
In today’s daily current affairs briefing for UPSC aspirants, we explore the latest developments that hold relevance for the upcoming civil services examination. Our focus today includes a critical analysis of recent policy changes, international affairs, and national developments, all of which play a pivotal role in shaping the socio-political and economic landscape of India. Stay informed and stay ahead in your UPSC preparations with our daily current affairs updates, as we provide you with concise, well-researched insights to help you connect the dots between contemporary events and the broader canvas of the civil services syllabus.
Contents
- 1 Climate Change Impact on Health
- 2 Labour Laws in India
- 2.1 In News:
- 2.2 Labor Framework in India: Constitutional and Legislative Dimensions
- 2.3 Constitutional Framework
- 2.4 Legislative Framework
- 2.5 Advantages of Labor Codes in India: Streamlining Laws for Economic Progress
- 2.6 Grey Areas in Current Labor Reforms: A Closer Look
- 2.7 Navigating the Future: Recommendations for Labor Reforms in India
- 3 BRICS
- 4 G-20
- 5 Furlough
- 6 Kambala
- 7 The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)
- 8 Central Adoption Resource Authority (CARA)
- 9 OPEC+
- 10 Inflation
- 11 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 11.1 Q: What are daily current affairs?
- 11.2 Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
- 11.3 Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
- 11.4 Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
- 11.5 Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
- 12 In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
Climate Change Impact on Health
Tag: GS-2 Polity
In News:
As climate change persists without abatement, it has the potential to exacerbate India’s dual challenge of dealing with both communicable and non-communicable diseases.
Climate Impact and Health Challenges in India: A Call for Urgent Action
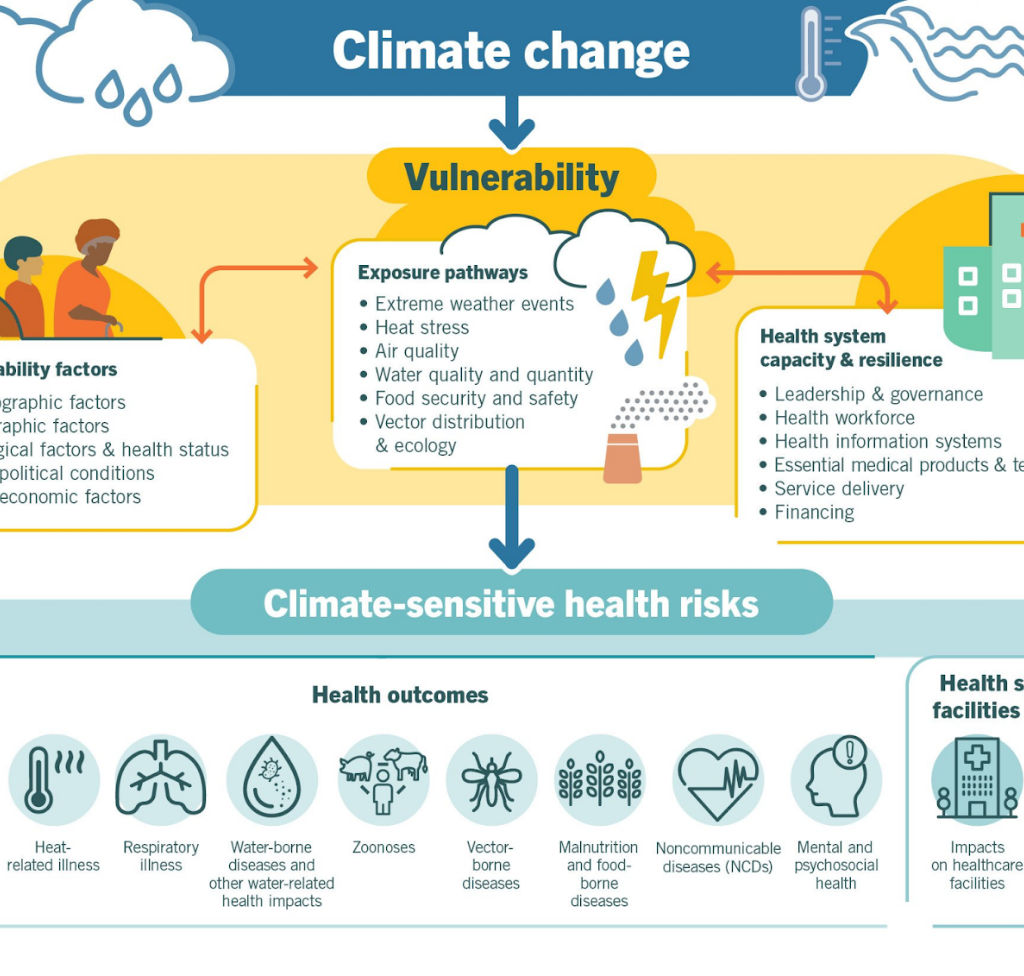
- India faces alarming consequences of climate change, with a 55% rise in heat-related deaths from 2000-2004 to 2017-2021.
