Urbanization in India has witnessed unprecedented growth in recent decades, leading to both opportunities and challenges for the country. As cities expand rapidly, the quality of urban life becomes a critical concern, encompassing issues such as infrastructure, sustainability, and overall citizen well-being. Recognizing the need for a holistic and transformative approach, the Government of India launched the ‘Smart City Programme’ as a visionary initiative to address these urban challenges. The program aims to enhance the quality of life for citizens by leveraging technology and innovation to make cities more efficient, sustainable, and livable. To transform selected cities into vibrant, citizen-centric hubs, the Smart City Programme prioritizes key areas such as efficient urban mobility, robust infrastructure, sustainable environment practices, and enhanced citizen services. This strategic initiative seeks to create cities that are not only technologically advanced but also inclusive, ensuring that the benefits of urban development are accessible to all segments of society. Through a combination of smart solutions, community engagement, and strategic urban planning, the Smart City Programme aspires to redefine the urban landscape in India, setting a precedent for smart, sustainable, and resilient cities across the nation.
Tag: Urbanization.
Contents
Decoding the Question:
- In the Introduction, try to write a brief background of the quality of urban life. Here you can put data by Census 2011.
- In Body,
- Define smart cities.
- Elaborate more on the objectives and strategy of the ‘Smart City Programme.’
- Conclude with the importance of using the ‘Challenge’ or ‘Competition’ method to select cities and its positive impact.
Answer:
According to Census 2011, nearly 31% of the total population lives in cities, a figure that is expected to rise to around 50% by 2030. The quality of life in urban areas is extremely diverse. Urban areas are expected to house 40% of India’s population and contribute 75% of India’s GDP by 2030. This requires comprehensive development of physical, institutional, social, and economic infrastructure. The development of Smart Cities is a step in that direction.
Quality of urban life in India:
Positive:
- Employment Opportunities: According to a report by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation, India’s urban unemployment rate was 7.9% in 2022-2023. In urban areas like Bengaluru, which is known as India’s Silicon Valley, there is a thriving IT sector that offers job opportunities to skilled professionals.
- Healthcare Facilities: As per the National Family Health Survey (NFHS-5), around 75% of urban households had access to government and private healthcare facilities in 2022-2023.Cities like Mumbai and Delhi have a wide range of healthcare facilities, including government hospitals, private clinics, and specialty centres.
- Public Transport & Connectivity: As of 2022, India had over 135 operational airports, connecting cities and regions across the country. Urban cities like Delhi, Mumbai, and Bengaluru have well-established public transportation systems. The Delhi Metro, for instance, carries millions of passengers daily and plays a crucial role in easing traffic congestion.
- Better Access & Technological Advancements: According to the Census of India (2011), urban households have better access to basic services. Around 87% of urban households had access to electricity, while 78% had access to tap water. As of 2022, India has over 700 million internet users, with a majority residing in urban areas, facilitating the adoption of digital services. Cities just like Gurugram, a rapidly developing urban city in Haryana, has seen significant improvements in access to basic services

Negative:
- Air Pollution: According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 21 of the world’s 30 most polluted cities are in India, with high levels of particulate matter (PM2.5) and other harmful pollutants in the air. For example, Delhi, the capital city of India, frequently experiences severe air pollution, especially during the winter months.
- Water Scarcity: A study by the National Institution for Transforming India (NITI Aayog) reported that 21 major Indian cities, including Delhi, Bengaluru, and Chennai, could run out of groundwater by 2020. For example, Chennai, a major city in South India, faced a severe water crisis in 2019 due to depleted groundwater levels and deficient monsoon rains.
- Traffic Congestion: A report by the Boston Consulting Group (BCG) estimated that traffic congestion costs the Indian economy around 1.47 lakh crore rupees (approximately 20.7 billion USD) annually. For example, Mumbai, India’s financial capital, is notorious for its heavy traffic congestion.
- Inadequate Housing and Slums: According to the 2011 Census of India, over 65 million people in urban areas live in slums, facing substandard living conditions and inadequate access to basic amenities. For example, Mumbai’s Dharavi, one of the largest slums in Asia, is an example of the housing challenges faced by urban dwellers.
- Waste Management Challenges: A study by the Centre for Science and Environment (CSE) estimated that urban India generates over 1.5 lakh metric tonnes of solid waste daily. For example,Bengaluru, a major IT hub in India, has been grappling with waste management issues.
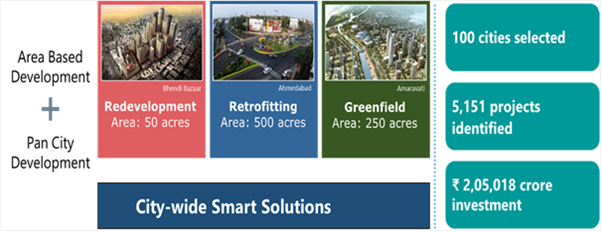
The objectives of the Smart City Programme :
- Infrastructure Development: As of June 2022, 5,151 projects worth INR 2,05,018 crores (approximately $27.5 billion) were under various stages of implementation across 100 Smart Cities in India. For example, the Bhubaneswar Smart City project in Odisha focuses on developing efficient public transportation systems and pedestrian-friendly streets.
- Technology Integration:The adoption of digital platforms has increased in Smart Cities, with 2,000 Wi-Fi hotspots installed in public places, and 8,497 smart classrooms established in schools as of June 2022. For example, the Surat Smart City project in Gujarat has implemented an Intelligent Traffic Management System to reduce congestion and improve traffic flow.
- Sustainability and Environment: The Smart City Programme emphasises sustainable development, including promoting green spaces, energy-efficient buildings, and renewable energy sources. As of June 2022, 4.55 million LED streetlights have been installed, saving 725 million kWh of electricity annually in Smart Cities. For example,The Kochi Smart City project in Kerala focuses on sustainable waste management and rainwater harvesting.
The Strategy of the ‘Smart City Programme:
- City Selection: In multiple rounds, 100 cities were selected based on their proposals and vision for smart city development. For example, cities like Bhubaneswar, Pune, and Jaipur were among the first 20 cities selected in the initial round.
- Area-Based Development: Each city develops a Smart City Proposal (SCP) for the chosen area, outlining the projects and interventions to be implemented. For example, Bhopal’s Smart City Proposal focuses on the development of the historic area known as “Bhimbetka Rock Shelters,” enhancing its tourism potential and preserving cultural heritage.
- Technology Integration: The program emphasises the integration of advanced technologies to improve urban services and infrastructure. For example, in Surat, a smart surveillance system with CCTV cameras and video analytics was implemented to enhance public safety and security.
Thus, this is the first time an Urban Ministry programme used the ‘Challenge’ or ‘Competition’ method to select cities for funding and used the strategy of area-based development. This captures the spirit of ‘competitive and cooperative federalism’. The Smart Cities Mission is meant to set examples that can be replicated both within and outside the Smart City, catalysing the creation of similar Smart Cities in various regions and parts of the country.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here


