Wednesday, 5th May 2021
Threshold for Significant Economic Presence (SEP)
In News
The Income Tax Department notified a threshold for Significant Economic Presence (SEP).
About the News
- India notified a revenue threshold of Rs 2 crore and a limit of 300,000 users for non-resident technology firms such as Google, Facebook, Netflix, to pay tax in India under new or revised bilateral tax pacts.
- The move would have implications for global ecommerce players that operate from jurisdictions such as Hong Kong that do not have a tax treaty with India. These come into effect from April 1, 2022.
- Considering that the threshold has been kept quite low, many non-residents would come under the ambit of SEP.
- However a non-resident can still take shelter under the tax treaties since India’s existing treaties contain the conventional concept of permanent establishment (PE) for taxing business profits of a non-resident and the inclusion of SEP in the Act will not be read into the tax treaties unless they are amended.
- Though the residents of treaty countries can claim the beneficial provisions of treaty, non-treaty jurisdictions and non-residents not eligible for treaty benefit, may have review their position on taxability and compliances.
What is SEP?
- The concept of SEP was introduced through the Finance Act 2018 and was defined to mean that any transaction in respect of any goods, services or property carried out by a non-resident in India, including the provision of download of data or software in India, systematic and continuous soliciting of business activities or engaging in interaction with such number of users as may be prescribed, in India through digital means.
- The provisions of significant economic presence seek to enlarge the scope of income of non-residents that accrues or arises in India, by establishing a ‘business connection’ of the foreign entities in India. The income attributable on account of ‘significant economic presence’ of a foreign entity in India is taxable in India.
- The SEP provision was deferred till 2022-23 on grounds that a multilateral solution under OECD is being deliberated where all tax treaties will get amended automatically.
- However, India expanded the scope of the equalisation levy over the last few years, to tax non-resident digital entities. While the levy applied only to digital advertising services till 2019-20 at the rate of 6 per cent, the government in April last year widened the scope to impose a 2 per cent tax on non-resident e-commerce players with a turnover of Rs 2 crore.
- The scope was further widened in the Finance Act 2021-22 through a clarification to cover e-commerce supply or service when any activity, including acceptance of the offer for sale, placing the purchase order, acceptance of the purchase order, supply of goods or provision of services, partly or wholly payment of consideration, takes place online.
India’s Approach to Refugees
In News
The High Court of Manipur orders safe passage to seven Myanmar nationals, to travel to the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) in New Delhi. The seven nationals had entered India secretly after the military coup in Myanmar.
Observation made by Manipur HC
- The HC held that though India is not a party to the UN Refugee Conventions, it is a party to the Universal Declaration of Human Rights of 1948and the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights of 1966.
- Article 21 of the Constitutionencompasses the right of non-refoulement.
- Non-refoulementis the principle under international law which states that a person fleeing persecution from his own country should not be forced to return to his own country where he would face torture, cruel, inhuman, or degrading treatment or punishment and other irreparable harm.

About United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees
- Headquartered in Geneva, UNHCR is the UN Refugee Agency that is dedicated to saving lives, protecting rights, and building a better future for refugees, forcibly displaced communities, and stateless people.
- The 1951 Refugee Convention is a United Nations multilateral treaty that defines a refugee, sets out which people qualify as refugees and grants certain rightsto people fleeing persecution. India is not a party to this convention.
- The 1967 Protocolincludes refugees from all countries as opposed to the 1951 Convention that only included refugees from Europe.
India’s Stand on Refugees
- India has no clear refugee protection policy and decisions are taken on a case-to-case basis.
- India has granted asylum to refugeesfrom the neighboring countries and has offered shelter to Tibetans, Chakmas of Bangladesh, ethnic Tamil refugees from Sri Lanka.
- India usually respects UNHCR’s recognition of the status of such asylum seekers, mainly from Afghanistan and Myanmar.
- The recent Citizenship Amendment Act, 2019 aims to grant citizenship to persons belonging to Hindu, Sikh, Buddhist, Jain, Parsi and Christian communities who have migrated to India after facing persecution on grounds of religion in Pakistan, Afghanistan and Bangladesh.
