Wednesday, 24th March 2021
Regulating Civil Society
A NITI Aayog group (the Working Group for Formulation of New National Policy for Voluntary Sector) is working on a national policy to regulate civil society organisations (CSOs).
Civil Society
- Civil society is the “third sector” of society, along with government and business. It comprises civil society organizations and non-governmental organizations.
- Civil society includes charities, development NGOs, community groups, women's organizations, faith-based organizations, professional associations, trade unions, social movements, coalitions and advocacy groups.
- Civil society organizations play multiple roles.
- They are an important source of information for both citizens and government.
- They monitor government policies and actions and hold government accountable.
- They also deliver services, especially to the poor and underserved.
- They defend citizen rights and work to change and uphold social norms and behaviors.
Need for Regulation
- There are more than 32 lakh civil society organisations registered under different Acts but the actual contributors to societal development are very few.
- Misgovernance of CSOs/NGOs: For example, less than 10% of the registered NGOs file their annual income and expenditure.
- Anti-development activities: Report by Intelligence Bureau (IB) report revealed stalling development projects by foreign-aided NGOs thus impacting GDP growth by 2-3% per annum.
- Poor implementation of CSO Policy: Although a 2007 policy named “National Policy on the Voluntary Sector”, by the erstwhile Planning Commission is in place, many aspects of the policy were never implemented.
- Policy recommended an “independent, national level, self-regulatory agency for the voluntary sector.
- Several violations of the new regulations, including the Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCRA), call for a revamped policy.
Steps taken by NITI Aayog
- NITI Aayog had launched a portal called DARPAN in 2016 for mandatory registration of CSOs.
- Portal collects data about funding through CSR, central ministries, state governments and FCRA. To receive tax exemptions, organisations must make a Unique ID on this portal.
- NITI Aayog has also been insisting on GIS mapping of NGOs’ projects and is working on DARPAN 2.0.
Conclusion
The NITI Aayog group aims to look at various aspects of the 2007 policy and propose a clear action plan along with an enabling policy for a healthy partnership between the government and the CSOs. The framework will ensure the Indian government abides by the guidelines of the Financial Action Task Force (FATF), a global body aimed at preventing money laundering and terrorist financing.
ISRO Makes A Quantum Communication Breakthrough
In News
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has announced that it has successfully demonstrated free-space Quantum Communication over a distance of 300 m.
Significance of the Quantum Communication Breakthrough
- According to ISRO, this is a major milestone for unconditionally secured satellite data communication using quantum technologies.
- With this breakthrough, India joins a handful of other nations such as the US, the UK, Canada, China and Japan who have made significant contributions in the field of quantum communication.
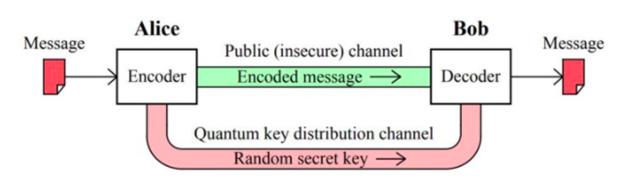
About Quantum Cryptography
Quantum cryptography is the use of quantum mechanical properties to achieve cryptographic tasks. Cryptography is the practice of creating secure communication.
Quantum Key Distribution Technology versus Conventional Encryption System
- The Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) technology underpins Quantum Communication technology that ensures unconditional data security by virtue of the principles of quantum mechanics, which is not possible with the conventional encryption systems.
- The conventional cryptosystems used for data-encryption rely on the complexity of mathematical algorithms, whereas the security offered by quantum communication is based on the laws of Physics.
- Quantum cryptography is considered as ‘future-proof’, since no future advancements in the computational power can break quantum-cryptosystems.
Significance of Quantum Key Distribution
- Military use: QKD system can be used in a unified Cipher Policy Committee (CPC) framework in India for more secure key management of various military cryptographic systems.
- Transmitting secret key over long distances: Quantum cryptography is the only known method for transmitting a secret key over long distances.
- Enable start-ups: The technology would be useful in enabling various start-ups and small and medium enterprises in the domain of quantum information.
The India-US Defence Partnership
In News
The US Secretary of Defence visited India.
Significance of the Visit
Timing of US Secretary of Defence visit to New Delhi is significant for many reasons.
- His visit this early in the new US President’s tenure indicates the important place India holds, on a par with the other two countries he visited prior to India: Japan and South Korea.
- The visit came just after the first ever Quad leaders’ summit which confirms the US’s focus on greater maritime cooperation in the Indo-Pacific.
