
In today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants, we explore the latest developments that hold relevance for the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political and economic landscape of India. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.
Contents
- 1 Climate Change and Mountain of Northern Hemisphere
- 2 Global Forest Watch
- 3 India Green Credit Scheme
- 4 National Research Foundation
- 5 Sea Lions and Alage Blooms
- 6 Schemes to promote the judicious use of fertilisers
- 7 Children impacted by armed conflict
- 8 UNODC World Drug Report 2023
- 9 2023 Global Competitiveness Index
- 10 Critical Minerals List
- 11 Global Environment Facility (GEF)
- 12 Nepal
- 13 Rwanda
- 14 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 14.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 14.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 14.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 14.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 14.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 15 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Climate Change and Mountain of Northern Hemisphere
Tag: GS-3 Environment
In News:
The Himalayas and other mountains across the Northern Hemisphere are likely to see 15 percent more rain for every 1-degree Celsius rise in temperature due to climate change, according to a new study.
About
A recent report reveals that the Rockies, Alps, and Himalayas, prominent mountain ranges in the Northern Hemisphere, are witnessing a significant shift in precipitation patterns. As temperatures rise due to climate change, these mountain regions are experiencing more rainfall and less snowfall.
Major Outcome of the Report:
Implications for Water Resources and Ecosystems:
- The transition from snow to rainfall has far-reaching implications for water resources and ecosystems in these mountainous areas.
- Snowmelt plays a vital role in providing water supply to downstream communities, agriculture, and ecosystems during the dry seasons. The shift to increased rainfall poses challenges for water availability and management.
Water Supply Challenges:
- The report emphasizes that the reduced snowpack resulting from less snowfall affects the availability of water resources downstream. Communities that rely on snowmelt as their primary water source may face increased water scarcity and challenges in water resource management.
- This shift in precipitation patterns demands the development of comprehensive adaptation strategies to address potential water supply challenges.
Environmental and Ecological Consequences:
- The changing precipitation patterns also have significant ecological implications. Snow accumulation provides insulation for plants, protecting them from extreme temperatures.
- The reduction in snow cover may expose plants to harsh conditions, affecting their growth and survival. Additionally, changes in the timing and volume of water runoff can disrupt ecosystems, impacting biodiversity and the overall health of mountain habitats.
Need for Adaptation Strategies
- To mitigate the adverse effects of reduced snowfall and increased rainfall, the report underscores the urgent need for adaptation strategies.
- It highlights the importance of understanding and anticipating the impacts of climate change on mountain ecosystems, water resources, and communities.
- Developing sustainable water management practices, enhancing water storage capacities, and implementing climate-resilient agricultural practices are among the proposed strategies to address the challenges posed by changing precipitation patterns.
The report’s findings emphasize the ongoing shifts from snow to rainfall in the Rockies, Alps, and the Himalayas due to rising temperatures caused by climate change. It stresses the need for proactive measures to ensure the sustainable management of water resources, protection of ecosystems, and resilience of communities in mountainous regions facing these changing precipitation patterns.

Source: Down to Earth
Global Forest Watch
Tags: GS – 3: Environment Conservation
Why in News:
A recent study quoted by World Resources Institute’s Global Forest Watch found that the tropical areas experienced a significant decline in forest cover in 2022.
Global Forest Watch:
- It is an open source web application to monitor global forests in near real-time.
- It is an initiative of World Research institute with partners including Google, USAID, the University of Maryland, Esri, Vizzuality and many other academic, non-profit, public and private organisations.
Key findings of the study:
- The primary forest cover loss in tropical region has been 10% higher in 2022 as compared to the previous year.
- The loss amounted to 4.1 million hectares equivalent to an area the size of 11 football fields disappearing every minute.
- Some countries like Brazil and the Democratic Republic of Congo with substantial tropical forest cover experienced significant losses in 2022.
- In case of India, there has been a loss of 44 thousand hectares of humid primary forest between 2021 and 2022 which amounts for 17% of the country’s total tree cover loss during that period.
