Tuesday, 20th April 2021
Radioactive Radium Salts
On April 20, 1902, Marie and Pierre Curie successfully isolated radioactive radium salts from the mineral pitchblende (radium does not occur freely in nature) in their laboratory in Paris. Radium was previously discovered in 1898. Ensuing results from groundbreaking investigations in the field of radioactivity led Madam Curie to be awarded the Nobel prize in 1903 and 1911, thus making her the first person to win two Nobel prize. She stood for women rights, her works led to important innovations in the field of nuclear physics and medical science. She died from leukemia caused by four decades of exposure to radioactive substances.

Startup India Seed Fund Scheme
In News
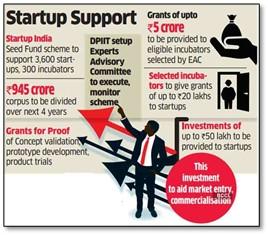
Union commerce minister launched a Startup India Seed Fund Scheme (SISFS) to handhold and financially support early-stage startups across 300 incubation centres.
About the Scheme
- Background: Despite the pandemic-led disruption, 11 startups turned unicorns in 2020, and over 30 are valued at over $1 billion. Startups are changing the demographic character of business, making India as one of the biggest nations in the startup ecosystem.
- Need for the Scheme: The Indian startup ecosystem suffers from capital inadequacy in the seed and ‘Proof of Concept’ development stage.
- The capital required at this stage often presents a make or break situation for startups with good business ideas.

- Aim of the Scheme: In order to further accelerate the startup ecosystem in India, Rs 945-crore scheme aims to provide financial assistance to startups for proof of concept, prototype development, product trials, market entry and commercialisation and has been approved for the period of next four years starting April 1, 2021.
- This would enable these startups to graduate to a level where they will be able to raise investments from angel investors or venture capitalists or seek loans from commercial banks or financial institutions.
- The scheme will also create a robust startup ecosystem, particularly in Tier 2 and Tier 3 towns of India, which are often deprived of adequate funding. The schemes also encourages the innovators from rural areas to come forward and benefit from this scheme.
- Incubator: Grants of up to ₹5 crore will be allocated to eligible incubators selected by an expert committee. An incubator will be responsible for the holistic development of the incubatee, including physical infrastructure, support testing and validation of ideas and mentorship.
- The sector-agnostic scheme doesn’t require physical incubation and allows startups to apply to three incubators
Ladakh standoff: China refuses to withdraw troops from Hot Springs, Gogra
In News
China has refused to withdraw its troops from Hot Springs and Gogra Post, two of the friction points between Delhi and China in Eastern Ladakh along the Line of Actual Control.
Background
- Border tensions between the two countries flared up in June last year after clashes between Indian and Chinese soldiers in Ladakh’s Galwan Valley.
- The disengagement process along Pangong Tso in Ladakh began on February 10 after military commanders began pulling out troops, tanks and artillery from the area in the first step towards full withdrawal. The process has been completed.
- On February 20, India and China held commander-level talks to discuss pulling back from other areas. Beijing’s refusal came even as India and China agreed to expeditiously resolve their outstanding matters at the 11th round of Corps Commander-level meeting held earlier in April.
- The two countries have completed disengagement at Pangong Tso in Ladakh. India and China had agreed to maintain stability in Eastern Ladakh and avoid any new incidents during the talks.
- Location of Hot Springs - The area is north of the Karakoram Range of mountains, which lies north of the Pangong Tso lake, and south east of Galwan Valley.
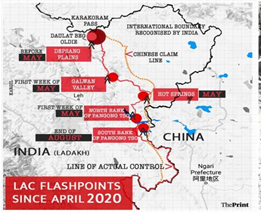
Significance of the Hot Springs and Gogra Post
- Close to Kongka Pass: which according to China marks the boundary between India and China.
- Proximity to Xinjiang and Tibet
- Important in China’s military history: Hot Springs was an important post even during the 1962 Indo-China conflict. Hot Spring had also served as a company headquarter for the Chinese military.
Sources
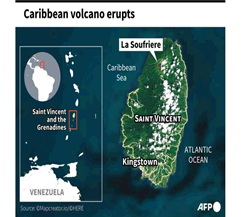
Sulphur dioxide from Caribbean volcano reaches India, WMO confirms
In News
According to a report from the World Meteorological Organisation, Sulphur dioxide emissions from the La Soufriere volcano eruption in the Caribbean have reached all the way to India.
