Friday, 9th April 2021
Image of the day- the first Indian woman sailor

Netra Kumanan from Chennai has become the first Indian woman sailor to qualify for the Tokyo Olympics. She is also the first person from the country to earn the spot at Olympics by winning a qualifying event. Previously, Bhavani Devi also made history by becoming the first fencer from India to get qualified for Tokyo Olympics.
Hydrogen Coalition
News
Given the opportunities in India’s green hydrogen space a coalition of energy and industrial firms named India H2 Alliance (IH2A) has come together for commercializing hydrogen technologies and creating a hydrogen economy.
About the News
- This alliance led by Chart Industries and Reliance Industries Ltd will work together to build the hydrogen economy and supply-chain in India.
- To achieve its objectives, the alliance will work with the Indian government on five areas:
- to develop a national hydrogen policy and roadmap 2021-30
- to create a national H2 taskforce and mission in a public-private partnership format
- to identify nationally large H2 demonstration-stage projects
- to help create a national India H2 fund
- to create hydrogen-linked capacity covering hydrogen production, storage and distribution, industrial use-cases, transport use-cases and standards.

About Hydrogen Energy
- Extraction of Hydrogen: Hydrogen exists only combined with other elements, and has to be extracted from naturally occurring compounds like water (which is a combination of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom). Although hydrogen is a clean molecule, the process of extracting it is energy-intensive.
- Clean Energy: Green hydrogen is a clean burning molecule, which can decarbonise a range of sectors including iron and steel, chemicals, and transportation. Also, renewable energy that cannot be stored or used by the grid can be channelled to produce hydrogen.
- Working of Hydrogen Fuel Cell: Hydrogen is an energy carrier, not a source of energy. Hydrogen fuel must be transformed into electricity by a device called a fuel cell stack before it can be used to power a car or truck.
- A fuel cell converts chemical energy into electrical energy using oxidising agents through an oxidation-reduction
- Fuel cell-based vehicles most commonly combine hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity to power the electric motor on board. Since fuel cell vehicles use electricity to run, they are considered electric vehicles.

- National Hydrogen Energy Mission: The Union finance minister has proposed the introduction of a National Hydrogen Energy Mission in her budget speech. It will aim to increase the penetration of domestic green hydrogen in industries such as fertilizer, steel and oil refineries.
https://www.energyinfrapost.com/reliance-other-energy-majors-form-hydrogen-coalition/
Life expectancy in India below the world average
In News
According to the estimates from the Sample Registration System (SRS)-based Abridged Life Tables 2014-18 of the Census and Registrar General of India, India’s life expectancy (for a child born in 2021) is 69 years and 4 months, less than the world’s average lifespan of 72.81 years.
Key findings in the SRS report about Life Expectancy in India
- A child in India has a lower chance of survival at birth compared to a one-year-old: The average life expectancy at birth for 2013-2017 was 69 years while the corresponding figure for age one was 70.8 years. A child in India has a lower chance of survival at birth compared to a one-year-old. Broadly, this means the mortality risk for people in India is highest in the first year of life. According to UN data, India had the highest number of neonatal deaths in absolute terms in 2019, with an infant mortality rate of 30 deaths for every 1,000 live births.
- Average life expectancy at birth for males exceeds that of females in some states: In some states like Bihar and Jharkahnd average life expectancy at birth for males exceeds that of females indicating gender discrimination and an anti-female bias in child survival.
- Gap between the rural and urban life expectancy has also narrowed: In case of life expectancy at birth, most of the states have reported higher life expectancy in urban areas than in rural areas, except for Kerala. There is a difference of about 4.6 years in urban-rural life expectancy at birth.
Reasons why Indian life span continues to be below world average
- Sanitation and Infrastructure: Lack of adequate infrastructure related to clean water and sanitation increases the vulnerability to diseases like diarrhoea, dysentery, hepatitis A and also exacerbates stunting.
- Affordability and privatized care: Nearly two-thirds of Indian households seek healthcare from the private medical sector, and that choice is further on the rise. The privatized nature of healthcare has increased the out-of-pocket expenses which most patients cannot afford causing a significant percentage of the population to go without care.
- Lack of health insurance coverage: Despite the emergence of a number of health insurance programmes and schemes, only 5% of households report that a household member has coverage of any kind.
