparity between rural and neighboring urban areas. Improvements in environment, landscape and resource conservation are eventually leading to sustainable development. |
CAN ALL RURAL AREAS SUCCESSFULLY DEVELOP RURAL TOURISM?
- According to the OECD, Over 75 percent of the land area of the world is rural. Studies revealed that factors involved in determining the suitability of rural tourism are not exclusive but dynamic. A few of the factors are :
- Scenic value includes mountains, seashores, lakes, islands, rivers, and special interest scenery. Eg Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Special wildlife assets. Eg. Jim Corbett National Park.
- Special facilities for sports including hunting, fishing, skiing, hiking, etc. Eg Manali
With Special focus on rural tourism in India, few highlights need to be noted down:
- Promoting agri tourism: Combining traditional agriculture with tourism has been gaining traction. Eg Malegaon in Pune
- Promoting Leisure Tourism: Showcasing the unique attractions, enhancing its amenities, and ensuring it offers a relaxing and enriching experience to visitors. Eg Jaisalmer in Rajasthan
- Promoting Marine tourism: Tapping the rich coastal and underwater heritage of a region. Eg. Goa.
- Adventure tourism: Himachal Pradesh and Ladakh due to its varied landscapes and terrain are known for trekking and mountaineering.
- Wellness and Ayurveda: Providing holistic treatments, yoga, meditation, and traditional Indian medicinal practices aimed at rejuvenating the body, mind, and spirit. Eg Rishikesh
- Tribal foods and cuisine: Diverse tribal communities, offering a unique array of tribal foods and cuisines that reflect the indigenous culture. Eg Great Hornbill festival in Nagaland.
- Religion and mythologies: Tawang monastery in Arunachal and Diskit in Ladakh happen to be the center of attraction for Buddhists.
SUSTAINABLE TOURISM IN INDIA
- Sustainable tourism is defined by the UN Environment Program and UN World Tourism Organization as “tourism that takes full account of its current and future economic, social and environmental impacts, addressing the needs of visitors, the industry, the environment, and host communities.
WHAT IS MICE TOURISM IN GUJARAT?
- The acronym “MICE” stands for “Meetings, Incentives, Conferences and Exhibitions”, and is essentially a version of business tourism that draws domestic and international tourists to a destination.
- The policy aims to make Gujarat one of the top five MICE tourism destinations in the country.
STEPS TAKEN BY THE GOVERNMENT TO PROMOTE TOURISM IN INDIA
- E – Visa: The government had launched the TVoA ( Tourist Visa on Arrival ) to facilitate short of duration international travelers.
- Sensitization campaigns: Promotion of the destination through the Incredible India Campaign across the globe.
- International Tourism & Travel Fairs & Exhibitions: India has currently participated in an international tourism trade fair in Madrid to help expedite the recovery of the country’s inbound tourism to the pre-pandemic levels.
- Niche Tourism: The Ministry of Tourism has recognized ‘Adventure Tourism’ as a ‘Niche Tourism’ product to promote India as a 365-day destination and attract tourists with specific interests.
- Tourism Potential of North East: Organising International Buddhist Conclave once in 2 years to showcase the Buddhist Heritage and International Tourism Mart every year.
GOVERNMENT PROGRAMMES TO PROMOTE TOURISM IN INDIA
| PROGRAMMES | OBJECTIVES |
| Dekho Apna Desh | Effort to showcase India’s rich diversity under “Ek Bharat Shreshtha Bharat.” |
| Swadesh Darshan Scheme | Central sector scheme with the funding available from Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) initiatives to harness tourism potential. |
| PRASHAD | Central Financial Assistance to States/UTs for the development of tourism related infrastructure in the country. |
| Helpline | Launch of 24×7 toll free multilingual tourist helpline in 12 International languages including Hindi and English |
| Adopt a Heritage Project | Heritage sites are being offered for adoption by the public sector, private sector and individuals to become ‘Monument Mitras’ for developing amenities. and facilities at these sites |
CONCLUSION:
Governments should acknowledge the importance of rural tourism in India and provide stakeholders with sustainable development. Furthermore, the government should provide appropriate funding and cost-effective infrastructure to encourage the growth of rural tourism. Tourism in rural regions can only be maintained if a comprehensive, inclusive planning strategy based on a multi-action, multi-stakeholder participatory approach is adopted and implemented.
