Friday, 12th March 2021
Govt begins groundwork to mechanise sewer cleaning
In News
The draft Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation (Amendment) Bill, 2020, proposes to completely mechanise the process of cleaning sewers and septic tanks and provides a legal basis for compensation to be provided for fatalities.
Plans for modernising sewer cleaning under the draft law
- The bill proposes to completely mechanise sewer cleaning and provide better protection at work and compensation in case of accidents.
- Setting up faecal sludge and septage management system for mechanised cleaning of septic tanks.
- Transportation and treatment of faecal sludge.
- Municipal authorities have responsibility for complete mechanisation.
- Setting up of Sanitation Response Units with a help line.
Challenges in mechanising sewer cleaning
- Gaps in the Manual Scavengers and Rehabilitation Act, 2013 – The current law prohibits persons from being engaged or employed for the hazardous cleaning of sewers and septic tanks. However, the Act is silent about alternative methods to get the job done.
- Lack of accountability - The cleaning of bigger drains and sewers that are maintained by state government agencies is mostly outsourced to contractors. While equipment like jetting and suction machines and safety gear for sanitation workers in case of emergency situations remain there as mandatory on paper, they fail to materialise on the ground.
- The problem is further complicated by the fact that there are multiple agencies involved in cleaning drainage system - Municipal corporations, Public Works Department, Department of Irrigation and Flood control. This also hampers fixing accountability.
- Machines not likely to work in all situations - Storm water drains in cities are clogged with solid waste such as construction material and plastic. Suction machines often fail to clean such clogging which inevitably demand manual intervention. A complete mechanisation plan will not be successful unless such inefficiencies are addressed.
Way ahead: Hyderabad model
- The Hyderabad municipal water supply and sewerage board tied up with the Dalit Indian Chamber of Commerce and Industry and provided a group of sanitation workers with small sewer jetting machines, and trained them how to use them. These machines use high pressure jets to clear obstructions in drains and sewers.
- The Hyderabad Metropolitan Water Supply and Sewerage Board is also planning to introduce robotic technology to avoid manual cleaning of choked sewer lines and manholes and help the water board keep an eye on the choked sewer lines.
INS Karanj, the Scorpene-class submarine inducted into service
In News
The Indian Navy recently inducted its third Scorpene-class conventional diesel electric submarine, INS Karanj, into service.
What are Scorpene-class submarines?
- The Scorpene class submarines are one of the most advanced conventional submarines in the world. The submarine has superior stealth features, such as advanced acoustic silencing techniques, low radiated noise levels and ability to attack with precision-guided weapons on board.
- The Indian Navy intends to use the submarines for missions such as area surveillance, intelligence gathering, anti-submarine warfare, anti-surface warfare and minelaying operations.
Scorpene Class Submarines
- INS Kalvari: It is India's first Scorpene-class submarine and was commissioned into the Indian Navy in December 2017
- INS Khanderi: INS Khanderi is India's second Scorpene-class attack submarine. It was commissioned in September 2019
- INS Karanj: Karanj is the third of the six Scorpene-class submarines built under the Project 75 programme.
- The remaining submarines (Vela, Vagir, and Vagsheer) in the series are in advanced stages of manufacturing and trials.
About Project 75I
- It is a follow-on of the Project 75 Kalvari-class submarine for the Indian Navy.
- Under this project, the Indian Navy intends to acquire six diesel-electric submarines, which will also feature advanced air-independent propulsion systems.
- This project is under the Strategic Partnership model which has been adopted in an effort to ensure building capacity in Indian Industry.
- This project is part of the 30-year Plan for indigenous submarine construction. And it got its approval by the Cabinet Committee on Security in 1999.
Gujarat High Court’s guidelines to end menstruation taboo, discriminatory practices
In News
Division bench proposed a set of guidelines that the state should follow to end menstruation taboo, discriminatory practices.
