Thursday, 25th March 2021
NITI Aayog Report on Flood Management
In News
NITI Aayog has released its report titled “Report of the Committee constituted for formulation of strategy for Flood Management Works in entire country and River Management Activities and works related to Border Areas (2021– 26)”.
Flood- an Introduction
- It is defined as, “High-water stages in which water overflows its natural or artificial banks onto normally dry land, such as a river inundating its floodplain.”
Table 1: Flood Prone Areas in India
|
Flood Prone Area |
40 Million Hectare (Mha) |
|
Annually affected Area |
7.17 Mha |
|
Annually affected Cropped Area |
3.94 Mha |
|
Area provided with reasonable degree of protection |
21 Mha |
|
Target area to provide reasonable degree of protection by 2035 |
35 Mha |
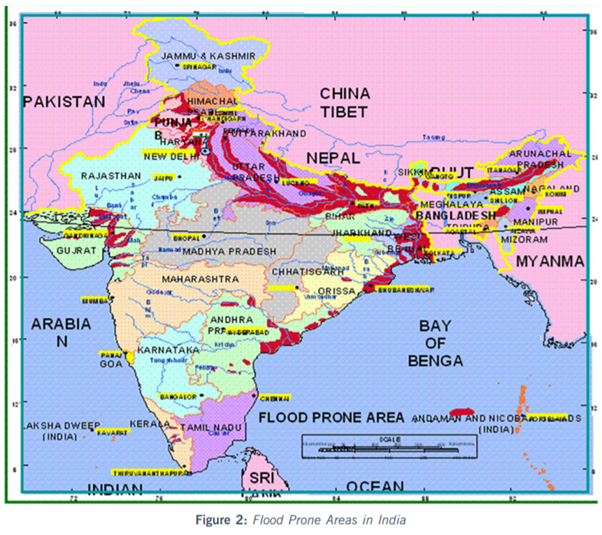
- Factors responsible for frequent floods in India:
- Wide variations in rainfall both in time and space with frequent departures from the normal pattern, inadequate carrying capacities of rivers, riverbank erosion, degradation of hilly catchment and silting of riverbeds, landslides, poor natural drainage in flood prone areas, glacial lake outbursts, cloud burst, etc.
- There is evidence of increasing number of high intensity rainfall event in the recent years varying non-uniformly in space and time. Such events lead to flash floods.
- Urban flooding due to storm water drainage congestion has also become common in towns/cities due to such extreme meteorological events.
- Impact of Climate Change on probability of flood: Broadly, climate change can exacerbate the flood situation in two-fold manner:
- Sea level rise due to melting of glaciers can submerge coastal areas of country degrading fresh water resources due to sea water intrusion.
- Variation in intensity of rainfall: The climate change has caused to increase the frequency of short duration heavy rainfall leading to higher water run-off.
- As per the report of Asian Development Bank, floods account for more than half of climate-related disasters in India and cause damages of $54.63 billion during 1990–2017.
Approach to Flood Management
Depending upon the nature of work, flood protection and flood management measures are broadly classified as under: (a) Structural Measures (b) Non-Structural Measures
- Structural Measures for Flood Management:
- To reduce flood flows and attenuate the flood levels: Building a reservoir, utilising natural depression, diversion of a part of the peak flow to another river or basin and constructing a parallel channel by-passing a particular town/reach of the river prone to flooding.
- To reduce spilling: River Embankments, Channel and drainage improvement work, River channelization works and Anti-erosion measures which prevent further loss of valuable land.
- Non-Structural Measures for Flood Management:
- Disseminating advance warning of incoming flood through a flood forecasting system and facilitating timely evacuation of the people to safer grounds.
- Discouraging creation of valuable assets/settlement of the people in the flood prone areas by enforcing flood plain zoning regulation.
Recommendations of NITI Aayog
- Give priority to non-structural measures like flood forecasting, flood plain zoning, flood proofing to accommodate high spat of water in majority of the places.
- Emphasis on the use of advanced technology like artificial intelligence, satellites, remote sensing and GIS for flood forecasting and warning systems.
- Design a National Water Model (NWM) for India to feed the information into a decision support system which can provide support services to Nation by predicting precipitation and forecasting flood and other water related events.
- NWM is a hydrologic modelling framework developed in USA that simulates observed and forecast streamflow over the entire continental United States.
- Formulate Flood Management Plans which can also help in rescue and relief works during and after the floods.
- NITI Aayog also proposes for the policy to provide flood cushion in the existing dams to accommodate peak time flood so that the tragedy like Kerala floods doesn’t repeat itself.
|
Constitutional Provision on Flood Management
|
Model Question: India is a highly prone country to floods with floods causing huge loss of lives and money every year. In this context, while discussing the approaches to flood management, suggest some concrete measures to reduce the vulnerability and losses due to floods.
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.