- US is undertaking a major review of its troops pull-out schedule and peace plan in Afghanistan.
As a result, all three areas: bilateral ties, the Indo-Pacific and Afghanistan came up for discussion during talks .
India-US defence partnership
The U.S.-India defense relationship has grown over the last decade to become a key component of the overall bilateral partnership. Key Partnership Activities are as follow-
- Framework for Defence Relationship:
- In 2005, a 10-year Framework for Defence Relationship established, followed by a Joint Declaration on Defence Cooperation in 2013. The Framework agreement was renewed in 2015 for another decade.
- The Framework laid out an institutional mechanism for areas of cooperation including joint exercises, intelligence exchanges, joint training for multinational operations including disaster relief and humanitarian assistance, technology transfer and a sharing of non-proliferation best practices.
- Major Defence Partner:
- In 2016, the United States designated India as a Major Defense Partner.
- In 2018, India was elevated to Strategic Trade Authorization tier 1 status, easing exports of sensitive defence technologies.
- These developments facilitated India in joining the export control regimes (Australia Group, Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR) and Wassenaar Arrangement).
- Defence Agreements:S.-India defense trade cooperation continues to expand with the Basic Exchange and Cooperation Agreement (BECA) for Geospatial Intelligence, Logistics Exchange Memorandum of Agreement (LEMOA), Communications, Compatibility and Security Agreement (COMCASA), General Security of Military Information Agreement (GSOMIA) and the Industrial Security Agreement (ISA) now in place.
- Defense Technology and Trade Initiative (DTTI): The DTTI seeks to deepen defense cooperation between India and the United States by elevating dialogue on cooperative research & development and defense trade to the highest levels of government.
- Current Bilateral defence trade stands at $20 billion.
- Increasing Maritime Security Cooperation/ Recognition of Indo-Pacific Realm: The term “Indo-Pacific region” has now replaced the term “Asia Pacific region” in the American diplomatic lexicon.
- The US administration has consistently described India as one of its major allies in the Indo-Pacific region;
- US renamed the former US Pacific Command as US Indo-Pacific Command (USINDOPACOM), emphasizing the strategic linkage between the Indian and Pacific Oceans.
- In 2019, India became eligible for funding under US’s Maritime Security Initiative, which conducts partner capacity building in the Indo-Pacific.
- Building peacekeeping cooperation: India is consistently among the top five contributors of military and police personnel to UN peacekeeping operations.
- From 2016 to 2019, India and the United States jointly taught the UN Peacekeeping Course for African Partners.
- The United States and India are now looking to expand collaboration on peacekeeping cooperation with Indo-Pacific partners.
- Knowledge Partnership in Defense Studies
- launched the S.-India Knowledge Partnership in Defense Studies.
- India participates in the International Military Education and Training (IMET) program, a United States security assistance program. IMET provides professional military education and training increase military professionalization and enhance interoperability with US forces.
- Military Exercises:
- In November 2019, the United States and India conducted Tiger Triumph, the first-ever tri-service (ground, naval, and air forces) exercise between the two countries.
- India also participates in the U.S.-led Rim of the Pacific (RIMPAC) exercise and trilateral Malabar exercise with the United States and Japan.
- These military exercises enhance U.S.-India relations and help create a more stable and secure Indo-Pacific region.
(Note: For more factual details of India-US defence partnership, refer to infographic. More focus should be given to following heads- 1. Major agreements and mechanisms, 2. Dialogues, 3. Major Joint Exercises, 4. Existing Defence Technology Cooperation).