Primary source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/7-myanmar-refugees-can-approach-unhcr/article34476231.ece
India-UK Virtual Summit: Roadmap 2030 to strengthen bilateral ties
In News
India and the UK recently adopted a ‘Roadmap 2030’ during the virtual bilateral summit between the Prime Ministers of the two countries during which it was discussed to elevate bilateral ties to a “Comprehensive Strategic Partnership.”
|
Enhanced Trade Partnership |
Launch of an Enhanced Trade Partnership and the leaders also announced their intent to negotiate a comprehensive Free Trade Agreement. They also agreed to continue removing trade barriers and to also set an ambitious target of more than doubling India-UK trade by 2030. |
|
Defence Partnership |
The two countries were also committed to strengthening their defence partnership, focusing on maritime and industrial collaboration. They also highlighted the importance of a free and open Indo-Pacific, recognizing their shared interest in regional prosperity and stability. The two countries agreed to build on existing government-to-government collaboration on India’s future combat air engine requirement. |
|
Cooperation in Maritime Issues |
The countries also agreed upon new cooperation on Maritime Domain Awareness which includes new agreements on maritime information sharing. India has also invited the UK to join India’s Information Fusion Centre. |
|
Covid 19 and Pandemic Preparedness |
The countries agreed to develop India-UK partnership on Vaccines, Therapeutics and Diagnostics and also expand the UK-India Vaccines Hub to develop distribution policy, clinical trials, regulations, research and innovation related to Covid-19. |
|
Clean Energy and Transport |
The two countries also committed to launch a Global Green Grids initiative at COP26 of the UNFCCC. This is intended to increase technical, financial, and research cooperation to help deliver India’s vision of One Sun One World One Grid. |
|
Migration and Mobility |
Both the leaders also welcomed the signing of the India-UK Migration and Mobility Partnership (MMP) that is aimed at reducing illegal immigration into the United Kingdom. |
|
Financial Cooperation |
The two countries agreed to implement the new annual India-UK Financial Markets Dialogue to share expertise, experiences and deepen collaboration between the financial sectors. Greater collaboration will also be promoted between the GIFT City and the UK financial services ecosystem. |
Significance of the Summit
- Trade relations: The India-UK virtual summit comes shortly after the finalisation of the EU-UK trade deal. During the last few years the UK has been actively negotiating bilateral free trade agreements with major economic partners like New Zealand, Australia, Japan. The summit can help both the countries push forth for finalising the Free Trade Agreement.
- Collaboration in tackling Covid 19: India has already cooperated with the UK with respect to the AstraZeneca/Oxford University Vaccine. India and the UK can further work together to boost the resilience of global medical supply chains to ensure supply of critical meduces. They can also commit to the multilateral effort, including through the COVAX facility, to support equitable vaccine access for developing countries.
- Altered dynamics with the UK after Brexit: India has for long treated the UK as its gateway to the rest of Europe. With the UK exiting the European Union, India has already begun reaching to other Nordic and Central European countries. Brexit has also impacted Indian firms who have invested in the UK.
- UK’s shift to the Indo-Pacific: The UK’s changing relationship with China has been key to why the concept of the Indo-Pacific has gained salience. The UK has recognized China as a threat particularly in the South China Sea. The UK recognizes India as an important partner for maintaining a rules based order in the Indo-Pacific.
Issues in India-UK relations
- Stagnancy in relations: India-UK relations remained stagnant over the last five years due to Britain’s Brexit preoccupation.
- Britain's concern over India’s domestic affairs: Britain’s concerns over farmers protests in India and the Citizenship Amendment Act led to responses from India regarding interference in India’s internal affairs.
- Illegal Migration: There are more than 1 lakh illegal Indian immigrants in the UK. Britain has over the years been putting pressure on the Indian government to ensure that Indians whose visas have expired be sent back. Britain has scrapped the post-study work permit for international students which led to a sharp drop in the numbers of Indian students.
Conclusion
The 10-year roadmap that has evolved as part of the summit will help the two countries strengthen their bilateral strategic partnership. The shared interests of the two countries will underpin greater cooperation in multilateral fora and the strengthened India UK relationship will build understanding among diverse partners on international security, healthcare, vaccines and critical national infrastructure.
Sources
3D printing
In News
Union Finance Minister recently inaugurated India’s first 3D printed house at IIT, Madras.
About the News
- The Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs provided support through the ASHA Incubator programme under the Global Housing Technology Challenge.
- Tvasta Manufacturing Solutions, deep tech startup founded by three IIT Madras alumni, created a single-storey, 1BHK project in just five days.