Key Highlights
- Potential of acid rain and pollution: The sulphur dioxide (SO2) emissions from a volcanic eruption in the Carribean that have reached India has enhanced the possibility of increased pollution levels in the northern parts of the country and acid rain. Sulphur dioxide reacts with water to form sulphuric acid which can come down with rainfall.
- Impact aviation: Climatologists have also pointed out that volcanic plumes can also cause aviation and air quality hazards.
- Aerosol particles in Stratosphere: The volcanic eruptions that occurred on April 10 were energetic enough for the plumes to be recorded at a height of 20 kilometres above the Earth’s surface as recorded by the Multi-Angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer instrument on NASA’s Terra satellite. NASA scientists have found evidence for the entry of sulphate aerosol particles (precursors for sulphuric acid) in the stratosphere, the second layer of the Earth’s atmosphere.
Environmental Impact of Volcanic Eruptions
- Cooling effect: Volcanic emissions reaching the stratosphere can have a cooling effect on global temperatures. It involves conversion of sulphur dioxide to sulphuric acid, which condenses rapidly in the stratosphere to form fine sulphate aerosols.
- The aerosols increase the reflection of radiation from the Sun back into space, cooling the Earth’s lower atmosphere or troposphere.
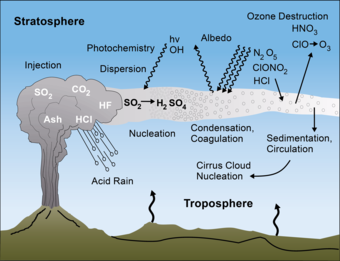
- Tropical Rainfall: Recent research suggests eruptions can affect the position of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ). If the eruption occurs predominantly in one hemisphere then it is expected the ITCZ would shift away from that hemisphere. There are also signs that volcanoes may promote El Niño conditions for a year or two, possibly followed by a tendency towards La Niña.
- CO2 release: According to British and US Geological Survey, underwater and land-based volcanoes are estimated to release around 100-300 million tonnes of CO2 each year. This accounts for around 1% of the amount of CO2 released from burning of fossil fuels.
Sources
https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2011/feb/09/volcanoes-climate
https://www.carbonbrief.org/what-do-volcanic-eruptions-mean-for-the-climate
Lost Golden City
Workers carry an ancient artifact- fish covered in gold, found in Luxor, Egypt. Archaeologists have unearthed this 3400-year-old “lost golden city" at the bank of river Nile in Egypt. The city, named as golden city because it was built during the golden age of Egypt, could be the largest city built during those times. It was called as “tehn Aten” (meaning dazzling Aten) and was built by Amenhotep III who is considered to be the wealthiest Pharaoh who ever lived.

Baikal-GVD Telescope
- Context- launch of one of the world’s biggest underwater neutrino telescopes GVD (Gigaton Volume Detector) in Lake Baikail, Russia (world’s deepest lake).
- Aim of this project- study the elusive fundamental particles called neutrinos and determine their sources. This will aid scientists to understand the origin of the universe.
- Location-the underwater telescope such as the GVD is designed to detect high-energy neutrinos that may have come from the Earth’s core, or could have been produced during nuclear reactions in the Sun.
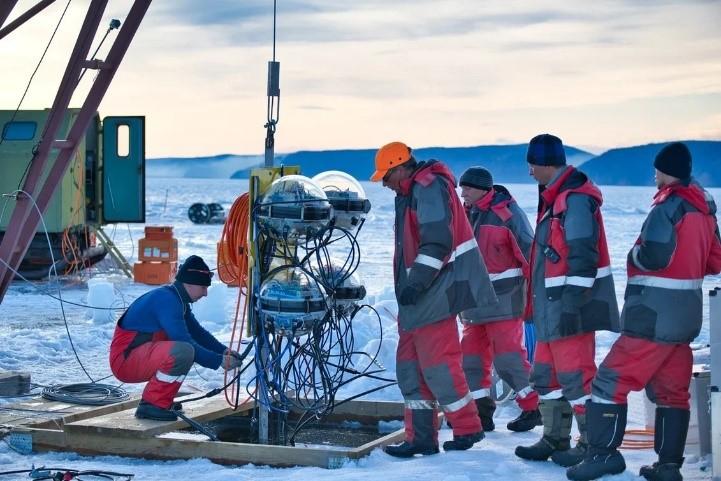

- The Baikal-GVD is one of the three largest neutrino detectors in the world along with the IceCube at the South Pole and ANTARES in the Mediterranean Sea.
