Thursday, 22nd April 2021
On this day- Subhash Chandra Bose had resigned from the Indian Civil Services
On April 22, 1921 Subhash Chandra Bose had resigned from the Indian Civil Services. He had joined the Cambridge University in 1919 to study for the Indian Civil Service Examination. Although he passed the I.C.S examination with honour in London, he never accepted the job. Netaji was determined to join the Indian National Congress to serve the cause of the country.

India’s Agriculture trade
In News
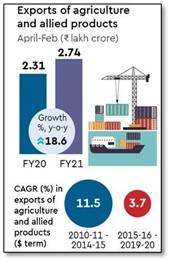
Despite the pandemic export of Agri and allied commodities during Apr, 2020 - Feb, 2021 shows an increase of 18.49%
About the News
- Trade balance: The export of Agri and allied commodities during April,2020 - Feb,2021 increased by 18.49%, which led to an increase of 41% in India’s foreign trade balance in agriculture.
- Commodities: The commodities which posted significant positive growth in exports were wheat, Other Cereals, Rice (other than Basmati), Soya meal, Spices, Sugar, Raw Cotton, Fresh Vegetable, Processed Vegetables, and Alcoholic Beverages etc.
- Export under G2G basis: On specific demand from countries, NAFED has exported 50,000 MT wheat to Afghanistan and 40,000 MT wheat to Lebanon under government-to-government (G2G) arrangement.
- Factors: This increase in exports is on account of multiple factors, mainly being India capturing new markets namely, Timor-Leste, Papua New Guinea, Brazil, Chile, and Puerto Rico.
- Trends: India has consistently maintained trade surplus in the agricultural products over the years.
- Imports: The imports of Agricultural and allied commodities during this period witnessed a slight increase of 2.93 per cent.
|
Commodity |
Percentage Increase ( April 2020 - Feb 2021) |
|
1. Agri and allied commodities |
18.49% |
|
2. Non-Basmati Rice |
132% |
|
3. Wheat |
727 % |
|
4. Soya meals |
132% |
About Agri Sector
- India occupies a leading position in global trade of agricultural products. However, its total agricultural export basket accounts for a little over 5 percent of world agricultural trade. The major export destinations were USA, Saudi Arabia, Iran, Nepal, and Bangladesh.
- The share of agriculture in GDP increased to 9 per cent in 2020-21 from 17.8 per cent in 2019-20. The last time the contribution of the agriculture sector in GDP was at 20 per cent was in 2003-04.
- During the pandemic period, agriculture has been the only sector to have clocked a positive growth of 3.4 per cent at constant prices in 2020-21, when other sectors slid.
- The Agriculture Export Policy (AEP), 2018, aims at achieving export target of $60 billion by 2022 and $100 billion within a few years, thereafter.
Digital yuan gives China a new tool to strike back at critics
In News
China has recently released its own version of a digital currency known as the digital yuan that is controlled by its central bank. China is also positioning the digital yuan for international use.
What is the digital yuan?
- The digital yuan is effectively a way for the central bank to digitize banknotes and coins in circulation. The Chinese market is already advanced in cashless payments. The digital yuan would be a way to speed that process up.
- It will be legal tender in China and no interest will be paid on it.
How does digital yuan differ from bitcoin?
- Bitcoin is a so-called decentralized cryptocurrency, which means that it is not controlled by any central authority like a central bank, unlike the digital yuan which will be issued by the PBOC (People’s Bank of China).
- Bitcoin is built on a technology known as blockchain. It is not clear as yet what kind of technical make up the digital yuan would have.
- Unlike bitcoin, the yuan is not based on anonymity. Digital yuan would have “controllable anonymity.” This would involve those operating digital yuan wallets to disclose transactions to the PBOC as the sole third party.
|
What is digital currency? Digital currency is a form of currency that is available only in digital or electronic form, and not in physical form. It is also called digital money, electronic money, electronic currency, or cyber cash. · Since digital currencies require no intermediary, they are often the cheapest method to trade currencies. · All cryptocurrencies are digital currencies, but not all digital currencies are cryptocurrencies. · Digital currencies are stable and are traded with the markets, whereas cryptocurrencies are traded via consumer sentiment and psychological triggers in price movement. |

Why is the digital yuan being introduced?
- Geopolitical significance: China’s development of a digital currency will make it harder for the U.S. to enforce sanctions. Digital yuan appears potentially more geopolitically significant as leverage over multinational companies and governments that want access to China’s large consumer base.