Where to use?
Paper I ( Geography Optional ): Tourism including ecotourism
EXTREME WEATHER EVENTS LEAD TO INCREASE IN CHILD MARRIAGES
Why in the news?
Droughts, floods and other extreme weather events intensify existing problems of gender inequality and poverty that lead families to marry their daughters early.
About:
Relationship between child marriages and extreme weather:
- Extreme weather causes an increase in the occurrence of child, early, and forced marriage (CEFM) by intensifying elements of structural oppression, such as gender inequality and poverty.
- Gender-based violence (GBV) and inequities worsen in extreme-weather contexts.
- Reasons for child marriage: Child marriage is often seen as a coping strategy to reduce economic vulnerability and food insecurity.
- Example: In Bangladesh, daughters were married early after Cyclone Aila in 2009 to reduce their economic and food burden on the household.
- Example: In Kenya, young brides are sought to help with increased labor demands, such as walking long distances to find food and water.
- Example: In Malawi, girls exposed to drought were more likely to be married early compared to those living in non-drought areas.
- Parents resorted to CEFM to protect daughters from sexual violence and avoid family dishonour.
- Rates of sexual assault often escalate during times of crisis, particularly in evacuation camps or temporary shelters.
- Link with bride price and dowry: Researchers found that girls in sub-Saharan Africa or Vietnam — where the groom’s family paying a bride price to the bride’s family is local custom — had an increased probability of CEFM during droughts and rainfall shocks.
- In regions where dowry is common such as India, girls were less likely to get married during a drought year, because the bride’s family could not afford dowry payment.
Factors responsible for Child, Early and Forced Marriages:
- Poverty: In cultures where dowries are the norm, younger brides might attract smaller dowries than older ones. Example : Despite the Dowry Prohibition Act in India, dowries are still exchanged, and younger brides are often more “affordable.”
- Cultural and Social Norms: In many societies, child marriage is a deeply rooted tradition that has been practiced for generations. Eg . Primitive tribes like Nats in Rajasthan
- Preservation of Honor: In parts of the Middle East and North Africa, there’s a practice called “shotgun weddings” where girls are married off quickly to preserve family honor if they’re suspected of pre-marital relationships.
- Gender Inequalities: In some societies, women and girls have a lower status than men.and fewer rights than men. Educational attainment and CEFM were inversely associated for girls in India and Malawi. Also, the incidence of CEFM decreased in India and Vietnam as parental education increased.
- Conflict and Crisis: In the Syrian conflict, many families, whether in Syria or as refugees in neighboring countries, married off their daughters young, fearing sexual violence or seeking stability in unstable environments.
Other Key Findings:
- Every year, 12 million girls get married before adulthood.
- COVID-19 as well as poverty may have spurred child marriages in India.
- The Global Slavery Index 2023 said climate change, along with other environmental factors, has exacerbated modern slavery in Africa. More than 3.1 million Africans are in forced marriage and more than 3.8 million in forced labour.
- Girls in their early or late adolescence are highly vulnerable to child marriage.
Conventions and Agreements that addresses issues of Child Marriage:
- Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Women covers the rights to protection from child marriage in Article 16.
- Convention on Consent to Marriage, Minimum Age for Marriage and Registration of Marriages.
- African Charter on the Rights and Welfare of the Child.
- Protocol to the African Charter on Human and People’s Rights on the Rights of Women in Africa.
Where to use?
Paper II ( Geography Optional ): Issues related to environment
Paper 1 ( General Studies ): Social Issues, Women related issues
FLOODPLAIN LOSS: BASINS OF IRRAWADDY, TAPI, INDUS, CAUVERY RIVERS FLOWING THROUGH INDIA ALTERED MOST DUE TO HUMAN ACTIVITIES
Why in the news?