- Lack of healthcare professionals: The doctor-population ratio in India is 1:1456 against the WHO recommendation of 1:1000. Also, health professionals in India avoid rural service.
- Impact of pollution: According to the World Air Quality Report, India was home to 35 of the world’s 50 most polluted cities. The life expectancy of a child in India is cut short by two years and six months due to constant exposure to polluted air in the country.
Sources:
https://science.thewire.in/health/india-life-expectancy-birth-srs-2013-2017-gender/
Anamaya: Tribal Health Collaborative launched
In News
The Ministry of Tribal Affairs has launched the Tribal Health Collaborative named Anamaya. The Collaborative is a multi-stakeholder initiative of the Ministry of Tribal Affairs supported by the Piramal Foundation and Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation.
About the Initiative
- Bringing together various stakeholders: This Collaborative is a unique initiative bringing together governments, philanthropists, national and international foundations, and NGO’s to end all preventable deaths among the tribal communities of India.
- Aim: It aims to build a sustainable, high-performing health ecosystem to address the key health challenges faced by the tribal population of India. It will converge efforts of various Government agencies and organisations to enhance the health and nutrition status.
- Operation: It will begin its operations with 50 tribal, Aspirational Districts (with more than 20% ST population) across 6 high tribal population states. Over a 10-year period, the work of the initiative will be extended to 177 tribal Districts as recognised by the Ministry of Tribal Affairs.
Status of Tribal Health in India
- Life expectancy: According to estimates published in Lancet, the life expectancy at birth for ST population in India is 63.9 years as opposed to 67 years for the general population.
- Maternal Health: NFHS data shows that 65% of tribal women in the age group of 15-49 years suffer from anaemia as opposed to 47% of non-ST women. 27% of tribal women still deliver at home, highest among all population groups.
- Burden of disease: The tribal population in India faces triple burden of diseases. While malnutrition and communicable diseases like TB and malaria continue to be rampant, rapid urbanization and environmental distress has led to increase in non-communicable diseases. The third burden includes mental illnesses, particularly addiction.
- Genetic Disorders: Sickle Cell Disease is widespread in many tribal groups of India especially among the tribes inhabiting malaria endemic regions. About 1 in 86 births among the Scheduled Tribe (ST) population have SCD, the prevalence being higher in Central, Western and Southern India.
Government Security Acquisition Programme (GSAP 1.0)
News
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) announced a secondary market government security acquisition programme (GSAP 1.0).
About the News
- RBI will conduct open market purchase of government securities (G-secs) of ₹1 lakh crore under the government security acquisition programme (G-SAP 1.0) from the secondary market in the first quarter of FY21-22.
- G-SAP will run alongside RBI's regular operations, including Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF), open market operations (OMOs) and Operation Twist.
- The RBI also announced that it will continue with a variable rate reverse repo to absorb excess liquidity.
- Immediate result: Following the G-SAP announcement, the 10-year G-Sec bond yields dropped.
What is Bond Yield?
- Bond yield is the return an investor gets on a bond or on a particular government security.
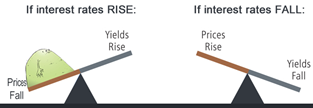
- A rise in bond yields means interest rates in the monetary system have fallen, and the returns for investors (those who invested in bonds and govt securities) have declined.
- The major factors affecting the yield is the monetary policy of the Reserve Bank of India, especially the course of interest rates, the fiscal position of the government and its borrowing programme, global markets, economy, and inflation
- Effects of Bond Yield:
- Equity Returns: Bond yields are inversely proportional to equity returns; when bond yields decline, equity markets tend to outperform, and when yields rise, equity market returns tend to falter.
- Stocks: A rise in bond yields raises the cost of capital for companies, which in turn compresses the valuations of their stocks.
- FPI: Traditionally, when bond yields rise in the US, FPIs move out of Indian equities. Also, it has been seen that when the bond yield in India goes up, it results in capital outflows from equities and into debt.
Why has the G-SAP been launched?
- Help government borrowing: The G-SAP, by providing more comfort to the bond market, will ensure that the government’s elevated borrowing for this year goes through without causing disruption.
- With the government’s Inflation target of 4 per cent (+2/-2) and well entrenched inflation-targeting framework, the G-SAP will give enough policy space to the central bank to act in an extraordinary situation.
- The announcement of this structured programme will help reduce the spread between the repo rate and the 10-year government bond yield. That, in turn, will help to reduce the aggregate cost of borrowing for the Centre and states in FY22.