Primary source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-what-is-a-telescope-doing-inside-the-worlds-deepest-lake-7254805/
Exotic animals
- Context- The Delhi High Court, recently issued an order directing the Centre to take a decision on framing rules to confer protection for exotic animals that are not under the purview of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.

- The term exotic animal generally refers to an animal that is more unusual and rarer than normal domesticated petslike cats or dogs. These are species which are not usually native to an area but are introduced to an area by humans.
- Previously, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change had issued an advisory to streamline and formalize the process of importing live exotic animals.
- Illegally traded exotic animals are confiscated under the provisions of Customs Act, 1962 and CITES. CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora) isan international agreement between governments that aims to ensure that international trade in specimens of wild animals and plants does not threaten the survival of the species to which India is a party.
Great Indian Bustard - State bird of Rajasthan
- Context- a group of hunters shot down twoGreat Indian Bustards (GIBs) in a protected area in Pakistan.

- Bustards are amongst the heaviest of flying birds and generally favor flat open landscapes with minimal visual obstruction and disturbance, hence, they adapt well in grasslands and are considered flagship grassland species, representing the health of the grassland ecology.
- Today, its population (less than 200) is confined mostly to Rajasthan and Gujarat and small population occur in Maharashtra, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh.
- It is Critically Endangered in IUCN Red list and is a part of schedule 1 of Wildlife Protection Act 1972.
- The bird is under constant threats due to collision/electrocutionwith power transmission lines, hunting, habitat loss and alteration because of widespread agricultural expansion, etc.
- GIB has been kept under the species recovery programunder the Integrated Development of Wildlife Habitats initiative. Various other programs to integrate GIB’s protection aim to build captive population of Great Indian Bustards and to release the chicks in the wild for increasing the population.
Primary source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/other-states/bustard-poaching-in-pakistan-desert-shocks-wildlife-activists/article34338082.ece
https://www.wwfindia.org/about_wwf/priority_species/threatened_species/great_indian_bustard/
Cities combating plastic entering the marine environment
- Context- India-Germany sign agreement under Swachh Bharat Mission (Urban)

- The project’s outcomes will be completely in line with the objectives of Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban focusing on sustainable solid waste management and the vision to phase out single use plastic by 2022.
- This will be combined with data management and reporting systems, civil society involvement and increased cooperation with recyclers and the recycling industry through a digital platform.
- The project is envisaged under the contours of the Joint Declaration in the field of ‘Prevention of Marine Litter’ signed between India and Germany in 2019.
|
Impacts of Marine Litter · Marine litter threatens ecosystems, adversely affects fishery and tourism industries and increases risk of micro-plastic particles entering the food chain. · It is estimated that 15-20% of all plastics are entering oceans via riverine ecosystems and 90% of it is contributed by 10 of the world’s most polluting rivers (two of them being Ganga and Brahmaputra). |
Primary source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1712652
Railway Freights
In News
The Indian Railways is aiming to increase its share in freight transportation from the present 28 % to 45 % by 2030 through better infrastructure and business development plans.
Why does the government want to increase the share of Railways in Freight?
- Network: Indian Railways is world’s fourth largest rail transport network by size. This enables it to from the base of multi-modal transportation system, interconnecting the other modes of transport like roadways, airways and waterways to each other.
- Cost Effective: As per industry estimates, the cost of transportation by railways is 1.36 per tonne per kilometre, as against Rs. 2.5 by roadways. At roughly 14% of India’s GDP, the logistics cost of India is one of the highest in the world, due to high dependency on roadways.
- Progressive graph: Railway freight volumes saw a 37% jump in volume from 2010 to 2019. Also, the railway freight revenue saw a rise in FY21, despite a bad economic state of the country.
- Eco-friendly: On an average, railways are three to four times more fuel efficient than trucks. That means moving freight by rail instead of truck lowers greenhouse gas emissions by up to 75%.
