Monday, 12th April 2021
India-Seychelles virtual meet
In News
A high-level virtual meet between the Prime Minister of India and the President of Seychelles was held recently. The Indian PM emphasized during the meeting that India and Seychelles share a strong and vital partnership in the Indian ocean neighbourhood.
Key highlights of the meeting
- Seychelles integral to India’s vision of SAGAR
- Joint inauguration of new projects: New Magistrates Court Building in Seychelles, a new naval ship, one MW solar power plant, 10 HICDPs (High Impact Community Development Projects).
- Fast Patrol Vehicle: It will be the fourth ship to be gifted by India to Seychelles. The other vessels gifted by India include PS Topaz (2005), PS Constant (2014), Patrol Boat Hermes (2016).
- Climate Change: It poses a special threat to island countries and India is assisting Seychelles in this respect by taking up sustainable projects like those related to solar power.
- Covid-19 vaccines: It was the first African country to receive 50,000 doses of Covid vaccine doses from India.
Significance of Seychelles for India
- Integral to India’s Indo-Pacific vision: The African littorals are an important stakeholder in India’s Indo-Pacific vision. Seychelles’ importance is high for India as it strives to tackle piracy in the Western Indian Ocean as well as battle terrorist threats from the sea.
- Indian Diaspora in Seychelles: The number of Persons of Indian Origin with Seychelles citizenship is estimated to be around 11% of the population of the country. Indians dominate the trading and construction sector in the island country. A cultural exchange programme was signed between the two countries in 2018.
- Maritime Security: The national maritime blueprint of India, Ensuring Secure Seas: Indian Maritime Security Strategy (2015), specifically notes Seychelles as a ‘primary area’ of interest that is in need of further engagement and collaborative efforts on part of both the governments. India gifted and installed six coastal surveillance radar systems in Seychelles in 2015 enabling better coastal security for Seychelles. The Seychelles government has leased the Assumption Island to the Indian Navy to build an overseas base of operations there.
- Competition with China: China has engaged in boosting trade and has undertaken several infrastructure projects in the nation, including the construction of its parliament building. Indian has also committed to infrastructure projects worth $91 million for Seychelles. In recognition of the strategic significance of Seychelles, it has been on priority during high level visits by the Prime Minister and the External Affairs Minister.
- Non-traditional security threats: Seychelles is important for India to deal with non-traditional security threats like illegal fishing and drug trafficking.
Way Ahead
- Boosting trade and investment: The bilateral trade and commerce with Seychelles is rather modest. There is a need to address issues that hamper bilateral trade like the lack of profitable shipping routes between the two countries, the lesser frequency of direct flights among others.
- Tourism: India could also capitalize on the tourism industry in the Seychelles by establishing India-owned and managed tourist businesses.
- Blue Economy: Focus on the blue economy along with investments in maritime resources which have been an integral part of the Indian Ocean Rim Association agenda along with increased information sharing mechanism can help to boost cooperation between the two countries.
- Strategic Zones of Convergence: India can also come up with strategic zones of convergences through the identification of potential growth structures like Seychelles-India- Maldives- Madagascar- as smaller zones- within the IORA for better development and cooperation. Given India’s potential in maritime capability, these small frameworks can be created for immediate solution to problems like natural disasters and humanitarian measures.
Sources
https://www.mea.gov.in/Portal/ForeignRelation/sey_dec.pdf
https://thediplomat.com/2020/12/india-and-the-seychelles-economics-first-defense-later/
Central government notifies Copyright (Amendment) Rules, 2021
In News
The Central government has notified the Copyright (Amendment) Rules, 2021 which amends the Copyright Rules, 2013 with the objective of bringing accountability and transparency.
What is Copyright?
- Copyright is a form of Intellectual Property protection granted under Indian Law to the creators of original works of authorship such as:
- Literary works (including computer programs)
- Dramatic, Musical, or artistic works.
- Cinematographic films and sound recordings
- These rights include the right to reproduce the work, to prepare derivative works, to distribute copies, and to perform and display the work publicly.
Copyrights Regime in India
- In India, the copyright regime is governed by The Copyright Act, 1957 and The Copyright Act, 2013.