- Efficient payment system: The digital yuan would make the payment system more efficient and could help with financial stability through a system of “controllable anonymity.”
- Increase competition in the payment space: Another reason for introducing the digital yuan is to increase competition in the payments space and reduce systemic risk. China’s digital payments arena is dominated by Alipay, which is run by Alibaba affiliate. The existing system is owned by private companies and it creates systemic risks.
What are the possibilities of digital currency being introduced in India?
- While the RBI had earlier expressed reservations regarding cryptocurrencies, it has announced that it is working on its own digital currency. The RBI has intended that it will tap the benefits of blockchain technology for this project.
- As the existing laws in India are inadequate to deal with the subject, the government has formed an inter-ministerial panel to examine the issue.
- According to the United Nations expert on blockchain, consumers in India could gain if the country adopts central bank digital currencies as it will not only reduce security breaches but also eliminate the need for having a bank account.
Sources
https://www.cnbc.com/2021/03/05/chinas-digital-yuan-what-is-it-and-how-does-it-work.html
World Earth Day

Earth Day is celebrated worldwide on April 22 annually to raise public awareness about the environment and inspire people to save and protect it. The day marks the anniversary of the birth of the modern environmental movement in 1970. The first Earth Day was celebrated on April 22 in 1970. Since then, it has been an annual event. This year, it will be 51st Anniversary of Earth Day. The theme of the day this year is “Restore Our Earth”. The theme “examines natural processes, emerging green technologies and innovative thinking that can restore the world’s ecosystems.
National Climate Vulnerability Assessment Report
In News
The report titled ‘Climate Vulnerability Assessment for Adaptation Planning in India Using a Common Framework’, was released by Ministry of Science & Technology.
Key Features of the Report
- The Report identifies the most vulnerable states and districts in India with respect to current climate risk and key drivers of vulnerability.
- The Report has identifiedJharkhand, Mizoram, Orissa, Chhattisgarh, Assam, Bihar, Arunachal Pradesh, and West Bengal as the eight most vulnerable States that require prioritisation of adaptation interventions.
- Among all states, Assam, Bihar and Jharkhand have over 60% districts in the category of highly vulnerable districts.
- Himachal Pradesh, Telangana, Sikkim and Punjab have been categorised as lower-middle vulnerable states.
- Uttarakhand, Haryana, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Nagaland, Goa and Maharashtra have been categorised as states with low vulnerability.
- The major drivers for the vulnerability of all the States included lack of forest area per 1,000 rural population, lack of crop insurance, marginal and small operational land holding, low density of health workers, low participation of women in the workforce, yield variability of food grains, and a high proportion of the population below the poverty line.
- The eastern and central states are more vulnerable because of their poverty levels; lack of irrigation; low forest cover in some cases; low adaptive capacity of the health sector.
Conceptualising vulnerability
- The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change’s Fifth Assessment Report (AR5) defines the risk of climate change as the interaction of three factors, namely, hazard, exposure and
- ‘Vulnerability’ is conceptualised as an ‘internal property of a system’. It represents the propensity or predisposition of the system to be adversely affected, independent of hazard and exposure (Figure 1).
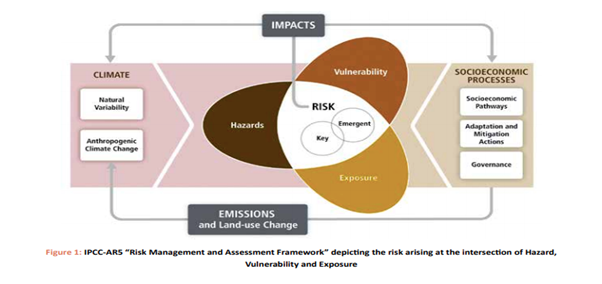
- Vulnerability is basically a function of sensitivity and adaptive capacity.
- Sensitivity: It refers to the degree to which ‘a system or species is affected, either adversely or beneficially by climate variability or change’. This determines the first-order impact of a hazard or stressor on the system.
- The effect may be direct, such as a change in the crop yield due to a change in the mean, range, or variability of temperature; or it could be indirect—damage due to an increase in the frequency of coastal flooding owing to sea-level rise.
- Adaptive capacity: It is defined as ‘the ability of systems, institutions, humans, and other organisms to adjust to potential damage, to take advantage of opportunities, or to respond to consequences’.
- For example, if a comprehensive crop insurance system is in place, farmers can cope with the damages to crops caused by hazards such as floods or drought.