- The government’s subsidy practices, especially the net negative carbon price in 2019, reflect significant support for fossil fuels, contributing to health threats.
- Overreliance on biomass and fossil fuels, comprising 61% of household energy, results in hazardous air quality, exceeding WHO recommendations.
- Urban areas, with 45% classified as moderately green, encounter economic losses, including 16,720 crore potential labor hours lost in 2021.
- Health impacts include a rise in dengue transmission and increased heatwave days, affecting vulnerable groups.
- Agricultural productivity decline and households facing energy poverty add to the urgent need for comprehensive climate and health strategies.
Integrating Health into Urban Redesign for Climate Resilience in India
- Addressing the intricate relationship between global warming, climate change, and human health is imperative for India.
- Urban redesign prioritizing health can offer solutions such as increased green spaces to combat urban heat, enhance air quality, and promote physical and mental well-being.
- Reducing reliance on fossil fuels is crucial for preventing health issues related to particulate matter.
- Implementing and adapting heat action plans, like the successful one in Ahmedabad, nationwide is essential.
- Minimizing the use of dirty fuels emerges as a critical step to mitigate health impacts.
- India needs a comprehensive approach to climate resilience that integrates health considerations into urban planning and energy choices.
Source: TH
Labour Laws in India
Tag: GS- 2 Centre-State Relations, Government Policies & Interventions, Welfare Schemes, Transparency & Accountability GS- 3 Planning, Employment, Inclusive Growth
In News:
The Punjab and Haryana High Court made a decision to nullifying the Haryana State Employment of Local Candidates Act, 2020, mandating 75% reservation for state residents in private sector jobs.
Labor Framework in India: Constitutional and Legislative Dimensions
- In India, the labor framework is shaped by a constitutional foundation and evolving legislative measures.
- The Constitution places labor in the Concurrent List, empowering both Central and State governments to enact legislation, with certain matters reserved for the Center.
Constitutional Framework
- Article 14-Ensures equality before the law or equal protection of laws.
- Article 16-Addresses the right to equal opportunity in public employment.
- Article 39(c)-Advocates against the concentration of wealth and means of production to the detriment of society.
Legislative Framework
- Numerous legislative and administrative initiatives have been undertaken to enhance working conditions and simplify labor laws.
- The latest development includes four consolidated labor codes introduced by the government, yet to be fully implemented:
- Code of Wages, 2019
- Industrial Relations Code, 2020
- Social Security Code, 2020
- Occupational Safety, Health and Working Conditions Code, 2020
Advantages of Labor Codes in India: Streamlining Laws for Economic Progress
Simplification of Law
- The Labor Codes streamline the intricate web of labor laws by consolidating 29 central laws that have been pending for nearly two decades.
- This consolidation is expected to provide a significant boost to industries, stimulate employment, and reduce confusion for businesses.
Easier Dispute Resolution
- The revamped adjudication processes simplify archaic labor laws, promoting quicker and more efficient dispute resolution mechanisms.
- This contributes to a more favorable business environment by minimizing legal complexities.
Facilitating Ease of Doing Business
- Economists and industry experts anticipate that these reforms will enhance investment opportunities and create a more business-friendly atmosphere.
- The reforms aim to mitigate internal contradictions, increase flexibility, and modernize regulations related to safety and working conditions.