- India is a member of the Berne Conventions and Universal Copyright Convention.
- The Government of India has also passed the International Copyright Order, 1999, according to which, any work first published in any country that is a member of any of the above conventions is granted the same treatment as if it was first published in India.
- India is a signatory to TRIPS (Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights)
Copyright (Amendment) Rules, 2021
- The amendments have been introduced with the objective of bringing the existing rules in parity with other relevant legislations.
- It aims to ensure smooth and flawless compliance in the light of the technological advancement in digital era by adopting electronic means as primary mode of communication and working in the Copyright Office. Mandatory requirement of publication in the Official Gazette has been done away with.
- It aims to deal with the undistributed royalty amounts and use of electronic and traceable payment methods during collection and distribution of royalties.
- The amendments have harmonized the Copyright Rules with the provisions of Finance Act, 2017 whereby the Copyright Board has been merged with Appellate Board.
- The time limit for the Central Government to respond to an application made before it for registration as a copyright society is extended to one hundred and eighty days, so that the application can be more comprehensively examined.
Primary source: https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1710417
Data Scraping
In News
Massive data breaches at two tech giants, Facebook and LinkedIn, took place last week.
About the News
- Facebook and Linkedin data: Facebook data of around 533 million users had leaked online, which includes the data of six million users from India.
- Data Scraping: In both the cases, the two companies claimed that there was no hacking of the system and no data breach. Rather, the data has been obtained by scraping it from respective platforms.
- Consequences: When a data breach like this happens, it leaves not just the company whose data is leaked vulnerable, but some of this data can be used to hack or access information and even money of individuals from other organisations.
- The massive database of over 500 million Facebook users was first posted on the dark web, a haven for illegal activities and stolen information ranging from the sale of data to hacking tools to drugs and weaponry.
What is Data Scraping?
- Data scraping refers to a technique in which a computer program extracts data from the output generated from another program. Data scraping is commonly manifested in web scraping, the process of using an application to extract valuable information from a website.
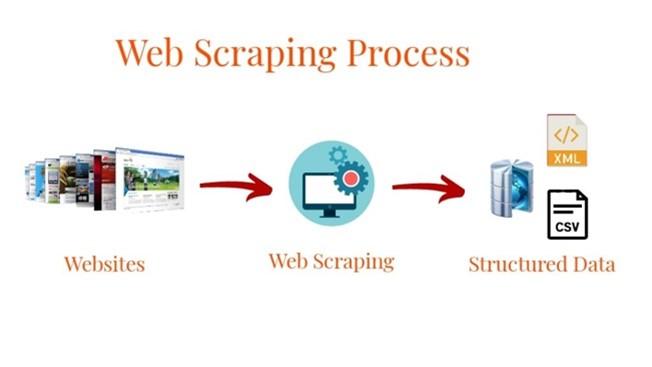
- Contact scraping, which is what has happened at LinkedIn, is executed when the perpetrator 'scrapes' locations like an online employee directory. By doing so, a scraper is able to aggregate contact details from bulk mailing lists.
- Use in non-malicious work: Data scraping tools are also used by marketing companies, content creators, and UI designers in their line of work.
- It can facilitate processes such as web content creation, business intelligence, finding sales leads, conducting marketing or advertising research, and developing personalization.
Sources:
https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/facebook-data-leak-explained-7268515/
Non-uniformity of Himalayas
In News
Scientists have found that the Himalayas are not uniform, which could result in significantly large earthquake events.
Findings of the Study and Reasons
- Area under the study: The study area covered the major seismo-tectonic units which are the Garhwal-Himalayan region, the Kangra-Chamba sector, and the Kinnaur segment of the NW Himalayan region.
- These lithospheric units are reported to be extremely heterogeneous and structurally complex due to the ongoing Indo-Eurasian collision.
- The Himalaya-Tibet orogen is a result of a collision between the Indian and Eurasian plates that has been ongoing since 50 Million years.
- Anisotropy: As per the findings, the Himalayas assume different physical and mechanical properties in different directions, a property present in crystals called anisotropy, which could result in significantly large earthquake events in the Himalayas.
