The Budget 2024-25 aims to set a clear five-year roadmap for India’s economy, focusing on sustainable growth and development. This budget outlines the government’s strategic plans to boost key sectors, enhance infrastructure, and promote digital innovation. With a vision to make India a global economic powerhouse, the budget addresses critical areas like healthcare, education, and employment. It also emphasizes fiscal discipline and efficient resource allocation. This comprehensive plan seeks to balance immediate needs with long-term goals, ensuring a prosperous future for all citizens.

Tags: GS – 2 , Polity & Governance- Parliament– Government Policies & InterventionsIndian Constitution, GS – 3, Economy- Inclusive Growth
Contents
- 0.1 Context
- 0.2 Noteworthy Aspect of NDA 3.0 First Budget: Commitment to Fiscal Consolidation
- 0.3 Some Other Positive Takeaways from the Budget Speech
- 0.4 Proposals Outlined in Budget Aimed at Rationalising Tax Structures:
- 1 Conclusion
- 2 UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
- 3 FAQs
- 4 To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
Context
- The first budget of the NDA government’s third term sets forth two primary expectations for the economy: a clear roadmap on fiscal consolidation and a strategy for medium-term interventions to address the challenges facing the economy.
- The budget eye on generating employment, improving infrastructure, and rationalising GST, Budget 2024 offers some elements of a medium-term framework for economic policy.
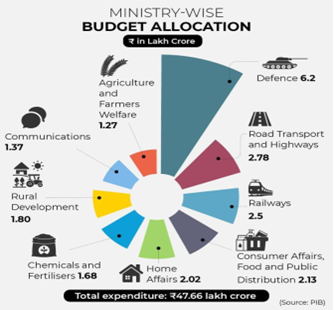
Noteworthy Aspect of NDA 3.0 First Budget: Commitment to Fiscal Consolidation
- Reduction in Fiscal Deficit:
- Fiscal deficit represents the gap between the government’s total expenditure and its total revenue (excluding borrowings).
- For the fiscal year 2024-25, the budget sets the fiscal deficit target at 4.9 percent of GDP, a reduction from previous estimates.
- This target is significant as it indicates a disciplined approach to managing public finances. Furthermore, the budget aims to achieve a fiscal deficit of 4.5 percent of GDP in the following fiscal year, moving closer to the long-term goal of a sustainable fiscal balance.
- This gradual reduction reflects a strategic balance between fiscal prudence and the need to support economic growth.
- Debt-to-GDP Ratio:
- The budget projects a decrease in the central government’s debt-to-GDP ratio from 58.2 percent to 56.8 percent.
- This reduction indicates a proactive effort to manage the country’s debt levels, ensuring that debt does not grow faster than the economy.
- Lowering the debt-to-GDP ratio is essential for maintaining investor confidence and ensuring the sustainability of public finances.
- Flexibility in Fiscal Policy:
- The incorporation of flexibility in fiscal policy allows the government to respond quickly to economic fluctuations and unforeseen challenges.
- The budget does not provide a detailed roadmap beyond 2025-26, instead proposing to keep the fiscal deficit each year such that the central government debt will be on a declining path as a percentage of GDP.
- This flexibility can be advantageous in dealing with economic uncertainties, though it may limit predictability for businesses and investors.
- Utilisation of Surplus and Efficient Resource Allocation:
- In recent years, the government has utilised surplus revenues, particularly from the Reserve Bank of India, to support fiscal consolidation.
- This year’s budget continues this trend, with surplus receipts contributing to the reduction of the fiscal deficit.
- By directing additional resources toward debt reduction, the government demonstrates fiscal prudence and a long-term vision for economic stability.
Some Other Positive Takeaways from the Budget Speech
- Balancing Fiscal Prudence and Expenditure Needs:
- Fiscal consolidation often necessitates a careful balance between reducing deficits and ensuring adequate public expenditure.
- The budget achieves this balance by not only focusing on deficit reduction but also addressing critical expenditure needs.
- Over the past three years, buoyant tax revenues have provided additional fiscal space, allowing for increased allocations to various spending programs.
- This year, some of the additional resources have been directed toward fiscal consolidation, while others have been allocated to essential public services and infrastructure projects.
- This balanced approach ensures that fiscal prudence does not come at the expense of necessary public investments.
- Medium-Term Economic Interventions:
- Addressing the challenges highlighted in the Economic Survey 2023-24, the budget outlines initiatives for the current year and the next five years.
- Key concerns include employability and employment for the youth and improved infrastructure.
- Initiatives to enhance employability through skilling and higher employment through financial support for provident fund contributions are proposed.
- While these initiatives are welcome, a comprehensive framework would help identify synergies among potential initiatives.
- The proposal to present an economic policy framework is a positive step, as it can help establish consistent medium-term expectations on likely reforms.
Proposals Outlined in Budget Aimed at Rationalising Tax Structures:
Indirect Tax Reforms: GST and Customs Duties:
- GST Rationalisation:
- The Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime has been relatively stable in terms of its structure and design.