- Stabilising the Yield Curve: Through the G-SAP, which is part of the liquidity management strategy for 2021-22, there will be Rs 1-trillion liquidity surplus in the system.
- The liquidity in the market will lower the market interest rates, which in turn will push for lowering of bond prices. As bond yields and prices move in opposite directions, so as bond prices go up, the bond yields will come down.
- Thus, the RBI will ensure orderly evolution of the yield curve and the positives of G-SAP 1.0 operations will be visible in the segments of the financial markets that rely on the G-Sec yield curve as a pricing benchmark.
Yield Curve: A yield curve is a line that plots yields (interest rates) of bonds having equal credit quality but differing maturity dates. The slope of the yield curve gives an idea of future interest rate changes and economic activity.
- RBI’s commitment to growth: The G-SAP will help to ensure cooling off of bond yield and financial stability given the global uncertainty around the risks related to COVID-19.
- RBI has demonstrated sustained commitment to growth and tried to maintain adequate liquidity in the financial system during the pandemic period, through steps to infuse liquidity, cut policy rates and eased regulatory norms.
- Clarity to Bond Market: With the G-SAP, the RBI has satisfied a long-standing demand of the bond market of an open market operation (OMO) calendar.
- Until now, the RBI used its discretion w.r.t. OMO. By giving up the discretion (under G-SAP), the RBI has given explicit assurance to markets that it will assist them in the conduct of the borrowing program.
- Also, announcing the purchase of government securities (G-secs) of ₹1 lakh crore, through the G-SAP, will help market participants plan their engagement in the borrowing programme.
- Support the Monetary Policy stance: As the policy rates have been kept unchanged, G-SAP will work as an instrument to run the monetary policy.
- In the past, all actions of the RBI were directed at moving the interest rate up or down and ensuring that proper transmission of rates happens across the market spectrum.
- But through G-SAP, the RBI is explicitly committing the specified amount of Rs 1 trillion, without waiting for the indirect channel of interest rates and prices to operate.
- It is an upfront assurance, without being timed to market situations or market movements.
- Positive Equity market: While a decline in bond yield is positive for the equities markets, the G-SAP will also help keep bond price volatility in control and help market participants to bid better in scheduled auctions and reduce volatility in bond prices. Not only will domestic investors move towards equity, FPI inflow into equities too could regain momentum.
References-
https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/g-sap-rbi-market-7263221/
Indian Energy Exchange
- Indian Energy Exchange LIMITED (IEX) is the first and largest energy exchange in India.
- It provides a nationwide, automated trading platform for physical delivery of electricity, Renewable Energy Certificates and Energy Saving Certificates.
- The exchange platform enables efficient price discovery and increases the accessibility and transparency of the power market in India while also enhancing the speed and efficiency of trade execution.
- The Exchange is a publicly listed company with NSE and BSE.
- It is regulated by Central Electricity Regulatory Commission (CERC) and has been operating since 2008.
Primary Source: https://www.iexindia.com/Aboutus.aspx?id=IT8b%2bZM5cBA%3d&mid=Gy9kTd80D98%3d
Madhukranti Portal and Honey Corners
- Madhukranti portal is platform for online registration and repository of honey and beehive products’ stakeholders- sources, marketing chain and sales.
- Its aim is to trace the of sources of honey and other beehive products on a digital platform.
- This will help in checking the quality and source of adulteration of honey with end to end record to track the source of honey.
- It is an initiative of National Bee Board (NBB) under National Beekeeping and Honey Mission (NBHM) and Indian Bank as its technical and banking partner.
- Honey corners are dedicated sale space meant for sale of honey at NAFED (National Agricultural Cooperative Marketing Federation) stores to promote marketing of honey and other beehive products.
Made-In-India Pneumococcal Conjugate vaccine
- The pneumococcal conjugate vaccine acts against potentially fatal pneumococcal infections such as pneumonia, septicaemia and meningitis caused by streptococcus pneumonia (bacteria) in infants.
- Conjugate vaccine is a type of vaccinewhich combines a weak antigen with a strong antigen as a carrier so that the immune system has a stronger response.
- This enhances the stability and the effectiveness of the vaccine.
- Serum Institute of India will start supplying this vaccine to Centre.
