Friday, 5th February 2021
Lithium Discovered in India (Business World)
In news
The Government in a written reply to Lok Sabha said that the preliminary surveys have shown presence of lithium deposits of 1,600 tonnes in Mandya district of Karnataka.
Importance of Discovery
· With increasing focus on renewable energy, sustainable batteries are a gaining traction as a viable alternative to conventional, fuel run batteries.
· The growing demand for Lithium in India is driven by the goal of Indian government to increase the number of electric vehicles by 30 percent by 2030.
· India is spending a considerable amount of money on Lithium import, which acts as a drain to the Forex.
Uses of Lithium
· Lithium is a key element for new technologies and finds its use in ceramics, glass, telecommunication and aerospace industries.
· Lithium is also used in psychiatric medications and in dental imprints.
· The well-known uses of lithium are in lithium ion batteries, lubricating grease, high energy additives to rocket propellants, optical modulators for mobile phones and as a converter to tritium used as a raw material for thermonuclear reactions i.e. fusion.
Other Steps taken by India
· KhanijBidesh India Limited had got into an agreement with an Argentinian firm to jointly prospect lithium in Argentina. The company has the specific mandate to acquire strategic mineral assets like lithium and cobalt abroad.
· India’s first Lithium plant has been set up at Gujarat in 2021. The refinery will use Lithium ore to produce base battery material. India currently relies on other nations like China, Japan, and Taiwan for its electric battery supply.
· TATA is working on 100% made in India Li-ion batteries for Electric mobility and Energy Storage Systems.
· India and Australia have signed an agreement with respect to Lithium trade in 2019.
Note: Bolivia is the leading producer with 2.10 crore tonnes lithium reserves, and Argentina is second largest with 1.7 crore tonnes reserves of lithium.
Centenary anniversary of the Chauri Chaura incident (PIB)
In news
Prime Minister inaugurated the Chauri Chaura Centenary Celebrations at Chauri Chaura, Gorakhpur, Uttar Pradesh. Prime Minister also released a postal stamp dedicated to the Chauri Chaura centenary during the event.
Chauri Chaura Incident
· On 2 February 1922, Non-cooperation Movement was led by a retired Army soldier BhagwanAhir against high food prices and liquor sale. The protestors were beaten by the local police and several leaders were imprisoned at the Chauri Chaura police station.
· In response to this incident, on 4 February 1922,a group of protestors gathered in front of the local police station, demanding the release of their leader and clashed with police.
· To control the situation, the sub-inspector in charge ordered the police to open fire on the advancing crowd-- killing three and injuring others.
· In the ensuing chaos, angry mob advanced and set the police station ablaze, killing all of its occupants. The incident resulted in the death of 22 policemen.
· In view of this incident, Martial law was imposed by the British administration in and around the Chauri Chaura area.
· On 12 February 1922, reacting upon the incident, Mahatma Gandhi halted the non-cooperation movement at the national level. In connection with the incident, Mahatma Gandhi was also arrested and sentenced to six years of imprisonment. However, he was later released on grounds of ill health in February 1924.
Link - https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1694344
Corpus for Micro Irrigation Fund is proposed to be doubled (PIB)
In News
Budget announcement has been made to double the initial corpus of Micro Irrigation Fund of Rs. 5000 created under NABARD, by augmenting it by another Rs. 5,000 crores. Micro Irrigation is a component of the Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana which has the objective of ‘more crop per drop.’
About Micro Irrigation
Micro irrigation is defined as the frequent application of small quantities of water directly above and below the soil surface; usually as discrete drops, continuous drops or tiny streams through emitters placed along a water delivery line.
Importance of Micro Irrigation:
· Improves on-farm water use efficiency
· Enhances crop productivity
· Ensures better returns to farmers due to reduced labour cost and fertilizer use
· Generates employment opportunities
Objective of the Micro Irrigation Fund
· Facilitate the States in mobilizing the resources to provide additional incentives to farmers for adopting micro irrigation practices.
· States may also access MIF exclusively for innovative integrated projects like high water duty crops (like solar linked systems, including projects in PPP mode.
· The central government provides 3% interest subvention on loans extended to the State Government under MIF.
Link - https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1695228
Special Series - Budget, Survey and Finance Commission
Topic 2 - Government announced the Disinvestment Policy in the Budget.
|
Highlights of Disinvestment/Strategic Disinvestment Policy Objectives a. Minimising presence of Central Government Public Sector Enterprises including financial institutions and creating new investment space for private sector b. Post disinvestment, economic growth of Central Public Sector Enterprises (CPSEs)/ financial institutions will be through infusion of private capital, technology and best management practices. c. Will contribute to economic growth and new jobs. d. Disinvestment proceeds to finance various social sector and developmental programmes of the government. Policy features a. Policy covers existing CPSEs, Public Sector Banks and Public Sector Insurance Companies. b. Various sectors will be classified as strategic and non-strategic sectors. c. The strategic sectors have been classified in four broad baskets: i) Atomic energy, Space and Defence (national security) ii) Transport and Telecommunications (critical infrastructure) iii) Power, Petroleum, Coal and other minerals (energy and minerals) iv) Banking, Insurance and financial services (financial services) d. In strategic sectors, there will be bare minimum presence of the public sector enterprises. The remaining CPSEs in the strategic sector will be privatised or merged or subsidiarized with other CPSEs or closed. e. In non-strategic sectors, CPSEs will be privatised, otherwise shall be closed. |
Other Budget announcements with regards to disinvestment
· The government has set a disinvestment target of Rs 1.75 lakh crore for 2021-22.