- Technique: Tvasta’s ‘Concrete 3D Printing’ technique utilises a concrete 3D Printer which accepts a computerised three-dimensional design file from the user and fabricates a 3D structure in a layer-by-layer manner by extruding a specialised type of concrete specifically designed for the purpose.
- Eco-friendly: The technology uses sustainable and green material like industrial waste and recycled material.
- As the houses built using 3D Printing are customised for geographical and climatic conditions of the area, any additional heating or cooling requirements are very minimal for the structure.
- Cost- Effective: Considering the nature of the current projects, the projects under this model are estimated to have 20-30% savings compared to conventional construction.
What is 3D printing?
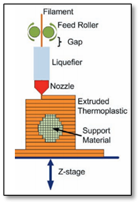
- Definition: Three-dimensional (3D) printing is a manufacturing method in which objects are made by fusing or depositing materials, such as plastic, metal, ceramics, powders, liquids, or even living cells, in layers to produce a 3D object. This process is also referred to as additive manufacturing (AM), rapid prototyping (RP), or solid free-form technology (SFF).
- Mechanism: The process begins with a 3D model of the object, usually created by computer-aided design (CAD) software or a scan of an existing artefact.
- Specialized software slices this model into cross-sectional layers, creating a computer file that is sent to the 3D printing machine.
- The machine then creates the object by forming each layer via the selective placement (or forming) of material.
- Two-dimensional (2D) radiographic images, such as x-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or computerized tomography (CT) scans, can be converted to digital 3D print files

Applications of 3D Printing
- Aerospace industry: In aerospace industry, 3D printing technology has potential to make light weight parts, improved and complex geometries, which can reduce energy requirement and resources.
- Automotive industry: 3D Printing technique enables making lighter and more complex structures in the fast time. 3D printing technology enables companies to try various alternatives and effective automotive design.
- Food industry: There is a growing demand for the development of customized food for specialized dietary needs. By using 3D printing technology, specific materials can be mixed and processes into various complicated structures and shape.
- Healthcare and medical industry: 3D printing technology can used to print 3D skin, drug and pharmaceutical research, bone and cartilage, replacement tissues, organ, printing for cancer research and lastly models for visualization, education, and
- Architecture, building, and construction industry: In the construction industry, 3D printing technology can be used to print entire building or can create construction components. The emergence of the Building Information Modelling (BIM) which is a digital representation of functional and physical characteristics facilitates better use of 3D printing
- Fabric and Fashion Industry: The combination of fashion and 3D printing may not seem like the most natural fit, but big companies like Nike, New Balance and Adidas are striving to development the mass production of 3D printed shoes. 3D printing technology can spread creative possibilities for fashion design.
- Electric and Electronic Industry: Various 3D printing technologies have already been used broadly for structural electronic devices like active electronic materials, electrode and devices with mass customization and adaptive design through embedding the conductors into 3D printed devices.
Advantages of 3D printing over traditional manufacturing techniques
- Incorporate increased part complexity: An immediately apparent benefit is the ability to create complex shapes that cannot be produced by any other means. It also allows designers to selectively place material only where it is needed. Taking inspiration from nature (e.g., coral, wood, bone), designers can now create cellular materials– strong and stiff structures that are also lightweight.
- Digital design and manufacturing: All 3D printing processes create physical parts directly from a standardized digital file (.STL), which is a representation of a three-dimensional solid model. These computer-controlled processes require a low level of operator expertise and reduce the amount of human interaction needed to create an object. It also ensures that the created part precisely represents the designer’s intent and thus reduces inaccuracies.
- Complexity is free: 3D printing is a “single tool” process—no matter the desired geometry, there is no need to change any aspect of the process. This, in effect, makes shape complexity free—there is no additional cost or lead time between making an object complex or simple.
- Instant production on a global scale: The representation of physical artefacts with a digital file enables rapid global distribution of products, thus potentially transforming product distribution. The digital file can be sent to any printer anywhere that can manufacture any product within the design parameters of the file.
- Waste reduction: Its processes are inherently “green.” Since material is added layer by layer, only the material needed for the part is used in production. There is virtually zero waste.