- The major contribution to this anisotropy is the strain induced by the Indo- Eurasia collision and the asthenospheric
- The study suggests that the degree of deformation due to the collision is found to be larger in the crust than in the upper mantle.
- Seismic anisotropy is commonly defined as the direction- dependent nature of the propagation velocities of seismic waves. Seismic anisotropy is a key measurement for imaging past and present deformation in the Earth's interior.
- Need for deep understanding: These seismic activities manifest large-scale subsurface deformation and weak zones, underlining the need for deeper insights into the ongoing deformation beneath these tectonically unstable zones.
- New Perspectives: The lack of homogenous physical and mechanical properties of the Himalayas can help explore new perspectives about deformations taking place at the Himalaya-Tibet crustal belt involved in the formation of the Himalayan Mountains.
Vulnerability of the Himalayas
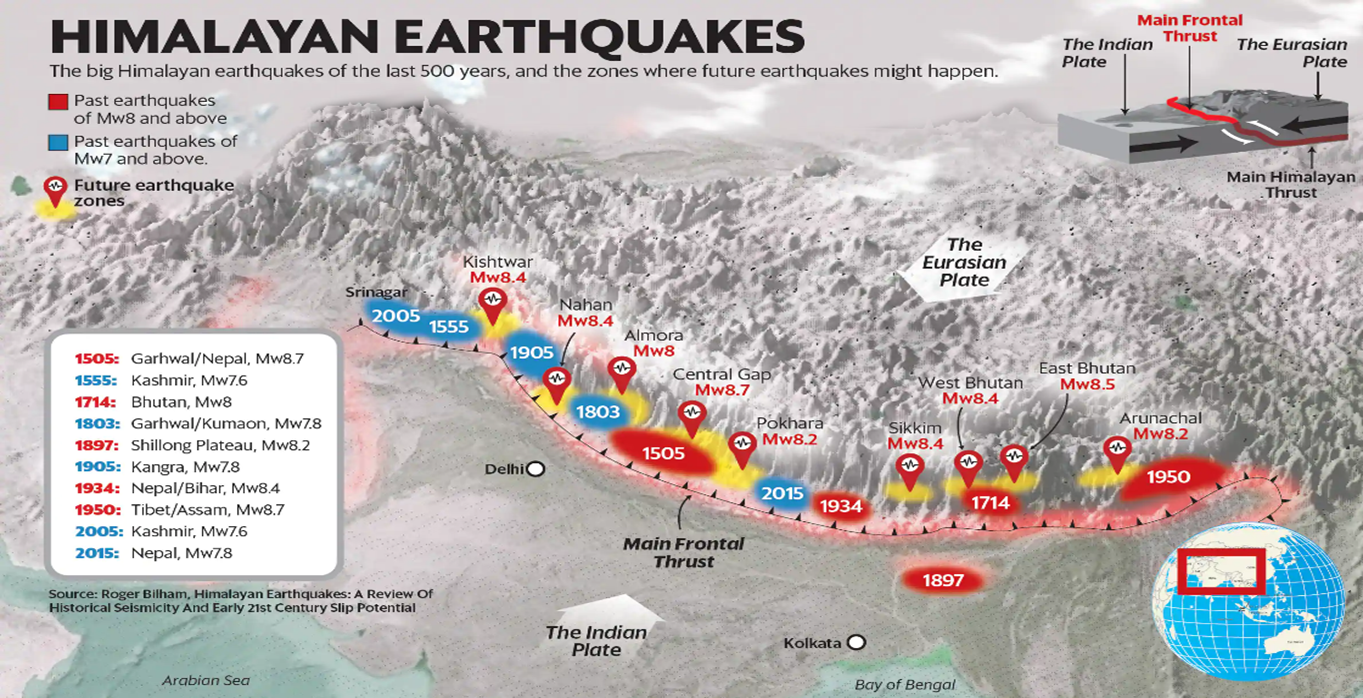
- History of major earthquakes: The study assumes significance because the area covering Garhwal and Himachal Pradesh has been hit by four destructive 'moderate to great' earthquakes since the beginning of the 20th century, which are the Kangra earthquake of 1905, the Kinnaur earthquake of 1975, the Uttarkashi earthquake of 1991, and the Chamoli earthquake of 1999.