Proposed guidelines
- It sought for prohibition of social exclusion of women on the basis of their menstrual status at all places, be it private or public, religious or educational.
- State government should spread awareness among various strata of citizens, including health workers, adolescents, parents and other such stakeholders, regarding social exclusion of women on the basis of their menstrual status through various mediums with a strategy aimed at raising the awareness among the adolescent girls related to menstrual health and hygiene.
- The court also proposed for sensitization of health workers, Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHA) and Anganwadi Workers pertaining to the biological process involved in menstruation biology so that they can further disseminate this knowledge in the community and mobilize social support against busting menstruation related myths.
- Adolescent Friendly Health Services Clinics must also have trained manpower to address these issues,
- To ensure implementation and awareness around menstruation the state government should allocate necessary funds for the implementation of the directions.
- The State Government should undertake surprise checks, create appropriate mechanism and to take such other actions, steps as may be necessary to ensure its compliance including imposition of appropriate penalty against the erring institution.
Need of such guidelines in absence of specific law
- Treating menstruating women differently amounts to a practice of untouchability.
- Exclusion on the basis of menstruation status is not only an infringement of women’s bodily autonomy but also an infringement of right to privacy.
- Such taboo and discriminatory practices lead to the denial of equal opportunities with a large number of girls dropping out of school when they begin menstruating.
- A special provision is also required to be made in view of the Convention on Discrimination on all form of Discrimination against Women.
Various Other judgements pertaining to menstruation
- The Sabarimala temple entry judgmentof the Supreme Court had addressed the evil practices of menstruation, with the judgment noting, “Notions of “purity and pollution”, which stigmatize individuals, can have no place in a constitutional regime.
- The Delhi High Court had asked government authorities to treat a PIL seeking direction to grant paid period leaveto all women employees for four days each month and payment of overtime allowance in case the women opt to work during the menstruation period, as a representation.
India’s agriculture export subsidy policies come under WTO lens
In News
India’s farm subsidy policies came under the scanner at the World Trade Organization (WTO) during the country’s trade policy review (TPR).
Disputes with different countries in WTO related to Agreement on Agriculture
- Members such as Canada, the US and Australia complained that India has not declared its agriculture export subsidies for more than eight years.
- The US argued that the government programme to purchase food products from farmers at minimum support prices distorts domestic market prices and incentivizes over-production of products such as rice and wheat.
- Guatemala has initiated dispute settlement proceedings questioning India’s sugar subsidy programmes at the WTO which has been joined by Australia and Brazil.
- India in its response to the WTO members over the concerns raised said the support given is largely to small and marginal farmers, and is in accordance with India’s commitments at the WTO.
WTO - Agreement on Agriculture
The Agreement on Agriculture (AoA) is an agreement under WTO which comprises specific commitments to reduce support and protection in the areas of domestic support, export subsidies and market access.
Domestic Support: Under this agreement, the developed countries have to limit their domestic support (covered under amber box subsidies) within 5% and developing countries to limit within 10% of total agriculture production. The de-minimis level or domestic support subsidies of total agriculture production to be calculated from base year 1986 –1988. The domestic support subsidies are categorized into three boxes that are as follows:
- Amber Box:It contains all domestic support measures that are mean to distort trade practices in agriculture. These are subject to limits, termed as ‘de minimis’ levels.
- Blue Box:It includes subsidies that are linked to one product, but that do not increase according to production levels. There are no limits on spending on blue box subsidies.
- Green Box: These are subsidies which causes no or little trade distortion in agriculture sector. They may include environmental protection, regional development, R&D or farmer training programs etc. These are therefore allowed without limits.
Market Access: It includes provisions related to tariff reduction and trade facilitation in agriculture products. Special Safeguard provision allows the imposition of additional duties when there are either import surges above a particular level or particularly low import prices as compared to 1986-88 levels.
Export Subsidies: These are direct subsidies given by Governments given in cash or in kind to producers of the agriculture products against export performance and export of non-commercial agriculture products.
