Wednesday, 28th December 2022
G 20: Opportunities and Concerns
In News
India has assumed the charge of the G20 presidency and the 18th summit will be held in India in 2023, after a tumultuous year in global geopolitics.
 What are the hard realities being faced by India while assuming the presidency of G-20?
What are the hard realities being faced by India while assuming the presidency of G-20?
- Russia-Ukraine war:
- The Russian invasion of Ukraine has impacted the global order and the world’s food and energy security.
- It is pushing the global economy towards a recession and the nuclear rhetoric by Russia has caused anxiety,
- China’s aggression
- The Ukraine war has also highlighted China’s aggression in the Indo-Pacific.
- India has been facing aggression on its border, in the form of skirmishes in Arunachal Pradesh, Galwan clashes, Doklam standoff
- Recent activities of constructing an island in the South China Sea are other examples of ingression.
- Ties with the West being tested:
- India is walking on a diplomatic tightrope while balancing its interest with Russia and the West.
- The absence of a full-time US ambassador, even after almost two years of the Biden administration, is perceived to have impacted communication.
- Engagement with Taliban:
- India reopened its operations in the Indian embassy in Kabul, less than a year after the Taliban’s recapture of Afghanistan.
- While India registered its apprehensions over the menace of extremism and the rights of minorities and women, it made a commitment of USD 80 million, over & above its USD 3 billion commitment in the last two decades.
- Pakistan turmoil: With the change of regime, rhetoric against India has lowered a bit, but there has been no headway in bilateral ties.
- Neighbourhood in crisis:
- The Sri Lankan economic and political crisis was a major challenge in the neighbourhood which India supported by providing humanitarian aid, fuel, medicines etc. in a short period of time.
- Delhi is also helped Sri Lanka in negotiating an economic debt relief package from the IMF.
- Engagement with Myanmar has continued in low-key visits and assistance to the military junta regime as Delhi has decided not to isolate the regime.
What are the opportunities for India amidst the challenges?
- Dealing with China: The Arunachal clashes have shown that Beijing is challenging the status quo, not just in eastern Ladakh but in other sectors along the 3,500-km border with India. Despite a direct conversation between leaders there has been no breakthrough. These disputes will have to be resolved through extended negotiations.
- Engaging with Russia: The border standoff with China has shown Russia’s importance in India’s strategic calculus. Russia has been a reliable supplier of defence equipment to India and has also acted as a negotiator between India and China. India’s effort will be to engage with both Russia and the West, and put its strategic defence and national security interests first.
- G20 as a global stage: The hosting of the G20 summit will be one of the biggest portrayals of India’s rise at the global stage and voice of the Global South. India will seek to put its priorities on the global forum.
- Mending Ties with the West: With India buying cheap oil and not joining the West against Russia, India will have to work to assuage the concerns of European and American partners. G20 preparations will give some opportunity to do that.
- Challenge in the neighbourhood: While India continues engaging constructively with Sri Lanka by providing it humanitarian, financial and political assistance, India tries to shun its big brother image from Maldives. India would also engage with Bangladesh and Nepal to build atmosphere or trust and reliability.
- Crucial year for Pakistan: The new civilian government and the Army chief in 2023 will shape Pakistan’s attitude towards India and provides opportunity to reengage with Pakistan, conditional to end on cross border terrorism.
Source:
https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-global/china-west-g20-opportunities-concerns-8347510/
CAG audit report on Assam’s NRC
In News: The Comptroller and Auditor-General of India (CAG) has recently released a report on the update exercise of the National Register of Citizens (NRC) in Assam.
- The compliance report has raised a number of concerns ranging from excessive spending and financial irregularities to dangers to the security of the NRC process that was conducted in Assam.
- It has also flagged serious irregularities, including “haphazard development” of software for the NRC exercise, and undue profits by the system integrator (SI) by violating the Minimum Wages Act.