- Sensitivity: It refers to the degree to which ‘a system or species is affected, either adversely or beneficially by climate variability or change’. This determines the first-order impact of a hazard or stressor on the system.
India’s Vulnerability to climate risks
- According to The Germanwatch Global Climate Risk Index- 2019 India ranked 5th out of 181 countries, implying an extremely high exposure and vulnerability.
- India had 2,081 deaths in 2018 due to extreme weather events caused by climate change – cyclones, heavy rainfall, floods and landslides.
- Overall, India’s economic losses due to climate change were the second-highest in the world, with a loss of Rs 2.7 lakh crore.
Significance of the vulnerability assessment
- The vulnerability assessment can assist in ranking and identification of the most vulnerable districts and states and help states prioritise adaptation planning and investments.
- It is critical for developing adaptation projects for the Green Climate Fund, Adaptation Fund, and funds from multilateral and bilateral agencies.
- It will also facilitate Nationally Determined Contributions, which aims to adapt better to climate change by enhancing investments in development programmes in sectors vulnerable to climate change, particularly agriculture, water resources, health sector and regions such as Himalayan region, coastal regions, etc.
- It may also aid to plan disaster management.
- A vulnerability assessment contributes to reporting under the Paris Agreement through
- the assessment of climate change impacts and vulnerability
- the formulation and implementation of a National Adaptation Plan, monitoring and evaluation of adaptation plans, policies and programmes
- the development and implementation of resilience of socio-economic and ecological systems.
Way forward
A vulnerability assessment is a first step towards adaptation planning. The Report suggests following tasks for the future:
- Need for development of climate change risk index, followed by risk ranking of states and districts, where: Risk = function of (Hazard, Exposure, Vulnerability).
- Development of a common framework, methodology and guidelines for risk assessment.
- All State Climate Change Centres funded by the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India are interested in developing a Risk Index for states. It requires building capacity for risk assessment and adaptation planning.
- Generation of data for risk assessment is important. There is need of a strategy for data generation for climate change risk and vulnerability assessment and adaptation planning.
Model Question: A vulnerability assessment is a first step towards adaptation planning. In this context bring out India’s vulnerability to Climate risks and explain how a National Climate Vulnerability Assessment is crucial for India’s fight with climate change.
Primary Sources
https://dst.gov.in/sites/default/files/Full%20Report%20%281%29.pdf
Secondary
Centre registers protest after US ship enters Indian waters without permission
In News
India has registered protests regarding the passage of US warship ‘USS John Paul’ through India's Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) without "prior permission". The US warship conducted military maneuvers and freedom of navigation operations near Lakshadweep.
Background
The passage of the US ship has come at a time when military cooperation between India and the US is on the rise. Their navies were involved in a joint exercise, along with navies of Japan, France and Australia in the eastern Indian Ocean region, in the La Pérouse exercise led by the French Navy. India and the US along with Australia and Japan make the Quadrilateral grouping where the commitment to a free and open Indo-Pacific has been emphasized.

India’s Objection
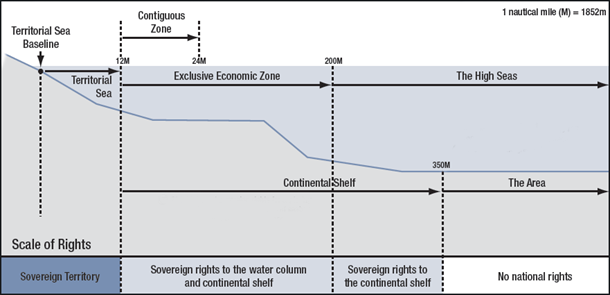
- Under Indian lawa — The Territorial Waters, Continental Shelf, Exclusive Economic Zone and Other Maritime Zones Act, 1976 — all foreign ships (other than warships including submarines and other underwater vehicles) shall enjoy the right of innocent passage through the territorial waters and a passage is innocent so long as it is not prejudicial to the peace, good order, or security of India.
- The Indian Government’s stated position on the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) is that the Convention does not authorize other States to carry out in the Exclusive Economic Zone and on the continental shelf, military exercises or maneuvers, those involving the use of weapons or explosives, without the consent of the coastal state.
US Response
- US forces operate regularly in the Indo-Pacific region and claim that the operations are conducted in accordance with international law.
- The US has emphasized that the passage of its ship was part of its regular Freedom of Navigation Operations.