- Suitable option in times of emergency: During the lockdown, the freight trains moved fast, cutting through lockdown regions to reach the destination, while trucks moved slowly due to multiple challenges, including state border issues.
But despite such advantages, the share of railways in freight transport has reduced from about 62% in 1990-91 to about 27% by 2014-15. Why?
- Infrastructural constraints: Delay in provisioning of adequate infrastructure and sharing of lines by passenger and freight trains, have resulted in significant shift of traffic from rail to road.
- Line capacity: Due to shortage or clear division of rail line between passenger and freight, majority of the Zonal Railways run in the range of optimal and higher than optimal utilisation of line capacity.
- Terminal infrastructure and operation: Basic infrastructure facilities like lack of modern equipment, mechanization, maintenance of fixed assets, security and safety issues, and poor access/ approach road condition are some of the concerns raised by the stakeholders.
- Higher transit time: IR has under-performed in providing timely delivery of services, which is one of the reasons for shift of short lead bulk traffic (cement, steel products, containers, etc.) or in some cases long lead traffic (like automobile, parcels, etc.) to roadways. Infrastructural constraints and priority of ‘moving people’ have resulted in lower average speed of freight trains.
- Price competitiveness of IR: Rising expenditure with lower growth in revenues, coupled with slowdown of investment in capacity augmentation and consistently higher tariff rates to subsidize the passenger movement has led to
- High operating ratio at 97.29% in the FY2019, which should be between 80–85%’. Operating ratio means the expenses as a portion of the revenue or the amount spent on every rupee earned by the railways
- Less competitiveness in IR when compared to roadways with its ever expanding road networks, cost competitiveness over railways, and door-to-door service.
- Lack of marketing approach to tap ‘traffic on demand’: Indian Railways has essentially followed the ‘take-it or leave-it’ approach of freight transportation. IR needs to adopt customer centric approach to increase loading of existing/bulk commodities, and diversify its freight basket.
What is being done by the government to improve the condition of railway freights?
- Exploring New Markets: Railways has increased its market share in automotive logistics this year. Indian Railways targets 30% automobile freight traffic by
- Kisan Rail scheme - The scheme aims to provide cheaper and faster transportation facility and provide seamless supply chain to the farmers, preventing the destruction of perishable farm produce.
- National Rail Plan 2030: Through the plan, the IR seeks to increase its modal share in freight by 45% from the existing 27% in 10 years.
- The plan also sought to rationalise freight tariffs to compete more effectively with the roadways, to reduce transit time and cost, and also achieve net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2030.
- Higher Budget Allocation: With allocation of Rs 1.10 lakh crore for the Indian Railways as part of Budget 2021, a 57 % jump from last year’s figure, the IR will focus on commissioning the eastern and western DFC, bringing down logistics cost, green railways and promote public-private partnership in the railways.
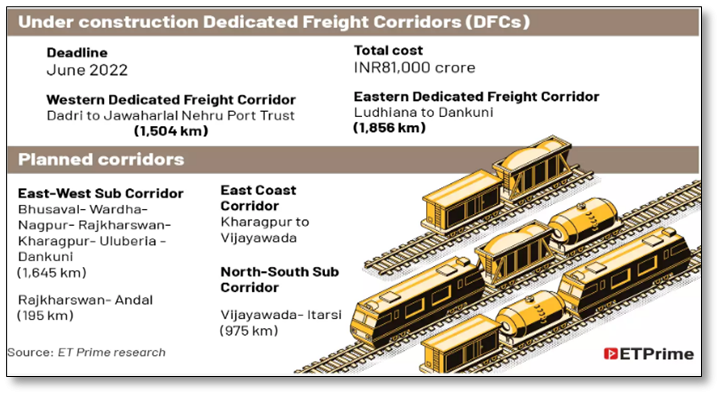
- Dedicated Freight Corridor: Conceived in 2004-05, dedicated freight corridor (DFC) project is being executed across IR’s network.
- Authority: The Dedicated Freight Corridor Corporation of India Ltd (DFCCIL) is a special purpose vehicle to undertake the project.