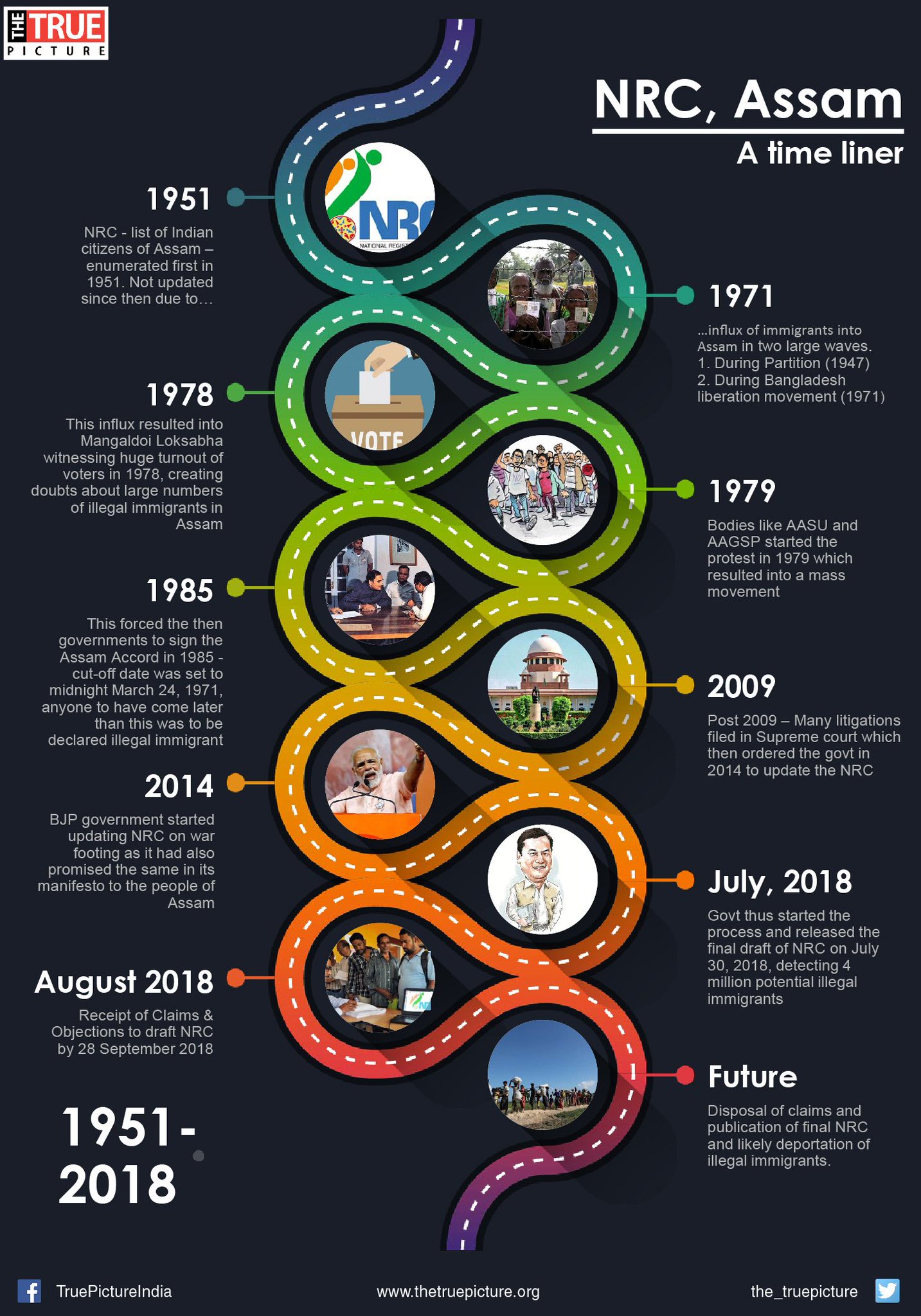
- Assam had faced an influx of people from Bangladesh since the early 20th century and is the only state having an NRC which was first prepared in 1951.
NRC:
- About: An NRC was first created in 1951 in Assam to identify those born in India and migrants from erstwhile East Pakistan, now Bangladesh.