- The US has also argued that India’s claim to EEZ is inconsistent with international law. The US officials also maintain a position that if India’s assertion is made the international standard, nearly 38 percent of the world’s oceans that were once considered high seas and open to unfettered military use will come under coastal state regulation and control.
About UNCLOS
The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) is an international treaty which was adopted and signed in 1982.
Ratification: The convention has been ratified by 168 parties and the European Union. India has ratified the UN Law of the Seas in 1995 but USA has not ratified it.
Reasons for the impasse
- Ambiguity of UNCLOS: The differing interpretations of India and the US on the rights and obligations in the EEZ flow from the ambiguous wording in Article 58 of the UNCLOS that deals with EEZ. Article 58 of the UNCLOS provides that in the EEZ, all states enjoy high seas freedoms of navigation and overflight and other internationally lawful uses of the seas. These “other internationally lawful uses of the seas” in Article 58 have led to a grey area which is interpreted by countries in different ways.
- Differing interpretations: Countries like India, Bangladesh, Brazil, Myanmar, Indonesia, Iran, etc. regulate or prohibit foreign military activities in the EEZ by stating that the whole spirit behind the UNCLOS is that the high seas shall be reserved for peaceful purposes.
- Technological advances and growing size of navy: The divergence in the perspective concerning the legality of foreign military activities in the EEZ between countries like India on the one hand and the USA on the other is expected to increase in the future due geopolitical factors, rise in the size of navies of many nations and technological advances to exploit the oceanic areas.
Associated Opinions
- Experts point out that the aim of USA’s FONOP stands accurate with respect to artificial Islands created by China to gain access of international sea routes and seabed as EEZ. But India’s Lakshadweep case is far from similar.
- USA’s public statement and India’s raising of concerns through “diplomatic channel” also questions India’s strategic autonomy over its marine space. It also leaves India in a vulnerable position with respect to future Chinese incursions.
- Experts say that though the international law has not been violated, such an act is a sign of “disrespect” to the nation in which EEZ is located. USA must inform about any such fleet movement as a matter of courtesy and not publicize such navigation.
Sources:
World Press Freedom Index
- Context: India retains 142nd position out of 180 countries in World Press Freedom Index 2021.
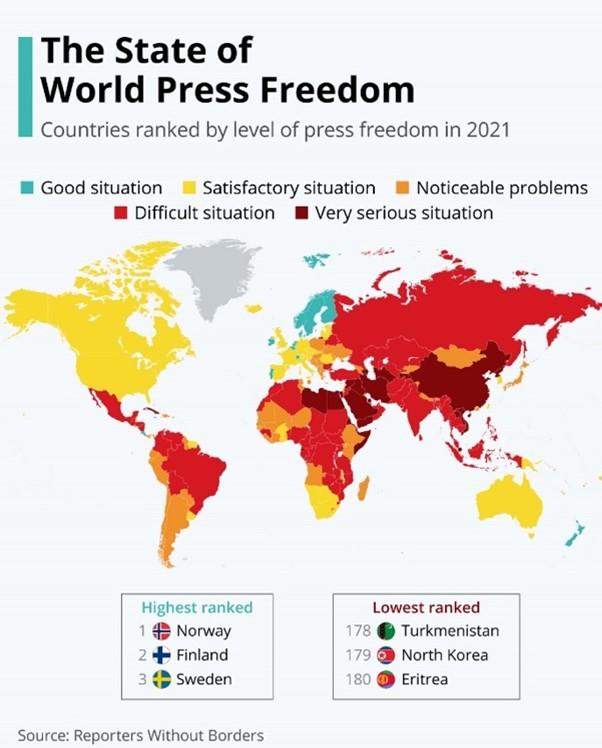
- World Press Freedom Index is published by Paris based not-for profit body Reporters Without Borders (RSF) since 2002.
- The Indexranks countries and regions according to the level of freedom available to journalists. The parameters include pluralism, media independence, media environment and self-censorship, legislative framework, transparency, and the quality of the infrastructure that supports the production of news and information.
- The index isnot an indicator on the quality of journalism.
- In the 2021 report, India is among the countries classified “bad” for journalismand is termed by the report as one of the most dangerous countries for journalists trying to do their jobs properly.
- The top three countries in the 2021 index are Norway, Finland and Denmark.
RESPOND Program: ISRO
- Context: Recently, Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) announced that it will support eight joint research projects initiated by Space Technology Cell(STC), IIT-Delhi under its RESPOND programme.

- Initiated in 1970 by ISRO, the RESPOND (Research Sponsored) Program has an objective of encouraging academia to participate and contribute in various space related research activities.
