Wednesday, 28th April 2021
This day in History-World Day for Safety and Health at Work

The International Labour Organization (ILO) celebrates the World Day for Safety and Health at Work on the 28 April to promote the prevention of occupational accidents and diseases globally. In 2003, the ILO began to observe World Day for Safety and Health. Theme of the World Safety day 2021 is ‘Anticipate, prepare and respond to crises: Invest now in resilient occupational safety and health systems’.
ISRO’s data relay satellite
In News
The Indian Space Research Organisation will launch a data relay satellite that will help maintain contact with the Gaganyaan mission throughout after the launch
About the News
- The satellite will be launched before the final leg of the Gaganyaan mission, which will send astronauts to the Lower Earth Orbit (LEO).
- Rs 800-crore has been allotted to the project, which has been approved and work is going on.
- Satellites in orbit cannot pass along their information to the ground stations on Earth if the satellite does not have a clear view of the ground station. A data relay satellite serves as a way to pass along the satellite's information.
- The NASA, with a robust human space mission programme, also has its own data relay satellite.
- It’s Tracking and Data Relay Satellite allows it to have global coverage of all the satellites round the clock without having to build extra ground stations on Earth.

About the Indian Data Relay Satellite System (IDRSS)
- The IDRSS is planned to track and be constantly in touch with Indian satellites, in particular those in low-earth orbits which have limited coverage of earth.
- IDRSS satellites of the 2,000 kg class would be launched on the GSLV launcher to geostationary orbits around 36,000 km away. In such apparently fixed orbits, they would be covering the same area on earth.
- A satellite in GEO covers a third of the earth below and three of them can provide total coverage.
- During the launch of the human mission and also when the crew craft orbits earth from a distance of 400 km, at least one ground station must see and track But with available ground stations, that would not be the case.
- Without data relay satellites, ISRO would have to create a large number ground stations everywhere or hire them globally and yet the crewed spacecraft would not be visible all the time.
- While the S. is putting up its third-generation advanced fleet of TDRS (Tracking & Data Relay Satellites), Russia has its Satellite Data Relay Network and Europe is building its own European Data Relay System. China is into its second generation Tianlian II series.
Sources:
https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/new-satellites-will-help-gaganyaan-crew/article30496759.ece
US support to India for COVID fight
In News
Acknowledging India's assistance last year when the United States was facing a healthcare crisis caused by COVID-19 pandemic, the US President has said that the US is determined to help India as it faces an unprecedented COVID-19 crisis.
What kind of assistance India needs from the US?
- Short Term Assistance: In the short term, what India’s needs from abroad are two-fold: medicines and oxygen-management devices, including containers, concentrators and generators.
- Long Term Assistance: In the longer term, India expects some policy changes from the US particularly with respect to setting aside patent rights for pharmaceuticals produced in the US. It also needs US assistance in supporting the India-South Africa petition at the World Trade Organization for waiving all TRIPS (Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights) so vaccines can be manufactured generically for the next few years.
How is the US planning to help India fight Covid 19?
- Raw materials for vaccine: The United States administration stated that it will be delivering raw materials to the Serum Institute of India (SII) for the production of the Oxford-AstraZeneca Covishield vaccine.
- Medical oxygen: The administration is also working on oxygen generation systems, including larger-scale as well as smaller-scale units, which have been used in US field hospitals.
- Technical assistance: The US experts are also engaged in technical discussions with their Indian counterparts to ensure that the supplied equipment, oxygen concentrators, and ventilators, are compatible with the devices in India. It will be providing additional technical assistance and materials to strengthen vaccine communications between India and the US and support vaccine readiness at the national and sub-national levels.
- Therapeutics, personal protective equipment, and tests.
