In the complex interplay between environmental sustainability and economic development, the contentious issue of coal mining emerges as a focal point. Despite its well-documented adverse environmental impact, coal mining remains an inevitable force driving global development. The undeniable demand for energy, particularly in burgeoning economies, necessitates the extraction of coal—a potent but environmentally deleterious resource. The paradox lies in the fact that while the world increasingly pivots towards renewable alternatives, the inherent challenges in transitioning swiftly leave many nations reliant on coal for their energy needs. Balancing the imperative for economic growth with the imperative to curb environmental degradation requires nuanced policymaking. This essay will delve into the multifaceted aspects of this dilemma, examining the global dynamics that perpetuate coal mining and the imperative for sustainable practices in the face of its environmental repercussions.
Tag: Geography.
Contents
Decoding the Question:
- In Introduction, try to write about coal mining briefly.
- In Body,
- Write how coal mining affects the environment.
- Also, write how it contributes to development.
- In Conclusion, try to write other alternative methods.
Answer:
Coal mining is the extraction of coal deposits from the surface of Earth and from underground. India has the 4th largest coal reserve in the world. It is recognized as a leading energy source in India for many decades and contributes to nearly 55% of India’s energy requirement. Right from its genesis, commercial coal mining in modern times in India has been dictated by domestic consumption needs.
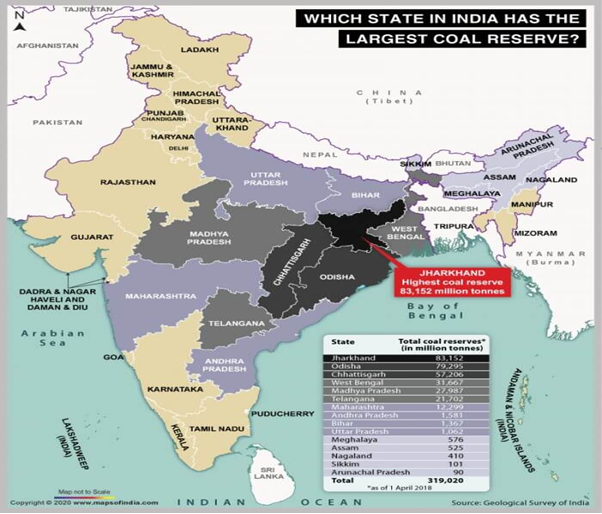

Adverse Environmental Impacts of Coal Mining:
- Air Pollution: Coal mining operations release a substantial amount of particulate matter, sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and other pollutants into the air. These emissions contribute to smog formation, acid rain, and respiratory problems in nearby communities.
Example: The Jharia coalfield in Jharkhand is one of India’s largest coal reserves and a significant contributor to air pollution.
- Water Pollution: Coal mining can lead to the contamination of surface and groundwater sources. Acid mine drainage (AMD) is a common issue, where water reacts with exposed coal and rock, releasing acidic and toxic substances into water bodies, harming aquatic life and polluting water supplies.
Example: In the Singrauli region of Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh, coal mining operations have led to the contamination of local rivers and water sources.
- Soil Degradation: Surface mining methods, such as mountaintop removal and strip mining, disrupt the natural landscape and result in the loss of topsoil and vegetation. This degradation of soil quality affects plant growth and reduces the land’s ability to support wildlife and agriculture.
Example: In the Raniganj coalfield in West Bengal, extensive strip mining and coal extraction have caused severe soil degradation and loss of fertile topsoil.
- Methane Emissions: Coal mining releases methane, a potent greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere. Methane emissions contribute to climate change and exacerbate global warming.
Example: Coal mining operations in the Godavari Valley Coalfield in Andhra Pradesh release significant amounts of methane during extraction.
- Land Subsidence: Underground coal mining can cause land subsidence, where the ground sinks or collapses due to the removal of coal from beneath the surface. This can damage infrastructure and disrupt the stability of the landscape.
Example: In the Jharia coalfield, extensive underground mining has caused land subsidence and the collapse of land above mined-out areas. This has led to infrastructure damage, including roads, buildings, and railways.
Coal Mining is Inevitable for Development: The statement “Coal Mining is Inevitable for Development” is a viewpoint that has been debated extensively in the context of economic development and energy needs. Here are some key arguments both in favour of and against this statement:
Arguments in Favour of Coal Mining for Development:
- Energy Source: According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), in 2020, coal accounted for around 37% of the world’s electricity generation, making it a major source of energy for electricity production, thus ensuring energy security.
- Economic Growth: The World Coal Association estimates that the coal industry supports over 7 million jobs worldwide, including direct employment in mining and jobs in associated industries like transportation and manufacturing.
- Industrialization: The industrial sector is a major consumer of coal-based energy. For example, in China, coal is a primary energy source for steel, cement, and chemical industries, vital for the country’s economic development and infrastructure growth.
Arguments Against Coal Mining for Development:
- Environmental Impact: The combustion of coal is responsible for about 40% of global CO2 emissions, making it a significant contributor to climate change and its associated impacts.
- Public Health Concerns: According to the World Health Organization (WHO), exposure to air pollutants from coal combustion leads to over 800,000 premature deaths annually globally due to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
- Climate Change: The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) states that coal-fired power plants are the largest source of global greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to rising temperatures and extreme weather events.
- Non-Renewable Resource: The U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) estimates that global proven coal reserves would last about 132 years at current consumption rates. Continued reliance on coal without alternative energy planning poses long-term energy security risks.
Conclusion:
Hence, Coal mining activity puts tremendous pressure on local flora and fauna, mainly where diversion of forest land for mining takes place. So, it is high time to think about any other alternative energy sources to achieve United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 7 (that aims to correct this enormous imbalance by ensuring everyone has access to affordable, reliable, and modern energy services by the year 2030).
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here


