Wednesday, 3rd February 2021
15th Finance Commission for 2021-26
It recommended that 41% of the net proceeds of union taxes be devolved to states in FY21. The Fourteenth Finance Commission had increased the devolution to states by 10 percentage points to 42%
Devolution Criteria: The Commission has used 2011 population data for determining the share of states during its entire award period. To reward efforts made by states in controlling their population, the Commission has used the Demographic Performance criterion. States with a lower fertility ratio will be scored higher on this criterion.
|
Criteria |
14th FC 2015-20 |
15th FC 2020-21 |
15th FC 2021-26 |
|
Income Distance |
50.0 |
45.0 |
45.0 |
|
Area |
15.0 |
15.0 |
15.0 |
|
Population (1971) |
17.5 |
- |
- |
|
Population (2011)# |
10.0 |
15.0 |
15.0 |
|
Demographic Performance |
- |
12.5 |
12.5 |
|
Forest Cover |
7.5 |
- |
- |
|
Forest and Ecology |
- |
10.0 |
10.0 |
|
Tax and fiscal efforts* |
- |
2.5 |
2.5 |
|
Total |
100 |
100 |
100 |
Note: #14th FC used the term “demographic change” which was defined as Population in 2011. *The report for 2020-21 used the term “tax effort”, however, there is no difference in the definition of the criteria.
Funding of defence and internal security: A dedicated non-lapsable fund called the Modernisation Fund for Defence and Internal Security (MFDIS) will be constituted to primarily bridge the gap between budgetary requirements and allocation for capital outlay in defence and internal security. Of this some amount will be transferred from the Consolidated Fund of India. Rest of the amount will be generated from measures such as disinvestment of defence PSUs and monetisation of defence lands.
Grants-in-aid: The Commission has recommended grants from the centre to states and local bodies worth Rs 10.3 lakh crore for the 2021-26 period. These include:
· Revenue deficit grants to 17 states: The Commission has recommended Grants-in-aid of revenues of States for revenue deficit.
· Grants to urban and rural local bodies: The Commission has recommended basing the inter-se distribution of grants for local bodies among the States, on population and area in the ratio of 90:10.
· Disaster management grants: The Commission has recommended allocation of disaster management funds to SDRMFs should be based on factors of past expenditure, area, population, and disaster risk index (which reflect States' institutional capacity, risk exposure, and hazard and vulnerability respectively).
· The Commission has recommended providing grants to State Governments in eight different sectors, namely health, school education, higher education, agriculture, maintenance of PMGSY roads, aspirational districts and blocks, judiciary, statistics.
· certain state-specific grants have also been provided.
Fiscal consolidation: Extra annual borrowing worth 0.5% of GSDP will be allowed to states during 2021-25 for undertaking power sector reforms. It recommended forming a high-powered inter-governmental group to: (i) review the fiscal responsibility legislation (FRBM Act), (ii) recommend a new fiscal responsibility framework and oversee its implementation.
FC suggested following glide path for fiscal deficit for the central government.
|
|
2020-21 |
2021-22 |
2022-23 |
2023-24 |
2024-25 |
2025-26 |
|
Fiscal Deficit |
7.4% |
6.0% |
5.5% |
5.0% |
4.5% |
4.0% |
|
Revenue Deficit |
5.9% |
4.9% |
4.5% |
3.9% |
3.3% |
2.8% |
|
Outstanding liabilities |
62.9% |
61.0% |
61.0% |
60.1% |
58.6% |
56.6% |
Union Budget 2021-22: Summary
Theme of the budget: A vision for AtmaNirbhar Bharat.
It rest on 6 pillars.
1. Health and Wellbeing
Taking holistic view,focus is on strengtheningthree areas: Preventive, Curative, and Wellbeing.
Health Systems:
· A new centrally sponsored scheme, PM Atma Nirbhar Swasth Bharat Yojana, will be launched to develop capacities of primary, secondary, and tertiary careHealth Systems, strengthen existing national institutions, and create newinstitutions, to cater to detection and cure of new and emerging diseases.This will be in addition to the National Health Mission.
Nutrition:
· Supplementary Nutrition Programme and the Poshan Abhiyan will be merged to form new Mission Poshan 2.0, which shall adopt an intensifiedstrategy to improve nutritional outcomes across 112 Aspirational Districts.
