Tuesday, 9th February 2021
41.75 accounts opened under Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana
In News
Government mentioned that a total number of 41.75 crore accounts have been opened by Public Sector Banks, including Regional Rural Banks and major Private Sector Banks.
About Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana
· It is a financial inclusion programme of the Government of India (launched in 2014) that aims to expand affordable access to financial services such as bank accounts, remittances, credit, insurance and pensions.
· Accounts opened under PMJDY are Basic Savings Bank Deposit (BSBD) accounts. As per RBI, banks are required to offer the following minimum banking facilities, free of charge, without any requirement of minimum balance:
o Deposit of cash at bank branch as well as ATMs/CDMs
o Receipt/ credit of money through any electronic channel or by means of deposit /collection of cheques drawn by Central/State Government agencies and departments
o No limit on number and value of deposits that can be made in a month
o Minimum of four withdrawals in a month, including ATM withdrawals
o ATM Card or ATM-cum-Debit Card
HC strikes down SEC order confining Minister to home
In News
Andhra Pradesh State Election Commissioner had ordered that a State Minister be confined to his residence to prevent him from vitiating the process of gram panchayat elections.
Powers of the State Election Commissioner in this regard
The SEC, in its order, has declared that it was invoking its plenary power under Article 243K of the Constitution and directing the DGP to confine the Minister to his residential premises until the completion of the local elections.
About the State Election Commission
● The SEC has the power of superintendence, direction and control of the preparation of electoral rolls for, and the conduct of all elections to the Panchayats and Municipalities.
● In the Kishan Singh Tomar vs Municipal Corporation of the City of Ahmedabad case, the SC directed that state governments should abide by orders of the SECs during the conduct of the panchayat and municipal elections, just like they follow the instructions of the EC during Assembly and Parliament polls.
FSSAI caps trans fatty acids in all oils & fats
In News
The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has announced that all edible refined oils, vanaspati, bakery shortening, margarines, vegetable fat spreads and mixed fat spreads may only contain up to 3 per cent trans fats by January 2021 and 2 per cent or less trans fats by January 2022.
Context
· The move is a step by FSSAI towards fulfilling its commitments made in 2018 to reduce trans-fats in both edible oils and in all foods.
· World Health Organisation (WHO) had called for global elimination of trans fat by 2023. It released a REPLACE action package in 2019 to support country actions, including a live policy tracking map – the TFA Country Score Card 1 – to monitor global progress towards the 2023 target.
· Sustainable Development Goal 3, target (3.4) calls to reduce by one third, premature mortality from non-communicable diseases (NCDs) by 2030.
Effects of trans fatty acids on Human health
· Industrially produced trans fatty acid is a toxic chemical that clogs our arteries and is a risk factor for heart attack and other diseases.
· Intake of trans fatty acid increases bad cholesterol or LDL while decreasing good cholesterol or HDL in the body. LDL or low density cholesterol is dangerous because it can penetrate through the protective layer of arteries and start building up plaque on the arterial walls.
· Consumption of industrially produced Trans fatty Acids (TFAs) is estimated to cause around 500,000 deaths globally and 75, 000 deaths in India every year due to coronary heart disease.
Srivilliputhur–Megamalai Tiger Reserve in TN approved
In News
The Central government has given its approval for the creation of a fifth tiger reserve in Tamil Nadu that will encompass the Meghamalai and Srivilliputhur Wildlife Sanctuaries.
|
Srivilliputhur Wildlife Sanctuary: · It is also known as the Grizzled Squirrel Wildlife Sanctuary (GSWS). · It was established with the objective of protecting the Near threatened grizzled giant squirrel. Megamalai Wildlife Sanctuary: · It is located in the Western Ghats in the state of Tamil Nadu. · It is famous for the Nilgiri Tahr, Lion-tailed Macaque, Great Indian Hornbill etc. · Wood snake is “point endemic” to Megamali Wildlife Sanctuary i.e. it is only found in that sanctuary and nowhere else. · Vaigai river originates from the top of Varusandu range of the sanctuary. |
Tiger Reserves in Tamil Nadu
· Mudumalai Tiger Reserve
· Anamalai Tiger Reserve
· Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve
· Kalakkad Mundanthurai tiger reserve
Public Financial Management System
● The Public Financial Management System (PFMS), earlier known as Central Plan Schemes Monitoring System (CPSMS), is a web-based online software application developed and implemented by the Office of Controller General of Accounts (CGA), Ministry of Finance.
● The primary objective is establish an efficient fund flow system as well as a payment cum accounting network.
● PFMS provides various stakeholders with a real time, reliable and meaningful management information system and an effective decision support system, as part of the Digital India initiative.
● PFMS is integrated with the core banking system in the country.
Shahtoot Dam
● The dam is expected to be built on the Maidan river, tributary of Kabul river in Afghanistan.
