Friday, 12th February 2021
Kerala orders probe into oil spill
In News
Furnace oil from the state-run Travancore Titanium Products Limited (TTPL) in Thiruvananthapuram leaked into the adjoining Arabian Sea, the government ordered a probe and launched an emergency cleaning operation.
How do oil spills happen?
Oil spills are very common and they happen in many different ways.
- Most of the spills are small, for example when oil spills while refuelling a ship. But these spills can still cause damage, especially if they happen in sensitive environments, like beaches, mangroves, and wetlands.
- Large oil spills are major, dangerous disasters. These tend to happen when pipelines break, big oil tanker ships sink, or drilling operations go wrong. Consequences to ecosystems and economies can be felt for decades following a large oil spill.
Environmental impact of Oil Spills
- Crude oil ruins the insulating and waterproofing properties of feathers and fur, and thus oil-coated birds and marine mammals may die from hypothermia.
- Ingested oil can be toxic to affected animals, and damage to their habitat and reproductive rate may slow the long-term recovery of animal populations from the short-term damage caused by the spill itself.
- Migratory patterns and nesting grounds can be contaminated by oil spills, with potentially disastrous effects on natural life cycles of many species of bird.
- Oil can also clog the blowholes of cetaceans such as dolphins and whales, affecting their ability to breathe and disrupting their communication through echolocation.
- Damage to plant life can be considerable as well; saltwater marshes and mangroves are two notable shore ecosystems that frequently suffer from oil spills.
Reforms in Coal Sector
In News
Government updated Parliament about some of the coal reforms that have been taken recently.
It was enacted to amend the Coal Mines (Special Provisions) Act, 2015 [CMSP Act] and the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957 [MMDR Act]. The amendments in the Acts enabled following:Mineral Laws (Amendment) Act, 2020
National Coal Index
TIFAC launches job portal
In News
Technology Information, Forecasting and Assessment Council (TIFAC), an autonomous organization under the Department of Science and Technology has launched job portal Saksham.
About Saksham
- The portal conducts skills mapping exercises as per requirements of MSMEs across the country. Hence, it will help labourers to get work who were compelled to return to their native lands due to pandemic.
- After the identification of skill proficiency level, the labourers will be provided with Skill Cards.
- It uses algorithm and Artificial Intelligence (AI) for geo spatial information on demand and availability which will provide job opportunities in proximate MSMEs and minimize their migration.
- This would eliminate the dependence of industry on the middlemen for their manpower requirements.
Kerala orders probe into oil spill from titanium factory to sea
In News
Furnace oil from the state-run Travancore Titanium Products Limited (TTPL) in Thiruvananthapuram leaked into the adjoining Arabian Sea, the government ordered a probe and launched an emergency cleaning operation.
How do oil spills happen?
Oil spills are very common and they happen in many different ways.
· Most of the spills are small, for example when oil spills while refuelling a ship. But these spills can still cause damage, especially if they happen in sensitive environments, like beaches, mangroves, and wetlands.
· Large oil spills are major, dangerous disasters. These tend to happen when pipelines break, big oil tanker ships sink, or drilling operations go wrong. Consequences to ecosystems and economies can be felt for decades following a large oil spill.
Environmental impact of Oil Spills
· Crude oil ruins the insulating and waterproofing properties of feathers and fur, and thus oil-coated birds and marine mammals may die from hypothermia.
· Ingested oil can be toxic to affected animals, and damage to their habitat and reproductive rate may slow the long-term recovery of animal populations from the short-term damage caused by the spill itself.
· Migratory patterns and nesting grounds can be contaminated by oil spills, with potentially disastrous effects on natural life cycles of many species of bird.
· Oil can also clog the blowholes of cetaceans such as dolphins and whales, affecting their ability to breathe and disrupting their communication through echolocation.
· Damage to plant life can be considerable as well; saltwater marshes and mangroves are two notable shore ecosystems that frequently suffer from oil spills.
Reforms in Coal Sector
In News
Government updated Parliament about some of the coal reforms that have been taken recently.