- The recent events of glacier burst near Raini village above Rishiganga river in Uttarakhand led to huge human tragedy and the earthquake on the Sikkim-Nepal border, wherein tremors were felt in north Bengal, Assam, and Bihar.
- Strain Release: The 2015 Nepal earthquake was caused by the ongoing tectonic collision of the Indian plate with the Eurasian plate. The three main fault lines in the Himalaya gather massive strain due to the tectonic movements.
- Earthquakes are the most effective way of releasing this strain and stress. It would take the really big, infrequent earthquakes of Mw8 and above to relieve the strain that has built up.
- As per a study, there haven’t been enough big earthquakes (Mw8 and above) to ease the accumulated strain in large sections of the Himalayan arc.
- In 100 years, the accumulated strain would need an Mw8.6 earthquake for release. In 350 years, a Mw9 earthquake would be required.
- The Inevitable major earthquake: Seismologists are increasingly certain that major earthquakes in the Himalayas over the past 100 years have only loaded greater strain where they occurred, making a big earthquake even more “necessary” to relieve the elastic strain built up in the faults
- Similarity with Aleutian subduction zone: A study notes that the sequence of future Himalayan earthquakes could be similar to the great earthquakes that occurred in the twentieth century along the Aleutian subduction zone, which extends from the Gulf of Alaska to Kamchatka in Russian Far East.
India’ vulnerability
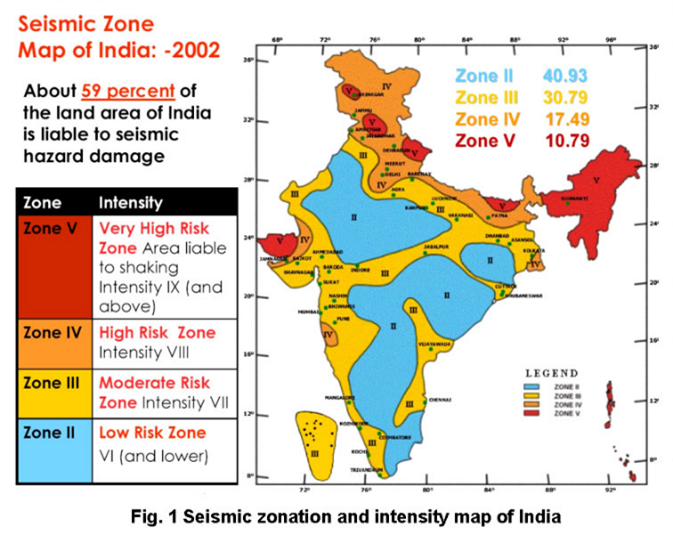
- Vulnerability: The National Disaster Management Authority’s (NDMA) earthquake hazard vulnerability profile estimates that 6% of the country lies in Zones III, IV and V, which means that it is prone to earthquakes of moderate to very high intensity.
- Survey: India plans to conduct airborne radar surveys to estimate the thickness of Himalayan glaciers, with a pilot study to be conducted in Lahaul-Spiti basin of Himachal Pradesh. Once the pilot project is done, similar studies will be conducted in Indus, Ganga and Brahmaputra sub-basins.
- Collaborative effort: As the Indian mega cities are likely to be rattled by a major earthquake in the near future, there is need for the academics, the construction industry and the government all work together to raise awareness of earthquake risk and to develop, uphold and enforce construction standards.
Image of the Day- ‘Cira-03’
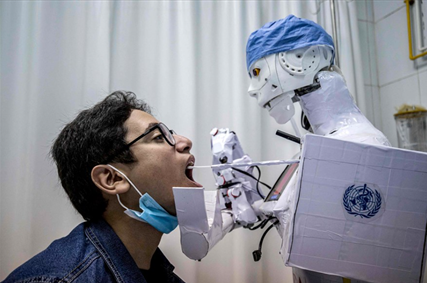
A remote-controlled robot named ‘Cira-03’ is being used to extract throat swab sample at a hospital in Egypt. It can also take blood samples, perform X-rays, and display results on a screen attached to its chest. Automation in the hospital and laboratory supply chain process can help limit exposure to infection and prevent the transmission of Covid-19. Notably, frontline health care workers are amongst the most vulnerable section in the process of handling Covid pandemic.
