The Circum-Pacific Zone, also known as the Ring of Fire, is seismically active, featuring high seismicity and numerous volcanoes. It encompasses the Pacific Ocean basin, marked by tectonic plate boundaries, resulting in earthquakes and volcanic activity. The region plays a crucial role in Earth’s geophysical dynamics.
UPSC Mains General Studies Paper – 1 Mains 2020
UPSC Mains Civil Services IAS Exam Question Paper – 2020
Tag: Salient features of the world’s physical geography.
Contents
Approach
- In Introduction, try to begin by writing about Circum-Pacific Zone.
- In Body, talk about physical features i.e., Area, Composition, etc., of the Circum-Pacific Zone.
- Conclude by citing the importance of Circum-Pacific Zone.
Answer
The Circum-Pacific Belt, also referred to as The Ring of Fire, is a path along the Pacific Ocean characterized by active volcanoes and frequent earthquakes. It stretches from the Bering strait in Siberia to New Zealand and the coast of Chile to Alaska. Its length is approximately 40,000 kilometers.
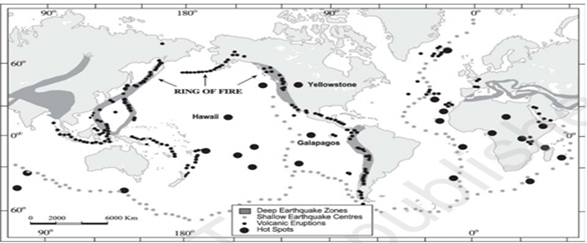
Characteristics of Circum-Pacific Zone
- Formation: This Circum-Pacific chain of volcanoes and the mountain ranges associated with it owe their formation to the repeated subduction of the oceanic lithosphere beneath the continents and the islands that surround the Pacific Ocean. The Ring of Fire is the result of plate tectonics (Convergent, Divergent Plate Boundary, Transform Plate Boundary).
- Volcanoes and Earthquakes: Approximately 75% of Earth’s volcanoes including underwater volcanoes are located along the Ring of Fire and 90% of Earth’s earthquakes occur along its path. Examples: Mount St Helens in the USA, Ojos del Salado on Andes Mountain, Mount Fuji of Japan.
- Location: A nearly continuous chain of volcanoes surround the Pacific Ocean. The chain passes along the west coast of North and South America, from the Aleutian Islands To the south of Japan, from Indonesia to the Tonga Islands, and New Zealand.
- Formation of Hotspots: The Ring of Fire is also home to hot spots, areas deep within the Earth’s mantle from which heat rises. This heat facilitates the melting of rock in the brittle, upper portion of the mantle. The melted rock, known as magma, often pushes through cracks in the crust to form volcanoes. The examples of volcanoes include Mount Fuji of Japan, Aleutian Islands of US, Krakatau Island of Indonesia, etc.
- Archipelago clusters: The Circum-Pacific zone consists of clusters of archipelago such as Japan, Philippines, Indonesia, Polynesia, Chile etc.
Conclusion
As the Circum-Pacific Belt harbors the majority of global Volcanic eruptions & Earthquakes, it holds immense significance regarding the study of the earth’s interior. The Circum-Pacific zone has some of the distinct features of the world that makes its study very important and critical. The study of this zone also proves the hypothesis such as, sea floor spreading. The deep study by scientists and geologists is used by policymakers for natural disaster management and mitigation programs.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here