- Background: The present exercise is in compliance with the Supreme Court’s directions in 2013 to the Centre and State to initiate an exercise in Assam to update the 1951 register.
- First list: The first draft was released in 2018 while the final list was published in 2019 which included Indian citizenship by being residents or descendants of people living in Assam before March 25, 1971 — the cut-off date for deportation of foreigners as per the Assam Accord of August 1985.
- Left-outs: As many as 06 lakh people out of 3.3 crore applicants have been excluded due to a lack of adequate documents to prove their citizenship.
- Criticism: Although the final list has been criticized for being “faulty”, it has been three years and yet the process is on pause as the Registrar General of India (RGI) is yet to notify the final list.
Major findings of CAG:
- Cost-escalation: At the time, the process to update the NRC was started in 2014 with a deadline for completion within a year, the project cost was pegged at ₹288.18 crore which increased five-fold to Rs 1,602.66 crore in 2022.
- Element of irregularities: The analysis of records has found irregularities in the utilisation of funds including “excess and inadmissible payment to vendors” especially the undue benefit to the system integrator beyond the 10% “reasonable profit margin”.
- Data threat: The CAG noted that against the secure and reliable software as required for the SC-directed exercise, multiple software utilities were added to the core software without following the due process of software development and vendor selection via tendering.
Recommendations:
- Penalty: The CAG has recommended fixing responsibility on erring authorities especially the State Coordinator of National Registration (SCNR) for the financial irregularities.
- Penalty: It has recommended penal action against the system integrator for violating the Minimum Wages Act.
- Accountability: The report has suggested fixing responsibility and action against the for the excess, irregular and inadmissible payments.
Source:
https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/what-is-the-cag-audit-report-on-assams-nrc/article66311741.ece#:~:text=A%20recent%20Comptroller%20and%20Auditor,undue%20profits%20worth%20crores%20amassed
India’s Foreign Policy - Edukemy Current Affairs
In news
As the year 2022 nears its end, India's foreign policy is under review in news, highlighting significant events.

Highlights of India's foreign policy 2022
- India's Non-alignment policy
- The war in Ukraine saw the government spell out its version of “non-alignment”, as it sought to keep a balance in the growing polarisation between the U.S. and the European Union on one side, and Russia on the other.
- Refusing to Vote on the Resolution
- In more than a dozen resolutions at the United Nation Security Council (UNSC), United Nations General Assembly (UNGA), International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), Human Rights Commission, and other multilateral platforms seeking to censure Russia for the invasion and humanitarian crisis, India chose to abstain.
- Returning to Free Trade Agreements (FTAs)
- In 2022, India signed trade agreements with the UAE and Australia, and hopes to progress on talks with the EU, Gulf Cooperation Council and Canada for others.
- India Neighbourhood relations
- India’s foreign policy was marked by economic assistance to Sri Lanka in the midst of its collapse.
- Foreign policy of India was marked by regional trade and energy agreements with Bangladesh, Bhutan, and Nepal that could see a South Asian energy grid emerge.
- The government kept channels open with repressive regimes like Afghanistan’s Taliban and the Myanmar Junta, opening a “technical mission” in Kabul and sending the foreign secretary to Myanmar to discuss border cooperation.
- However, ties with Pakistan remain flat, with a big showdown at the UN in December 2022 between the foreign ministers of the two nations.
- With regard to China, Despite a visit to Delhi by China’s Foreign Minister and disengagement at some stand-off points, tensions at the Line of Actual Control remained high.
Challenges to India's Foreign Policy
- Pakistan-China Strategic Nexus
- The most formidable threat India faces today is from the Pakistan-China strategic nexus that seeks to change the status quo at the contested borders and undermine India’s strategic security
- Balancing Big Power Relations
- India’s strategic autonomy precludes New Delhi to join any military alliance or strategic partnership that is inimical to another country or group of countries.
- For India to balance an assertive China, it has to rely on external balancing in the Indo-Pacific to overcome the security dilemmas posed by the Pakistan-China hybrid threats.