- Public Health assistance: The US will constitute a team of public health experts to work in close collaboration with the Indian health ministries and experts. The team will be engaged in a number of areas including laboratory services, surveillance, epidemiology, bioinformatics for sequencing and modeling of the disease.
|
What are the ways in which other countries have extended support for India? · UK: The United Kingdom has announced that it will ship over 600 pieces of vital medical equipment to help India fight COVID-19. This will include oxygen concentrators, non-invasive ventilators and manual ventilators. · Australia: Australia has announced that it will send oxygen, ventilators and personal protective equipment (PPE) kits to India as part of an immediate support package. · Saudi Arabia: Saudi Arabia is shipping 80 metric tonnes of liquid oxygen to India, in cooperation with the Adani group and British multinational company Linde. · Russia: Russia is planning to send COVID-19 assistance including oxygen concentrators, generators, and drugs needed to treat the disease. Russia had also announced that it would send 3,00,000-4,00,000 units of Remdesivir injection – an important drug that is currently in shortage across India. |
Sources
Supply Chain Resilience Initiative (SCRI)
In News
India, Japan and Australia formally launched the Supply Chain Resilience Initiative (SCRI) in a virtual trilateral ministerial meeting.
About SCRI
- SCRI aims to build resilient supply chains in the Indo-Pacific region, attain strong, sustainable, balanced and inclusive growth in the region.
- Possible policy measures may include: (i) supporting the enhanced utilization of digital technology; and (ii) supporting trade and investment diversification.
- It seeks to build upon the existing bilateral frameworks like the Asean-Japan Economic Resilience Action Plan and India-Japan Industrial Competitiveness Partnership and attract foreign direct investment in the region.

What does supply chain resilience mean?
- In the context of international trade, supply chain resilience is an approach that helps a country to ensure that it has diversified its supply risk across a clutch of supplying nations instead of being dependent on just one or a few.
- Unanticipated events, whether natural, such as volcanic eruptions, tsunamis, earthquakes or even a pandemic; or manmade, such as an armed conflict in a region, that disrupt supplies from a particular country or even intentional halts to trade, could adversely impact economic activity in the destination country.
Why has the need for Resilience in Supply Chain arisen?
- Reduce dependence on China: Availability of cheap skilled labor and well- developed supply chain network alongside an integrated infrastructure, which cannot be easily replicated elsewhere, has helped China solidify its position as a lucrative source of cheap and steady manufacturing for many large firms around the globe.
- Vulnerabilities of Global Supply Chain: The pandemic had revealed supply chain vulnerabilities globally and also the 2008 financial crisis exposed the vulnerability of Global Value Chains (GVCs) to external shocks.
- These examples have confirmed that global trade, which involves multiple production stages, is more prone to economic shocks, affects firms operating in final goods and also creates fluctuations in the supply and demand of intermediate goods via forward and backward linkages in GVCs.
- Demand for diversification: There is now a resounding demand in the global economy for the diversification of supply chains. Countries which can fill the supply vacuum are Vietnam, Cambodia and India.
- Countries are aiming to bring all or part of their production activities back home or close to home.
Understanding the SCRI Matrix
- Japan’s interest
- Japan’s need to diversify its trade base: To reduce its dependence on China, Japan has incentivised its companies to move their manufacturing out of China.
- In addition, the U.S.-China trade tensions have caused alarm in Japanese trade circles.
- Australia’s Interests
- Australia, Japan and India are already part of another informal grouping, the Quad, which includes the U.S.
- China has been Australia’s largest trading partner and that it counts for 32.6% of Australia’s exports. But relations between the two have been deteriorating, due to factors like import bans, tariffs and blame of racism in Australia.
- India’s stand
- Following the border tensions between India and China, need for alternative supply chains has arisen in India.
- China’s share of imports into India in 2018 stood at 14.5% and India is fully dependent on China in areas such as Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients for medicines. In electronics, China accounts for 45% of India’s imports. But these supplies have been impacted by supply chain issues arising out of the pandemic.
What can be challenges to the SCRI?
- China’s strong presence in Global Economy: China is deeply integrated into the global manufacturing supply chains to the extent that any diversification of supply networks will not reduce its overall significance in GVCs. Although tech giants such as Apple, Microsoft, and Google are considering shifting a portion of their production to Southeast Asian countries, their dependence on China for raw materials and equipment will remain.
- Differences in economic objectives of the three countries: Australia and Japan are high income countries, India is a lower-middle income country. This translates into very distinct economic policy preferences, which have been a major liability when it comes to trade cooperation.