Promoting Gender Parity
- The Labor Codes ensure gender parity by allowing women to work at night across all sectors. However, stringent security arrangements must be in place, and women’s consent is a prerequisite for night work.
Grey Areas in Current Labor Reforms: A Closer Look
- While the recent labor reforms in India aim to bring positive changes, certain grey areas and ambiguities have emerged, necessitating further clarification and adjustments.
- Key concerns include the role of an “Inspector-cum-Facilitator,” lack of clarity in defining workers and employees, exclusion of small startups and the informal sector from social security coverage, non-inclusion of charitable or non-profit-based establishments, and the oversight of “invisible labor.”
- These issues highlight the need for comprehensive review and fine-tuning to ensure inclusivity and equitable treatment across various sectors and worker categories.
- As India undergoes significant labor reforms, the way forward involves strategic initiatives to optimize and empower the labor force.
- Priorities include establishing accrediting agencies for vocational training institutes, interlinking vocational training with academic education, enacting state-level legislation for the welfare of unorganized workers, and enhancing employment information services through e-governance.
- Additionally, a forward-looking approach is essential to address challenges posed by automation, robotics, AI-powered workforces, and bioengineering, ensuring that the rights and well-being of workers are safeguarded in the evolving landscape.
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Prelims (2017) Q. Consider the following statements: The Factories Act, 1881 was passed with a view to fix the wages of industrial workers and to allow the workers to form trade unions. N.M. Lokhande was a pioneer in organizing the labour movement in British India. Which of the above statements is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 Ans: (b) Mains(2015) Q. “Success of ‘Make in India’ programme depends on the success of ‘Skill India’ programme and radical labour reforms.” Discuss with logical arguments. |
Source: TH
BRICS
Tag: GS-2 IR
In News:
Recently, Chinese President Xi Jinping called for an immediate ceasefire and the suspension of hostilities by all parties engaged in the Israel-Palestinian conflict.
About BRICS
- BRICS is an acronym representing the alliance of the world’s major emerging economies: Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa.
- Coined by British Economist Jim O’Neill in 2001, BRICS was formalized during the inaugural meeting of BRIC Foreign Ministers in 2006. South Africa joined in 2010, leading to the adoption of the acronym BRICS.
- BRICS comprises five significant developing nations, representing 41% of the global population, 24% of the global GDP, and 16% of global trade.
- The forum’s chairmanship rotates annually among members following the B-R-I-C-S acronym. India held the chair in 2021.
Key Initiatives
New Development Bank (NDB)
- Established during the Sixth BRICS Summit in 2014 in Fortaleza, Brazil.
- Aims to foster development projects in BRICS nations.
Contingent Reserve Arrangement
- Signed in 2014 to address short-term balance of payments pressures and enhance financial stability among BRICS nations.
BRICS Payment System
- In response to Russia’s exclusion from SWIFT post-Ukraine war, BRICS nations are working on an alternative payment system.
Customs Agreements
- Signed to streamline and facilitate trade transport coordination among BRICS countries.
Remote Sensing Satellite
- Launched a constellation of remote sensing satellites involving India, China, Russia, and Brazil-China collaboration.
Advancing BRICS Cooperation: A Holistic Approach
Cooperation Within the Group
- For BRICS to sustain its relevance, it must shift away from China-centric centrality, fostering internal balance and diversification.
- Realistic assessments of opportunities and limitations by each member are crucial.
- Exploring ‘BRICS plus’ cooperation on multiple levels will amplify representation, influence, and global contributions.
Upholding Universal Security
- BRICS nations should be advocates of universal security, avoiding actions that jeopardize others.
- Prioritizing dialogue over confrontation, they should contribute to building a balanced, effective, and sustainable regional security architecture.
- Strengthening mutual trust, security cooperation, and addressing core interests are paramount.
Securing Economic Interests
- As contributors to common development, BRICS countries must navigate de-globalization and unilateral sanctions.
- Emphasizing cooperation in supply chains, energy, food, and financial resilience is vital.
- Establishing an institutional research wing akin to the OECD can provide tailored solutions for the developing world.
A Global Governance Philosophy
- BRICS should adopt a global governance philosophy emphasizing extensive consultation, joint contribution, and shared benefits.