Mineral Laws (Amendment) Act, 2020
It was enacted to amend the Coal Mines (Special Provisions) Act, 2015 [CMSP Act] and the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957 [MMDR Act]. The amendments in the Acts enabled following:
· Allocation of coal blocks for composite prospecting license-cum-mining lease which will help in increasing of the inventory of coal, lignite blocks for allocation.
o Previous approval of Central Government has been done away with.
· Provided flexibility to the Central Govt. in deciding the end use of Schedule II and III coal mines under the CMSP Act.
o Companies which do not possess any prior coal mining experience in India can now participate in auction of coal blocks.
· Salient features of methodology for auction of coal and lignite mines / blocks for sale of coal / lignite on revenue sharing basis are as under:
- Applicable to fully explored as well as partially explored coal blocks under the CMSP Act and MMDR Act.
- Successful bidder shall be provided incentives for early production and for gasification or liquefaction of coal.
- Exploitation of Coal Bed Methane (CBM) is allowed.
- There shall be no restriction on the sale and/or utilisation of coal from the coal mine.
National Coal Index
In order to arrive at the revenue share based on market prices of coal, one National Coal Index (NCI) was conceptualized.
· The NCI is a price index which reflects the change of price level of coal on a particular month relative to the fixed base year. The base year for the NCI is FY 2017-18.
· Prices of coal from all the sales channels of coal, including import, are taken into account for compiling the NCI.
· Indices are separate for Non-coking and Coking Coal. NCI is composed of a set of five sub-indices: three for Non-Coking Coal and two for Coking Coal.
TIFAC launches job portal
In News
Technology Information, Forecasting and Assessment Council (TIFAC), an autonomous organization under the Department of Science and Technology has launched job portal Saksham.
About Saksham
· The portal conducts skills mapping exercises as per requirements of MSMEs across the country. Hence, it will help labourers to get work who were compelled to return to their native lands due to pandemic.
· After the identification of skill proficiency level, the labourers will be provided with Skill Cards.
· It uses algorithm and Artificial Intelligence (AI) for geo spatial information on demand and availability which will provide job opportunities in proximate MSMEs and minimize their migration.
· This would eliminate the dependence of industry on the middlemen for their manpower requirements.
Major Ports Authorities Bill 2020
In News
“Major Ports Authorities Bill 2020” has been passed by Parliament and is set to replace the Major Port Trusts Act, 1963 after the assent of President. It aims to address the various regulatory issues plaguing the port’s sector in India.
Rationale behind new Law
Rakesh Mohan led National Transport Development Policy Committee (2013) had observed that
- The current governance structure of major ports—the public service port model— lacks the potential to attract private capital and encourage competitiveness.
- There is need to transform the current port trusts into publicly-owned statutory landlord port authorities through a new law to impart functional and financial autonomy.
- The maritime states where these ports are located should be encouraged to have substantial shareholding in them to ensure their participation in the development, functioning and expansion of the ports.
- Committee recommended market pricing of port services also.
- These regulatory issue had led to inefficiencies in port’s operations as:
- Currently, the vessel & container-related charges at Indian ports are much higher than foreign ports. This adds to the cost of logistics of the country.
- Longer turnaround time and low output per ship berth and lack of adoption of advanced technologies also plagues the ports in India.
- Higher costs at major ports such as JNPT lead to ripple effect as non-major ports use these costs as a benchmark for their own tariffs, thus resulting in higher tariffs. This adds to the overall cost of logistics of the country.
The Salient Features of the Bill:
- Applicability: The new law will supersede a 1963 Act governing the country’s 12 major ports.
- Major Port Authorities Board: The Bill proposes to create a simplified composition of Board of Major Port Authority, for each major port. These Boards will replace the existing Port Trusts under the 1963 Act.
- Composition of Board: The Board will comprise of a Chairperson and a Deputy Chairperson, to be appointed by the central government on the recommendation of a selection committee.
- Further, it will include one member each from (i) Concerned State Government (ii) Ministry of Railways (iii) Ministry of Defence (iv) Customs Department.
- The Board will also include two to four independent members, two members representing the interests of the employees of the Major Port Authority, and one member not below the rank of Director (nominated by the Central Government).