- Refugee Crisis
- The challenge for India is to balance the protection of human rights and national interests.
- Despite India not being a party to the 1951 Refugee Convention and its 1967 Protocol, India has been one of the largest recipients of refugees in the world.
Source
Explained | Have there been changes in India’s foreign policy?
India’s Efforts to beat Cervical Cancer
Why in news?
- Recently, the government is expected to roll out indigenously developed CERVAVAC vaccines for the prevention of cervical cancer to girls aged between 9 and 14 years through schools by mid-2023.
- The National Technical Advisory Group for Immunisation (NTAGI) had recommended the introduction of the Human Papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine in the Universal Immunisation Programme (UIP).
- The UIP is one of the largest public health programmes which offers free vaccines for at least 12 diseases, and has successfully eradicated diseases like polio and maternal and neonatal tetanus
|
About Cervical Cancer
|
About CERVAVAC
- It is India’s first indigenously developed quadrivalent human papillomavirus (qHPV) vaccine which will be effective against four strains of the virus: Type 6, Type 11, Type 16 and Type 18.
- A quadrivalent vaccine stimulates the immune system's responses against four different antigens, such as four distinct viruses or other organisms.
- CERVAVAC is based on VLP (Virus-Like Particles), similar to the Hepatitis B vaccination.
- The vaccine has received the approval of the Drugs Controller GeneraI of India and the government advisory panel NTAGI has also cleared it for use in the public health programme.
Significance:
- It would be beneficial if integrated into national HPV vaccination campaigns and provided at a lower cost than current immunisations because it has a substantial potential to eradicate cervical cancer.
- The vaccine is extremely effective only when it's administered before the first sexual intercourse.
- The girls who do not attend schools will be given the vaccines by community outreach and mobile health teams.
What are the challenges?
Substantial geographical and socioeconomic inequalities in cervical cancer globally:
- The study shows a clear gradient of increasing rates for countries with lower levels of human development.
Lack of Screening:
- Together with vaccination, screening programmes need to be conducted regularly to detect early signs of the disease that will allow time for treatment.
- A WHO paper in 2021 said fewer than 1 in 10 women had been screened for cervical cancer in the last five years.
Lack of Resources:
- The biggest obstacle will be assigning adequate funds and manpower to vaccinate the vast population of adolescent girls between the ages of 9 and 15, in order to ensure that they are protected from HPV early.
Lack of awareness:
- Contrary to Covid and the vaccination programme, there is very little awareness about cervical cancer.
- A huge awareness programme is needed, since this is a preventable disease.
What lies ahead?
- Once the vaccine is launched through the UIP, which is a well-oiled network in India, it should reach the maximum number of the targeted population.
- The surveillance systems and infrastructure used for COVID-19 vaccinations may also be customised to improve HPV vaccination, monitor national cervical screening programmes and improve health system capacity to deliver more efficient preventive services.
Content Source Link:
https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/health/how-is-india-trying-to-beat-cervical-cancer/article66311737.ece/amp/,
https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/health/centre-to-provide-cervical-cancer-vaccines-for-girls-aged-9-to-14/article66293235.ece
Cold Wave - Edukemy Current Affairs
- Context: According to IMD cold waves will abate over northwest India.
- A cold wave, also known as a cold snap or deep freeze, is a weather event involving the cooling of the air, or the invasion of very cold air, over a large area.

- Conditions:
-
- The minimum temperature ≤ 10° C in the plains and is 5 to 6.4° C below the normal temperature.
- For hilly regions, the minimum temperature ≤ 0° C and 5 ° C to 6.4 ° C below the normal.
- Factors responsible for Cold Wave in India
-
- Build up for ridge (relatively high atmospheric pressure) in the jet stream over Northwest Asia.
- Formation of surface high-pressure over north and central India.
- Movement of cold air masses in response to steering by upper-level winds.
- Triggering mechanisms like a strong westerly wave approaching northwest India to enhance winds for the transport of cold air southeastward.
- Extensive snow covers over Northwest Himalayas.