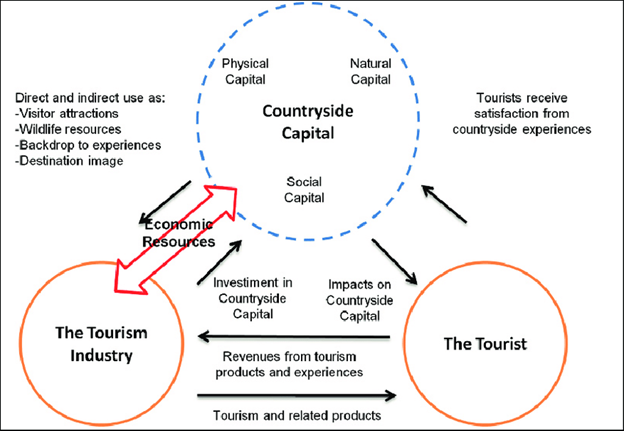
Asia lost the biggest area of floodplains among all continents from 1992-2019
About:
- According to the report titled Human alterations of the global floodplains 1992–2019, over 460,000 square kilometers of floodplain area was lost to agriculture, while another 140,000 square kilometers was redeveloped to new areas over the existing floodplain.
- Continent-wise, Asia lost the biggest area of floodplains — a little over 200,000 square kilometers — among all the continents, followed by South America (92,000 square kilometers) and Africa (73,000 square kilometers).
Reasons for flood plain alterations:
- Agricultural Expansion: Floodplains are often fertile due to frequent silt deposition, attracting agriculture. Eg. Amazon and Yangtze river basins, which translates to proportional increase in agricultural extent and subsequent decrease in forest area.
- Dam and Reservoir Construction: The World Commission on Dams report points out that large dams have affected the ecological integrity of river basins globally. Eg.The Farakka Barrage on the Ganges impacts sediment flow and flood dynamics downstream, affecting both Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal.
- Sand and Gravel Mining: The World Wildlife Fund (WWF) warns of the ecological repercussions of unregulated riverbed mining. Eg.Sand mining in the Narmada and Godavari rivers has not only altered floodplain dynamics but also led to groundwater depletion.
- Urbanization and Infrastructure Development: According to the World Bank, over 55% of the global population now resides in urban areas, with this figure set to rise. Eg.The Yamuna floodplains, once an ecologically rich zone, now face encroachments, reducing its natural water absorption capability. State governments are also planning river fronts which could be further devastative. Eg Gomti River front.
Other Key Finding:
- Difficult to independently calculate the actual flood plain loss in India because:
- Indus flows from India and into Pakistan and the Brahmaputra flows across three countries.
- Irrawaddy witnessed the highest alteration (4.6 per cent loss), according to the data. While Irrawaddy majorly flows across Myanmar the river-basin extends to some parts in Northeast India
- Tapi river basin recorded the highest alteration with over 3 per cent of the floodplain area lost due to human activities, followed by Indus (3.2 per cent) and Cauvery (2.7 per cent).
Where to use?
Paper I ( Geography Optional ): Ecosystems, their management and conservation.
Paper II ( Geography Optional ): Ground and surface water, Contemporary and ecological issues
Key terms
- Culturable Command Area: It is that part of Gross Command Area, which is fit for cultivating crops. So, cultivable area excludes forest and barren land from the Gross Command Area. What is left is uncultivable area.
- Super blue moon: A super blue moon combines a supermoon and a blue moon. A supermoon occurs when the moon aligns closely with Earth during its orbit, making it appear larger and brighter.This alignment, called perigee, contrasts with apogee, when the moon is farthest in its elliptical orbit around earth.
- Lagrange point: Lagrange Points are are positions where the gravitational pull of two large masses precisely equals the centripetal force required for a small object to move with them.
- Medicanes: Medicanes are extra-tropical hurricanes observed over the Mediterranean Sea. They occur more in colder waters than tropical cyclones, hurricanes and typhoons.The main societal hazard posed by Medicanes is not usually from destructive winds but through life-threatening torrential rains and flash floods.
- Boreal Forest: They are defined as forests growing in high-latitude environments where freezing temperatures occur for 6 to 8 months and in which trees are capable of reaching a minimum height of 5 m and a canopy cover of 10%. It is typically comprised of coniferous tree species such as pine, spruce and fir with some broadleaf species such as poplar and birch.
Places in news:
Mattur:
Why in news?
Recently the World Sanskrit Day was observed on 31st August.
- It is a village in Shivamoga district of Karnataka.
- It is known for usage of Sanskrit for day to day communication.
- Tunga river flows near it.
- Approximate: Shivamoga
Chempazhanthy:
Why in news?
Recently, the Prime Minister paid tributes to Sree Narayana Guru on his Jayanti.