- Powers of the Board: The Boards of Port Authority have been delegated full powers to enter into contracts, planning and development, fixing of tariff except in national interest, security and emergency arising out of inaction and default.
- Adjudicatory Board: The Bill proposes to constitute an Adjudicatory Board, to be appointed by the Central Government, to replace the existing Tariff Authority under the 1963 Act.
- Provision of CSR by Port Authority have been introduced.
Concerns related to the bill
- It does not provide adequate representations to the State Governments where the ports are situated, to the employees of the ports and the labour working there in the composition of the board.
- There is no clarity with respect to the Selection Committee that will appoint the Chairperson to the Adjudicatory Board is concerned.
Reforms done with the new act
- Simplified to promote the expansion of port infrastructure and facilitate trade and commerce.
- Aims at decentralizing and transparent decision making and infuse professionalism in governance of major ports.
- The Bill is aimed at reorienting the governance model in central ports to landlord port model in line with the successful global practice bringing transparency in operations of Major Ports.
- It will assist in market-determined fixation of tariff rather than regulated tariff which will help boost investment in the sector, thus be beneficial for the stakeholders, customers and end-users.
Conclusion
Maritime trade contributes over 95% of trade by volume and over 70% by value in India. India plays a prominent role in global maritime trade due to its strategic location and accounts for only 2.1% of global trade. While India has 204 ports, 55% of the cargo traffic is handled by the 12 major ports. Thus, reforms brought by the bill are significant in improving efficiency and increasing India’s share in global trade.
Special Series – Budget, Survey and Finance Commission
Topic 8 Inequality and Growth: Conflict or Convergence?
Context
Economic Survey has examined if inequality and growth conflict or converge in the Indian context and what should be the focus of policy makers. This question becomes pertinent especially because of the inevitable focus on inequality following the COVID-19 pandemic.
Why focus on inequality is needed?
· As per the World Bank the Gini coefficient in India went up from 0.43 (1995–96) to 0.47 (2018–19) while Food and Agriculture Organization assessment shows that COVID-19 may cause an increase in each country’s Gini by two per cent.
· The report by Oxfam indicated that the top billionaires in India became richer by 35 per cent during the pandemic, while millions of poor Indians lost their jobs.
· International Labor Organization (ILO) estimated that nearly 400 million workers in India’s informal economy are at risk of falling deeper into poverty.
|
Economic inequality: Economic inequality refers to disparities among individuals' incomes, pay and wealth. Gini Coefficient: The Gini coefficient measures inequality across the whole of society rather than simply comparing different income groups. If all the income went to a single person (maximum inequality) and everyone else got nothing, the Gini coefficient would be equal to 1. If income was shared equally, and everyone got exactly the same, the Gini would be equal to 0. The lower the Gini value, the more equal a society. |
Trade-off between growth and inequality for Policy makers
· The Economic Survey 2019-20 argued that ethical wealth creation, by combining the invisible hand of markets with the hand of trust, provides the way forward for India to develop economically. An often repeated concern expressed with this economic model pertains to inequality.
· In the advanced economies, economists like Piketty have shown that higher inequality leads to adverse socio-economic outcomes but income per capita, a measure that reflects the impact of economic growth, has little impact.
· Thus,advanced economies may choose to focus on alleviating inequality given their stage of development, their potential rate of economic growth and the absolute levels of poverty that they face. Thus, they may resolve the trade-off between growth and inequality by leaning towards alleviating inequality.
· However, despite facing the same trade-off, the policy objective of focusing on inequality may not apply in the Indian context given the differences in the stage of development, India’s higher potential rate of economic growth and the higher absolute levels of poverty.
Policy Implication for India as per Economic Survey
· It examines the correlation of inequality (focus on redistribution) and per-capita income with a range of socio- economic indicators, including health, education, life expectancy, infant mortality, birth and death rates, fertility rates, crime, drug usage and mental health.
· The Survey highlights that both economic growth – as reflected in the income per capita at the state level –and inequality (focus on redistribution) have similar relationships with socio-economic indicators which is different from that observed in advanced economies.