There are some Barriers to 3D printing which need to be resolved
- Safety and Security: 3D printing has given rise to safety and security issues that merit serious concern. 3D printers have already been employed for criminal purposes, such as printing illegal items like guns and gun magazines, master keys, and ATM skimmers.These occurrences have highlighted the lack of regulation of 3D printing technology.
- Patent and Copyright Concerns: Manufacturing applications of 3D printing have been subject to patent, industrial design, copyright, and trademark law for decades.However, there is limited experience regarding how these laws should apply to the use of 3D printing by individuals to manufacture items for personal use, non-profit distribution, or commercial sale.
- Regulatory Concerns: Securing approval from regulators is another significant barrier that may impede the widespread medical application of 3D printing. A number of fairly simple 3D-printed medical devices have received the FDA’s approval. However, fulfilling more demanding FDA regulatory requirements could be a hurdle that may impede the availability of 3D-printed medical products on a large scale.
Conclusion
3D printing has become a useful and potentially transformative tool in a number of different fields, including medicine. As printer performance, resolution, and available materials have increased, so have the applications. Researchers continue to improve existing medical applications that use 3D printing technology and to explore new ones. The medical advances that have been made using 3D printing are already significant and exciting, but some of the more revolutionary applications, such as organ printing, will need time to evolve.
Sources: https://indianexpress.com/article/cities/chennai/fm-indias-first-3d-printed-house-iit-m-7292236/
This Day in History- Karl Marx

On May 5, 1818 Karl Marx, born in Trier, Germany, was a revolutionary, sociologist, historian, and economist. He published the Manifest der Kommunistischen Partei (1848), commonly known as The Communist Manifesto and the book Das Kapital. Marx’s Dialectical materialism, a philosophical approach to reality holds that everything that exists is material and is derived from matter, matter is in a process and constant change and all matter is interconnected and interdependent. The world, including human beings, is "matter in motion" and that progress occurs through struggle.
Image of the Day- '516 Arouca’

It is the image of world's longest pedestrian suspension bridge '516 Arouca’ in Portuguese town of Arouca. Hidden between rock-strewn mountains covered with lush greenery and yellow flowers inside the UNESCO-recognized Arouca Geopark, the bridge hangs 175 meters above the fast-flowing River Paiva. Held up by steel cables and two massive towers on each side, it wobbles a little with every step.
P-8I Aircraft
- Context: Sale of six P-8I patrol aircraft to India by USA.
- It is a long-range maritime reconnaissance and anti-submarine warfare aircraft.
- The P-8I can detects threats and neutralizes them, if required, far before they come anywhere near Indian shores.
- Indian Navy became the first international customerfor the P-8 aircraft in 2009.
- The six P-8I patrol aircraftwill come fitted with encrypted systems, as India has signed the Communications Compatibility and Security Agreement (COMCASA) with the US.
|
COMCASA Agreement · COMCASA stands for Communications Compatibility and Security Agreement and is India-specific version of the Communication and Information on Security Memorandum of Agreement (CISMOA). · The agreement facilitates India to use the United States' encrypted communications equipment and systems. Through this, Indian and the US military counterparts can communicate through secure networks in peace and war. Eg. C-17, C-130 and P-8Is. |
Primary source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/us-clears-sale-of-six-p-8i-patrol-aircraft-to-india/article34455535.ece/amp/
https://www.naval-technology.com/projects/p-8i-maritime-patrol-aircraft-india/
E Way Bill
- Context: The recent E-Way bill data suggests that GST receipts could see a decline in May.
- E-Way Bill or Electronic-Way bill is a compliance mechanismwherein by way of a digital interface, the person causing movement of goods uploads the relevant information prior to the commencement of movement of goods and generates an e-way bill (unique bill number) on the GST portal.
- A GST registered person cannot transport goods within State or inter-State in a vehicle whose value exceeds Rs. 50,000 without an e-way bill.
- It was launched to facilitate faster movement of goods and improve the turnaround time of vehicles.

Computed Tomography (CT) Scan
- Context: AIIMS Director has told not to conduct CT scans for mild COVID cases and warned that increased exposure to radiation escalates the risk of cancer.
- A computerized tomography scan (CT or CAT scan) uses computers and rotating X-ray machines to create cross-sectional images of the body.
- These images provide more detailed information than normal X-ray images. It creates images of structures inside the body which helps doctors get a look at the internal organs and then advise further treatment.