- Pneumonia is a contagious infection caused by bacteria, viruses or fungi in one or both lungs. It is single largest infection that is the cause of death in children worldwide.
Plough to plate, hand held by the Indian state- The Hindu
Essence- Article discusses reasons why intervention of Indian state in agriculture must continue to ensure welfare of both farmers and consumers. First, specificities of agriculture- various limiting factors like uncertainty of weather, soil fertility and water availability make difficult to increase returns in farming. Also, it is difficult to assembly line the production process due to various factors. Second, to establish balance of power between traders and farmers; third, to tackle the ill effects of green revolution by greatly expanding the basket of public procurement to include more crops, more regions and more farmers; fourth, to include farmers in large procurement operations for providing them a large and steady market; fifth, to get rural people off the land and move them into industry and urban areas to remove growing inequalities. And to bring above reforms we need to strengthen state capacities instead of promoting privatization in this sector.
Why you should read this article?
- To understand why state’s role is significant in Indian agriculture.
- To get an overview of problems faced by Indian agriculture and their farmers.
- To know what could be the possible solutions for the same.
Explaining Pakistan’s flip-flop on trade with India
Essence - Pakistan’s double U-turn on resuming trade with India highlights the fact that shadow of politics still looms over trade. On March 31, Pakistan decided to import cotton, yarn, and 500,000 metric tons of sugar from India. A day later, Pakistan’s cabinet overruled the decision saying, as long as India does not review the unilateral steps it took on August 5, 2019 on J & K, normalising relations with India will not be possible. Pakistan’s decision was based on Pakistan’s immediate economic needs and not designed as a political confidence-building measure to normalise relations with India.
There has been a 30% decline (2020-21) in cotton production. This would mean, Pakistan’s cotton export would reduce, creating a domino effect on what goes into Pakistan’s garment industry. Sugar exports came down substantially last year, by over 50%, thus sugar industry in Pakistan is also in crisis. It is evident that the interests of its own business community and its export potential have become secondary. Pakistan has been saying that the onus is on India to normalise the process. Perhaps, it is New Delhi’s turn to tell Islamabad that it is willing, but without any preconditions, and start with trade.
Why you should read this article?
- To know about the recent flickering of Pakistan on issue of imports from India.
- To understand the economic troubles of Pakistan & how politics is swaying against the interest of many industries.
- To know about south Asian trouble in finding a ground to prosper, & placing politics over economics.
Developing a counterinsurgency strategy that actually works - IE
Essence - The killing of 22 security personnel by Maoists in Bijapur district of Chhattisgarh serves as a grim reminder that left-wing insurgency continues to be one of the biggest internal security threats for the country. This article while briefly highlighting key strengths of Maoists, debates about the nature of the Counterinsurgency (COIN) strategy, which governments both in the states and at the Centre are adopting or should adopt.
Why you should read this article?
- Briefly know about the strengths of Maoists which could be critical in developing any counterinsurgency strategy
- Understand the difference between people centric approach and enemy centric approach and examples of their judicious mix as employed by States like Andhra Pradesh.
- Know about other steps required to defeat the insurgents militarily and fully quell the insurgent impulses such as launch of coordinated operations by States, economic development, opening negotiation channels and implementing policies like surrender and rehabilitation and creating a system where the distribution of power is not controlled by the traditional elite.
obs round the year: How MGNREGA made Balangir job-secure
Migrants from Odisha
- Odisha is a major source state from where people migrate to developed states of Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu.
- Majority of Migration is from rural to urban areas and is a type of distress migration due to low profitability from agriculture.
- Odisha government took efforts to curb distress migration. By increasing the job under MGNREGA to 300 days of labour per year; payment for the additional 200 days of work is borne by the state government.
How MGNREGA made a difference?
- Orissa Watershed Development Mission renovated the pond, created watershed across the state and de-silted the water bodies under MGNREGA.
- This promoted good agricultural practices in the state which reduced distress migration from the state.
- Under MGNREGA, lot of construction works were undertaken which boosted employment in the district.
Outcome
- It improved production of food crops like rice, wheat, pulses and also non-food crops.
- It facilitated better irrigation practises and helped in recharging the ground water table.
- As many as 3,122 workers who used to migrate for work on a regular basis are registered under MGNREGA.
Where can we use this case study?
Innovative case study for MGNREGA, Case study to prevent distress migration, watershed development and rural prosperity, boosting agricultural income.
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.