· This includes strategic sale of IDBI Bank, BPCL, Air India, among others.
· Besides IDBI Bank, the government would also privatise two public sector banks and one general insurance company in this financial year.
· Government also plans to bring the IPO of LIC along with minority share sale in other PSUs.
Basics
Disinvestment means the sale or liquidation of assets by the government, usually of Central and state public sector enterprises, projects, or other fixed assets. The government undertakes disinvestment to reduce the fiscal burden on the exchequer, or to raise money for meeting specific needs, such as to bridge the revenue shortfall from other regular sources.
Strategic disinvestment is the transfer of the ownership and control of a public sector entity to some other entity (mostly to a private sector entity). It includes both Majority Disinvestment and Complete Privatisation. Department of Investment and Public Asset Management (DIPAM) has been made the nodal department for the strategic stake sale in the Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs).
Different Approaches to Disinvestments:
· Minority Disinvestment: the government retains a majority stake in the company, typically greater than 51%, thus ensuring management control.
· Majority Disinvestment: Government, post disinvestment, retains a minority stake in the company i.e. it sells off a majority stake.
· Complete Privatisation: Complete privatisation is a form of majority disinvestment wherein 100% control of the company is passed on to a buyer.
Why Disinvest?
· Strategic disinvestment in India has been guided by the basic economic principle that the government should not be in the business to engage itself in manufacturing/producing goods and services in sectors where competitive markets have come of age.
· The economic potential of such entities may be better discovered in the hands of the strategic investors due to various factors, e.g. infusion of capital, technology up-gradation and efficient management practices etc.
· Disinvestment is aimed at reducing the financial burden on the government due to inefficient PSUs and to improve public finances.
· It introduces competition and market discipline and helps to depoliticise non-essential services as well as free up resources for government to focus on essential services like education and health.
Way Forward
· It needs to be ensured that Privatisation (Strategic Disinvestment) leads to greater competition in all cases.
· It should be ensured that the proceeds of such strategic sales aren’t frittered away in interest or salary pay-outs but are reinvested prudently in long-term infrastructure assets that can yield enduring returns to the economy.
· To allay concerns of cronyism, the strategic sale process needs to be fair and transparent with a minimum reserve price that does justice to the valuable assets being auctioned off. A third-party valuation of every PSU’s assets and a minimum number of bidders, should be necessary pre-conditions to going ahead with each sale.
Model Question – Mention some of the features of the recently announced Disinvestment Policy. Also, bring out the rationale behind opting for disinvestment.
India can be the net security provider in Indian Ocean Region: Rajnath (Business Standard)
In News
Defence Minister Rajnath Singh recently said that India can take on the role of being the net security provider in the Indian Ocean Region as geopolitically it is a reliable partner in the IOR.
What is meant by the term net security provider?
The term net security provider is usually meant as enhancing mutual security of more than one country by addressing common security concerns, including dealing with transnational piracy, or responding to disasters, etc. Specifically, it encompasses four different activities: (i) capacity building; (ii) military diplomacy; (iii) military assistance; and (iv) direct deployment of military forces to aid or stabilise a situation.
India’s current approach
● Modernisation of defence forces - Over the last decade or more India has spent a lot of money on modernising its defence forces. This includes buying aircraft carriers, submarines and aircraft that give it the ability to respond to security problems throughout much of the Indian Ocean region.
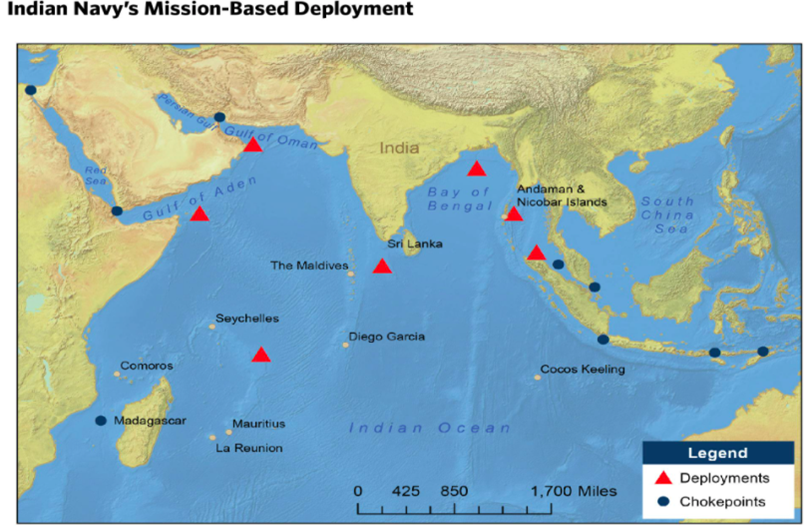
● Mission based deployment of the Indian Navy - The MBD concept deploys mission-ready ships at seven key locations in the IOR, overseeing all entry and exit points in the region. (see map below)
● Humanitarian assistance to the IOR countries - India has been one of the first responders in case of any natural disasters in the region.