- The world is not on track to meet its forest related commitments. Two key goals set by the World Resources Institute include:
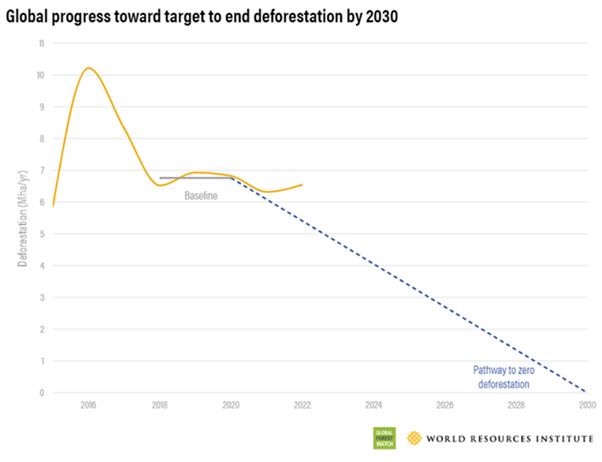
- Ending deforestation by 2030: The global deforestation rate needs to decrease by at least 10% annually to meet the 2030 target. The deforestation rates reduced by 3.1% compared to the 2018-2020 baseline. But it is still exceeded the level by over one million hectares which shows a clear deviation from the 2030 goal.
- Restoring 350 million hectares of lost and degraded forests by 2030: The overall change in tree cover over the past two decades has been a net loss of 100 million hectares. This indicates that forests are still being lost instead of being restored at the required rate.
Primary Forests:
- These are mature and undisturbed natural forests that have not experienced significant human intervention or alteration in recent history.
- These are also called as Old-grown forests or Virgin Forests.
- They play a crucial role in storing carbon and supporting biodiversity.
Source: The Hindu
India Green Credit Scheme
Tags: GS – 3: Conservation, Environmental Pollution and Degradation
Why in News:
Recently, The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change has notified the draft ‘Green Credit Programme (GCP)’ implementation rules 2023.
Green Credit Programme:
- Under this programme, “green credit” will be awarded to those individuals, industries, FPOs, Urban local bodies, gram panchayats, private organisations, etc. for undertaking environment-friendly actions.
- These green credits will be tradable on a proposed domestic market platform.
- The objective of this programme is to create a market based (supply and demand) mechanism for incentivising voluntary environmental actions/ individual or community behaviour. Another objective is to encourage the private sector as well to meet their existing obligations, stemming from other legal frameworks.
- It follows the principle of LiFE – Lifestyle for Environment which encourages sustainable lifestyle and incentivises environment-friendly practices.
Green Credit Activities: Green credit activities are generally classified into 8 categories for generating credits:
- Tree Plantation based Green Credit: To promote activities for increasing green cover across the country through tree plantation and related activities.
- Water based Green Credit: To promote water conservation, water harvesting and water use efficiently.
- Sustainable Agriculture based Green Credit: To promote natural and regenerative agricultural practices and land restoration to improve productivity, soil health and nutritional value of food.
- Waste management based Green Credit: To promote sustainable and improved practices for waste management and its treatment.
- Air Pollution reduction based Green Credits: To promote measures for reducing air pollution.
- Mangrove Conservation and restoration based Green Credit: To promote measures for the conservation and restoration of mangroves.
- Eco-mark based Green Credit: To encourage manufacturers to obtain an eco-mark label for their goods and services.
- Sustainable building and infrastructure based Green Credit: To encourage the construction of buildings and other infrastructure using sustainable technologies and materials.
Significance of the programme:
- It is a first of its kind instrument that seeks to value and reward multiple ecosystem services to allow green projects to achieve optimal returns beyond just carbon.
- The guidelines bring together mechanisms to quantify and support ecosystem services together which would help and incentivise the organic farmers and FPOs.
Challenges:
- Its implementation would be difficult due to difficulty in establishing the equivalence between various actions.
- Challenges related to monitoring, reporting and verification.
- Experts are concerned that the market-based mechanism of green credits may lead to Greenwashing.
Way Forward:
- Trained capacity building should be done to monitor the system and prevent malicious activities.
- Incentivising will bring more transformational pollution control and environment protection efforts.
Source: The Print
National Research Foundation
Tags: GS-3: Government Policies; Education
In News:
Cabinet approves Introduction of National Research Foundation Bill, 2023 in Parliament to strengthen research eco-system in the country:
About National Research Foundation:
- Ministry of Science & Technology has recently released the NRF Bill, 2023 proposing establishment of a body “National Research Foundation (NRF)”.
- NRF will be an apex body established to promote and strengthen research and development (R&D) in India.
- It aims to foster a culture of research and innovation in universities, colleges, research institutions, and R&D laboratories.
- The foundation will provide high-level strategic direction for scientific research in the country, in line with the recommendations of the National Education Policy (NEP).
- Composition:
- As per the bill, the Department of Science and Technology (DST) will serve as the administrative department of NRF.