Peace Clause: It came into force in 2013 at 9th WTO Ministerial Conference at Bali. According to it agricultural subsidies committed under AoA cannot be challenged until the permanent solution for subsidies is in place. India has invoked the peace clause of the World Trade Organisation. This follows the country exceeding the ceiling of 10 per cent on support it offered to rice farmers in the marketing year 2018-19.
Land Records Digitization in India
In News
NCAER Land Record and Services Index (N-LRSI) 2021, revealed that almost all States and Union Territories have shown an improvement in their efforts to digitize land records compared to the previous year.
Importance of Improving Property Record Systems
- Easier transfer and access to credit for citizens with accurate and reliable data with regards to the ownership and details of land and property will have substantive impact on improving lives.
- Security of tenure for small farmers and for the poor and vulnerable in both rural as well as urban areas, will be ensured with the maintenance of proper land records.
- Improves investment scenario: Accessible, high quality records help increase the visibility and availability of land for large-scale investment opportunities across industries along with reducing Costs of projects.
- Vibrant real estate sector: It will bring much needed boost to employment intensive real estate sector. The real estate sector, which accounts for about 11 per cent of India’s GDP, is characterised by an extremely inefficient property market.
- Increased tax collection: Transparency brought through digitization of land records will make it difficult for the general public to evade property tax leading to reduction in black money as well.
- Reduced Litigations: Land-related disputes in India account for about 60 to 70 per cent of all civil litigation. About 25 per cent of all cases decided by the Supreme Court involve land disputes.
How digitisation will Improve land records?
- A web-enabled “anytime anywhere” access to records saves citizens time and effort in obtaining hard copies of the records.
- Automatic and automated property mutations can also significantly reduce the scope of fraudulent property deals.
- It allows for better servicing of clients by enhancing access to records and connected services, while also enabling analysis to guide policy for achieving real-time accuracy.
- Computerisation of registration is essential not only for ensuring efficient and hassle free property registration.
- The application of digitised processes for entry of registration data, calculation of the taxes due, and for making payments, and use of online systems to approve registration and deliver final documents, further reduce discretion in the entire process.
Land records digitisation in India
- Karnataka was the first state in India to computerize land records under the “Bhoomi Project” followed by Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu in the year 2001.

- According to the rural development ministry, under the Digital India Land Record Modernisation Programme (DILRMP), computerisation of registration of land, cadastral maps and land records have been completed in more than 90 per cent of the states.
- The Government of India launched the Survey of Villages and Mapping with Improved Technology in Village Areas (SVAMITVA) scheme in April 2020. This scheme seeks to confer land titles in hitherto unmapped and inhabited parts of rural India.
Challenges in digitisation of land records and Way Forward
- Coordination between departments/agencies is much needed as lack of clear and sufficient data and mismanagement between the various agencies handling land records, the data registered at various government levels is not identical.
- Capacity building: Various types of information like property maps and sale deeds are maintained by different departments at the village level. Most of the times, functionaries in these departments lack training on digital access.
- Land record should be free of any encumbrances: The focus must shift from mere digitisation to the creation of more accurate and comprehensive land record data bases that also provide the ease of fair, transparent, and efficient land transactions with good price discovery for both sellers and buyers.
- States can also consult and take feedback from developers on the main topics of sourcing, tracking, executing various land records.
- At regular intervals, a fresh survey of every parcel of land to update records will help everyone in purchasing, transferring and selling land, giving deeds, and easing all kinds of land transactions with the press of a button.
Additional Information
NCAER Land Record and Services Index (N-LRSI) 2021
- The Index measures the performance of states and UTs across four broad parameters of Digitisation of textual and spatial records, Computerisation of the registration process, and the quality of land records.
- It finds that all states/UTs have shown positive change or retained their scores in 2020-21.
- Madhya Pradesh ranked first for the second time in a row.