- Strengthening unity with emerging markets and developing countries, BRICS must play an active role in safeguarding the international system, promoting inclusive international rules, and ensuring shared development outcomes.
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Prelims (2016) Q. Consider the following statements: New Development Bank has been set up by APEC. The headquarters of the New Development Bank is in Shanghai. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 Ans: (b) Prelims (2015) Q. The ‘Fortaleza Declaration’, recently in the news, is related to the affairs of (a) ASEAN (b) BRICS (c) OECD (d) WTO Ans: (b) Prelims (2014) Q. With reference to a grouping of countries known as BRICS, consider the following statements: The First Summit of BRICS was held in Rio de Janeiro in 2009. South Africa was the last to join the BRICS grouping. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 Ans: (b) |
Source: TH
G-20
Tag: GS-2 IR Bilateral Groupings & Agreements, Groupings & Agreements Involving India and/or Affecting India’s Interests
In News:
Recently, China announced that its premier would participate in the virtual G-20 Leaders’ Summit at the invitation of India.
About G20
- The G20, consisting of 19 countries and the European Union, serves as a key intergovernmental forum.
- Representing about 90% of the global economy, 75–80% of international trade, and two-thirds of the world’s population, it was established in 1999 in response to economic crises.
- The G20, convening annually since 2008, operates without a permanent secretariat. Member nations take turns chairing meetings, with India and Brazil hosting the 2023 and 2024 summits.
- In addition to core economic topics, the G20 addresses inclusive growth, focusing on issues such as migration, digitization, healthcare, and the empowerment of women, aligning with global priorities like the UN Sustainable Development Goals and the Paris Climate Agreement adopted in 2015.
India’s Key Priorities and Contributions in the G20
India actively engages in the G20 process, recognizing its significant role as a major developing economy with a vested interest in global economic and financial stability. The country’s agenda in G20 Summits revolves around fostering inclusivity in the financial system, preventing protectionist tendencies, and safeguarding the growth prospects of developing nations.
Key Thrust Areas for India in G20
Terrorism
- Advocating international cooperation to address terrorism, acknowledging its global nature.
- Emphasizing the importance of coordinated action against the financial networks supporting terrorism.
Economic Offenders
- Highlighting the challenge of dealing with economic offenders.
- Seeking cooperation from G20 countries to address this issue, a proposal well-received by member nations.
Taxation
- Addressing global taxation challenges through initiatives like the Base Erosion and Profit Sharing (BEPS) framework.
- Advocating the need to strengthen frameworks to tackle challenges from global supply chains and expanding e-commerce.
New Digital Technologies
- Acknowledging the rapid spread of digital technologies globally.
- Collaborating with G20 nations to address issues such as privacy, data security, and digital governance associated with these technologies.
Shaping an Inclusive and Responsible Digital Agenda: India’s G20 Presidency 202
- In 2023, India’s G20 presidency presents the challenge of establishing a globally accepted framework for digital technology amidst increasing protectionism.
- Key issues include the distrust in safeguarding citizens’ data by foreign entities and substantial digital disparities among nations.
- Drawing from G20 experiences, India proposes a working group to address cross-border health data flows and telemedicine requirements.
- The initiation of a ‘digital twins’ initiative aims to link cities across member nations, fostering digital infrastructure projects for enhanced connectivity.
- Although India did not sign the Osaka Declaration in 2019, focusing on “Data Free Flow with Trust,” its proactive stance on open government data persists.
- During its G20 leadership, India suggests broadening open government data principles beyond anti-corruption measures, advocating for a standardized, interoperable cloud framework.
- This framework facilitates seamless data sharing among government levels, supporting evidence-based policy decisions. Success hinges on India’s ability to exhibit itself as an inclusive, responsible, and adept digital leader on the global stage.
Source: TH
Furlough
Tag: GS-2
In News:
Recently, Dera Sacha Sauda chief Gurmeet Ram Rahim Singh, who is currently serving a 20-year jail term for the rape of two women disciples, walked out of Rohak’s Sunaria Jail.
About Furlough
- Similar to parole but with notable distinctions, furlough is granted specifically in cases of extended imprisonment.
- The duration of furlough for a prisoner is considered a remission of their sentence.