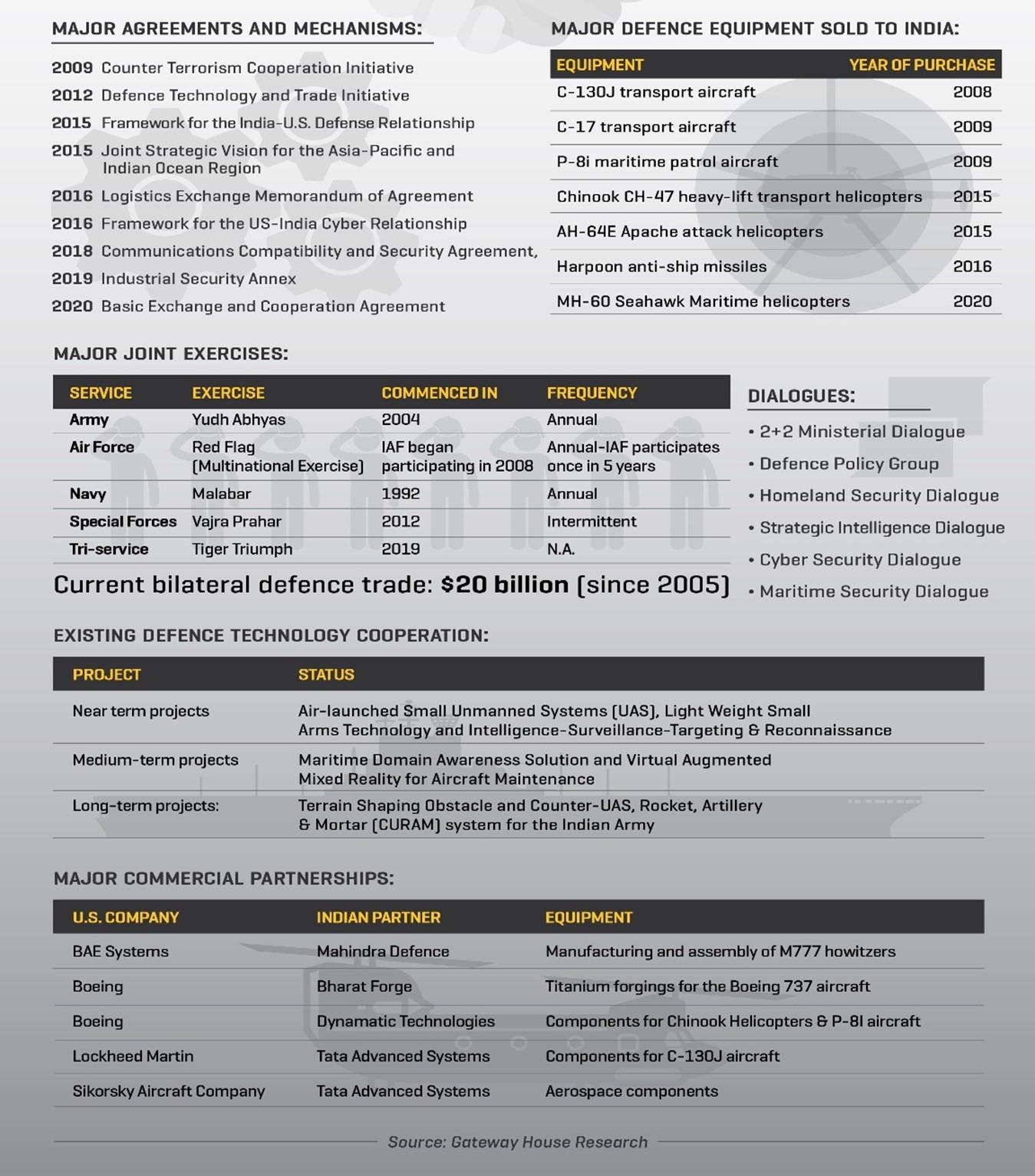
Model Q: Elaborate how the India- US defence partnership has evolved over the last decade?
After nearly 40 years, India’s first river-linking project Ken-Betwa finally begins
In News
About four decades after conceptualisation, India’s first river interlinking project, connecting Ken river in Madhya Pradesh with Betwa in Uttar Pradesh, is finally set to get off the drawing board. Union Jal Shakti Minister signed a tripartite agreement for the project implementation with Madhya Pradesh Chief Minister and Uttar Pradesh Chief Minister.
About the Ken Betwa Link Project
- First Project under National Perspective Plan: The Ken-Betwa Link Project is the first project under the National Perspective Plan for interlinking of rivers. Under this project, water from the Ken river will be transferred to the Betwa river. Both these rivers are tributaries of river Yamuna.
- Expected benefits: The project is expected to provide an annual irrigation facility to 10.62 lakh hectares, drinking water supply to about 62 lakh people and also generate 103 MW of hydropower.
- Impact on Panna Tiger Reserve: Out of the 6,017 ha of forest area coming under submergence of Daudhan dam of Ken Betwa Link Project, 4,206 ha of area lies within the core tiger habitat of Panna Tiger Reserve.
Regions expected to benefit from the project
- Project to benefit Bundelkhand region: The Ken-Betwa Link Project lies in Bundelkhand, a drought-prone region, which spreads across 13 districts of Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh.
- Districts to be benefitted are shown in the map.
