Monday, 19th April 2021
Aryabhata, India’s first satellite
Aryabhata, India’s first satellite, was launched on 19th April 1975. It was built by ISRO and launched from Kapustin Yar (rocket launch and development site in Russia). It was named after the 5th century AD Indian mathematician-astronomer Aryabhata.
IAEA confirms Iran has started enriching uranium to 60% purity
In News
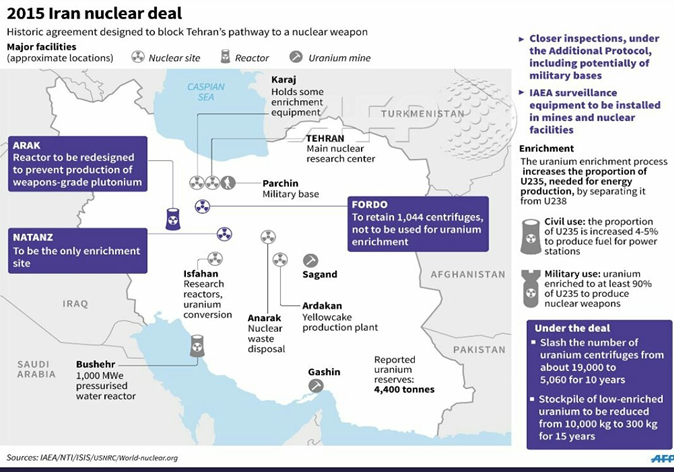
The International Atomic Energy Agency has recently highlighted that Iran has started the process of enriching uranium to 60% fissile purity at an above ground nuclear plan at Natanz.
|
Understanding Uranium Enrichment · Natural uranium consists of two different isotopes - nearly 99% U-238 and only around 0.7% of U-235. U-235 is a fissile material that can sustain a chain reaction in a nuclear reactor. · To be useful for either of these purposes, the concentration of uranium-235 must be increased by separating it from uranium-238 through a process known as enrichment.
How much enrichment is necessary for use in reactors or weapons? · Uranium enriched to concentrations above 0.7% but less than 20% uranium-235 is defined as low enriched uranium (LEU). Most nuclear reactors use LEU that is about 3-5% uranium-235.
· Uranium enriched to more than 20% uranium-235 is defined as highly enriched uranium (HEU). All HEU is weapons-usable, but the lower the enrichment level the greater the amount of material required to achieve a critical mass—the amount of material required to build a bomb. · States with nuclear weapons typically use so-called weapons-grade HEU, which is typically defined as 90% HEU or above, to minimize weapons’ size. Smaller and lighter nuclear weapons are much easier to deliver; ballistic missiles in particular can only deliver highly miniaturized nuclear weapons. |
Implications of the move
- Impact Vienna talks and heightened Iran-US tensions: The ongoing talks in Vienna are intended to bring US and Iran closer to ending their standoff over the nuclear deal. Iran had been earlier enriching Uranium up to 20% although the deal limited Iran’s enrichment to 3.67%. As a part of the talks, Iran’s President has sought to allay Western concerns over Tehran’s decision to boost uranium enrichment by stressing that the programme is “peaceful”.
- Increased Iran-Israel rivalry: The present decision for enrichment comes shortly after an explosion at the plant in Natanz which Iran claims was carried out by Israel. Iran’s decision to begin enriching to 20% purity a decade ago nearly triggered an Israeli strike targeting its nuclear facilities, tensions that only abated with the 2015 nuclear deal. Israel being a regional ally of the US has opposed any deal with Iran and accuses Iran of secretly developing a nuclear weapon. Iran has denied the charges maintaining that its nuclear facilities are under inspection by the International Atomic Energy Agency.
Sources
U.S. Treasury keeps India on currency watch list
In News
India is one of the 11 countries on the U.S. Treasury’s ‘Monitoring List’ (Currency Manipulators Watch List) with regard to their currency practices.
What does the term ‘currency manipulator’ mean?
- This is a label given by the US government to countries it feels are engaging in “unfair currency practices” by deliberately devaluing their currency against the dollar.