- The NRF will be governed by a Governing Board consisting of eminent researchers and professionals from various disciplines.
- The Governing board will have the Prime Minister as the ex-officio President while the Union Ministers of Science & Technology and Education as the ex-officio Vice-Presidents.
- The NRF’s Executive Council will be chaired by the Principal Scientific Adviser to the Government of India to govern its functioning.
- The NRF will be responsible for forging collaborations among industry, academia, government departments, and research institutions.
- It will create an interface mechanism to encourage participation and contribution from industries and State governments.
- The NRF Bill, 2023 will also repeal the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB) and subsume it into NRF, expanding its scope and activities.
- At present, the estimated cost of establishing NRF over a period of five years (2023-2028) has been sanctioned at Rs. 50,000 crores.
- Overall, the establishment of the foundation is a significant step towards strengthening the research ecosystem in India besides propelling the country to a global leader in science and technology.
Source: PIB Gov.
Sea Lions and Alage Blooms
Tags: GS-3: Environment
In News:
California coast witnesses a surge in sick sea lions washing ashore attributing to a recent outbreak of algae bloom.
About Sea Lions and Algae Blooms:
- Sea lions in California are falling ill and washing ashore due to an outbreak of algae bloom, also known as red tide.
- The algae bloom produces a neurotoxin called domoic acid, which can affect marine mammals such as sea lions and dolphins.
- Sea lions are considered as sentinel species by marine biologists and they are indicative of environmental risks to humans.
- The algae bloom can occur naturally, but human activities like climate change and excess nitrates in the ocean can contribute to its proliferation.
- Consumption of infected shellfish is the primary concern for human health, as the neurotoxin can accumulate in these organisms.
- Sick sea lions exhibit various symptoms, including head swaying, foaming at the mouth, seizures, and listlessness.
- Overall, monitoring and understanding these occurrences are essential for protecting marine ecosystems and ensuring human health and safety. \
Source: The Hindu
Schemes to promote the judicious use of fertilisers
Tag: GS-3 Agriculture
In News:
The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) approved a package of innovative schemes with a total outlay of Rs.3,70,128.7 crore, which focuses at overall wellbeing and economic betterment of farmers by promoting sustainable agriculture.
About the CCEA’s Initiatives and Approvals:
- Fertiliser Subsidy: CCEA approved continuation of Urea Subsidy Scheme to ensure availability of urea at a constant price. Rs. 3,68,676.7 Crore out of the total outlay has been committed for urea subsidy Fertiliser subsidy of GoI has increased from Rs. 73,067 Cr in 2014-15 to Rs. 2,54,799 Cr in 2022-23.
- Nano Urea eco-system strengthened: By 2025-26, eight Nano urea plants with production capacity of 44 Crore bottles equalling to 195 LMT of conventional urea will be commissioned.
- Setting up and revival of 6 urea production units at Kota Rajasthan, Panagarh, West Bengal, Telangana, Gorakhpur-UP, Sindri-Jharkhand and Barauni-Bihar since 2018 has helped in making India atma nirbhar in terms of urea production.
- PM Programme for Restoration, Awareness Generation, Nourishment and Amelioration of Mother – Earth (PM-PRANAM) for promoting natural / organic farming, alternate fertilizers, Nano Fertilizers and bio-Fertilizers.
- Market Development Assistance (MDA): Rs. 1451.84 crore have been approved for MDA for promoting Organic Fertilizers from Gobardhan Plants
- Introduction of Sulphur coated Urea (Urea Gold) to address sulphur deficiency of soil and save input costs for the farmers.
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samruddhi Kendras (PMKSKs): For the convenience of farmers, farm inputs are being provided as a one-stop solution for all needs of farmers. About one lakh PMKSKs have already come up in the country.
Benefits of the scheme
- Improved soil health leads to increased nutrient efficiency and a safe environment.
- Better utilisation of crop residue like ‘parali’ and resolution of air pollution.
- No extra charges for farmers to purchase urea despite global price volatility.
- Reducing input cost of cultivation due to judicious use of chemical fertilizers.
Source: PIB Gov.
Children impacted by armed conflict
Tag: GS-2 Issues Related to Children
In News:
The UN has removed India from its report compiling an annual list of countries where children are impacted by armed conflict, in view of measures taken by India, specifically in J&K , to better protect children.
About the Report:
- The annual report highlights the disproportionate impact of war on children and identifies them as the primary victims of armed conflict.