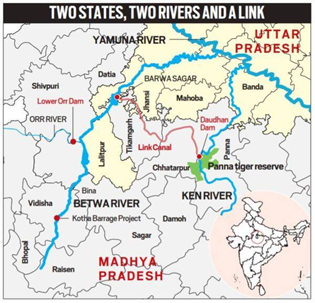
Issues raised against the project
- Environmental impact: Certain environmental and wildlife conservation concerns are likely to arise with the projects like the Ken-Betwa that passes through critical tiger habitat of the Panna Tiger Reserve. The engineering structure of the dam will isolate the upstream aquatic fauna of the Panna National Park and this may have a direct impact on the breeding habits of aquatic life forms both upstream and downstream of the dam.
- Economic impact: The Central Empowered Committee of the Supreme Court had earlier raised questions about the validity of the Ken Betwa Link project. The CEC also noted that the primary objective of the KBLP of providing irrigation facilities and alleviating poverty can be achieved through alternative methods of water conservation and harvesting at the local level and at a much cheaper cost.
- Issues of rehabilitation: It was pointed out by the CEC that there exists a visible disconnect between the information about river linking in the national media and the information available to the communities that will be impacted. The villages along the Ken river lacked information about the project and the upper catchment area of the river is not modernised in respect of roads, electricity and chemical farming.
- Improving water efficiency over large infrastructure: Globally the scientific community has advocated for improving water efficiency and conservation over large infrastructure projects that disrupt the river flow and damage ecosystems. Labelling river basins as 'surplus' or 'deficit' is not scientifically appropriate as river volumes can change due to climate change.
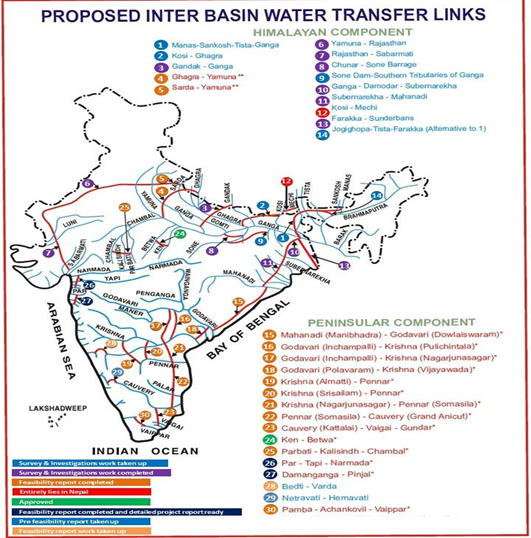
Previous examples of river linking in India
- In the past, several river linking projects have been taken up. For instance, under the Periyar Project, transfer of water from Periyar basin to Vaigai basin was envisaged.
- Similarly, other projects such as Parambikulam Aliyar, Kurnool Cudappah Canal, Telugu Ganga Project, and Ravi-Beas-Sutlej were undertaken.
|
About the National Perspective Plan · The National River Linking Project (NRLP) formally known as the National Perspective Plan, envisages the transfer of water from water ‘surplus’ basins where there is flooding, to water ‘deficit’ basins where there is drought/scarcity, through inter-basin water transfer projects. · The NPP comprised two components: (i) Himalayan Rivers Development; and (ii) Peninsular Rivers Development. · Based on the NPP, the National Water Development Agency (NWDA) identified 30 river links—16 under Peninsular component and 14 under Himalayan Component. |
Jal Shakti Abhiyan: Catch the rain campaign
- This campaign with the tagline, “Catch the rain where it falls, when it falls”, is to nudge the states and the stakeholders to create appropriate Rain Water Harvesting Structures (RWHS) suitable to climatic conditions and sub-soil strata before monsoon in the respective areas.
- It will be implemented across the country in both rural and urban areas from March – November 2021 pre-monsoon and monsoon period.
- To facilitate these activities, states would open “Rain Centers” in each district that will be manned by an engineer well trained in RWHS. This centre acts as a technical guidance centre to all in the district as to how to catch the rain, as it falls.
- Efforts would be made so that all buildings in the district would have rooftop RWHS and that maximum quantity of rain water falling in any compound should be impounded within the compound itself.
- MGNREGS funds will be used for water conservation.
Shaheed Diwas
- Shaheed Diwas, observed on March 23, marks the day when Indian freedom fighters Bhagat Singh, Sukhdev and Rajguru were executed by the British government for their acts of ‘dramatic violence’, and their role in the struggle for Indian independence.