- The place is known to be the birthplace of Indian spiritual leader and social reformer , Sri Narayan Guru.
- It is a village in the suburbs of Thiruvananthapuram City, the capital of Kerala state
- Chempazhanthy was the hereditary base of the “Chempazhanthy Pillai”, who was prominent among the so-called Ettuveetil Pillamar.
- Approximate: Thiruvananthapuram
Yankti Kuti Valley:
Why in news?
Recently it is reported that glaciers in the Yankti Kuti valley are responding to climate change.
- Located in Uttarakhand, it is the last valley before the border with Tibet.
- It runs along an NW to SE axis, formed by the river Kuti Yankti, which is one of the headwaters of the Kali River that forms the boundary between India and Nepal in this region.
- This valley is mainly dominated by Byansis, one of the four Bhotiya communities of Kumaon, with the others being Johar, Darmiya and Chaudansi.
- Approximate: Pithoragarh
Mollem National Park:
Why in news?
Recently Goa prohibits entry to Mollem National Park and other places.
- Located in the Western Ghats region of Goa
- The Mandovi river flows through the park.
- Around 70% of Goa’s flowering plant species are present here.
- Approximate: ( Panaji)
Karajgaon:
Why in news?
A project installing water sources and drip irrigation was conducted at Karajgaon.
- It is located in Talasari taluka of Palghar district , Maharashtra.
- It belongs to Vidarbha region and Amravati Division.
- It is one of the backward districts and facing huge scarcity of water.
- Approx: Palghar
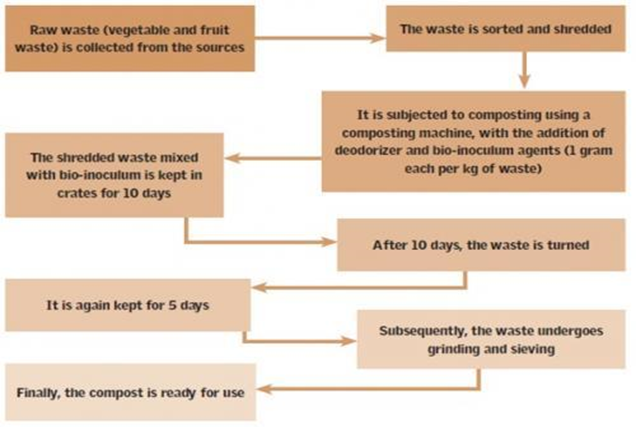
CASE STUDY : AGRA’S DECENTRALISED GARBAGE PROCESSING PLANTS
- The Municipal government of Agra established two units to manage waste generated from three sabji mandis (vegetable markets) and a plant to manage flower waste generated from temples.
How composting works?
- First, waste comprising vegetables and fruit residues from markets, along with flowers from temples, are collected. It employs the following processes:
- Pit composting is employed to transform flower waste into compost.
- Cow dung is used as a covering material for leaf and flower waste.
- Bio-inoculum is added during the composting process, with regular turning of the waste taking place.
- The compost produced by the decentralised plants in city parks, contributing to sustainable landscaping practices. In addition, compost derived from flower waste has been made available on e-commerce sites Jio-mart and Amazon at Rs 15 per kg.
Where to use?
Paper II ( Geography optional ): Argo based industries, Concept of sustainable growth.
Paper I ( General Studies ): Solid waste management
FORTNIGHTLY KOSMOS MCQ PRACTICE
1. With reference to the Segur elephant corridor consider the following statements:
- It is situated in the Anaimalai Biosphere Reserve.
- The dominant forest type found here is Tropical rainforest.Moyar
- River flows through the Segur Plateau.
Which of the above-mentioned statements is/are correct?
- A. Only 1
- B. 2 and 3
- C. 1, 2 and 3
- D. 1 and 2
2. What are the main causes of dam failures?
- 1. Foundation problems
- 2. Well-planned Construction
- 3. Inadequate Spillway
- 4. Uneven Settlement
Which of the following are correct.
- a. 1 and 2 only
- b. 1, 2, 3, and 4
- c. 1, 3 and 4
- d. 2, 3, and 4
3. Which region of the solar system, located beyond Neptune’s orbit, is known for containing numerous small icy bodies and is often considered the source of short-period comets?