Universal Coverage of Water Supply:
· Jal Jeevan Mission (Urban) will be launched. It aims at universalwater supply in all 4,378 Urban Local Bodies with 2.86 crores household tapconnections, as well as liquid waste management in 500 AMRUT cities. Itwill be implemented over 5 years.
Swachch Bharat, Swasth Bharat:
· Urban Swachh Bharat Mission 2.0 will focus on completefaecal sludge management and waste water treatment, source segregationof garbage, reduction in single-use plastic, reduction in air pollution byeffectively managing waste from construction-and-demolition activities andbio-remediation of all legacy dump sites.
Clean Air:
· To tackle the burgeoning problem of air pollution, special provision has been done for 42 urban centres with a million-pluspopulation in this budget.
Voluntary Vehicle Scrapping Policy:
· This will be launched to phase out old and unfit vehicles. This will help in encouraging fuelefficient, environment friendly vehicles, thereby reducing vehicularpollution and oil import bill.
Vaccines:
· The Pneumococcal Vaccine, a Made in India product, presentlylimited to only 5 states will be rolled out across the country. This will avertmore than 50,000 child deaths annually.
· 35,000 crores for Covid-19 vaccinehas also been provided in BE 2021-22.
2. Physical and Financial Capital and Infrastructure
Textiles:
A scheme ofMega Investment Textiles Parks (MITRA) will be launched in addition to thePLI scheme. This will create world class infrastructure with plug and playfacilities to enable create global champions in exports. 7 Textile Parks willbe established over 3 years.
Infrastructure: 3 ways to finance NIP
a. Infrastructure financing - Development Financial Institution (DFI)
· A sum of `20,000 croreshas been allocated to capitalise this institution. Proposed to have a lending portfolio of atleast `5 lakh crores for this DFI in three-year time.
b. Asset Monetisation
· A “NationalMonetization Pipeline” of potential brownfield infrastructure assets will belaunched. An Asset Monetization dashboard will also be created fortracking the progress and to provide visibility to investors. It will include highways, DFCs, Airports, transmission lines, pipelines and warehouses etc.
c. Sharp Increase in Capital Budget
· A sharp increase in capital expenditure which is 34.5% more than the BE of 2020-21. Over and above this expenditure, morethan 2 lakh crores to States and Autonomous Bodies for their CapitalExpenditure will be provided.
Railway Infrastructure
· Indian Railways have prepared a National Rail Plan for India – 2030.
· 100% electrification of Broad-Gauge routes will be completedby December, 2023.
· High density network andhighly utilized network routes of Indian railways will be providedwith an indigenously developed automatic train protection systemthat eliminates train collision due to human error.
Urban Infrastructure
· A new scheme tosupport augmentation of public bus transport services. The scheme willfacilitate deployment of innovative PPP models to enable private sectorplayers to finance, acquire, operate and maintain over 20,000 buses.
· Two newtechnologies i.e., ‘MetroLite’ and ‘MetroNeo’ will be deployed to providemetro rail systems at much lesser cost with same experience, convenienceand safety in Tier-2 cities and peripheral areas of Tier-1 cities.
Power Infrastructure
· A framework togive consumers alternatives to choose among manyDistribution Companies.
· Arevamped reforms-based result-linked power distribution sector schemewill be launched. Thescheme will provide assistance to DISCOMS for Infrastructure creationincluding pre-paid smart metering and feeder separation, upgradation ofsystems, etc., tied to financial improvements.
· Hydrogen EnergyMission in 2021-22 for generating hydrogen from green power sources.
Ports, Shipping, Waterways
· 7 projects will be offeredby the Major Ports on Public Private Partnership mode in FY21-22.
· A scheme to promote flagging of merchant ships in India will belaunched by providing subsidy support to Indian shipping companies inglobal tenders floated by Ministries and CPSEs.
Petroleum & Natural Gas
· Ujjwala Scheme will be extended to cover 1 crore more beneficiaries.
· 100 more districts to be added in next 3 years to the City GasDistribution network.
· An independent Gas Transport System Operator will be set up forfacilitation and coordination of booking of common carrier capacityin all-natural gas pipelines on a non-discriminatory open accessbasis.
Financial Capital
· Proposal to consolidate the provisions of SEBI Act, 1992,Depositories Act, 1996, Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act, 1956 andGovernment Securities Act, 2007 into a rationalized single SecuritiesMarkets Code.
· A system of regulated gold exchanges in the country will be established. For thispurpose, SEBI will be notified as the regulator and WarehousingDevelopment and Regulatory Authority will be strengthened to set up acommodity market eco system arrangement including vaulting, assaying,logistics etc. in addition to warehousing.