- La Nina can cause an increase in moisture over the Indian subcontinent resulting in abundant rain and snowfall.
|
India Meteorological Department
|
Source:
https://mausam.imd.gov.in/imd_latest/contents/pdf/pubbrochures/Cold%20Wave%20Warning%20Services.pdf
https://theprint.in/india/severe-cold-wave-conditions-persist-in-delhi/1285793/?amp
US Tax Credit Scheme for Electric Vehicles
- Context: The new tax credit, which lasts until 2032, is intended to make zero-emission vehicles affordable to more people.

- In 2023, Americans will qualify for a tax credit for buying an electric vehicle.
- The credit is designed to spur EV sales and reduce greenhouse emissions, and falls under the “Inflation Reduction Act”.
- A credit of up to $7,500 will be offered to people who buy certain new electric vehicles as well as some plug-in gas-electric hybrids and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles.
- For people who buy a used vehicle that runs on battery power, a $4,000 credit will be available.
- New EVs must be made in North America and forty per cent of battery minerals will have to come from North America or a country with a U.S. free trade agreement or be recycled in North America. (That threshold will eventually go to 80%.)
- The credits are part of roughly $370 billion in spending on clean energy — America’s largest investment to fight climate change — that was signed into law in August by President Joe Biden.
Sources:
https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-economics/what-is-us-tax-credit-scheme-for-electric-vehicles-8347268/
Image source:
https://auto.economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/passenger-vehicle/uv/mm-gears-up-for-new-ev-journey-by-recruiting-900-engineers-for-chennai-research-hub/92903301
Zero COVID Strategy - Edukemy Current Affairs
- Context: Recently there has been a significant surge in Omicron variant cases in China.
- Zero COVID strategy is a strategy that aims to drive down the number of Covid-19 cases by imposing strict lockdowns, closing borders and imposing travel bans and is also known as ‘dynamic zero’.

- Initially, countries adopted a mitigation approach by strengthening healthcare capacity to deal with possible flare-ups.
- But later, another strategy “the elimination approach” was applied by Australia, New Zealand, China, Hong Kong and several other Asia Pacific countries involving highly restrictive measures.
- The dynamic zero-COVID strategy essentially is aimed at stamping out outbreaks with mass testing and lockdowns to achieve zero cases.
- Zero-COVID was never only about the successful suppression of the virus; it was also meant to be living proof of a superior system of governance. Now, countries must relax restrictions, combined with expanding primary vaccination and booster coverage with effective vaccines, especially among the elderly and other vulnerable.
Source:
https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/everyday-explainers/explained-zero-covid-strategy-china-7994669/
https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/lead/handling-the-fallout-of-chinas-wilted-covid-strategy/article66311351.ece/amp/
Brain-eating amoeba - Edukemy Current Affairs
- Context: South Korea has recently reported its first case of infection from Naegleria fowlerior-a “brain-eating amoeba”.
- The brain-eating amoeba (Naegleria fowleri) destroys brain tissues and causes a dangerous infection called primary amebic meningoencephalitis.
- It was first discovered in Australia in 1965 and is commonly found in warm freshwater bodies.

- The amoeba destroys brain tissues and causes a dangerous infection known as primary amebic meningoencephalitis (PAM).
- SYMPTOMS:
- The first signs of PAM start showing within one to 12 days after the infection, and symptoms are headache, nausea and fever.
- In the later stages, one can suffer from a stiff neck, seizures, hallucinations, and even coma. Once the infection spreads rapidly it causes death within about five days.
- TREATMENT:
- As the infection is rare and progresses quickly, there are no effective treatments yet.
Sources:
https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-health/brain-eating-amoeba-kills-south-korean-man-what-is-this-infection-8346969/
Image Source:
https://zeenews.india.com/world/amid-covid-scare-south-korea-registers-first-death-linked-to-brain-eating-amoeba-2554453.html
Madan Mohan Malviya - Edukemy Current Affairs
Why in news? Recently, Nepal celebrated the 161st Birth Anniversary of Bharat Ratna Mahamana Madan Mohan Malviya in Kathmandu.