● The dam will provide potable water to residents of Kabul and irrigate about 400 hectares of land.
● Pakistan had earlier expressed reservations about the project and claimed that the dam will restrict water flow to Pakistan’s Khyber Pakhtunkhwa region.
● India and Afghanistan could sign a pact this week for the construction of this dam.
Special Series – Budget, Survey and Finance Commission
Topic 4 - Growth vs Debt Sustainability
Context - COVID-19 induced recession has forced government agencies globally to spend at an unprecedented level contributing to the outstanding debt. Thus, question arises whether Government should focus on making the debt sustainable or focus on more growth.
Measurement of Debt levels
· Debt-to-GDP ratio (debt level divided by GDP of the country) is a useful measure which helps in analysis the debt level of a country.
· The evolution of debt is essentially a function of three variables: The primary deficit (fiscal deficit net of interest payments) and the relationship between nominal GDP growth and the government’s cost of borrowing.
Importance of Debt Sustainability
· Debt-to-GDP ratio greater than 77% can negatively affect growth of a nation in the long run, according to the World Bank.
· Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Act states that the government should maintain a debt-to-GDP ratio at 60% except in extreme situations.
· Too much of external debt can cause considerable damage, especially in countries with limited foreign reserves who could find it hard to repay in the future.
· When a nation borrows with prudence and uses the funds to build efficient infrastructure, it improves its capacity to grow at a faster rate.
The confusion about causality – from growth to debt sustainability or vice-versa
Argument supporting higher debt leading to lower growth: (focus on debt sustainability)
· Higher levels of public debt are accompanied by more taxes in the future to pay for the debt, thereby leading to lower lifetime wealth, which may decrease consumption and savings, eventually resulting in lower aggregate demand and growth rates.
· Higher incremental debt to lower growth rate is based on potential crowding out of private investment as well.
Argument supporting higher debt leading to Higher growth: (Prefer growth over debt sustainability)
· For emerging economies such as India, an increase in public expenditure in areas that boost private sector’s propensities to save and invest, may enable private investment rather than crowding it out.
Factors for sustainable debt
· As per the economic survey, “If the interest rate paid by the government is less than the growth rate, then intertemporal budget constraint (like FRBM) facing the government no longer binds.”
· This phenomenon highlights that debt sustainability depends on the “interest rate growth rate differential” (IRGD), i.e., the difference between the interest rate and the growth rate in an economy. A negative IRGD thus creates an enabling environment for debt sustainability.
Structure of India’s Debt
· India’s overall debt levels as a per cent of GDP are the lowest amongst the group of G-20, OECD countries and also among the group of BRICS nations.
· The Government’s debt portfolio is characterized by very low foreign exchange risk as the external debt is only 2.7 per cent of GDP (5.9 per cent of total Central Government liabilities).
· Of the total public debt, 70 per cent is held by the Centre.
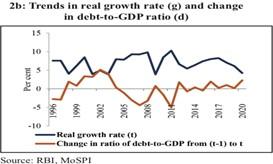
Why India should choose the growth over debt sustainability?
· As a norm in India, over the last two and a half decades, GDP growth rates have been greater than interest rates.
· Higher GDP growth leads to lower public debt through the increase in the denominator, i.e., GDP and it is a higher growth that provides the key to the sustainability of debt for India.
· As per the survey even at high primary deficits, low real growth and high nominal interest rates, India’s debt will remain sustainable.
Model Question - What is the importance of debt sustainability? Explain the rationale behind India choosing the path of growth over debt sustainability. (GS3- Topic- Budgeting)
Topic 5 - Climate Risk Insurance (CRI)
Context - Economic Survey 2020-21 (Vol 2 Chapter 6) recommends the need for Climate Risk Insurance to mitigate the harmful impacts of climate and climate change induced vulnerability.
What is Climate risk insurance (CRI)?
CRI is a facilitative mechanism which provides effective and expeditious post-disaster financial support at an individual, community, national and regional level against the loss of assets, livelihoods and lives due to climate-related risks.
Need for CRI
Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) predicts the risks associated with climate change and extreme weather events will further increase with rising temperatures. Moreover, the adverse effects of climate change are not evenly distributed across the world because of differing exposures, vulnerabilities, and coping capabilities.
· India specific need for CRI: Some facts on India’s vulnerability and losses
o As per the Global Climate Risk Index, in 2018, India lost US$ 37 billion due to climate events.
o India’s 68% area is vulnerable to droughts, over 7500 km long coastline is vulnerable to cyclones and sea level rise, and the Gangetic-Brahmaputra Valley is flood prone.
o Urban flood has become recurrent. In 2015, Chennai’s record-breaking 272 mm rainfall in 12 hours affected over 10 thousand MSMEs and caused around $250 million in damage.
o As per ILO’s study, India would lose 5.8% of its working hours by 2030 due to heat stress with Agriculture and Construction being the worst affected sectors.
