India’s economic trajectory has been marked by consistent growth, showcasing its potential on the global stage. Despite these commendable strides, the nation grapples with persistently low indicators of human development, raising pertinent questions about the inclusivity and balance of its developmental endeavors. The paradox between economic advancement and human development underscores a complex interplay of multifaceted challenges that hinder the achievement of more equitable and comprehensive progress. One of the primary impediments lies in the stark regional disparities that persist across the country, with certain regions enjoying the fruits of economic growth while others lag. This regional imbalance not only exacerbates social inequalities but also perpetuates a cycle of underdevelopment in marginalized areas. Moreover, issues such as inadequate access to quality education, healthcare, and employment opportunities contribute to the persistence of a divided society. Discrimination based on gender, caste, and socio-economic status further exacerbates these challenges, limiting the potential for a harmonious and inclusive development. Tackling these systemic issues necessitates a holistic and targeted approach, addressing the root causes of inequality and fostering a more balanced and inclusive developmental framework for India.
Tag: Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources.
Contents
Decoding the Question:
- In the Introduction, try to write facts on growth and human development indicators.
- In Body,
- Discuss the reasons behind the lowest human development indicators in India.
- Suggest some measures for the balanced and inclusive development of India.
- In Conclusion, try to assert the significance of human development and mention various government steps.
Answer:
Human development is increasingly viewed as the ultimate goal of development. It has multiple dimensions such as life expectancy at birth, education, standard of living, healthcare, inequalities, etc. and these can be improved and achieved with rapid economic growth.
After the economic reforms of 1991, India has witnessed rapid economic growth. Since 1991 the average economic growth has been around 7 percent. India is one of the fastest-growing economies in the world, but it is faring poorly on the human development front, which means that millions of Indians have poor access to healthcare and education. According to the Human Development Index 2018, India ranks 130 out of 189 countries, which is far lower than other developing countries like Sri Lanka, Maldives, etc.
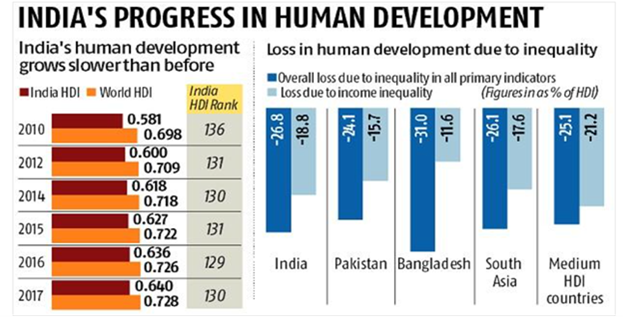

Reasons Behind Low Human Development Indicators:
- Unequal Distribution of Wealth and Non-inclusive Growth: In the last five years, only 1% of the wealthiest in India increased their share in wealth by around 60% and the richest 10% in India own more than four times more wealth than the remaining 90%.
- Disparity: As per the study of the World Economic Forum, India’s richest one percent holds more than four times the wealth held by 953 million people who make up the bottom 70 percent of the country’s population. Thus, high inequality prevails in Indian society leading to non-inclusive growth, low human development, etc.
- Jobless growth: The report of NSSO (2017-18) reveals that India’s Unemployment rate is highest (6.1%) in the last four decades. With a rising population, the number of unskilled laborers would increase, resulting in unhealthy growth.
- Illiteracy and poor health care: In comparison with similarly placed emerging economies, India spends way too little in the education and health sector. India spends 3% of GDP on education and 1.5% of GDP on health.
- Caste system: Indian society is divided based on caste. There are many groups, especially Scheduled Castes (SCs), Scheduled Tribes (STs), and other weaker sections are discriminated against, while accessing various services and hinder inclusive development.
- Gender discrimination: Indian society is patriarchal; women are not given equal status and opportunity in the social, political, and economic spheres in society. India’s rank in the Gender Gap Index (2018) was low at 108th out of 149 countries. Women who constitute 50% of the population have a lack of education, poor sanitation, and health facilities. This hinders the overall development of the country.
- Digital Divide: Also, there is a disconnect between the rate of technological growth and the ability to distribute the gains from it by adequately focusing on skilling (via knowledge, and education) and health, which is critical for greater resilience and sustained productivity.
Measures for Balanced and Inclusive Development of India:
- The government needs to increase public expenditure on health and education as envisaged by National Health Policy 2017 (2.5% of GDP) and Draft Education Policy 2019 (6% of GDP).
- For the development of the rural economy, more emphasis should be given on agrarian reform and promoting rural enterprises.
- Efforts are needed for employment generation, labor reform, credit creation, etc., for more inclusive economic development.
- Skill framework in India needs to integrate with industries, to increase the employability of the Indian labour force.
- The government should make efforts to curb the digital divide, as it creates and reproduces socio-economic backwardness.
Human development and economic growth share a cause and effect to each other’s relationship. Therefore, without investing in Human capital and addressing the current economic slowdown, the goal of becoming a $5 trillion economy, will remain a pipe dream for India. The government has initiated various schemes like Ayushman Bharat Abhiyan, Poshan Abhiyan, MUDRA Yojana, Skill India mission, Startup India, etc., for the Balanced and Inclusive development of India.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here