- In contrast to parole, furlough is regarded as a entitlement for prisoners, provided at regular intervals regardless of any specific justification.
- Its primary purpose is to allow prisoners to maintain family and social connections and counteract the adverse effects of prolonged incarceration.
What is Parole?
- Parole is a mechanism involving the temporary release of a prisoner with the suspension of their sentence.
- This release is contingent upon specific conditions, often related to behavior, and mandates regular reporting to authorities for a predetermined duration.
- Unlike furlough, parole is not an inherent right for prisoners; rather, it is granted for particular reasons, such as a family death or the wedding of a close relative.
- The approval or denial of parole is at the discretion of the competent authority, and even if a prisoner presents a compelling case, release may be withheld if it is deemed contrary to the interests of society.
Source: IT
Kambala
Tag: GS-1 Art and Culture
In News:
Following backlash over inviting a BJP MP, organizers of the inaugural Kambala buffalo race event in Bengaluru acknowledged the oversight and announced that the individual would not be attending the event
About Kambala
- Kambala is a traditional buffalo race conducted in slush-filled paddy fields, primarily occurring in coastal Karnataka (Udupi and Dakshina Kannada) between November and March.
- Historically, local Tuluva landlords and households in coastal districts sponsored this event.
- The Tuluva people, an ethnic group in Southern India, are native speakers of the Tulu language.
- During the race, participants endeavor to control the buffaloes by tightly holding their reins and using whips.
- In its traditional manifestation, Kambala was non-competitive, with buffalo pairs racing sequentially in paddy fields.
- Additionally, it served as a form of thanksgiving to deities for safeguarding the animals from diseases.
- However, the sport faces criticism from animal activists who argue that Kambala involves cruelty towards animals that are not physiologically suited for racing.
- They contend that the buffaloes run in the race out of fear of being whipped.
- Activists assert that such practices violate the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (PCA) Act of 1960, which prohibits activities causing unnecessary pain to animals, amounting to cruelty.
Source: TH
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)
Tag: GS-2 IR International Institutions
In News:
The OECD report indicates that economically developed countries failed to mobilize $100 billion annually for addressing the climate mitigation needs of developing nations.
What is OECD?
- The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) is an international body comprising 38 nations dedicated to promoting democracy and market economies.
- Typically, OECD members are democratic countries that endorse free-market economic principles.
- Established on December 14, 1960, by 18 European nations, the United States, and Canada, the OECD’s headquarters are located in Paris, France.
- The primary objective of the OECD is to shape policies that advance prosperity, equality, opportunity, and well-being globally.
- It achieves this goal through the publication of economic reports, statistical databases, analyses, and forecasts pertaining to worldwide economic growth.
- Additionally, the organization is actively involved in global efforts to combat bribery and financial crime.
- The OECD administers a “black list” comprising nations identified as uncooperative tax havens.
- Alongside its member countries, the OECD maintains collaborative relationships with non-member economies, including India, to further its objectives and initiatives.
Source: TH
Central Adoption Resource Authority (CARA)
Tag: GS-2 Statutory and Non-Statutory Bodies
In News:
The court mandates that States and Union Territories initiate a bi-monthly drive to identify children in the orphaned, abandoned, surrendered category in institutions.
About CARA
- Established as a statutory body under the Ministry of Women and Child Development, the Central Adoption Resource Authority (CARA) serves as the pivotal entity for overseeing the adoption process of Indian children.
- Its core responsibilities encompass the regulation and monitoring of both domestic and international adoptions.
- CARA holds the significant designation of being the Central Authority for managing inter-country adoptions, aligning with the guidelines outlined in the Hague Conventions on Inter-Country Adoptions, ratified by the Government of India in 2003.
- In its capacity, CARA focuses on facilitating the adoption of orphaned, abandoned, and surrendered children, collaborating with affiliated and recognized adoption agencies.
- As a central agency, CARA plays a crucial role in ensuring the welfare and ethical considerations in the adoption procedures, safeguarding the rights and interests of the children involved.
The Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction
- The Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction is a multilateral treaty established on December 1, 1983.
- This international agreement is designed to facilitate the swift return of a child who has been taken away from their “habitual residence” country.