- The Day is also known as Sarvodaya Day.
- The trio was hanged in the Lahore Central Jail, located in Pakistan today.
- They were tried and then executed in 1931 for fatally shooting a 21-year-old British police officer, John Saunders in 1928 whom they had mistaken for British police superintendent James Scott, whom they had originally targeted.
- The trio wanted to avenge the death of Lala Lajpat Rai and believed that Scott was responsible for Rai’s death, who succumbed to injuries sustained during a lathi charge.
Gandhi Peace Prize
- Gandhi Peace Prize is an annual award instituted by Government of India since 1995, the 125th Birth Anniversary commemoration year of Mahatma Gandhi for those involved in social, economic and political transformation through non-violence other Gandhian methods.
- The award is open to all persons regardless of nationality, race, language, caste, creed or sex.
- The Jury for Gandhi Peace Prize is chaired by Hon’ble Prime Minister, and comprises of two ex-officio members, namely the Chief Justice of India and Leader of the single largest Opposition Party in Lok Sabha. Two eminent members part of the Jury include Speaker of the Lok Sabha, and Founder of Sulabh International Social Service Organisation.
- The award carries an amount of 1 crore, a Citation in a scroll, a plaqueas well as an exquisite traditional handicraft/handloom item.
- The prize can be conferred upon individuals, associations, institutions or organizations.
- It has been awarded to
- For the year 2020 - Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman (Bangladesh)
- For the year 2019 - Late Sultan Qaboos bin Said Al Said of Oman
The surge of geopolitics in South Asia’s power trade – The Hindu
Essence - Editorial is exploring the possible implications of India’s new rules governing the trade of electricity across its borders. They are placing clear limits on who can buy from and sell into India in South Asian electricity market. Since Bangladesh, Bhutan, and Nepal have aligned their energy futures with the Indian market, this will have ramifications on their plans. These rules strongly discourage the participation of plants owned by a company situated in “a third country with whom India shares a land border” and “does not have a bilateral agreement on power sector cooperation with India”, thereby limiting the expansion plan of Chinese companies in power sector of South Asia.
India’s geographic centrality combines with size of its economy, give it a natural advantage in determining the shape of this market. Some theorists proposed an independent regional body governing trade, but this is not likely to happen soon. Impartial institutions for planning, investments and conflict resolution are crucial to multi-country power pools.
Why you should read this article?
- To understand, how India’s new trade rules are being considered political & what advantages they provide to India.
- To know about patterns of development in South Asian electricity market.
- To understand the need of independent regional body governing electricity trade & this trust building can help further the cause of renewable energy transition in near future.
Structural pitfalls of MGNREGA – Down to Earth
Essence - Since the pandemic gripped the country, media reports have regularly highlighted how MGNREGA has provided, among other things, employment to the highest number of households, surpassing the previous record in 2011-12. In this context, this article while evaluating how MGNREGA has contributed to rural livelihoods during the ongoing public health crisis, analyses whether the programme has made some course corrections over the years to address the structural and operational hitches.
Why you should read this article?
- Briefly know the benefits of the MGNREGA programme
- Understand what are some of the inherent flaws in the design of schemes as well as operational issues which continue to affect implementation of the programme and limit its effectiveness as a tool of poverty alleviation.
- Analyse with the help of data and examples, that though there is high level of employment generation under MGNREGA in six HPS States recently but the figure is still well below the states’ share in rural poverty.
Link - https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/governance/structural-pitfalls-of-mgnrega-76037
Energy Cane: Innovative Solution For Ethanol Blending:
Present Situation:
- 85% of our India’s Crude oil requirement is imported. To achieve energy security, biofuel production and blending was proposed as an innovative solution in National Biofuel Policy, 2018
- Current level of blending is only 5-6%, though the target envisaged was 20% ethanol blended petrol by 2025
Lessons from Brazil:
- Brazil has produced ENERGY CANE and converted itself to a biofuel economy without compromising food security.
- High biomass productivity of energy-cane lead to better ethanol production which has lowered the GHG emission.
- It is grown on drier and lower fertility soils not suitable for conventional cultivation which puts an end to food V/s Fuel debate

Outcome
- It can help India achieve energy security, lower the pollution and GHG
- Precious Forex Reserves can be saved
- It can help India to fulfil its Nationally Determined Contribution promised under Paris Agreement.
Where can this case study be used: Innovative Solution under to achieve the targets of ethanol blended petrol, Case study to lower the GHG and pollution and pollution
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.