- However, since CT scan exposes the body to more radiation than typical X-rays, there arises the risk of cancer caused by radiation (repeated/multiple scanning). One CT scan is equivalent to 300-400 chest X-rays.
Primary source: https://www.indiatoday.in/coronavirus-outbreak/story/global-research-backs-aiims-chief-s-warning-on-ct-scan-1798793-2021-05-04
Article 164(4)
- Context: Mamata Banerjee becomes CM despite losing her election from her constituency- Nandigram.
- Article 164 of the Indian Constitution, which deals with appointment of Chief Minister and other ministers, says, “A Minister who for any period of six consecutive months is not a member of the Legislature of the State shall at the expiration of that period cease to be a Minister.”
- This means that an unelected member can assume the office of a Chief Minister, but he/she must either win a by-poll or get elected to the Legislative Council within 6 months to retain the position. In this case, Ms. Banerjee will get six months to get elected from any WB constituency in a by-poll to hold on to the CM’s chair.
- A similar provision of becoming minister in union govt (Article 75) and getting elected to Parliament later exists in federal structure.

Primary source: https://www.hindustantimes.com/india-news/how-didi-can-remain-cm-despite-losing-nandigram-101619986018021.html
Covid-19: When the courts step in - HT
Essence - Editorial is discussing scope & issues related Judicial governance in this unprecedented medical crisis. High court (HC) under Art. 226 & Supreme Court (SC) under Art. 32 (extraordinary jurisdiction to protect personal liberty) are intervening to ensure actions from executive on production and allocation of medical oxygen and the urgent requirement of basic medical infrastructure such as beds and drugs. According to some sections, suo motu petition being heard by SC is an act of interference in the executive policy domain, specifically on the issue of vaccination. During the 2G spectrum litigation, a Constitution Bench held that the court cannot enforce a policy decision on the executive.
But, if we look at the current vaccine situation, we find that Centre failed to anticipate the urgent requirement for vaccination. The apex court categorically asked the Centre that, the right to life (Article 21) is a fundamental guarantee under the Constitution and the current vaccine policy has a direct effect on this guarantee to life, has the Centre finalised its policy keeping in view the commitment to protecting public health, has the socio-economic disparity between citizens been considered when shifting the burden of cost onto them.
SC is not seeking to take policy decisions, but is seeking public accountability and transparency on the executive’s policy decisions and its failure to act in time, an essential facet of constitutional democracy.
Why you should read this article?
- To know about the issue application of Judicial review & judicial overreach in pandemic response.
- It is providing cursory view on preparation status of government with respect to covid immunisation program & challenges thereof.
- To know about some important questions asked by the apex court from the Centre on its policy for mass inoculation and medication.
- To know how HC & SC are making attempts to fulfil extraordinary constitutional responsibility of protecting the lives of people & ensuring the federal cooperation between the Union and states.
Link - https://www.hindustantimes.com/opinion/covid19-when-the-courts-step-in-101620131726967.html
Arun ePDS: ICT and Process Re-engineering for an efficient Public Distribution System in Arunachal Pradesh
Present Situation
- In India, PDS suffers from several issues like problems in accurate targeting, pilferage of PDS commodities, wastage of food grain in one place along with the issue of inaccessibility of food grains for many places, problems of bogus ration cards.
- Arunachal Pradesh has its own set of problem like inaccessibility of food grains to common masses due to difficult terrain, the state does not have a civil supplies corporation to manage the movement of food grains from the Food Corporation of India godowns to Fair Price Shops.
- To solve these issues, Arun e-PDS was conceptualised.
Arun e-PDS
- It is a simple, accountable, and efficient intervention of technology for streamlining the public distribution system in Arunachal Pradesh.
- It aims to improve delivery through process re-engineering and use of Information and Communication Technologies.
- It has centralised reporting and monitoring system which can help in creating efficient allocation of commodities and to track supply chain from FCI godowns to FPS.
Outcomes
- It has significantly reduced the pilferage of food rations.
- It has led to rapid redressal of grievances due to detection of ghost ration cards and issuance of cards to people hitherto excluded from the system.
- It has led to better accuracy in projecting requirement.
- It has facilitated citizen-centric functioning and rapid grievance redressal.
Where can we use this case study
Reforms to improve PDS system across all the states, innovative practise at local level to solve the issues of citizens, use of ICT tools in functioning of the PDS system.
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.