E9 initiative
- Origin: The E-9 Initiative was established at the Education for All Summit in New Delhi in
- Aim: The initiative aims to accelerate recovery and advance the SDG4 agenda by driving rapid change in education systems by providing support to teachers, investment in skills and narrowing of the digital divide.
- Member Countries: Spearheaded by the UN, the E9 countries are Bangladesh, Brazil, China, Egypt, India, Indonesia, Mexico, Nigeria and Pakistan.
- Significance: The E9 initiative is significant for the countries in the group because these countries constitute over two-thirds of the world’s illiterate adults and over half of the world’s out-of-school children reside in these countries, with similar acute education challenges to overcome.
- Recently, Minister of State for Education attended the meeting of Education Ministers of E9 countries.
- Theme: ‘E9 initiative: Scaling up digital learning to accelerate progress towards Sustainable Development Goal 4’.
https://en.unesco.org/education2030-sdg4/coordination/e9-partnership
https://in.one.un.org/page/sustainable-development-goals/quality-education-in-india-sdg-4/
SARTHAQ
- Context- The Department of School Education and Literacy has developed an indicative and suggestive Implementation Plan for School Education called SARTHAQ- Students’ and Teachers’ Holistic Advancement through Quality Education.
- The plan is being implemented to meet the following aims of the New Education Policy 2020:
- curriculum reforms for school education and early childhood care.
- improvement of the enrollment ratio of children at all levels and a reduction in dropouts and out of school children.
- access to quality ECCE (Early Childhood Care and Education) and Universal Acquisition of Foundational Literacy and numeracy by Grade 3.
- implement vocational education, sports, arts, knowledge of India, 21st century skills, values of citizenship, awareness of environmental conservation in the curriculum.
- improve the quality of Teacher Education Program and experimental learning.
- integration of technology in educational planning and governance.
Primary Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetailm.aspx?PRID=1710438
International Monetary and Financial Committee (IMFC)
- Context – IMFC held its 43rd Meeting
- The IMFC advises and reports to the IMF Board of Governors on the supervision and management of the international monetary and financial system.
- Although the IMFC has no formal decision-making powers, in practice, it has become a key instrument for providing strategic direction to the work and policies of IMF.
- The IMFC operates by consensus, including on the selection of its chairman.
Primary Source: https://www.imf.org/en/About/Factsheets/A-Guide-to-Committees-Groups-and-Clubs#IC
Satkosia Tiger Reserve (STR)
- Context- Following the closure of the Tiger relocation project, the lone tigress in the STR may not get a companion.
- Non-availability of sufficient prey and the existence of villages in STR are the reasons behind failure of the country’s first interstate translocation tiger project.
- Satkosia Tiger Reserve, Bhubaneswar, comprises of two adjoining Sanctuaries of central Odisha named as Satkosia Gorge Sanctuary and Baisipalli Sanctuary.
- It owes its name to the narrow stretch of River Mahanadie. “Sat-Kosh''or seven miles long.
- The Satkosia Gorge is a unique feature in geomorphology of Indiabecause here Mahanadi cuts right across the Eastern Ghats and forms a magnificent
- The area supports deciduous forest and moist peninsular Sal forest.
- Fauna:It is known for Gharials, Mugger crocodile and rare freshwater turtles like Chitra indica and Indian softshell turtle. It is also home to tigers, leopards, elephants, herbivores, etc.
Primary source: http://www.satkosia.org/
Secondary source: https://www.wildlife.odisha.gov.in/WebPortal/PA_Satkosia.aspx
B.1.617: Indian Double Mutant Strain
- India’s double mutant coronavirus strain has been named 1.617 (formal scientific classification).
- Double mutation happens when two mutated variants of the virus come together to form a third variant.
- The one reported in India is a combination of E484Q and L452R (linked to increased infectivity)
- 1.617 was first detected in Indiain December, 2020.
- Nearly 70% of the genome sequenceswith the mutations characterizing B.1.617 are from India.
- 1.617 is yet to be classified as ‘Variant of Concern’.