About:

- Madan Mohan Malaviya was born on 25th December 1861 in Allahabad.
- He took part in numerous activities like the freedom struggle movements, the economic and social development of the country, education, the development of the Hindi language
- He was given the title of ‘Mahamana’ by Mahatma Gandhi and the second President of India, Dr S. Radhakrishnan gave him the status of a ‘Karmayogi’.
- He became the Indian National Congress President four times.
- He started a Hindi weekly, Abhyudaya in 1907 and made it a daily in 1915 and also a Hindi monthly, Maryada in 1910. He started an English daily- Leader in 1909. Malaviya was the editor of Hindi weekly, the Hindustan and Indian Union.
https://newsonair.com/2022/12/25/nepal-celebrates-161st-birth-anniversary-of-bharat-ratna-mahamana-madan-mohan-malviya-in-kathmandu/
Dark patterns - Edukemy Current Affairs
Why in news? Some Internet-based firms have been tricking users into agreeing to certain conditions or clicking a few links.
 About:
About:
- Dark Patterns are unethical UI/UX (user interface/user experience) interactions, designed to mislead or trick users to make them do something they don't want to do.
- By using dark patterns, digital platforms take away a user’s right to full information about the services they are using and their control over their browsing experience.
- Examples of Dark Patterns include “baseless” countdowns for online deals, making cancellation buttons hard to see or click, making ads appear as news reports or celebrity endorsements etc.
https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/technology/dark-patterns-on-the-internet-how-companies-are-tricking-its-users/article66296690.ece/amp/Dark
Denotified, Nomadic and Semi-Nomadic Tribes
Why in news? Recently, The Parliamentary panel has asked the government to expedite the categorisation of Denotified, Nomadic and Semi-Nomadic Tribes under either the SC/ST/OBC lists.
 About:
About:
- These are communities that are the most vulnerable and deprived.
- DNTs (Denotified) are communities that were ‘notified’ as being ‘born criminals’ during the British regime under a series of laws starting with the Criminal Tribes Act of 1871.
- These Acts were repealed by the Independent Indian Government in l952, and these communities were "De-Notified".
- Nomadic and semi-nomadic communities are defined as those who move from one place to another rather than living in one place all the time.
- Historically, Nomadic Tribes and De-notified Tribes never had access to private land or home ownership.
https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/expedite-categorisation-of-denotified-nomadic-semi-nomadic-tribes-house-panel/article66307303.ece
Delhi High Court Grants Interim Injunction
Why in news? Recently, The Delhi High Court granted an interim injunction in favour of Hamdard Laboratories in its plea against Sadar Laboratories Private Limited for infringing its registered trademark.
 About:
About:
- A trademark is a sign capable of distinguishing the goods or services of one enterprise from those of other enterprises.
- Trademarks are protected by Intellectual Property Rights (IPR).
- In India, trademarks are governed by the Trademarks Act 1999, which was amended in 2010.
- It legally differentiates a product or service from all others of its kind and recognizes the source company's ownership of the brand.
https://indianexpress.com/article/cities/delhi/delhi-high-court-rooh-afza-trademark-infringement-case-8338129/
Green methanol - Edukemy Current Affairs
Why in news? Recently, NTPC has signed an MoU with Tecnimont Private Limited to explore the possibility to develop Green Methanol Production.