· Unlike in advanced economies, economic growth and alleviation of inequality (focus on redistribution) converge in terms of their effects on socio-economic indicators in India.
· Economic growth has a far greater impact on poverty alleviation than inequality (focus on redistribution).
· Given India’s stage of development, India must continue to focus on economic growth to lift the poor out of poverty by expanding the overall pie.
· Redistribution is only feasible in a developing economy if the size of the economic pie grows.
Model Question - Covid-19 pandemic has led to increase in inequality in India. With already large population below poverty line, is it prudent to focus on inequality rather than growth in India? Analyse.
Major Ports Authorities Bill 2020
In News
“Major Ports Authorities Bill 2020” has been passed by Parliament and is set to replace the Major Port Trusts Act, 1963 after the assent of President. It aims to address the various regulatory issues plaguing the port’s sector in India.
Rationale behind new Law
Rakesh Mohan led National Transport Development Policy Committee (2013) had observed that
· The current governance structure of major ports—the public service port model— lacks the potential to attract private capital and encourage competitiveness.
· There is need to transform the current port trusts into publicly-owned statutory landlord port authorities through a new law to impart functional and financial autonomy.
· The maritime states where these ports are located should be encouraged to have substantial shareholding in them to ensure their participation in the development, functioning and expansion of the ports.
· Committee recommended market pricing of port services also.
· These regulatory issue had led to inefficiencies in port’s operations as:
o Currently, the vessel & container-related charges at Indian ports are much higher than foreign ports. This adds to the cost of logistics of the country.
o Longer turnaround time and low output per ship berth and lack of adoption of advanced technologies also plagues the ports in India.
o Higher costs at major ports such as JNPT lead to ripple effect as non-major ports use these costs as a benchmark for their own tariffs, thus resulting in higher tariffs. This adds to the overall cost of logistics of the country.
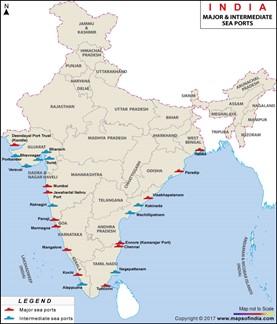
The Salient Features of the Bill:
· Applicability: The new law will supersede a 1963 Act governing the country’s 12 major ports.
· Major Port Authorities Board: The Bill proposes to create a simplified composition of Board of Major Port Authority, for each major port. These Boards will replace the existing Port Trusts under the 1963 Act.
· Composition of Board: The Board will comprise of a Chairperson and a Deputy Chairperson, to be appointed by the central government on the recommendation of a selection committee.
o Further, it will include one member each from (i) Concerned State Government (ii) Ministry of Railways (iii) Ministry of Defence (iv) Customs Department.
o The Board will also include two to four independent members, two members representing the interests of the employees of the Major Port Authority, and one member not below the rank of Director (nominated by the Central Government).
· Powers of the Board: The Boards of Port Authority have been delegated full powers to enter into contracts, planning and development, fixing of tariff except in national interest, security and emergency arising out of inaction and default.
· Adjudicatory Board: The Bill proposes to constitute an Adjudicatory Board, to be appointed by the Central Government, to replace the existing Tariff Authority under the 1963 Act.
· Provision of CSR by Port Authority have been introduced.
Concerns related to the bill
· It does not provide adequate representations to the State Governments where the ports are situated, to the employees of the ports and the labour working there in the composition of the board.
· There is no clarity with respect to the Selection Committee that will appoint the Chairperson to the Adjudicatory Board is concerned.
Reforms done with the new act
· Simplified to promote the expansion of port infrastructure and facilitate trade and commerce.
· Aims at decentralizing and transparent decision making and infuse professionalism in governance of major ports.
· The Bill is aimed at reorienting the governance model in central ports to landlord port model in line with the successful global practice bringing transparency in operations of Major Ports.
· It will assist in market-determined fixation of tariff rather than regulated tariff which will help boost investment in the sector, thus be beneficial for the stakeholders, customers and end-users.