- Another key performance indicator assessed by the NCAER with respect to the land records is Accessibility, which evaluates states and UTs based on the ease of access, comprehensiveness of the information available, user interface, and the efficiency of the help and assistance functionalities on their respective land records related web platforms.
- Odisha, West Bengal, Karnataka, Bihar and Uttar Pradesh are the top performing states in this index.
Survey of Villages and Mapping with Improved Technology in Village Areas (SVAMITVA) scheme
- SVAMITVA is a Central Sector Scheme of the Ministry of Panchayati Raj which aims to provide the ‘record of rights’ to village household owners in rural areas and issue Property Cards.
The Scheme is being implemented across the country in a phased manner over a period of four years (2020-2024) and would eventually cover around 6.62 lakh villages of the country.
International Lunar Research Station (ILRS)
- The Chinese and the Russian space agencies have signed an MoU on cooperative construction of an international lunar research station.
- The International Lunar Research Station (ILRS) is a comprehensive scientific experiment base built on the lunar surface or on the lunar orbit.
- It can carry out multi-disciplinary and multi-objective scientific research activities that includes:
- exploration and utilization,
- lunar-based observation,
- basic scientific experiment
- technical verification,
- long-term autonomous operation etc.
- The project will be open to all interested countries and international partners.
Bharat Bangla Maitri Bridge
- The Bharat Bangla Maitri Bridge is in Tripura’s South district, and would serve as a new trade corridor between India and Bangladesh.
- It has been built over the Feni riverwhich flows between Indian boundary in Tripura State and Bangladesh.
- The connectivity through this bridge will strengthen India’s cordial ties with Bangladesh and will boost trade relations, helping the Northeast states grow.
- Tripura will become the‘Gateway of North East’ with access to Chittagong Port of Bangladesh, which is just 80 km from Sabroom, Tripura.
Ramagundam Solar Plant
- It is being developed by NTPC in the reservoir of its thermal plant at Ramagundam in Peddapalli district of Telangana.
- It would be the country’s biggest floating solar power plant, by generation capacity.
- It would be one of the renewable (solar) energy plants with an installed capacity of 447MW in the Southern Region.
- The entire capacity would be commissioned by March 2023.
- Floating solar plants is an opportunity to generate power without incurring high cost due to land acquisition.
Working towards climate justice in a non-ideal world – The Hindu
Essence – The Article is analysing the resurgence of environmental agenda in global governance & how it’s important for India to become proactive, so as to ensure that emerging carbon & policy space is in sync with its developmental aspirations. Recent call by US President Mr. Joe Biden for reconvening Major Economies Forum (MEF) is being considered as an important step at this juncture. All countries are being told to commit to net zero GHG (Green House Gas) emissions by 2050, with credible plan. Countries representing 65 % of global CO2 emissions have agreed to it & UN Secretary General would like this figure to reach 90 % by within 2021. Developed countries have been averse to commit to the idea of Historical responsibilities & differentiation, but willing to incorporate solutions like border levies on those who do not take on high carbon cut down targets.
Why you should read this article?
- To understand, how climate negotiations are not just about environment or human well-being & they have lot to do with global governance.
- To know the recent changes in role of USA in climate issues.
- It is explaining some of the most promising discourses related to climate talks nowadays.
- It is also providing insights on role of UN, WTO & policy measures to incentivise renewables
Sticking points in carbon market rules – HinduBusiness Line
Essence - The Paris Agreement, which aims to keep global average temperature rise to well below 2oC from pre-industrial levels, kicked in on January 1, 2021. With the end of the second commitment period of the KP on December 31, 2020, countries are jostling amongst themselves to ensure that rules and a framework are decided upon in the working of Article 6 of the Paris Agreement, which deals with carbon markets for the new regime. In this context, the article brings out several contentious issues for countries like countries such as India, Brazil and China.
Why you should read this editorial?