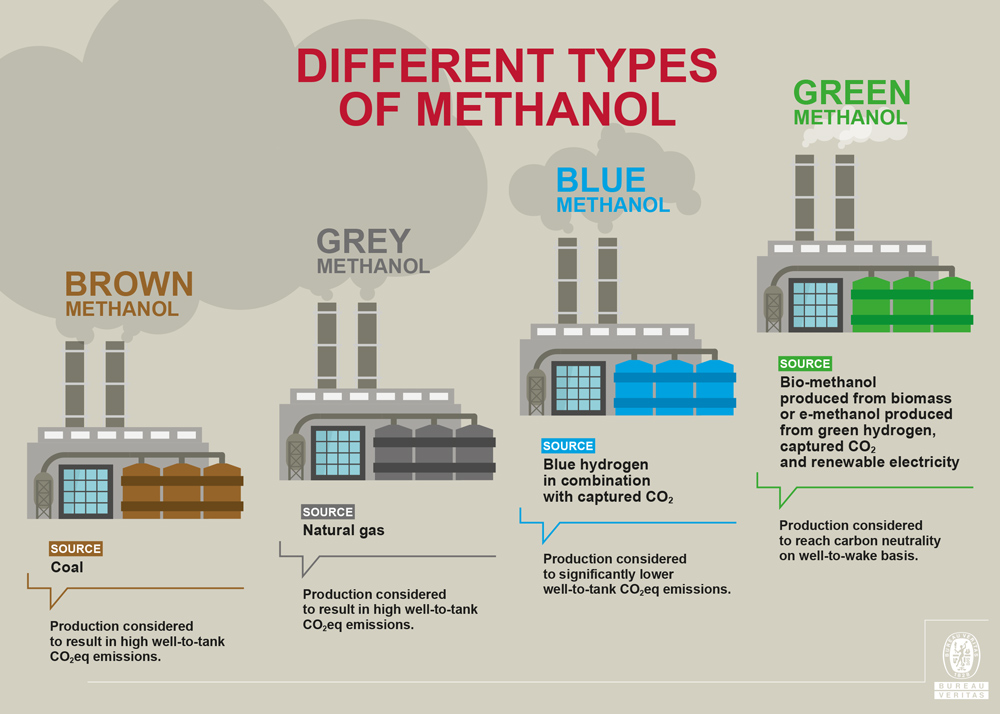
About:
- Green methanol is a low-carbon fuel that can be produced from either biomass gasification or renewable electricity and captured carbon dioxide (CO2).
- Applications: Green Methanol serves as a base material for the chemical industry, storing renewable electricity, and even as a transportation fuel.
- It is also considered as a substitute fuel for maritime fuel applications.
https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1886729
One nation one gas grid - Edukemy Current Affairs
Why in news? The national gas grid project has slowed down, with progress in parts of southwest and southeast India yet to pick up.

About:
- Currently, the Indian Power system for planning and operational purposes is divided into five regional grids.
- One Nation, One Gas Grid refers to the joining of several regional grids, creating a national grid, and supplying multiple stakeholders, including the central government, state governments, the public sector, and the commercial sector, with natural gas-produced energy.
- The Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board (PNGRB) is the organisation responsible for approving the construction of pipelines.
https://www.livemint.com/news/india/bottlenecks-slow-progress-of-one-nation-one-gas-grid/amp-11672073176136.html
Boost R&D Spending: India's Global Leadership Goal
Spending on Research and Development
Exam View: Research and Development, Spending related to research and development, Atal innovation mission, Global Innovation Index, Ministry of Science and Technology, Sustainable development goal agenda, Production Linked Incentive
In News: With the G20 presidency, India has an opportunity to set the global agenda and be in the limelight for at least a year. India needs to increase its spending on research and development to become a global leader. India needs not only technological development and brilliance in various sectors ranging from defence to agriculture to manufacturing, but it desperately needs innovations that can safeguard its basic environment — land, water, and air.
As per the latest figure, India spends only 0.66 per cent of its GDP on Research and Development. This is below the expenditure of countries like the US (2.8), China (2.1) and Israel (4.3). The allocations to various R&D organisations in the recently presented 2022-23 budget show continued stagnation.
Government expenditure, almost entirely the Central Government, is the driving force of R&D in India. This is in contrast to the advanced countries where the private sector is the driving force of R&D spending. Higher spending in R&D by the private sector will happen as the manufacturing sector expands in the country.
Research and Development role in the development of the nation

R&D Statistics

- PhDs in STEM: In comparison to China, there are less than half of Indian STEM Ph.D. students in the US. Fewer students have been enrolling for such degrees either due to lucrative career options after a master’s degree or rising work visa challenges. However, there has been an increase in the no. of PhD enrolments in India.