- The main idea is to establish strong links with premiere academic institutions and develop capacity to carry out research and derive useful outputs to support ISRO programs.
- ISRO helps these institutions to establish the necessary technical facilities, infrastructure, provide fellowships and financial support to researchers.
Primary source: https://www.isro.gov.in/capacity-building/respond-projects
Nongkhyllem Wildlife Sanctuary
- Context: India’s first disk-footed bamboo-dwelling bat named Eudiscopus Denticulus was recorded in Nongkhyllem Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Located in Ri Bhoi district of Meghalaya, Nongkhyllem Wildlife Sanctuary is a part of Eastern Himalayan Global Biodiversity hotspot.
- The sanctuary is rich in floral and faunal wealth and is found to be the best protected area in the North East, according to Management Effectiveness Evaluation (MEE) Report of national parks and wildlife sanctuaries.
- Nongkhyllem is an area where annual community hunting was part of tradition, but with sensible intervention of the forest department and support of the neighboring communities, it is now a pristine sanctuary.
Primary Source: http://www.megforest.gov.in/wildlife_parks.html
With design changes, Svamitva scheme can be a game changer - HT
Essence - The Survey of Villages Abadi and Mapping with Improvised Technology in Village Areas or Svamitva scheme, launched in April 2020, can play a key role in ensuring secure property rights for rural India. This article, while highlighting the key provisions and the associated benefits, suggest improvements in the scheme’s legal, social and economic design.
Why you should read this article?
- Briefly know about the scheme and how it can help transform rural India through creation of accurate land and property records by providing a Record of Rights (RoRs).
- Identify the changes needed in the design principles of the scheme, which can ensure the realisation of rural India’s aspirations such as legal validity of the property cards, recognition of women’s ownership rights, empower panchayats to both collect and utilise property tax.
Data and a new global order – The Hindu
Essence - Editorial is demystifying the role of data in new global order. The shift of global power from the Atlantic to the Indo-Pacific raises strategic questions for India like Is the world divided because of an assertive China, Should India take sides or bide its time as a neutral contender to both China and the U.S.
China’s digital technology-led capitalism is moving fast to utilise the economic potential of data, pushing the recently launched e-yuan and shaking the dollar-based settlement for global trade. India’s goal is to become a $5-trillion economy by 2025.While the country is fast-tracking its digital rupee, the challenge is promoting engagement with major powers while retaining its data for innovation and competitive advantage.
Why you should read this article?
- To know about key factors responsible in shifting centre of gravity of global order from Atlantic to Indo-pacific region.
- To understand the interconnection between Mobile digital payment, their impact on society and the international system.
- To know about a comparative study of online transactions in India, China, and the United States, and its advantages.
- To comprehend the trade-offs of fluid ties between major powers, as well as the premise of New Delhi's Indo-Pacific strategy.
Link - https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/op-ed/data-and-a-new-global-order/article34379479.ece
Environment Management Initiative: A unique low-cost model in Andaman and Nicobar Islands
Situation before the initiative
- Campus of Dr. B.R. Ambedkar Institute of Technology faced Severe Waste Management problems like those universally felt across urban settlements which negatively affect the environment and public health.
- Issues like irregularity in collection of waste, No Waste segregation by the students, Littering and piling up of waste leading to growth of harmful bacteria which posed a health risk to all
- Environment management initiative was introduced in response to this scenario.
Environment Management Initiative
- B.R. Ambedkar Institute of Technology launched an environment management initiative which focussed on implementation of different waste management techniques like recycling of paper, effluent treatment, Solid waste management.
- It also focussed on rainwater harvesting within the campus with an aim to promote environmental conservation and sensitise the individual towards the needs of environment
Outcome
- Paper recycling plant produces 500 file folders every semester and upholds the Principle of Circular Economy: Reduce, Re-use and Recycle
- Solid waste management has helped reduce solid waste and converted biodegradable solid waste into organic manure
- Effluent treatment plant has made 50,000 litres of water available for horticulture and other activities
- Due to Rainwater harvesting nearly half of the institute campus’ water requirement is being met via this method.
- Nudge Effect: Clean and hygienic living environment inside the campus has encouraged other students to adopt practices that improve their surroundings for better living
Where can this case study be used?
Innovative example for low cost environment conservation model, As a case study to promote Circular Economy across various Institutions, Effective solid waste Management: Converting Waste to Wealth, Example of Nudge Effect.
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.