
The India-Middle East-Europe Corridor holds the potential to be a transformative force in shaping the global geopolitical landscape. This ambitious project, with its extensive infrastructure investments and enhanced trade routes, has the capacity to bolster economic ties between regions that have historically held significant influence. As it forges a path from the Indian subcontinent through the Middle East and into Europe, it not only opens new avenues for trade but also fosters diplomatic connections that could redefine global alliances and power structures. The corridor could serve as a catalyst for a new world order, where the economic and political center of gravity shifts towards these interconnected regions, challenging traditional superpowers and sparking a realignment of interests on a global scale.
Tag: GS-2 Global Trade and International Relations
Exam View: About IMEC; Movement of Goods through IMEC; Significance of IMEC
Contents
- 1 Context:
- 2 About India-Middle East-Europe Corridor (IMEC):
- 3 Movement of Goods through IMEC:
- 4 Significance of IMEC:
- 5 Challenges for IMEC
- 6 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 6.1 Q: What is the India-Middle East-Europe Corridor, and why is it being hailed as a catalyst to a new world order?
- 6.2 Q: What are the key benefits of the India-Middle East-Europe Corridor?
- 6.3 Q: How does the India-Middle East-Europe Corridor impact existing global alliances and superpowers?
- 6.4 Q: Are there any challenges or obstacles facing the India-Middle East-Europe Corridor project?
- 6.5 Q: How can businesses and industries benefit from the India-Middle East-Europe Corridor?
- 7 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Context:
The signing of MoU for development of India-Middle East-Europe Corridor during G20 has been a landmark event. It has immense potential to put India, Middle East and Europe on collective path to growth, triggering regional and global cooperation
About India-Middle East-Europe Corridor (IMEC):
| Features | Description |
| Name | India-Middle East-Europe Corridor |
| Type | Multimodal trade and transit corridor |
| Objective | Promote trade and investment between India, the Middle East, and Europe |
| Route | The corridor will connect India to Europe through the Middle East. The exact route is still being finalised, but it is expected to pass through countries such as Iran, Turkey, Greece, and Bulgaria. |
| Modes of transport | The corridor will use a mix of road, rail, and sea modes of transportation. |
| Status | The corridor is still under development. However, a number of projects have been completed or are underway, such as construction of new roads & railways. |
| Key projects | The Chabahar Port in Iran The International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC) The Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan (BTC) pipeline Jordan-Haifa Land Route |
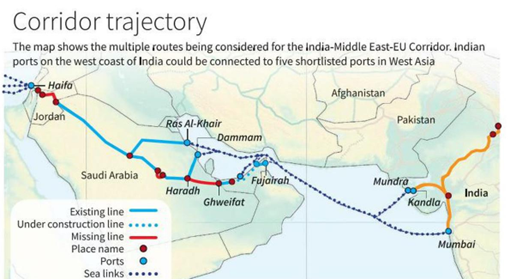
Movement of Goods through IMEC:
- India to Arabian Gulf (Sea Route): IMEC links major ports of western India including JNPT, Kochi, Kandla and Mundra with major shipping ports of the Gulf, including Jebel Ali, Fujairah, Ras Al-Khair, Dammam, Duqm, and Salalah.
- Gulf ports to West Asian ports on the Mediterranean (Land Route): From these ports, cargo will be transported by the Saudi rail network on their north-south line to the port of Haifa in Israel through Jordan.
- Mediterranean Ports to European Ports (Sea Route): Haifa, being a deep seaport, can handle bulk container trains and carry cargo to European ports like Piraeus, Kavala (Greece), Trieste, La Spezia (Italy), Marseille-Fos (France), Barcelona, and Valencia (Spain).
- European Ports to hinterlands of Europe (Land Route): Road container trailers or container cargo trains will thereafter transport goods across Europe.
Significance of IMEC:
- Economic Benefits: IMEC is expected to boost trade and investment between India, the Middle East, and Europe, leading to economic growth and job creation.
- Reliable and Cost-Effective transport solution: It envisions a reliable, cost-effective railway and ship-to-rail transit network to supplement maritime and road routes, enabling goods and services to move between India, the UAE, Saudi Arabia, Jordan, Israel and the EU.
- Reduce transportation time due to shorter routes as compared to Suez Channel route, making it more efficient to move goods and services between these regions.
- Development of Infrastructure: This proposed economic corridor project would help deal with the lack of infrastructure needed for growth in lower and middle-income nations
- Promotion of Intra-regional Connectivity: It will promote Intra-regional connectivity and enhance trade, prosperity and connectivity.
- Geopolitical Benefits: IMEC provides connectivity to accelerate the development and integration of Asia, the Arabian Gulf, and Europe as a new locus of global power.
- IMEC will also enhance India’s strategic position in the region, giving it a greater say in global affairs.
- Reduction of dependence on Suez Canal, a major chokepoint in global trade.
- Counter to Chinese Belt and Road Initiative (BRI): India Middle East Europe Corridor (IMEC) is an ambitious counter to China’s BRI project.
- Geopolitical Stability in Middle East: This Corridor will help to bring countries in the Middle East together and establish that region as a hub for economic activity instead of as a “source of challenge, conflict or crisis”
- Environmental benefits:
- Hydrogen Fuel pipelines: IMEC, envisages the laying of cables for electricity and a pipeline for transporting clean hydrogen. The greening of this project will contribute to the global effort to lower greenhouse gas emissions.
- Reduced fuel usage due to decreased travel time because of shorter routes and consequently lesser pollution.
Challenges for IMEC
- Non-binding MoU: The MoU of IMEC does not create any rights or obligations under international law, and is only a political commitment.
- Implementation challenges: Early implementation and construction of the corridor is a challenge due to the need to develop and commit to an action plan with relevant timetables.
- Financial Sourcing: The corridor would require massive finance for its construction, which is a challenge considering the recession and difficulty in mobilization of private sector finance.
- Chinese resistance: The corridor faces the challenge of Chinese pushback as China has already invested heavily in the BRI project and is making considerable investments in the Middle East.
Source: The HINDU
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the India-Middle East-Europe Corridor, and why is it being hailed as a catalyst to a new world order?
A: The India-Middle East-Europe Corridor is a proposed transcontinental trade and transportation network connecting India to Europe via the Middle East. It is considered a catalyst to a new world order because it has the potential to reshape global geopolitics by enhancing economic ties and diplomatic relationships across regions, challenging traditional power structures.
Q: What are the key benefits of the India-Middle East-Europe Corridor?
A: The corridor offers several benefits, including the facilitation of trade, reduced transportation costs, improved connectivity, and enhanced economic cooperation among the involved regions. It can also serve as a catalyst for diplomatic ties and potentially lead to a shift in global power dynamics.
Q: How does the India-Middle East-Europe Corridor impact existing global alliances and superpowers?
A: The corridor’s development may lead to a realignment of global interests by challenging the dominance of traditional superpowers. It can encourage countries to diversify their alliances and partnerships, thereby altering the existing geopolitical landscape.
Q: Are there any challenges or obstacles facing the India-Middle East-Europe Corridor project?
A: Yes, challenges include infrastructure development, political cooperation, and potential security concerns in some regions along the corridor. Navigating these issues will be crucial in ensuring the project’s success.
Q: How can businesses and industries benefit from the India-Middle East-Europe Corridor?
A: Businesses and industries can benefit from the corridor by gaining access to new markets, reduced transportation costs, and enhanced trade opportunities. It can also create a more stable and predictable environment for investment, fostering economic growth and development in the involved regions.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here