- A. Oort Cloud
- B. Asteroid Belt
- C. Kuiper Belt
- D. Scattered Disc
4. What is the concept of tourism carrying capacity?
- A. The maximum number of tourists a destination can accommodate without economic losses.
- B. The minimum number of tourists required for infrastructure development.
- C. The threshold number of tourists that can visit a destination without harming its environment and culture.
- D. The number of tourists needed to boost local employment opportunities.
5. Consider the following statements regarding Deoxygenation:
- 1. Overall increase in the oxygen content of oceanic and coastal waters
- 2. Deoxygenation occurs when oxygen consumption is greater than oxygen replenishment through photosynthesis, ventilation, mixing.
Which of the above mentioned statements is / are correct ?
- A. Only 1
- B. Only 2
- C. Both 1 and 2
- D. Neither 1 nor 2
6. Consider the following statements regarding World Ozone Day:
- 1. World Ozone Day is celebrated on 16th September each year to commemorate the signing of the Kyoto Protocol.
- 2. The theme for World Ozone Day 2023 is “Kyoto Protocol: fixing the ozone layer and reducing climate change”.
Which of the above mentioned statements is / are correct ?
- A. Only 1
- B. Only 2
- C. Both 1 and 2
- D. Neither 1 nor 2
7. Which geological feature characterizes the Kermadec-Tonga subduction zone, where the Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai volcano is located?
- A. A large mountain range
- B.A massive underground cave system
- C. A tectonic plate boundary
- D. A chain of active volcanoes
8. Consider the following statements regarding the Narmada River:
- 1. Orsang, Jonk, Hasdeo and Heran are the tributaries of Narmada River.
- 2. The Narmada River is one of the few rivers in India that flows from west to east and eventually empties into Arabian Sea
Which of the above-mentioned statements is/are correct?
- A. Only 1
- B. Only 2
- C. Both 1 and 2
- D. Neither 1 nor 2
9. Consider the following statements regarding “Storm Daniel”:
- 1. It is an extreme rainfall from a storm system
- 2. Storm Daniel hit parts of the central and eastern Mediterranean.
Which of the above-mentioned statements is/are correct?
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
10. Consider the following statements regarding International Coastal Clean-up Day:
- 1. It aims to raise awareness of the problem of marine litter.
- 2. The Indian Military Force has been coordinating this activity in India since 2006.
Which of the above-mentioned statements is/are correct?
- A. Only 1
- B. Only 2
- C. Both 1 and 2
- D. Neither 1 nor 2
11. What is the typical climatic effect of El Niño in the western tropical Pacific region?
- a. Increased rainfall and cooler temperatures.
- b. Decreased rainfall and warmer temperatures.
- c. Consistently dry conditions throughout the year.
- d. A complete absence of hurricanes and typhoons.
12. Which of the following factors contributes to land degradation?
- A) Afforestation and reforestation efforts
- B) Sustainable agricultural practices
- C) Overgrazing by livestock
- D) Proper soil conservation measures
Select the correct option:
- a. A and B only
- b. C and D only
- c. A, C, and D only
- d. B and C only
13. With reference to ‘ fly ash’ produced by the power plants using coal as fuel, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- 1. Fly ash can be used in the production of bricks for building construction.
- 2. Fly ash can be used as a replacement for some of the Portland cement contents of concrete.
- 3. Fly ash is made up of silicon dioxide and calcium oxide only, and does not contain any toxic elements.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- A. 1 and 2
- B. 2 only
- C. 1 and 3
- D. 3 only
14. What is the primary function of “Ionization technology” in the context of ambient air pollution reduction?
- A. Initiating chemical reactions to neutralize harmful compounds.
- B. Creating a physical barrier to prevent pollutants from entering buildings.
- C. Releasing negatively charged ions to remove particulate matter and pollutants.
- D. Enhancing the dispersion of air pollutants for effective monitoring.
- a. Hybrid Brinjal
- b. Hydroelectric power generation
- c. Mediterranean hurricane.
- d. Tsunami
MCQ ANSWER with EXPLANATION
1. Answer: b. 2 and 3
Explanation: Statement 1 is incorrect. It is situated in the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve.
Statement 2 is correct. The dominant forest type found here is Tropical rainforest. Montane forests, Tropical dry forests and Tropical moist forests are also found here. The Sigur Plateau is notable as an important wildlife corridor in the Western Ghats to sustain elephant and tiger numbers and their genetic diversity. It is also home to the largest population of critically endangered species of vultures in southern India.