- However, the budget signals the need for further rationalisation of GST rates. This includes streamlining the tax slabs to reduce complexity and improve compliance.
- By making the GST structure more coherent, the government hopes to boost economic activity and enhance revenue collection.
- Expansion of GST Base:
- The budget proposes to expand the GST base and this involves bringing more goods and services under the GST ambit, thereby increasing the tax net.
- Expanding the base can help in raising additional revenue without increasing the tax rates.
- It also promotes fairness by ensuring that more sectors contribute to the tax system.
- This approach is crucial for achieving a more inclusive and balanced tax regime.
- Recalibration of Customs Duties:
- The government uses customs duties to achieve multiple objectives, including protecting domestic industries and enhancing competitiveness.
- The budget proposes regular recalibration of customs duties to address varying economic concerns.
- For instance, duties may be reduced to lower the cost of essential imports or increased to protect nascent domestic industries from international competition.
Direct Tax Reforms: Simplification and Equity:
- Review of the Income Tax Act:
- The budget proposes a comprehensive review of the Income Tax Act to make it more concise, lucid, and user-friendly.
- This initiative aims to simplify the tax code, making it easier for taxpayers to understand their obligations and comply with the law.
- Vivad se Vishwas Scheme 2024:
- To address the long-standing issue of tax disputes, the budget introduces the Vivad se Vishwas, 2024 scheme.
- This scheme aims to resolve pending litigation by offering taxpayers a one-time opportunity to settle disputes by paying a reduced amount of the contested tax.
- Limiting Appeals and Enhancing Dispute Resolution:
- In addition to the Vivad se Vishwas scheme, the budget proposes measures to limit the number of appeals by tax departments in cases involving small liabilities.
- This step is intended to reduce unnecessary litigation and focus on significant cases.
- Addressing Inequality: Taxing Capital Gains and High-Income Earners:
- Globally, there is an increasing concern about rising economic inequality and the need for progressive taxation.
- The budget addresses this issue by proposing higher taxes on capital gains, both short-term and long-term.
- While this move may impact investors, it is intended to ensure that those who benefit significantly from capital markets contribute their fair share to the economy.
- To balance this, the budget raises the exemption limit for retail investors to Rs. 1.25 lakh, providing relief to small investors.
- Enhanced Securities Transaction Tax (STT):
- Additionally, the budget proposes an enhanced STT on futures and options transactions.
- This measure aims to curb speculative activities in the capital markets and bring stability.
- By cooling some of the fervour in the markets, the government hopes to reduce volatility and create a more stable investment environment.
Conclusion
The commitment to fiscal consolidation in the NDA 3.0 government’s first budget is evident. Balancing fiscal prudence with essential public expenditure needs, the budget lays a robust foundation for sustainable economic growth and financial stability, developing confidence among investors and citizens alike.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q:1 Along with the Budget, the Finance Minister also places other documents before the Parliament which include ‘The Macro Economic Framework Statement’. The aforesaid document is presented because this is mandated by (2020)
- Long standing parliamentary convention
- Article 112 and Article 110(1) of the Constitution of India
- Article 113 of the Constitution of India
- Provisions of the Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act, 2003
Ans: (d)
Mains:
Q:1 Distinguish between Capital Budget and Revenue Budget. Explain the components of both these Budgets. (2021)
Source: IE
FAQs
Q: What is the Budget 2024-25 about?
- Answer: The Budget 2024-25 outlines the government’s financial plan for the upcoming year and sets a five-year roadmap for India’s economy. It includes proposals on spending, taxes, and economic policies aimed at fostering growth and development.
Q: Why is a five-year roadmap important in the Budget 2024-25?
- Answer: A five-year roadmap is important because it provides a long-term vision for the economy. It helps ensure that the government’s plans and policies are sustainable and focused on achieving specific goals, like boosting infrastructure, improving healthcare, and supporting education.
Q: What are some key highlights of the Budget 2024-25?
- Answer: Key highlights include increased spending on infrastructure projects, tax relief for middle-income families, investment in green energy, and initiatives to support small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). These measures are designed to stimulate economic growth and create jobs.
Q: How will the Budget 2024-25 impact everyday people?
- Answer: The budget aims to benefit everyday people by improving public services, reducing tax burdens, and creating employment opportunities. For example, better infrastructure can lead to more jobs, while tax relief can increase disposable income for families.
Q: What challenges might the Budget 2024-25 face?
- Answer: Challenges include managing the fiscal deficit, ensuring the effective implementation of proposed projects, and navigating global economic uncertainties. The government will need to balance spending with revenue and ensure that policies are efficiently executed to achieve the desired outcomes.
To get free counseling/support on UPSC preparation from expert mentors please call 9773890604
- Join our Main Telegram Channel and access PYQs, Current Affairs and UPSC Guidance for free – Edukemy for IAS
- Learn Economy for free- Economy for UPSC
- Mains Answer Writing Practice-Mains Answer Writing
- For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here