· Towards investor protection, introduction of an investorcharterwill be done as a right of all financial investors across all financial products.
Increasing FDI in Insurance Sector
· Insurance Act, 1938 will be amended to increase thepermissible FDI limit from 49% to 74% in Insurance Companies and allowforeign ownership and control with safeguards.
Stressed Asset Resolution by setting up a New Structure
· An Asset Reconstruction Company Limited and Asset Management Company wouldbe set up to consolidate and take over the existing stressed debt and thenmanage and dispose of the assets to Alternate Investment Funds and otherpotential investors for eventual value realization.
Company Matters
· Under the Companies Act, 2013for definition of Small Companies will be revised by increasing their thresholds for Paid up capital from“not exceeding `50 Lakh” to “not exceeding `2 Crore” and turnover from“not exceeding `2 Crore” to “not exceeding `20 Crore”.
· Incentives for incorporation of One PersonCompanies (OPCs) by allowing OPCs to grow without any restrictions onpaid up capital and turnover, allowing their conversion into any other typeof company at any time, reducing the residency limit for an Indian citizen toset up an OPC from 182 days to 120 days and also allow Non ResidentIndians (NRIs) to incorporate OPCs in India.
· Dataanalytics, artificial intelligence, machine learning driven MCA21 Version 3.0 will have additional modules for e-scrutiny, e-Adjudication,e-Consultation and Compliance Management.
Disinvestment and Strategic Sale
· Other than IDBI Bank, privatization of two Public Sector Banks and one General Insurance company in the year 2021-22 is proposed along with IPO of LIC.
· Policy of strategic disinvestment of public sector enterprisesprovides a clear roadmap for disinvestment in all nonstrategic and strategic sectors. Four areas have been kept that are strategic where bare minimum CPSEs will be maintained and rest privatized.
· The non-coreassets largely consist of surplus land with governmentMinistries/Departments and Public Sector Enterprises. Monetizing of landcan either be by way of direct sale or concession or by similar means. A SpecialPurpose Vehicle in the form of a company would carry out this activity.
Government Financial Reforms
· To further streamline the‘Ease of Doing Business’a separate Administrative Structure for Cooperatives will be set up.
3. Inclusive Development for Aspirational India
· SWAMITVAScheme: Under this, a record of rights is being given to property owners invillages. This will be extended to coverall states/UTs.
· Scope of ‘Operation Green Scheme’ that is presently applicableto tomatoes, onions, and potatoes, will be enlarged to include 22 perishableproducts.
· 1,000 more mandis will be integrated with e-NAM.
Fisheries
· To start with, 5 majorfishing harbours – Kochi, Chennai, Visakhapatnam, Paradip, and Petuaghat will be developed as hubs of economic activity.
· To promote seaweed cultivation, aMultipurpose Seaweed Park to be established in Tamil Nadu.
Migrant Workers and Labourers
· Launch of a portal that will collectrelevant information on gig, building, and construction-workers amongothers. This will help formulate Health, Housing, Skill, Insurance, Credit, andfood schemes for migrant workers.
Financial Inclusion
· To further facilitate credit flow under the scheme of Stand Up Indiafor SCs, STs, and women, reduction in the margin moneyrequirement from 25% to 15% has been done
4. Reinvigorating Human Capital
· More than 15,000 schools will be qualitatively strengthened toinclude all components of the National Education Policy.
· 100 new Sainik Schools will be set up in partnership with NGOs/private schools/states.
Higher Education
· In 9 cities, formal umbrella structures will be created so that academic institutions can have bettersynergy, while also retaining their internal autonomy.
· For accessible higher education in Ladakh, A Central University will be set up in Leh.
Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes Welfare
· A target of establishing 750 Eklavya modelresidential schools in the tribal areas.
Skilling
· Realignment of the existing scheme of National Apprenticeship Training Scheme(NATS) for providing post-education apprenticeship, training of graduatesand diploma holders in Engineering.
5. Innovation and R&D
· A scheme is proposed that will provide financial incentive to promotedigital modes of payment.
· A new initiative – National Language TranslationMission (NTLM) - To enable the wealth of governance and policyrelated knowledge on the Internet to be translated in Indianlanguages.
· The firstunmanned mission as a prelude to Gaganyan mission to be launched in December 2021.