- Develop an understanding about carbon markets and Article 6 of the Paris Agreement
- Identify key issues such as fate of several unsold tradeable carbon credits generated under the CDM, consequences in terms of double counting or claiming of emission reductions, carry-over of Kyoto credits due to lack of agreement on the rules of the Paris Agreement.
- Know about San Jose Principles for High Ambition and Integrity in International Carbon Markets and related issues.
Scientific research needs focused funding – The Tribune
Essence - The pandemic has demonstrated the critical role long-term investments in research and development (R&D) play in meeting new challenges. In this context, the article throws light on the state of R&D ecosystem and in particular, funding, in India. The article argues that there is a need for an overarching Central research funding agency which is autonomous not attached to any administrative ministry.
Why you should read this article?
- To get an overall idea of the research ecosystem in India and how over the years, the number of scientific departments has ballooned and have got subsumed in the dominant bureaucratic culture.
- Analysis of the recent step of establishing a National Research Foundation (NRF).
- Understand the need for an autonomous body for research and to keep it free from both bureaucratic interference and political influence.
Link - https://www.tribuneindia.com/news/comment/scientific-research-needs-focused-funding-223999
India must take the lead in regulating cryptos – Hindu Business Line
Essence - Editorial is doing scrutiny of decision to ban private cryptocurrency in India and suggesting need to look for other practical ways. Cryptocurrencies have become a reason of discontent among finance ministry and RBI, because they operate in a boundary-less digital world, in total regulatory vacuum. And can threaten interest of investor, RBI is also concerned about money laundering and terror financing through cryptocurrencies. Banning private cryptocurrencies in one country makes the ecosystem go underground & work in same manner from different countries. Since it’s ownership is scattered across the globe, it’s impossible to ban it. Government needs a record of all the existing cryptocurrencies in the country and those that are freshly created. Trading of private cryptocurrencies on trading platforms can also be allowed. But with regulatory oversight.
Why you should read this article?
- To understand the fundamentals of cryptocurrency & challenges it poses.
- It is providing information on reactions of Finance ministry & RBI until now.
- To know about the regulatory steps which can be used by government - towards private cryptocurrency holders, miners & trading platforms operating in India.
Lake Restoration: Two successful model of lake restoration in Rajasthan and Karnataka
- A large number of lakes in urban India are in dire need of conservation and restoration.
- Mansagar lake in Jaipur and Kaikondrahalli lake in Bengaluru were one such of many lakes facing many issues like:
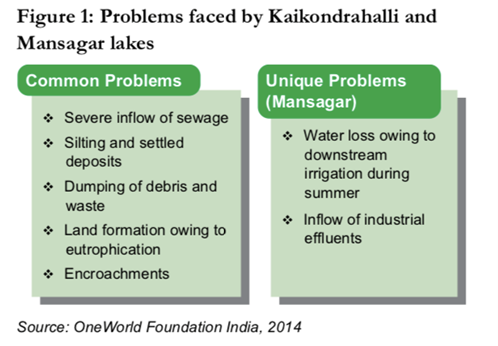
Innovative Models: Restoration of Mansagar Lake
- Mansagar Lake required diversion of polluted drain water so a natural filter was created using boulders, sand and degraded mud to filter out the big pollutants
- Waste water was then moved into chamber with vegetation cover.
- This strategy reduced BOD of water and improved flora and fauna around the lake.
Restoration of Kaikondrahalli Lake
- It followed a phased approach which ensured regular flow of fund and mapping of the lake to stop illegal encroachment around the lake.
- It was followed by diversion of sewage inflow via a pipeline, de-siltation and de-weeding of lake leading to increase in the storage capacity of the lake and afforestation helped to improve the water quality
Outcome
- It has lead to revival of local ecology and has attracted a lot of birds leading to creation of recreation urban spots
- The two different yet successful strategies for lake restoration offer replicable models that other states can learn from.
Where can we use this case study?
- Innovative model for restoration of natural ecology in urban areas, Problems faced by lakes in urban areas, Importance of urban lake, Sustainable Urbanisation etc.
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.