- The practice would mean that the country in question is artificially lowering the value of its currency to gain an unfair advantage of trade over others.
- This is because the devaluation would reduce the cost of exports from that country and artificially show a reduction in trade deficits as a result.
Currency Manipulator Watch List
- The US Department of Treasury releases asemi-annual report called the Currency Manipulators Watch List to track developments in international economies and inspect foreign exchange rates.
- It reviews currency practices of the US’ 20 biggest trading partners.
- Inclusion in the list does not subject to any kind of penalty and sanctionsbut it deteriorates the global financial image of the country in the financial markets in terms of foreign exchange policies.
What are the parameters used?
- An country meeting two of the three criteria in the Trade Facilitation and Trade Enforcement Act of 2015 is placed on the Monitoring List which includes:
- A “significant” bilateral trade surplus with the US — one that is at least $20 billion over a 12-month period.
- A material current account surplus equivalent to at least 2 percent of gross domestic product (GDP) over a 12-month period.
- “Persistent” one-sided intervention — when net purchases of foreign currency totaling at least 2 percent of the country’s GDP over a 12 month period are conducted repeatedly, in at least six out of 12 months.
- Once on the Monitoring List, the specific country will remain there for at least two consecutive reports to help ensure that any improvement in performance versus the criteria is durable and is not due to temporary factors.
- India’s Status: - It met two of the three criteriae the trade surpluscriterion and the “persistent one-sided intervention” criterion.
Primary source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/currency-manipulation-explained-india-us-currency-watchlist-7108379/
https://www.thehindu.com/business/us-treasury-keeps-india-on-currency-watch-list/article34339096.ece
Haemophilia
In News
April 17 is observed as World Hemophilia Day every year.
What is Haemophilia?
- Haemophilia is an inherited condition that causes bleeding for a long time after injury or surgery and painful swelling of the joints either after injury or even without injury. ("Inherited” means that the disease is passed from parents to children through their genes).
- Haemophilia is due to a deficiency of clotting factor, this results in increased bleeding. There are two types of Haemophilia A, which is more common and occurs in about 1 in 5,000 births. Haemophilia B is less common and occurs in around 1 in about 20,000 births.
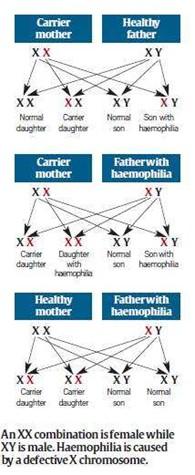
Why is it more prevalent in Males?
- Haemophilia is caused by a defect in the X chromosome. If a girl is born with one defective X chromosome, her other X chromosome can compensate for it. In such a case, she is a carrier of haemophilia but will not suffer from the condition herself. Only if both her X chromosomes are defective will she suffer from haemophilia herself.
- On the other hand, if a boy is born with a defective X chromosome, he does not have the second X chromosome to compensate for it, and will suffer from haemophilia. That is the reason haemophilia is more common among men.
Haemophilia and India
- According to the World Federation of Haemophilia’s Annual Global Survey 2017, there were over 1.96 lakh persons living with haemophilia across the world in 2017. In the country-wise data, India emerges with the highest count at nearly 19,000.
- Though the government has done enough under the National Health Mission for haemophilia, proper diagnostic centres have not come up in remote belts of the country.
Treatment
- There is no known cure for this disorder.
- The best way to treat haemophilia is to replace the missing blood clotting factor so that the blood can clot properly. This is done by infusing (administering through a vein) commercially prepared factor concentrates.
- Researchers are trying to find ways to correct the defect in the genes that cause haemophilia. Gene therapy has not yet developed to the point that it's an accepted treatment for haemophilia.
Sources: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/this-word-means-world-haemophilia-day-5679369/
Carbon tax could help Asian countries hit climate targets: IMF
In News
According to a new IMF research, a carbon price that starts low and rises steadily could help Asian countries reach their targets under the Paris climate accord over the next decade. There was growing consensus that carbon pricing was the most efficient and cost-effective way to curb emissions.
