UPSC Mains General Studies Paper – 1 Mains 2023
UPSC Mains Civil Services IAS Exam Question Paper – 2023
Contents
Introduction
India is a land of remarkable ecological diversity, hosting a wide range of Natural Vegetation types and ecosystems. Additionally, the country’s commitment to conservation is evident in the establishment of Wildlife Sanctuaries, which play a crucial role in protecting the fragile ecosystems of rainforests.
Body
Factors responsible for diversity of Natural Vegetation in India:–
- Precipitation – The varied rainfall pattern, influenced by the southwest and northeast monsoon, determines the type of vegetation, from rainforest in the northeast in the western ghats to the thorny shrubs in the arid regions of the west.
- Topography–
- Altitude – the varying altitudes specially in the Himalayan region, lead it to different types of vegetation
- Example – tropical vegetation is found at lower altitudes, followed by temperate forests, Meadows, and Alpine vegetation as one ascends.
- Soil type – different regions in India have varied soil types
- Example-fertile alluvial in northern plains, laterite soils in the western coastal region, red soil in the Deccan Plateau. Each soil type supports different kinds of vegetation.
- Types of local ecosystem – it consists of mangroves, estuaries, swamps etc.
- Mangroves- according to the India state of Forest report 2019, the mangrove cover in India is 4975 km², which is 0.15% of the country’s total geographical area. Example- Bhitarkanika mangroves, Godavari Krishna mangroves, Pichavaram in Tamil Nadu
- Coastal wetlands, shallow lake and ponds, marshes, swamps, Bogs and estuaries.

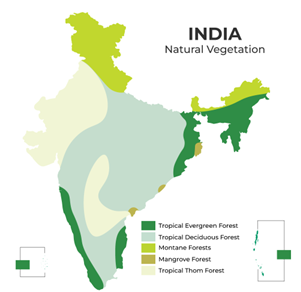
- Overall temperature distribution of India- it can be further divided into subtypes-
- Tropical evergreen rainforest – ex- Mahogany ,Ebony, Rosewood in places of Nicobar regions, South of western Ghats and parts of north-eastern regions.
- Tropical deciduous forest-ex- Sal ,teak, peepal, neem and sheesham.
- Thorn forests – ex- Cactus, khair, Babul, Keekar in places of Rajasthan, Punjab, Haryana, eastern slopes of western Ghats and Gujarat
- Mountain vegetation-ex-chir, Pine, Deodar
- Mangrove forest-ex- important trees like sundari found mainly in Sundarbans in West Bengal and in Andaman and Nicobar islands.
Significance of wildlife sanctuary in the rainforest of India is as follows:-
- Map locating the wildlife sanctuary in the rainforest regions. Example- Vembanad wildlife sanctuary, Periyar Wildlife sanctuary, Parambikulam wildlife sanctuary, hornbill wildlife sanctuary , galathiya bay , Narcondam Wildlife Sanctuary etc.
- Eco-tourism and economic benefits – e.g.. Dan deli wildlife sanctuary in Karnataka.
- Ecosystem services -Rainforests provide essential services like water purification, soil stabilization, and nutrient cycling, as observed in the Nigiri Biosphere Reserve.
- Carbon sequestration– forest conservation efforts adding to higher carbon capture.
- Species specific conservation primarily for animals. Ex- elephants, tigers, hornbill, lion tailed macaque
- To counter man animal conflict. Ex- development of elephant corridor
- Awareness and sensitization of local communities
- Protection of endangered species-to keep an eye on the endangered species and help them reproduce an increase their number
Challenges –
- Habitat Destruction: Expansion of agriculture, logging, and infrastructure encroaches on sanctuaries, leading to habitat loss and fragmentation, disrupting ecosystems and reducing wildlife populations.
- Illegal Activities: Rainforests face illegal logging and poaching, driven by demand for valuable resources. This threatens rare species, contributes to habitat loss, and disrupts the balance of ecosystems.
- Climate Change: Altered climate patterns impact rainforest sanctuaries, affecting wildlife distribution and Behaviour. Shifts in vegetation and food sources can threaten certain species’ survival.
- Invasive Species: Introduction of invasive species harms native flora and fauna by outcompeting or preying upon them, leading to population declines and habitat degradation.
- Human-Wildlife Conflict: As human populations grow, conflicts with wildlife increase, resulting in crop damage, livestock losses, and risks to human safety, potentially leading to negative attitudes toward conservation.
- Resource Constraints: Limited funding, staffing, and resources hinder effective conservation efforts, including monitoring, law enforcement, and conservation programs.
Conclusion:
Thus, it is imperative to continue efforts to protect and conserve this valuable ecosystem for future generations as they are very crucial for preserving these natural wealth’s ensuring survival of flora and fauna.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 8792740517.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here
Visit our YouTube Channel – here