- India’s perceived protectionist policies: Australia and Japan are not only committed trade liberalisers, but also seek agreements such as investment, intellectual property and digital commerce. It is claimed by few experts that India maintains far higher levels of trade protection, and is unwilling to engage in liberalising initiatives that clash with its trade policy priorities.
- India’s infrastructure gaps: While India appears an attractive option for potential investors both as a market and as a manufacturing base, trade experts point to the need for India to accelerate progress in ease of doing business and in skill building. Tax incentives, as the one recently announced to compete with the likes of Vietnam and the Philippines for investments in manufacturing, alone may not suffice.
Conclusion
Initiatives like SCRI by like-minded partners may help in setting up alternatives to these nations’ economic dependence on China, as each country in the Austria-Japan-India trilateral recognizes that alone, they are no match for China’s economic power. Alone, each is much more vulnerable because of their dependence. But together, they might be able to find some solutions. Whether this will work is yet to be seen, but a beginning is being made.
Sources:
Image of the Day- Thanatosis

A dice snake pretends to be dead next to a creek. Snakes, invertebrates, birds, and more have evolved several reasons for feigning death. Scientifically known as thanatosis, or tonic immobility, playing dead occurs across the animal kingdom, from birds to mammals to fish. Many insects feign death after a predator has grabbed them, a phenomenon called post-contact immobility. Males in nursery web spider feign death to attract a mate.
PowerGrid Infrastructure Investment Trust (PGInvIT)
- Context: The Power Grid Corporation of India (PGCIL) haslaunched its Infrastructure Investment Trust (InvIT).
- Infrastructure Investment Trust (InvIT) is a collective investment scheme similar to a mutual fund, that enables direct investmentof money from individual and institutional investors in infrastructure projects to earn a small portion of the income as return.
- InvITs are modified version of REITs (real estate investment trusts)designed to suit the specific investments in operational infrastructure assets like roads, power transmission lines, gas pipelines, etc.
- Units of InvITscan be listed and traded on a stock exchange, providing them liquidity. They are regulated by the SEBI.
- PowerGrid Infrastructure Investment Trust (PGInvIT): This is the first time a state-owned entity (PGCIL) is monetizing its infrastructure assets through the InvIT route. (The InvIT route was proposed by the Centre as an alternative fundraising routefor state-run companies to manage funding requirements without having to depend on government support).
Primary source: https://www.business-standard.com/article/companies/power-grid-launches-pginvit-could-offer-18-more-assets-in-future-121042600522_1.html
Chandler Good Government Index (CGGI)
- Context: India ranks 49thin the Chandler Good Government Index.
- Released by the Chandler Institute of Governance- a private nonprofit organization headquartered in Singapore, the index classifies 104 countries in terms of government capabilities and outcomes.
- It aims to support government leaders and public officers worldwide in nation buildingand strengthening public institutional capacity through training, research, and advisory work.
- Sri Lanka ranked 74th, Pakistan 90thand Nepal 92nd.
- Finlandhas topped the list.

Primary source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/india-ranked-49th-in-cggi/article34417911.ece
Trachoma - Edukemy Current Affairs
- Context: Gambia has become the second African country to eliminate Trachoma after Ghana.
- Caused by an obligate intracellular bacterium called Chlamydia trachomatis, trachoma is the leading infectious cause of blindness worldwide.
- The infection is transmitted by direct or indirect transfer of eye and nose discharges of infected people, especially young children by particular species of flies.
- Transmission of the disease happens due to inadequate hygiene, crowded households, inadequate access to water and sanitation.
- WHO-recommended SAFE strategy which consists of: Surgery to treat the blinding stage, Antibiotics to clear infection, Facial cleanliness; and Environmental improvement was adopted in 1993 for elimination of the disease. WHO has set a renewed target for global elimination of Trachoma by 2030.
- India eliminated cases of active trachoma in 2017.
Primary source: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/trachoma
Saudi Green Initiative and Middle East Green Initiative
- Context: To combat climate change, Saudi Arabia has launched the Saudi Green Initiative and Middle East Green Initiative.