Highlights of the IMF research
- Benefits of carbon pricing: By raising energy prices overall, carbon pricing creates incentives for households and firms to shift toward greener options, while promoting energy efficiency, boosting green investments and spurring innovation.
- Carbon price floors: The IMF has urged the world's largest emitters to adopt carbon price floors to ensure more substantial climate change mitigation.
- Revenue generation: Carbon taxes could also generate substantial revenues, and countries could use other instruments, such as China's coal tax, which could eventually be scaled up to curb CO2 emissions.
|
Carbon Pricing Carbon Pricing is a market based strategy for lowering global warming emissions by putting a price on carbon emissions. There are two main types of carbon pricing: emissions trading systems (ETS) and carbon taxes. · Emission Trading System: This is also referred to as a cap-and-trade system – caps the total level of greenhouse gas emissions and allows those industries with low emissions to sell their extra allowances to larger emitters. By creating supply and demand for emissions allowances, an ETS establishes a market price for greenhouse gas emissions. · Carbon Tax: A carbon tax directly sets a price on carbon by defining a tax rate on greenhouse gas emissions or – more commonly – on the carbon content of fossil fuels. |
Rationale for carbon pricing
- Effective tool for meeting domestic emission mitigation commitments: This increases the prices of fossil fuels, electricity, and general consumer products. This promotes switching to a lower-carbon field in power generation, conserving energy use, among other things.
- Raising revenues: Another important argument for carbon taxes is that they could raise a significant amount of revenue, typically 1–2 percent of GDP for a $35 a ton tax by 2030. This revenue can be used to offset the harmful macroeconomic effects—reduced employment and investment—of higher energy prices. For developing countries carbon tax revenues can be used to fund investments for achieving the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals.
- Significant domestic environmental benefits: for example, reductions in the number of people dying prematurely from exposure to local air pollution caused by fossil fuel combustion.
- Easy to administer: Carbon charges can be integrated into existing road fuel excises, which are well established in most countries and applied to other petroleum products, coal, and natural gas.
Ways in which the Private Sector can introduce Carbon Pricing
|
Shadow Pricing |
Internal carbon tax |
Internal cap and trade |
Implicit carbon price |
|
Companies attach a notional value to carbon emissions in order to assess the risks of business investments under anticipated government policies that increase emissions-related costs. The key to success in shadow pricing is anticipating how it will influence strategic planning, risk management and capital investment decisions. |
A company charges itself a fee for each ton of carbon emissions that it generates, creating an internal fund that can be applied to emissions reduction projects with long-term payback periods. The difference between a shadow price and a carbon tax is that the shadow price is applied to projected emissions of future investments, while a carbon tax is applied on current emissions. |
This approach sets an upper limit on total emissions from all business activities. The company creates an allowance for each ton of carbon emitted, and business units can buy, sell or trade any excess allowances amongst each other. This results in a value or price being attached to GHG emissions. |
This is calculated based on how much it costs a company to implement emissions reduction projects, such as renewable energy purchases or energy-efficiency upgrades. |
Carbon Pricing in India
- Coal Cess: A new cess on coal production, called the GST Compensation Cess, has been initiated at the rate of Rs 400 per tonne.
- Renewable Purchase Obligation: According to the Indian Electricity Act, Renewable Purchase Obligation (RPO) mandates that all electricity distribution licensees should purchase or produce a minimum specified quantity of their requirements from Renewable Energy Sources.
- Emission Trading Scheme: The Gujarat Government launched a cap and trade programme in 2019. Gujarat’s cap-and-trade programme sets an overall cap on the permitted Particulate matter emissions in Surat’s textile industry. The government then allocates permits to companies which enable them to discharge a specific amount of pollutants.
Issues with carbon pricing
- Weak government policies: Governments responsible for creating the carbon markets have not been imposing costs to industry in a way that makes businesses consider the transition more seriously. The caps on carbon have overall been weak and the price of carbon has generally been too low to generate any market response.