- The first Special Representative for Children and Armed Conflict was named in 1997 by the Secretary-General to help enhance the protection of children affected by armed conflict, and foster international cooperation to that end.
Why was India included in the list, at the first place?
- On the basis of allegations that separatist militant groups operating in J&K were recruiting young boys.
- Additionally, there were allegations that Indian security forces in Kashmir detained young boys, accusing them of being associated with militant groups.
Major Highlights of the Report:
- The report includes trends regarding impact of armed conflict on children and information on violations committed.
- As per the report, the highest number of violations were committed in the Congo, Israel, Palestine, Somalia, Syria, Ukraine, Afghanistan, and Yemen.
- The countries where the worst deterioration occurred were Myanmar, South Sudan, and Burkina Faso.
- There were 1,163 attacks on schools recorded, and 647 attacks on hospitals, a 112% increase.
- Widespread military use of schools both by armed forces & armed groups.
- Nearly 2,500 children were detained, a practice that should only be used as a last resort and for the shortest period.
- Some of the measures taken by the Government –
- Training of security forces in protection of children;
- Suspension of use of pellet guns by security forces;
- Juvenile Justice Act (Care and Protection of Children), 2015;
- Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act, 2012.
Source: Down to Earth
UNODC World Drug Report 2023
Tags: General Studies – 2 Government Policies & Interventions
Why in news?
Recently, the UNODC World Drug Report 2023 (a yearly report) highlights the expanding illicit drug markets and the challenges they pose to health services and law enforcement.
About:
Key findings of the report:
- Globally, over 296 million people used drugs in 2021, an increase of 23 percent over the previous decade.
- Drug use disorder cases have surged by 45% in the last ten years.
- The increasing dominance of synthetic drugs, such as methamphetamine, and fentanyl which have transformed illicit drug markets due to their low cost and ease of production.
- Only one in five people suffering from drug-related disorders were in treatment for drug use in 2021 with widening disparities in access to treatment across regions.
- Youth populations are the most vulnerable to using drugs and are also more severely affected by substance use disorder in several regions.
- Drug trafficking is accelerating environmental devastation, particularly in the Amazon Basin.
- Illicit drug economies exacerbate conflicts, human rights abuses, and environmental devastation.
- Illicit drug trade finances non-state armed and insurgency groups in the Sahel region.
- The opium ban in Afghanistan had a positive result, but concerns remain about the production of synthetic drugs. However, farmers’ income has suffered in Afghanistan due to the Opium ban by the Taliban.
key recommendations:
- Public health, prevention, and access to treatment services must be prioritized worldwide.
- Law enforcement forces need to keep pace with criminal business models and the proliferation of cheap synthetic drugs that are easy to bring to market.
UNODC:
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime established in 1997.
- It focuses on the trafficking and abuse of illicit drugs, crime prevention and criminal justice, international terrorism, and political corruption.
- It is a member of the United Nations Development Group.
- HQ: Vienna
Source: UNODC
2023 Global Competitiveness Index
Tags: General Studies –3 Economy
Why in news?
India has been ranked 40th on the latest world competitiveness ranking released by the International Institute for Management Development (IMD).
About:
Highlights of the Report:
- Denmark, Ireland, and Switzerland have been named the top three among 64 economies measured for their global competitiveness.
- India with 40th rank which is still in a better position than it was between 2019-2021 when it was placed 43rd three years in a row.
- India improved in government efficiency but fared slightly poorer than other countries in business efficiency, infrastructure, and economic performance.
- Specifically, the top three measures that helped India in its score are exchange rate stability, compensation levels, and improvements in pollution control.
More Information:
- Global Competitiveness Index is different from The Global Competitiveness Report (GCR) (a yearly report published by the World Economic Forum)
Source: Money Control
Critical Minerals List
Tags: General Studies – 1 Mineral & Energy Resources, General Studies – 2 Government Policies & Interventions
Why in news?
Recently, the Ministry of Mines, Government of India unveiled the first-ever report on “Critical Minerals for India” prepared by an expert team constituted by the Ministry of Mines.
About:
- Critical minerals are a group of minerals that are essential for various industrial sectors and have strategic importance for a country’s economy and security.
- These minerals are characterized by their scarcity, high economic value, and criticality in the production of advanced technologies and defence systems.
- It is a dynamic process, and it can evolve over time as new technologies, market dynamics, and geopolitical considerations emerge.
- Different countries may have their own unique lists of critical minerals based on their specific circumstances and priorities.