- The provisions of the Convention specifically pertain to children under the age of 16.
Source: TH
OPEC+
Tag: GS-2 Important International Institutions
In News:
Oil prices didn’t change much in Asia because the expected increase in U.S. crude oil supply offset the positive impact of potential cuts in oil production by the OPEC+ group.
What is OPEC+?
- Countries outside of OPEC that export crude oil are referred to as OPEC plus nations.
- These include Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Brunei, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Mexico, Oman, Russia, South Sudan, and Sudan.
About OPEC
- Established during the Baghdad Conference in 1960 by Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela, the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) is a permanent intergovernmental organization.
- Its primary objective is to effectively manage global oil supply, stabilizing oil prices to prevent economic disruptions in both producer and consumer nations.
- OPEC’s headquarters are situated in Vienna, Austria, and membership is open to countries with significant oil exports that align with the organization’s principles.
- While Gabon ended its membership in January 1995, it re-entered the organization in July 2016.
- As of 2023, OPEC consists of 13 Member Countries, including Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), Saudi Arabia, Algeria, Libya, Nigeria, Gabon, Equatorial Guinea, the Republic of Congo, Angola, and Venezuela.
Source: ET
Inflation
Tag: GS-3 Economy
In News:
The Finance Ministry noted that while inflationary pressures have eased, the ongoing concerns are price increase, potential impacts on the rupee’s value and the balance of payments situation.
About Inflation
- Inflation, the rise in prices of goods and services, can be categorized into Demand Pull Inflation, driven by increased aggregate demand surpassing supply, and Cost Push Inflation, caused by factors such as reduced aggregate supply and artificial scarcity.
- In India, inflation is measured by Wholesale Price Index (WPI) and Consumer Price Index (CPI).
- While a certain level of inflation is essential for economic vitality, excessive inflation impacts the cost of living and economic growth negatively.
- The central government, particularly the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation in India, monitors and measures inflation.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) plays a crucial role in controlling inflation through its Monetary Policy Committee, utilizing tools like bank rate, repo rate, and open market operations.
- The government also employs fiscal policy, adjusting government revenue and expenditure, to curb inflation.
- Additionally, price control measures are implemented, although they offer short-term relief rather than a long-term solution.
| UPSC Previous Year Questions Prelims (2016) Q. With reference to Indian economy, demand-pull inflation can be caused/increased by which of the following? Expansionary policies Fiscal stimulus Inflation-indexing of wages Higher purchasing power Rising interest rates Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1, 2 and 4 only (b) 3, 4 and 5 only (c) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only (d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 Ans: (a) Prelims (2020) Q. Consider the following statements: The weightage of food in Consumer Price Index (CPI) is higher than that in Wholesale Price Index (WPI). The WPI does not capture changes in the prices of services, which CPI does. Reserve Bank of India has now adopted WPI as its key measure of inflation and to decide on changing the key policy rates. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 2 only (c) 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (a) |
Source: TH
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are daily current affairs?
A: Daily current affairs refer to the most recent and relevant events, developments, and news stories that are happening around the world on a day-to-day basis. These can encompass a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science, technology, sports, and more.
Q: Why is it important to stay updated with daily current affairs?
A: Staying updated with daily current affairs is crucial because it helps individuals make informed decisions in their personal and professional lives. It enables people to understand the world around them, stay aware of significant events, and engage in informed discussions about important issues.
Q: Where can I access daily current affairs information?
A: There are various sources for daily current affairs, including newspapers, news websites, television news broadcasts, radio programs, and dedicated apps or newsletters. Social media platforms are also widely used to share and access current affairs information.
Q: How can I effectively incorporate daily current affairs into my routine?
A: To incorporate daily current affairs into your routine, consider setting aside specific times each day to read or watch news updates. You can also subscribe to newsletters or follow news apps to receive curated content. Engaging in discussions with peers or participating in online forums can further enhance your understanding of current events.
Q: What are some tips for critical analysis of daily current affairs?
A: When analyzing daily current affairs, it’s essential to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy. Additionally, consider the source’s credibility and bias, if any. Develop the ability to identify the main points and implications of news stories, and critically evaluate the significance and impact of the events reported.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here