- Climate change framed as market failure: GHG emissions are viewed as a negative externality because the social costs flowing from climate change impacts are not reflected in the market price of carbon-intensive goods and services. Framing the climate challenge as a market failure, however, fails to seriously appreciate its scope and depth. Addressing the climate challenge, involves fundamental changes to existing systems, rather than just focussing on market-based solutions.
- Universal versus Context Sensitive Policy: Carbon pricing functions well in sectors, such as electricity, with large, fixed-point sources, where alternative technologies are available and polluters cannot easily relocate; it’s more difficult to implement in agro-food, transport, and heavy industry. Carbon pricing strategies tend to ignore that policies need to be tailored to local and/or sectoral contexts in order to address specific sources.
Way Ahead
- Carbon pricing to be accompanied with climate and energy policies: Other climate and energy measures should complement the carbon price policy in order to address GHG emissions and climate change.
- Engage civil society and cultivate a broad consensus for a long term rising carbon price: Civil society and environmental NGO’s play an important role in formulating robust climate change policy and countering polluting industry interest groups which often lobby for abolishing carbon pricing policies.
- Factor in important carbon pricing co-benefits: Effective carbon pricing has important co-benefits such as reducing deaths due to air pollution and importantly raising revenue that can be invested for making a just transition to a low carbon economy.
Sources:
https://www.wri.org/insights/4-ways-companies-can-price-carbon-lessons-india
https://www.pnas.org/content/117/16/8664
Image of the Day-Victoria Cruziana Flower
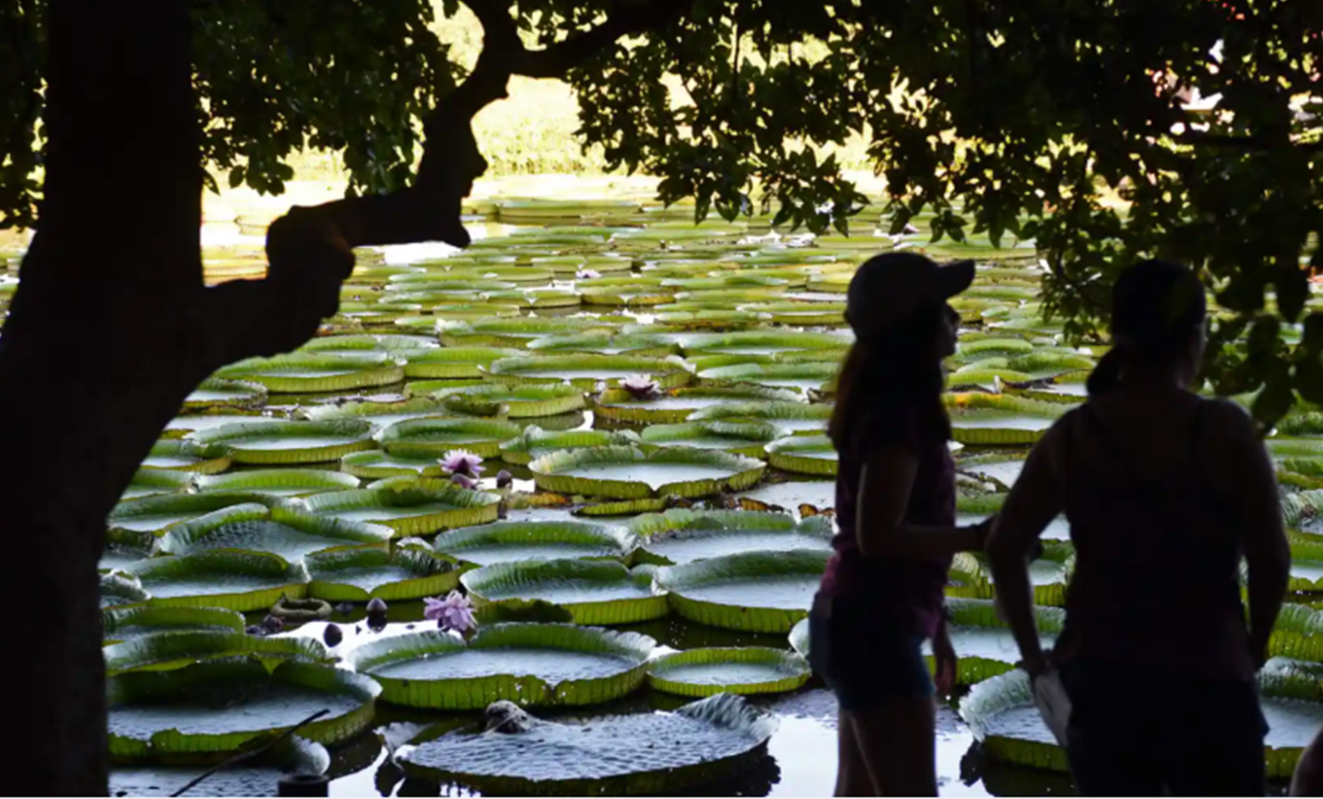

Victoria Cruziana Flower at Paraguay River, Asuncion, Paraguay- These tropical species of flowering water lilies are popular water garden plant native to South America. They blossom once in 3-4 years and its leaves can grow up to 2m wide with a think rim up to 20 cm high.