· Why poor need CRI?
o They work in sectors that are most affected by natural hazards (e.g., agriculture).
o Without access to formal protection schemes they often resort to a variety of coping strategies (e.g., selling assets, reducing food consumption, taking children out of school, or borrowing) during a crisis.
o They lose more in the occurrence of an extreme weather event. They are least able to prevent, cope with and adapt to extreme weather events.
|
CONTRIBUTION OF CLIMATE RISK INSURANCE |
DETERMINANTS OF RESILIENCE |
|
|
CATALYZING |
· Risk assessment |
ANTICIPATE |
|
PROTECTING |
· Improving financial liquidity after a disaster · Reducing distress asset sales · Increasing food security |
ABSORB |
|
PROMOTING |
· Increasing savings, productivity & investment in higher return activities |
ADAPT |
|
SPURRING TRANSFORMATION |
· Incentivizing risk reduction behavior · Fostering culture of prevention-focused risk management |
|
Progress in respect of CRI
· The Sendai Framework, Paris Agreement and the Warsaw International Mechanism for Loss and Damage, all highlight the importance of mechanisms for disaster risk transfer and insurance.
· Climate Risk Insurance Initiative (InsuResilience) announced by G7 in 2015.
· PM Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY) has the insurance for crop destruction on account of natural hazards.
Hindrances in making CRI popular in India
· Agriculture: Insurance in Indian agriculture is challenging because of
a. Small and scattered landholdings, varying climatic and soil conditions and variety of agricultural practices, Widespread lack of knowledge about nature and functions of crop insurance.
b. Example: Weather index insurance for agriculture introduced in 2003 suffered from complex processes, moral hazard, adverse selection, and low penetration of institutional credit.
· Infrastructure:
a. Lack of integration of climate concerns in land use planning and project planning.
b. Non-compliance of infrastructure projects with national guidelines and lack of adequate by-laws lead to ambiguity and lack of legal basis for insurance. E.g., slum dwellers lack legal documents to claim insurance.
· Poverty: Cost is a prime factor as most of poor cannot afford to pay premiums for insurance.
Way Forward
Following principles for benefiting the poor and vulnerable with CRI can be utilised-
|
Principles for Climate Risk Insurance |
|
|
Comprehensive Needs-Based Solutions |
Solutions to protect the poor and vulnerable from extreme weather events must be tailored to local needs and conditions. |
|
Client Value |
Providing reliable coverage that is valuable to the insured is crucial for take-up of insurance products. |
|
Affordability and Accessibility |
Efficient and cost-effective delivery channels aligned with the local context are needed. |
|
Participation, Transparency & Accountability |
Successful insurance schemes are based on the inclusive, meaningful and accountable involvement of (potential) beneficiaries in the design, implementation and review of insurance products. |
|
Sustainability |
Safeguarding economic, social and ecological sustainability. |
Model Question - India’s vulnerability and losses due to climate induced hazards underscore the need for investment in building resilience and adoption of policies for mainstreaming risks through building appropriate social protection systems. In this context discuss the challenges and opportunities for Climate Risk Insurance in India.
The long and the short of India’s Naypyitaw dilemma – The Hindu
Essence- Editorial is written in backdrop of recent coup in Myanmar, which has created need to relook on comfortable space that New Delhi’s Myanmar policy occupied for close to a decade
Why you should read this article?
· To understand whether we need to look at this coup as something which backtracked the work done in India Myanmar ties or we can manoeuvre India’s interests.
· To know past India’s relationship dynamics with Former state counsellor Aung San suu kyi & military generals.
· To understand China’s angle & impact west sanctions on Myanmar.
· It is also providing account, on how these changes are going to impact Rohingya issue.
On the farm bills: Farmers forming cooperatives will be able to negotiate better prices on their produce - TOI
Essence - This article analyses the differences between the farmers belonging to the states such as in south India, northeast and east India, and those belonging to Punjab, Haryana and western Uttar Pradesh, with respect to important matters of farm laws such as the dissolution of the mandis, possible withdrawal of minimum support price, and entry of corporates in farms.
Why should you read this editorial?
· Data/facts related to small and marginal farmers.
· Reasons why small and marginal farmers in most of the states are debt ridden.
· Need for interlinkages and creation of an efficient supply chain by developing a closely knit network of farmers through cooperatives.
Panchayat Banks: Pragya Kendra’s providing banking facilities at the village level in Jharkhand
• The strategy was ‘One Block, One Bank’ for streamlined payments.
• It is a key initiative under Lead Bank Scheme which aim to promote financial inclusion.
• It has improved access to a range of services provided by government such as Pensions, Scholarships and MGNREGA wage payments
• It has promoted creation of local entrepreneur for self-sustainability.
• It has reduced the need of travelling long distances and prevented loss of time.
• Also, it led to reduction of systemic leakages, reduced petty corruption and increased transparency in accessing government benefits.
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.