- The Saudi Green Initiative aims to raise the vegetation cover, reduce carbon emissions, combat pollution and land degradation, and preserve marine life.

Primary Source: https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/lead/marking-the-beginning-of-a-green-era/article34424848.ece
To implement developmental agenda, civil servants must have stake, independence - IE
Essence - Prime Minister Modi, replying to the debate on the motion of thanks to the President’s address to the Lok Sabha, made a strong case for the privatisation of PSUs. The PM’s goal of making India a $5-trillion economy needs a coherent structural transformation agenda and extraordinary implementation capacity. In this context, the article analyses the challenges that lies ahead and suggest steps to overcome those.
Why you should read this article?
- Identify challenges such as lack of all no all-encompassing development agenda, limitations of market mechanisms, and the prevalent corruption-transfer mechanism which undermine the autonomy of bureaucracy.
- Understand the steps required to tackle the challenges such as corporate coherence and autonomy of action within the bureaucracy and develop ability to fight the increasing tendency to grab public resources and replace it by a shared developmental agenda acceptable to both business and landed elites.
Link - https://indianexpress.com/article/opinion/columns/civil-services-independence-bureaucracy-7288907/
Reorienting India’s global value chains post COVID-19 - ORF
Essence- India needs to upgrade its trade policy and existing manufacturing global value chains (GVCs) with growing digitalization and amid the ongoing pandemic. India has seen sharp decline in merchandise export growth and also its comparative advantage in its traditional exports has been shrinking. India falls behind other developing countries in terms of its participation rate in GVCs and has very few GVCs of its own with Indian firms as the lead potentially due to skills shortages, lack of access to finance and customs procedures.
The article suggests digitalisation as a new pathway for export diversification where a positive relationship between IT investment and export performance is seen in the Indian pharmaceutical industry. But currently, India lags behind many developing countries in the digitalisation of manufacturing exports; the value added by digital services in India’s exports is largely concentrated in the computer, programming and telecommunication services sectors. To face these twin challenges, Fourth Industrial Revolution and COVID-19 pandemic, India must reorient its trade policy to achieve V-shaped recovery and build resilience.
Why you should read this article?
- To understand why India needs to upgrade its trade policy and existing GVCs.
- To understand why export diversification is significant.
- To know why linking into GVCs is not enough and understand why India’s participation rate in GVCs is low.
- To understand what India should do to achieve V-shaped recovery and build resilience.
Link - https://www.orfonline.org/expert-speak/reorienting-india-global-value-chains-post-covid19/
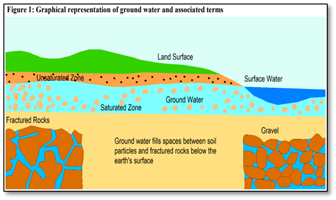
Mazhapolima: Ensuring water security through participatory well recharge in Kerala
Present Situation in Kerala
- Kerala has a unique water resources management problem.
- The state has a large number of perennial springs, streams, rivers. It receives an average of 3,000 mm of rainfall in a year.
- Paradoxically, the per capita availability of water in Kerala is substantially lower than the national average.
- This is a result of accelerated surface water runoff to sea. Most of the open wells run dry in summer. There is also the problem of groundwater exploitation.
- For better water management, Mazhapolima has been proposed.
About Mazhapolima
- It is a participatory climate change adaptation initiative which was launched by the Government of Kerala in Thrissur district in 2008.
- It aims to alleviate the problem of water scarcity by harvesting rainwater from rooftops and feeding it into open dug wells, which traditionally form the water security mechanisms of the state.
- Active participation of Gram Panchayats, private agencies and beneficiaries led to the installation of over 10,300 Mazhapolima units with government subsidy.
Outcome
- Better participation and strong public interest in water management in Kerala
- Improvement in water quality due to decrease in in pH levels in the water collected from the recharged area
- Improvement in the ground water table
- Better tackling of drought due to recharge of water
Where can we use this case study?
Example to promote conservation of water at local level, adaptative efforts towards climate change, innovative steps for management of agriculture, land and water.
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.