National Internet Exchange of India (NIXI)
- Context: 3 Initiatives launched by NIXI to spread awareness about IPv6.
- NIXI is a not-for-profit organization under Companies Act 2013, working towards spreading the internet infrastructure since the year 2003. Its initiatives include:
- Internet Exchangesthrough which the internet data is exchanged amongst Internet Service Providers (ISP’s), Data Centers and Content Delivery Network (CDNs).
- .IN Registry, managing and operation of .IN country code domainand .BHARAT IDN (Internationalized Domain Name) domain for India.
- Indian Registry for Internet Names and Numbers(IRINN), managing and operating Internet Protocol (IPv4/IPv6).

- NIXI was set up for the purpose of routing the domestic traffic within the country, instead of taking it all the way to US/Abroad.
- This results in better quality of service (reduced latency) and reduced bandwidth charges for ISPs by saving on International Bandwidth.
- IP Guru, NIXI Academy, NIXI-IP-INDEXhave been launched to facilitate adoption of IPv6 and create an environment to ensure smooth transition from IPv4 to IPv6.
- IP:‘IP’ stands for ‘Internet Protocol’. It is a set of rules that dictate how data should be delivered over the public network (Internet).
- IPv4 was the first major version of IP and IPv6 is the most recent version of the Internet Protocol.
Primary source: https://nixi.in/en/mission-vision
Whitest Paint
· Context- A team of researchers from Purdue University in the US have created “whitest paint”.

- The new ultrawhite white paint reflects 99% of all lightthat hits it, remaining significantly cooler than the ambient temperature, even when sitting in full sunlight.
- Paints currently available in the market reflect only 80-90% of the sunlight and therefore, they can’t make surfaces cooler than their surroundings.
- Typical commercial white paint gets warmer instead of cooler.
- The older formulation of ultra-white paint that was made of calcium carbonate, while the new one is made up of barium sulphate.
- This breakthrough technology can help incombating the woes of global warming.
Primary source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/white-paint-research-sunlight-weather-7276431/
CT value in Covid-19 RT-PCR test
- Context- Maharashtra state had requested the Centre to revisit the norms for Covid testing. The ICMR has written back saying the proposed revision in the positivity criteria will cause too many infections to be missed and further transmit the disease.
- CT stands for cycle threshold and it refers to the number of cycles needed to amplify the viral RNA to a detectable level.
- If there is more genetic material to begin with, then fewer cycles of amplification would be sufficient to detect the DNA.
- The lower the Ct level, the greater the amount of target nucleic acid in the sample and hence, the higher the viral load is supposed to be.
- While the cycle threshold (Ct) value can be suggestive of the amount of virus in an infected person, there is no reliable way of correlatingthe Ct value with COVID-19 disease severity or infectiousness.