Conclusion
Maritime trade contributes over 95% of trade by volume and over 70% by value in India. India plays a prominent role in global maritime trade due to its strategic location and accounts for only 2.1% of global trade. While India has 204 ports, 55% of the cargo traffic is handled by the 12 major ports. Thus, reforms brought by the bill are significant in improving efficiency and increasing India’s share in global trade.
National Beekeeping & Honey Mission
- It is to promote holistic growth of beekeeping industry for income & employment generation for farm and non-farm households.
- To enhance agriculture/ horticulture production, developing infrastructural facilities, including setting up of Integrated Beekeeping Development Centre (IBDC), honey testing labs, bee disease diagnostic labs, nucleus stock, bee breeders, etc.
- Empowerment of women through beekeeping for their financial independence.
- To create awareness about scientific bee keeping, post-harvest management of beekeeping etc.
Pangong Tso Lake - Edukemy Current Affairs
- It is a long narrow, deep, endorheic (landlocked) lake situated at a height of more than 14,000 ft in the Ladakh Himalayas.
- Extending to almost 160km, one-third of the Pangong Lake lies in India and the other two-thirds in China. The Line of Actual Control passes through the lake.
- The brackish water lake freezes over in winter and is in the process of being identified under the Ramsar Convention as a wetland of international importance. This will be the first trans-boundary wetland in South Asia under the convention.
National Beekeeping & Honey Mission (NBHM)
· It is to promote holistic growth of beekeeping industry for income & employment generation for farm and non-farm households.
· To enhance agriculture/ horticulture production, developing infrastructural facilities, including setting up of Integrated Beekeeping Development Centre (IBDC), honey testing labs, bee disease diagnostic labs, nucleus stock, bee breeders, etc.
· Empowerment of women through beekeeping for their financial independence.
· To create awareness about scientific bee keeping, post-harvest management of beekeeping etc.
Pangong Tso Lake - Edukemy Current Affairs
· It is a long narrow, deep, endorheic (landlocked) lake situated at a height of more than 14,000 ft in the Ladakh Himalayas.
· Extending to almost 160km, one-third of the Pangong Lake lies in India and the other two-thirds in China.The Line of Actual Control passes through the lake.
· The brackish water lake freezes over in winter and is in the process of being identified under the Ramsar Convention as a wetland of international importance. This will be the first trans-boundary wetland in South Asia under the convention.
How tech can transform law enforcement – Hindustan Times
Essence
In India, the police to population ratio is less than 150 per 100,000. Whereas the United Nations recommends 222 police officials per 100,000 residents. In this context, there is an urgent need for law enforcement agencies (LEAs) to adopt technology in their operations as it can act as a force multiplier.
Why you should read this article?
- Identifies the areas where technology can increase the efficiency and effectiveness of LEAs – digitizing citizen-facing services, crime detection and prevention, improving internal efficiency and real-time integration.
- Elaborates upon the above identified areas and provides relevant insights that for in-depth understanding.
Link
https://www.hindustantimes.com/opinion/how-tech-can-transform-law-enforcement-101613053457914.htmlWTO and its role in reducing the economic shock of the pandemic – ORF
Essence
When world was hit by COVID pandemic & there was desperate need of coordination to provide secure and predictable access to essential goods, WTO served as a constructed focal point.
Why you should read this article?
- To understand the need of right policy framework across different nations in time of world crises.
- To know about steps taken by WTO for aiding countries in absorbing pandemic blow.
- To know why export ban restrictions by some countries could’ve been counterproductive for steps taken against COVID spread.
- To understand application of WTO pacts like GATT & TRIPS during pandemic.
Link
https://www.orfonline.org/expert-speak/wto-its-role-reducing-economic-shock-pandemic/What explains the Budget’s fiscal stance? – Business Standard
Essence
The article throws light on the change in fiscal stance of the government as indicated in the budget. While it was expected that government would return to the path of fiscal consolidation, it chose to go for providing stimulus and spread it over two or more years. This was done in the background of higher than expected fiscal deficit. The article argues that shortfall in revenues seems to have been the deciding factor. An increase in taxes or cut in expenditure would have derailed the ongoing economic recovery.