Statement 3 is correct. The north side of the plateau is defined by the Moyar River. The Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve, which includes Sigur Plateau and the Nilgiri Hills, is part of the UNESCO World Network of Biosphere Reserves.
Why in News:
A Supreme Court-appointed committee recently declared 12 private resorts, along the Segur elephant corridor, illegal.
2. Answer: c. 1, 3 and 4
Explanation:
Main causes of dam failure are foundation problems (40%), inadequate spillway (23%), poor construction (12%) and uneven settlement (10%).
Why in News:
Libya dam collapse: More than 11,000 people have been killed and tens of thousands are missing following the catastrophic collapse of two dams in the eastern Libyan city of Derna.
3. Answer: c. Kuiper Belt
Explanation:
The Kuiper Belt is a region of the solar system located beyond the orbit of Neptune. It is known for containing numerous small icy bodies, including Pluto and other dwarf planets, as well as various small objects. The Kuiper Belt is often considered the source of short-period comets. These comets originate from the Kuiper Belt when their orbits are perturbed, and they are pulled into the inner solar system by the gravitational influence of Neptune or other planets.
Why in News:
Japanese scientists find ‘Earth-like planet’ in our solar system
4. Answer: c. The threshold number of tourists that can visit a destination without harming its environment and culture.
Explanation:
The concept of “tourism carrying capacity” refers to the threshold number of tourists that can visit a destination without causing harm to its environment, culture, and various other factors. It represents the maximum number of visitors a destination can sustainably accommodate without detrimental impacts on its physical, cultural, social, and economic aspects. This concept is crucial for regulating and managing tourism activities in hilly areas and other destinations to ensure sustainable and responsible tourism.
Why in News:
Sustainable tourism: Carrying capacity assessment can be a tool for protecting hilly areas. It is the need of the hour to regulate unmanaged tourism activities to maintain the ecological balance and facilitate tourism.
5. Answer: b. Only 2
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect. Deoxygenation is the overall decline in the oxygen content of oceanic and coastal waters.
Statement 2 is correct. Deoxygenation occurs when oxygen consumption (e.g. from respiration, or breathing) is greater than oxygen replenishment through photosynthesis, ventilation, mixing.
Why in News:
The findings of a study led by the Pennsylvania State University showed that of nearly 800 rivers across the United States and Central Europe, warming occurred in 87 percent and oxygen loss in 70 percent.
6. Answer: d. Neither 1 nor 2
Explanation:
Statement 1 and 2 both are incorrect: Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC), celebrated the 29th World Ozone Day on 16th September to commemorate the signing of the Montreal Protocol, an international environmental treaty for phasing out of production and consumption of Ozone Depleting Substances, that came into force on this day in 1987.
Why in News:
The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC), celebrated the 29th World Ozone Day on 16th September.
7. Answer: c. A tectonic plate boundary
Explanation:
The Kermadec-Tonga subduction zone, where the Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai volcano is located, is characterized by a tectonic plate boundary. It is a seismically active region in the Pacific Ocean, known for its geological activity, including volcanic eruptions and earthquakes, due to the interaction of tectonic plates. This subduction zone plays a significant role in the formation and activity of submarine volcanoes in the area.
Why in News:
In 2023, temperatures have reached historical highs, and researchers suggest that the eruption of the Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai underwater volcano in the South Pacific in 2022 may have contributed to this phenomenon
8. Answer: d. Neither 1 nor 2
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect. Jonk and Hasdeo are the tributaries of Mahanadi. Orsang and Heran are the tributaries of Narmada River.
Statement 2 is incorrect. Narmada River flows from East to West into the Arabian Sea.
Why in News:
The discharge of a significant volume of water from the Sardar Sarovar Dam (SSD) has resulted in substantial flooding in the Narmada district’s low-lying regions
9. Answer: c. Both are correct
Explanation:
Both statements are correct: Extreme rainfall from a storm system called Storm Daniel hit parts of the central and eastern Mediterranean, leading to devastating flooding and massive loss of life in Libya, the worst affected country, as well as in Greece, Türkiye and Bulgaria.