- Corridors under construction: The Eastern DFC with key funding from the World Bank and Western DFC with key funding from the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA).
|
DFC a game Changer? · Capacity Enhancement: The DFC will increase the loading capacity of the Indian Railways, which carries the fourth highest tonnage of freight globally, at over 1,200 million tonnes. · Cost Effective: Since these freight corridors will be exclusively meant for goods trains, they will have one station every 50 km as compared to the existing railways, which has one every 10 km. This would mean that the cost of manpower, maintenance and operation for the DFC will be much lower. · Enhances transportation Speed: With shift of 70 % of the goods train to exclusive tracks on the DFC and envisioned speed at around 80 kmph, the trains through the DFCs will be able to carry the cargo carried by 1 lakh trucks in a single day. · Green Initiative: DFCCIL will decongest already saturated road network & promote shifting of freight transport to more efficient rail transport. It is expected that DFC will save more than 450 million ton of CO2 in first 30 years of operation (Assessment based on Ernst & Young study).
|
Sources:
https://shaktifoundation.in/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/Full-Report.pdf
Even after the withdrawal of US forces, Afghanistan will continue to shape regional strategic matrix - IE
Essence - Editorial is giving a 360° outlook of ongoing transition in Afghanistan’s domestic landscape post US withdrawal, role & stature of different stakeholders. The exit of US and NATO forces after two decades of military intervention underlines the end of the unipolar moment in international affairs. But, US remains the most significant global power even after the end of the unipolar moment. US will figure prominently in any Taliban strategy to win international diplomatic recognition and political legitimacy.
Russia, the great power successor to the Soviet Union, is determined to play an important role in the future of Afghanistan. China is also widely seen as the biggest beneficiary of US withdrawal. Both Kabul and the Taliban have seen China as a valuable partner. China is also vulnerable to religious and ethnic separatism in its Muslim majority Xinjiang province. Through the last four decades and more, Afghanistan has been the incubator of Islamic radicalism and a laboratory for its weaponisation for geopolitical ends. The focus on external powers should not give the impression that the local actors in Afghanistan are mere pawns. The Taliban is quite capable of making independent deals with the rest of the world.
Why you should read this article?
- To understand the background of US intervention & now planned exit from Afghanistan.
- To understand the importance of Afghanistan in shaping international politics.
- To know about interest & roles of other nations in Afghanistan peace process.
- To look through the lens of history & understand, how Afghanistan became a fertile ground for religious extremism to serve strategic need of other powers.
Sharing the burden of care – The Hindu
Essence - There has been a consistent failure in India to prevent the spread of the COVID-19 pandemic, which has resulted in the second wave. It is unfortunate that people are dying not because of inadequate solutions (technology and knowledge) for dealing with the virus but due to inadequate access (economic, physical and others) to that knowledge and technology. In this context, this article emphasises on strengthening community health centres to remove this serious injustice.
Why you should read this article?
- Know about the reactive approach, which was carried out by most of the State governments, and its major fallouts
- Understand the importance of a community health centre (CHC) as envisaged in a three-tier structure of health services in India and how can it be a more feasible and sustainable solution in combating pandemics like COVID.
Link - https://www.thehindu.com/todays-paper/tp-opinion/sharing-the-burden-of-care/article34362859.ece
Ghar Doghaanche Abhiyan: Joint ownership of housing by husband and wife in Maharashtra
Present Situation
- Property rights for women in India are governed by a complex set of personal laws with separate provisions for communities belonging to different religion. There is no single Property Law for women in India.
- Due to lack of awareness, prejudices and patriarchy, women do not receive rightful share in the property.
- Lack of property right becomes a reason for vulnerabilities faced by many married women like unfair and unequal treatment within the family, domestic abuse and no say in the important matters within the family.
Awareness Generation Initiative in Maharashtra
- Women’s Economic Empowerment Wing of Government of Maharashtra is spreading awareness that seeks to make women aware of their rights to their husbands’ house and property.
- Awareness drive and ‘Home of Two campaign’ encourage the co-ownership of property by both husband and wife.
- The initiative has taken a targeted approach towards the enforcement of women’s property rights, an approach that is unparalleled elsewhere in the country.
Outcome
- It has instilled a sense of security among the women in the rural areas.
- Women have resisted domestic abuse with the knowledge that they cannot legally be thrown out of their houses.
- Contributed towards Women Empowerment as women now enjoy greater confidence due to increased awareness
- Upheld principle of equality as it based on the notion of equal rights for both the gender.
Where can this case study be used
Innovative case study for giving equal inheritance right to women, awareness generation in the village about the property rights of women, case study for the social empowerment of women.
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.