- Critical Minerals List for India:
- Expert Committee under Ministry of Mines has identified a set of 30 critical minerals for India.
- These are Antimony, Beryllium, Bismuth, Cobalt, Copper, Gallium, Germanium, Graphite, Hafnium, Indium, Lithium, Molybdenum, Niobium, Nickel, PGE, Phosphorous, Potash, REE, Rhenium, Silicon, Strontium, Tantalum, Tellurium, Tin, Titanium, Tungsten, Vanadium, Zirconium, Selenium and Cadmium.
- Creation of Centre of Excellence for Critical Minerals (CECM) in the Ministry of Mines is also recommended by the Committee.
- CECM will periodically update the list of critical minerals for India and notify the critical mineral strategy from time to time.
- Critical Minerals List prioritizes minerals essential for industrial sectors like high-tech electronics, telecommunications, transport, and defence.
Source: PIB Gov.
Global Environment Facility (GEF)
Tags: General Studies –3 Environment & Ecology
Why in news?
Recently, at the 64th Global Environment Facility (GEF) council meeting in Brazil, the governing body approved the disbursement of $1.4 billion to accelerate efforts to tackle the climate, biodiversity, and pollution crises.
About:
- Of the total 4 billion, $653 million has been allocated specifically for biodiversity, aiming to support countries in updating their National Biodiversity Strategies and Action Plans and meeting the targets of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework by 2030.
- This is the second work program of the GEF-8 funding period, which runs from 2022 and 2026.
- The United Nations Development Programme, UN Environment Programme, and Food and Agriculture Organization are the top recipients among the 18 implementing agencies for GEF.
- Latin America and the Caribbean region receive the most funding, followed by Africa.
- A new trust fund called the Global Biodiversity Framework Fund will be established to support the implementation of the Kunming-Montreal biodiversity framework.
Global Environment Facility
- The Global Environment Facility (GEF) was established on the eve of the 1992 Rio Earth Summit of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) with the aim of addressing critical environmental challenges faced by our planet.
- GEF has 184 member countries, including India, and operates as an international partnership for environmental action and sustainable development.
- GEF is a collection of funds dedicated to addressing issues such as biodiversity loss, climate change, pollution, and the degradation of land and ocean health.
- It provides financial support for five major international environmental conventions, namely:
- Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD).
- United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC)
- Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs)
- UN Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD)
- Minamata Convention on Mercury
| Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework: |
| It is a global agreement adopted at the 15th Conference of Parties (2022) to the UN Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD). It sets forth four goals and 23 targets to be achieved by 2030 to address the biodiversity crisis. The framework aims to restore and conserve ecosystems, reduce species extinction risk, mitigate pollution, promote sustainable practices, and allocate financial resources for biodiversity conservation. It also emphasizes the need for international cooperation and monitoring to track progress. |
Source: Down to Earth
Nepal
Tags: General Studies –1 Geography
Why in news?
Recently, the Supreme Court of Nepal has issued an interim order directing the government to establish a “transitional mechanism” to ensure the registration of marriages for “same-sex couples”.
About:
- Nepal is a landlocked country located in South Asia, lying along the southern slopes of the Himalayan Mountain ranges.
- It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain.
- It is located between India to the east, south, and west and the Tibet Autonomous Region of China to the north.
- West Bengal’s narrow Siliguri Corridor separates Nepal and Bangladesh.
- The capital and largest city of Nepal is Kathmandu.
Source: Hindu
Rwanda
Tags: General Studies –1 Geography
Why in news?
Recently, The UK Court of Appeal has ruled against the government’s plan to send asylum seekers to Rwanda, dealing a blow to Prime Minister Rishi Sunak’s administration.
About:
- Rwanda is a landlocked country in the Great Rift Valley of Central Africa, where the African Great Lakes region and Southeast Africa converge.
- It is located a few degrees south of the Equator.
- Rwanda is situated in the Great Lakes region of Africa and is bordered by Uganda to the north, Tanzania to the east, Burundi to the south, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the west and Lake Kivu.
- The country is known as the “Land of a Thousand Hills” due to its mountainous terrain.
- The capital and largest city of Rwanda is Kigali, located in the centre of the country on the Ruganwa River.
More Information:
- The ‘Rwanda policy’ as it is known, is part of the British government’s “stop the boats” strategy, i.e., a plan to deter migrants from crossing the English Channel to enter the U.K. The policy — which seeks to send potential asylees to Rwanda while their applications are adjudicated — applies to other asylum seekers in the U.K. as well.
Source: Indian Express
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