- Patents: According to WIPO, India is the seventh largest patent filing office in the world. However, India produces fewer patents per capita.
- According to UNESCO’s Institute for Statistics (UIS) latest report, the G20 nations accounted for 90.6 per cent of global GERD (current, PPP$) in 2018. Global R&D expenditure has reached a record high of about 2.2 trillion current PPP$ (2018), while Research Intensity (R&D expenditure as a percentage of GDP) has gradually increased from 1.43 per cent in 1998 to 1.72 per cent in 2018.
Improving the R&D ecosystem in India
- The growth in the R&D expenditure should be commensurate with the economy’s growth.
- It should be targeted to reach at least 2% of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) by 2022.
- To stimulate the private sector’s investment in R&D, a minimum percentage of turnover of the company may be invested in R&D by medium and large enterprises registered in India.
- To keep the industry enthused to invest in R&D, the weighted deduction provisions on R&D investment should continue.
- The states can partner with Centres to jointly fund research and innovation programmes through socially designed Central Sponsored Schemes (CSS).
- Creating a dedicated R&D Exports Hub with cross-cutting themes which are of national interest.
- National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, states: Research and innovation at higher education institutions in India is critical.
- NEP 2020 suggested the establishment of a National Research Foundation (NRF) to fund competitive, peer-reviewed grant proposals from universities, colleges, and institutions of higher learning.
Way Forward
- There is a need for greater participation of State Governments and the private sector in overall R&D spending in India, especially in application-oriented research and technology development.
- The Economic Survey 2021-22 suggested that the private sector needs to raise its share of spending from 37 per cent to 68 per cent of the total spending on R&D like the other high spenders.
- There is a need to encourage investor-led research. In this direction, the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB) has already been established.
- It is a promising start that needs to expand with more resources and creative governance structures.
- With increased allocations, joint R&D projects between public institutions and start-ups/industries must also be supported.
During India’s G20 presidency, the engagement group, Science20, has the theme of “Disruptive Science for Innovative and Sustainable Development” focusing on universal holistic health; cure and prevention of disease; clean energy for a greener future; and connecting science to society and culture. It will be interesting to see how India can leverage this for the shared prosperity of the world.
https://indianexpress.com/article/opinion/columns/india-g20-presidency-research-and-development-8343821/
Regenerative Agriculture - Edukemy Current Affairs
Background
Farmers in Madhya Pradesh adopted regenerative farming methods which reduced the need for frequent irrigation, and helped in conserving water and energy.

About Regenerative Farming:
- Regenerative agriculture is a holistic approach to agriculture that focuses on the interconnection of farming systems and the ecological system as a whole.
- The practices include the use of natural inputs, minimum-till, mulching, multi-cropping and sowing of diverse and native varieties. Natural inputs help improve soil structure and its organic carbon content while planting water-guzzling and water-efficient crops together or in alternating cycles reduces the frequency and intensity of irrigation.
- This farming practice goes a step ahead of sustainable agriculture and aspires not only to maintain the resources like soil and water but also to improve them.
- Zero-budget natural farming, organic farming like systematic rice intensification and climate-suitable agricultural practices help in reducing the input cost of agriculture.
- In India, the government is promoting regenerative agriculture in states like Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Sikkim and Gujara
What is the need for regenerative farming in India?
- Groundwater extraction: Green Revolution which pulled India from the brink of starvation and made it capable to feed its population has also made India the world’s biggest extractor of groundwater.
- Food security: 39 million hectares of land in the country under wheat, rice and maize has not shown improvement in the past decade posing risks to food security.
- Declining soil quality and productivity from the land due to increased use of chemicals and irrigation.
- High input cost of agriculture results in financial stress on farmers
Advantages of Regenerative Agriculture
- Water conservation is due to increased water-use efficiency.
- Better soil health and preservation of soil organic matter.
- Conservation of energy
- Sustainable agriculture ensures food security.
Source:
https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/agriculture/restore-by-use-regenerative-agriculture-can-help-save-water-here-is-how-86065
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.