|
Other initiatives in the IOR ● Security and Growth for all the Region (SAGAR): India seeks to deepen economic and security cooperation with its maritime neighbours and assist in building their maritime security capabilities ● Information fusion centre- Indian Ocean Region: To improve information sharing along the sea lanes of communication. ● Logistics agreements: Logistics agreements with France and USA to get access to important ports like Djibouti, Reunion Island etc. |
Factors that inhibit India from emerging as a net security provider
● Reluctance to be part of military alliances - India has not been comfortable with the idea of military alliances or even multilateral groupings under some dominant power. Moreover partnering exclusively with the United States is highly contentious in domestic politics and requires deft political handling. This factor explains to a large extent, Indian opposition to U.S. led initiatives or even bilateral issues emphasising interoperability including the Logistical Support Agreement.
● Performance and capacity of the Indian defence industry - India’s state owned defence industry has often been criticised for its products and its performance. A downturn in the Indian economy also affects its ability to invest in the military modernisation of partner countries.
Way ahead for India
● Improved information exchange - It must work out the modalities of sharing information with partner countries and using the available data. Delhi must work with the Regional Maritime Information Fusion Centre (RMIFC) hosted in Madagascar and the Information Fusion Centre (IFC) in Singapore.
● Ensure presence of Indian Navy at key locations - Indian presence at key locations such as the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, La Reunion, and Cocos Keeling would allow for effective monitoring and surveillance of key chokepoints. This presence is crucial in India’s quest to remain a leading power in the IOR.
● Other include – engaging with actors outside the traditional IOR, focusing on speedy completion of its commitments etc.
Reference Article - https://www.business-standard.com/article/current-affairs/india-can-be-the-net-security-provider-in-indian-ocean-region-rajnath-121020301779_1.html
British National Overseas (BNO) citizenship (Indian Express)
· It is a type of British nationality created in 1985 that people in Hong Kong could apply for before the 1997 handover to China to retain a link with the UK.
· The lifelong status, which cannot be passed down to family members, did not give holders any special rights.
· It meant only they could visit the UK for six months without a visa.
· But the new system, in place from 31 January 2021, allows these BNO citizens and their close family to apply for two periods of five years to live and work in the UK.
· After the first five years, they are able to choose to apply for indefinite leave to remain, which means an individual can live and work without reapplying for a visa.
· China in response has declared that it will “no longer recognize” the British National (Overseas) passport for Hong-Kongers.
Stardust 1.0 (Indian Express)
· Stardust 1.0 has become the first commercial space launch powered by biofuel, which is non-toxic and carbon neutral for the environment as opposed to traditionally used rocket fuels and was launched recently from Loring Commerce Centre in Maine, US.
· The rocket is manufactured by Maine-based aerospace company bluShift.
· It can carry a maximum payload mass of 8kg and during its first launch carried three payloads.
· It reached a height of 1,219 metres in the space before parachuting back to Earth.
· These rockets will help to launch small satellites called cubesats into space.
India-China economic ties: Impact of Galwan - ORF
Essence- As we go through current trade scenario, it gets clear that the nationalistic notions of bringing China to its knees — by boycotting Chinese goods — has not been fruitful. India-China economic ties are so intertwined that historical animosities and border disputes though crucial but passes onto back seat of this relationship drive.
Why you should read this article?
· To know about attempts that have been made to reduce the India-China trade deficit.
· To get fodder on areas where Indian industries & their export is dependent on China’s inputs like India’s pharmaceutical industry for which 2/3rds of its key ingredients come from China.
· To understand sector wise impact on Indo-China trade due to lockdown &Galwan valley issue.
· It also cover steps taken by govt. to support AatmaNirbhar Bharat - mandated all products to have the Country of Origin tag for products on the Government e-Marketplace, specifically restricting Chinese companies in several sectors and networks import from China citing cyber and security threats.
Link - https://www.orfonline.org/expert-speak/india-china-economic-ties-impact-galwan/
DharaVikas: Ensuring Water Security through Spring-shed development in Sikkim
· Nearly 80% of the Sikkim’s rural households depend on springs for drinking water and irrigation
· To ensure water security, Government of Sikkim has conceptualised DharaVikas initiative
· It is innovative programme to revive and maintain drying springs in Sikkim by spring-shed development, developing a Village Spring Atlas and a Water Source Atlas for the state.
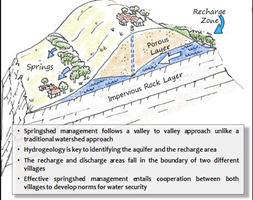
· It allows more water to percolate down to recharge underground aquifers.
· It has helped to alleviate the problem of rural water scarcity by reducing surface runoff of rainwater.
· It has significant impact on crop patterns and yields and has improved sanitation practices within the state.
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.