Why you read this article?
- To understand the arguments that have been made by the government behind the change in fiscal stance. Those arguments include – shift in expenditure in favour of capital expenditure, growth fueled by higher capital expenditure will take care of the fiscal deficit and old fiscal limits are not valid in new world of reforms.
- The article analyses each one of the arguments put forward by the government in detail. It also has points that the government can keep an eye out for going forward.
Link
https://www.business-standard.com/article/opinion/what-explains-the-budget-s-fiscal-stance-121021102114_1.htmlHow tech can transform law enforcement – Hindustan Times
Essence - In India, the police to population ratio is less than 150 per 100,000. Whereas the United Nations recommends 222 police officials per 100,000 residents. In this context, there is an urgent need for law enforcement agencies (LEAs) to adopt technology in their operations as it can act as a force multiplier.
Why you should read this article?
· Identifies the areas where technology can increase the efficiency and effectiveness of LEAs – digitizing citizen-facing services, crime detection and prevention, improving internal efficiency and real-time integration.
· Elaborates upon the above identified areas and provides relevant insights that for in-depth understanding.
Link - https://www.hindustantimes.com/opinion/how-tech-can-transform-law-enforcement-101613053457914.html
WTO and its role in reducing the economic shock of the pandemic – ORF
Essence – When world was hit by COVID pandemic & there was desperate need of coordination to provide secure and predictable access to essential goods, WTO served as a constructed focal point.
Why you should read this article?
· To understand the need of right policy framework across different nations in time of world crises.
· To know about steps taken by WTO for aiding countries in absorbing pandemic blow.
· To know why export ban restrictions by some countries could’ve been counterproductive for steps taken against COVID spread.
· To understand application of WTO pacts like GATT & TRIPS during pandemic.
Link - https://www.orfonline.org/expert-speak/wto-its-role-reducing-economic-shock-pandemic/
What explains the Budget’s fiscal stance? – Business Standard
Essence–The article throws light on the change in fiscal stance of the government as indicated in the budget. While it was expected that government would return to the path of fiscal consolidation, it chose to go for providing stimulus and spread it over two or more years. This was done in the background of higher than expected fiscal deficit. The article argues that shortfall in revenues seems to have been the deciding factor. An increase in taxes or cut in expenditure would have derailed the ongoing economic recovery.
Why you read this article?
· To understand the arguments that have been made by the government behind the change in fiscal stance. Those arguments include – shift in expenditure in favour of capital expenditure, growth fueled by higher capital expenditure will take care of the fiscal deficit and old fiscal limits are not valid in new world of reforms.
· The article analyses each one of the arguments put forward by the government in detail. It also has points that the government can keep an eye out for going forward.
Forest Produce Tracking System: Facilitating resource management from Source to Sink
- Prior to Forest Produce Tracking System (FPTS), Karnataka Forest Department had a manual system to manage and regulate the extraction of natural resources such as timber, minerals and firewood.
- Manual System was very time consuming, was ineffective in monitoring and regulation, has rampant corruption.
- FPTS is India’s first end-to-end online system for tracking forest produce.
- It represents a radical shift in the approach toward Transit Management as User Departments have access to all the data on a single, simplified dashboard.
- FPTS automatically tracks a voluminous number of transactions, handling approximately 4,000–5,000 Transit Passes issued daily.
- This has empowered Tribal Population, streamlined the process and has reduced corruption.
Forest Produce Tracking System: Facilitating resource management from Source to Sink
· Prior to Forest Produce Tracking System (FPTS), Karnataka Forest Department had a manual system to manage and regulate the extraction of natural resources such as timber, minerals and firewood.
· Manual System was very time consuming, was ineffective in monitoring and regulation, has rampant corruption.
· FPTS is India’s first end-to-end online system for tracking forest produce.
· It represents a radical shift in the approachtoward Transit Management as User Departments have access to all the data on a single, simplified dashboard.
· FPTS automatically tracks a voluminous number of transactions, handling approximately 4,000–5,000 Transit Passes issued daily.
· This has empowered Tribal Population, streamlined the process and has reduced corruption.
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.