· A Deep Ocean Mission which willcover deep ocean survey exploration and projects for the conservation ofdeep sea bio-diversity will be launched.
6. Minimum Government, Maximum Governance
· Further measures to rationalize thefunctioning of Tribunals.
· Tobring about transparency, efficiency and governance reforms in the nursingprofession, The National Nursing and Midwifery Commission Bill will beintroduced.
· To have ease of doing business for those who deal with Governmentor CPSEs, and carry out contracts, proposal to set up a ConciliationMechanism and mandate its use for quick resolution of contractualdisputes.
· For the welfare of Tea workersespecially women and their children in Assam and West Bengal, A specialscheme will be devised.
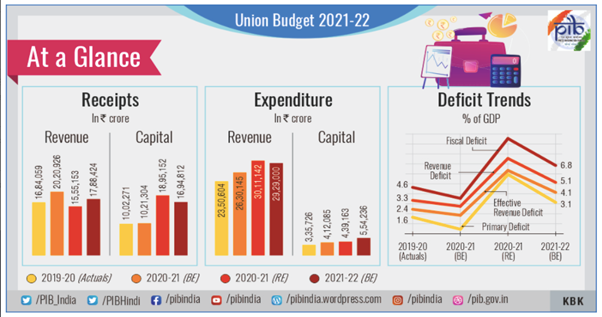
Fiscal Position
· The fiscal deficit in RE 2020-21 is pegged at 9.5% of GDP while in BE 2021-2022 it is estimated to be 6.8% of GDP.
· Path of fiscalconsolidation intend to reach a fiscal deficit level below 4.5% of GDP by2025-2026 with a fairly steady decline over the period.
· TheContingency Fund of India is being proposed to be augmented from `500crores to `30,000 crores through Finance Bill.
· Extra Budgetary Resources: discontinue the NSSF Loan to FCI for Food Subsidy and accordingly BudgetProvisions have been made in RE 2020-21 and BE 2021-22.
PART B
Direct Tax Proposals
Relief to Senior Citizens
· Senior citizens who are 75 years of age and abovewho only have pension and interest income, exemptionfrom filing their income tax returns.
Reduction in Time for Income Tax Proceedings
· Reductionin time-limit for re-opening ofassessment to 3 years from the present 6 years. In serious tax evasion casestoo, only where there is evidence of concealment of income of `50 lakh ormore in a year, can the assessment be re-opened up to 10 years. Even thisreopening can be done only after the approval of the Principal ChiefCommissioner, the highest level of the Income Tax Department.
Setting up the Dispute Resolution Committee
· To further reduce litigation for small taxpayers, a Dispute Resolution Committee will be constituted, which will be facelessto ensure efficiency, transparency and accountability. Anyone with a taxableincome up to `50 lakh and disputed income up to `10 lakh shall be eligibleto approach the Committee.
Faceless ITAT
· ANational Faceless Income Tax Appellate Tribunal Centre will be established. All communicationbetween the Tribunal and the appellant shall be electronic. Where personalhearing is needed, it shall be done through video-conferencing.
· To further incentivise digital transactions and reduce complianceburden,turnover limit for tax audit for persons will bechanged from`5 crore to `10 crore.
· Notified Infrastructure Debt Funds will be eligible to raisefunds by issuing tax efficient Zero Coupon Bonds.
Affordable Housing/Rental Housing
· Incentives such tax holiday for one more year and an additional deduction ofinterest, amounting to `1.5 lakh, for loan taken to purchase an affordablehouse.
· Notified Affordable Rental Housing Projects will continue to be allowed tax exemption.
Pre-filling of Returns
· To further ease filing of returns, details of capital gainsfrom listed securities, dividend income, and interest from banks, post office,etc. will also be pre-filled.
Relief to Small Trusts
· To reduce compliance burden on small charitable trustsrunning educational institutions and hospitals blanketexemption to such entities, whose annual receipt does not exceed`1 crorewill be increased to `5 crore.
Incentives for Start-ups
· Extension ofthe eligibility for claiming tax holiday for start-ups by one more year – till31st March, 2022. Further, in order to incentivise funding of the start-ups, extension of the capital gains exemption for investment in start-upsby one more year - till 31st March, 2022.
Indirect Tax Proposals
· For greater domestic valueaddition, customs duty on some parts of mobiles will move from ‘nil’rate to a moderate 2.5%.
· An AgricultureInfrastructure and Development Cess (AIDC) on a small number of items will be imposed.
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.