- These are variants for which there is evidence of an increase in transmissibility, more severe disease, significant reduction in neutralization by antibodies generated during previous infection or vaccination, reduced effectiveness of treatments or vaccines, or diagnostic detection failures.
Primary source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/indian-double-mutant-strain-named-b1617/article34274663.ece
Why the Personal Data Protection Bill matters – The Hindu
Essence - The recent alleged data breach at MobiKwik could stand to be India’s biggest breach with the data of 9.9 crore users at risk. Robust data protection regimes are necessary to prevent such events and protect users’ interests. Unfortunately, the existing data protection regime in India does not meet this standard. In this context, this article analyses how can the Personal Data Protection Bill, 2019, protect users’ interests in the digital economy.
Why you should read this article?
- Understand the issues and short comings with the current data protection regime.
- Know about the major changes proposed in the Personal Data Protection Bill, 2019, which seeks to provide effective protection to users and their personal data.
- Briefly identify the provisions in the Bill which can undermine the regime’s effectiveness and contradict the objectives of the Bill.
Through a backchannel, steps forward – The Hindu
Essence - Editorial is presenting analysis on the existence & importance of back channel diplomacy between India and Pakistan. As the name suggests, working of these channels remain away from public view. They have operated in the worst of times, including wars, terror strikes and military action, and their existence brought to light only years later. After the Pathankot attack in 2016, the Doval-Janjua backchannel worked to ease tensions and facilitate the visit of a Pakistani investigative team to the scene of the terrorist attack. “Terror and talks cannot go together but talks on terror can definitely go ahead,” the MEA spokesperson had explained.
Pakistan’s dire economic condition and the mounting pressure from the Financial Action Task Force to shut down all terrorist safe havens or face severe sanctions is clearly one imperative for Islamabad’s willingness to engage via the backchannel even after India’s decision on Jammu and Kashmir. For India, the stand-off with the People’s Liberation Army at the Line of Actual Control in Ladakh has made the possibility of a two-front war more real, and fuels the push to reduce tensions with Pakistan.
Why you should read this article?
- To understand the utility of back channel diplomacy in India Pakistan landscape.
- To know about interesting incidents related to these channels in past.
- To understand the reasons which make continuous back channel work more important in present scenario for India & Pakistan.
Link - https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/lead/through-a-backchannel-steps-forward/article34296888.ece
Valuation of water: Best Practice to manage water crises.
Present Situation
- As per World Economic Forum, 1 in 10 people are still living without clean water leading to sickness, poverty, endless drudgery of collecting water .
- Women and girls around the world collectively spend around 200 million hours/year walking to fetch water.
- Less that 1% of total global climate investment goes to protecting water services for poor communities.
- This is because of inadequate valuation of water and lack of incentive to invest in water needs.
Valuation of Water
- It was launched during World Economic Forum in 2019 with an aim to put the UN Valuing Water Principles into practice
- It conducts valuation not only in raw economic terms but also in its competing uses like economic, cultural, environmental uses to reflect multiplicity of views in decision-making.
Blended Finance Initiative
- Valuation of Water when backed by Blended Finance can become a game changer to manage water.
- Blended Finance gives practical life to the concept of Valuation of Water.
- It brings together public and private sector to ensure that no community is left behind, governments take on up-front costs, while private sector invests in funding & technology
- Resilient Water Accelerator demonstrate how this blend could practically work. It showcases how finance is fast tracked towards protecting communities’ vital water services \
Outcomes
- Economic Sense: According to UN, every $1 invested in safe drinking in urban areas water yields more than $3 in saved medical costs and added productivity. In rural areas, $7 is saved for every $1 invested
- Increase Blue Investment like water storage, cleaning etc by mobilising all sections of society to invest in integrated, inclusive & sustainable water projects
- Ensure Right to Water by making sure that the poorest individuals are not priced out of the market.
- Access to sanitation like Clean water by developing sustainable water solutions.
Where can this Case Study be Used
- Best Practises as Sustainable solution for management of water.
- Highlighting the importance of valuation of water for better health, reduced migration, better food security etc
- Case Study to attract private investment in Blue Investments.
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.