Why in News:
Eastern Libya experienced a catastrophic event as floods caused by Storm Daniel
10. Answer: a. Only 1
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: The Indian Coast Guard conducted International Coastal Clean-up Day – 2023 (ICC-2023) across all Coastal States and Union Territories on 16 Sep 2023. The International Coastal Clean-up day is held worldwide on the third Saturday of September every year under the aegis of United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and South Asia Co-operative Environment Programme (SACEP) in the South Asian Region. This day aims to encourage people to clean up the coastal line and raise awareness about the significance of preserving the oceans and waterways
Statement 2 is incorrect: The Indian Coast Guard has been coordinating this activity in India since 2006.
Why in News:
Indian Coast Guard Conducts International Coastal Clean-up Day 2023 Across Coastal States And UTs
11. Answer: b. Decreased rainfall and warmer temperatures.
Explanation:
El Niño is a climate phenomenon characterized by the periodic warming of sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean. This warming of ocean waters can have significant impacts on global weather patterns. In the tropical Pacific region, El Niño is associated with decreased rainfall and warmer temperatures.
During an El Niño event, the warm ocean waters lead to changes in atmospheric circulation patterns, which can result in:
1. Reduced rainfall: The warmer ocean temperatures cause the air above the ocean to become more stable, inhibiting the development of convection and rainfall. This often leads to drought conditions in some regions.
2. Warmer temperatures: The reduced cloud cover and rainfall can result in higher temperatures in affected areas.
It’s important to note that the specific impacts of El Niño can vary depending on the region and the strength of the El Niño event. While the tropical western Pacific experiences decreased rainfall and warmer temperatures, other parts of the world, such as the western coast of South America, may experience increased rainfall and flooding during El Niño events.
Overall, El Niño events have far-reaching effects on global climate and weather patterns, influencing everything from tropical cyclone activity to agricultural conditions.
Why in News:
Peru president proposes international pact to combat El Nino effects
12. Answer: c. A, C, and D only
Explanation:
Land degradation is the deterioration of the land’s quality due to various factors, including human activities and natural processes. Afforestation and reforestation efforts (Option A) can help prevent land degradation by improving vegetation cover, but overgrazing by livestock (Option C) can contribute to land degradation by stripping the land of vegetation. Proper soil conservation measures (Option D) are essential to combat land degradation by preventing soil erosion and maintaining soil health. Sustainable agricultural practices (Option B) also play a crucial role in preventing land degradation, so it is not a contributing factor. Therefore, options A, C, and D are the correct choices.
Why in News:
Land the size of Central Asia lost since 2015 due to degradation
At this rate, restoring 1.5 billion hectares of land by 2030 will be necessary to achieve a land-degradation-neutral world.
13. Answer: 1. 1 and 2
Explanation:
Statement 1 and 3 are correct. Fly ash can be used in the production of bricks for building construction and as a replacement for some of the Portland cement contents of concrete.Fly ash is made up of aluminium silicate, silicon dioxide, calcium oxide. Fly ash particles are oxide rich and consist of silica, almina, oxides of iron, calcium and magnesium and toxic heavy metals like lead, arsenic, cobalt and copper. Statement 3 is false as it says Fly ash is made up of only two components namely: silicon dioxide and calcium oxide.
14. Answer: C. Releasing negatively charged ions to remove particulate matter and pollutants.
Explanation:
Ionization technology involves the emission of negatively charged ions into the air. These ions attach themselves to airborne particles, including particulate matter and pollutants. As a result, the charged particles are attracted to surfaces or grounded, effectively removing them from the air. This process helps to reduce the levels of pollutants in the ambient air, contributing to improved air quality. Recently, the Minister of Environment, Forest and Climate Change provided valuable insights into the projects related to deploying various technologies to address Air Pollution in Indiaduring a written reply in the Lok Sabha.
15. Answer: c. Mediterranean Hurricane
Explanation:
Storm Daniel developed in Greece and was named by the Hellenic National Meteorological Service. As it moved towards Libya, Storm Daniel developed the characteristics of a Medicane – MEDIterranean hurriCANE. This hybrid phenomenon shows some characteristics of a tropical cyclone and others of a mid-latitude storm. Activity historically peaks between September and January.
Why in News:
Eastern Libya experienced a catastrophic event as floods caused by Storm Daniel
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here