- Presently, all patients with a CT value of equal to or less than 35 are considered positive, while those with a CT value greater than 35 are considered negative. Maharashtra has requested to implement Covid detection with CT value 24. The globally accepted cut-off for CT value for Covid-19 ranges from 35-40.
Primary source: https://www.indiatoday.in/amp/coronavirus-outbreak/story/ct-value-covid19-coronavirus-rt-pcr-test-all-you-need-to-know-1791844-2021-04-16
The Election Commission of India cannot be a super government – The Hindu
Essence - Article is discussing important dimensions related to role of Election commission in Indian democracy. From a time where no one knew that election commission had any credible power to stop electoral malpractices to a time where election commission has showed its mettle under Mr. TN Seshan in early 1990’s, election commission has chalked a long way.
Supreme Court held in Mohinder Singh Gill vs Chief Election Commissioner (AIR 1978 SC 851) that Article 324 contains plenary powers to ensure free and fair elections and these are vested in the ECI which can take all necessary steps to achieve this constitutional object.
Model code of conduct framed on the basis of a consensus among political parties, it has not been given any legal backing. If it’s declared as a part of law, all matters connected with the enforcement of the code will be taken to court, which would delay elections.
Why you should read this article?
- To understand the journey of model code of conduct in Indian democracy & being a shield for free & fair elections.
- To understand the debate related to legitimacy of various actions taken by Election commission like withdrawing recognition of a recognised political party if it refuses to observe the model code of conduct.
- To know about the constitutional position of Election commission with regard to transferring officials under state government by its order.
- To understand the necessity of removing ambiguity from powers of Election commission, for integrity and independence of the electoral process.
Link - https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/lead/the-eci-cannot-be-a-super-government/article34353019.ece
Protect the rights of women migrant workers - HT
Essence - Article is discussing important dimensions related to role of Election commission in Indian democracy. From a time where no one knew that election commission had any credible power to stop electoral malpractices to a time where election commission has showed its mettle under Mr. TN Seshan in early 1990’s, election commission has chalked a long way.
Supreme Court held in Mohinder Singh Gill vs Chief Election Commissioner (AIR 1978 SC 851) that Article 324 contains plenary powers to ensure free and fair elections and these are vested in the ECI which can take all necessary steps to achieve this constitutional object.
Model code of conduct framed on the basis of a consensus among political parties, it has not been given any legal backing. If it’s declared as a part of law, all matters connected with the enforcement of the code will be taken to court, which would delay elections.
Why you should read this article?
- To understand the journey of model code of conduct in Indian democracy & being a shield for free & fair elections.
- To understand the debate related to legitimacy of various actions taken by Election commission like withdrawing recognition of a recognised political party if it refuses to observe the model code of conduct.
- To know about the constitutional position of Election commission with regard to transferring officials under state government by its order.
- To understand the necessity of removing ambiguity from powers of Election commission, for integrity and independence of the electoral process.
Link - https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/lead/the-eci-cannot-be-a-super-government/article34353019.ece
Organic Rice Production by SRI: Empowering women in Maharashtra
Present Cultivation method deployed in Rice
- Rice is majorly cultivated by Transplantation method which requires lot of water, labour needs and heavy inputs
- This method makes it difficult for marginal farmers to grow rice crops sustainably so a new method of production is being propagated in Maharashtra.
Organic Rice Production by SRI
- Tejaswini Rural Women’s Empowerment Programme has empowered marginal women farmers by propagating practices like Organic Farming and System of Rice Intensification.
- System of Rice Intensification is a low water, labour-intensive method for organic rice production.
Outcomes
- Costs of production have reduced by 30 percent in the area which used these innovative methods
- Increased women’s participation in decision-making matters of the household due to empowerment of women in field
- Reinforced faith of rural citizens in the capacity and potential of women-related government schemes in agriculture
- Increased acceptance of other government related scheme like Crop Insurance, Krishi Sinchayee Yojana
- Increased yield, sustainability of crops due to use of innovative methods.
Where can we use this case study?
Innovative example of modernisation of agricultural practise, Good example for Self Help Group, promotion of Organic Farming.
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.





