Tuesday, 11th May 2021
Green panel allows Great Nicobar plan to advance
In News
The Environment Appraisal Committee that had earlier flagged concerns over the NITI Aayog’s Great Nicobar Plan, has now recommended it for grant of terms of reference.
|
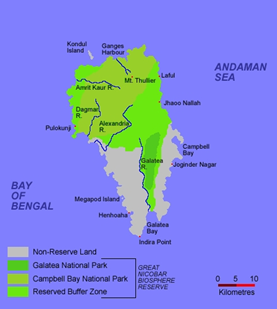
What is the Great Nicobar Development Plan? ● The Plan envisages the use of 244 sq.km. region of the Great Nicobar region for development purposes. ● Phase 1 of the Project included the following components: • 22 sq. km. airport complex, • Transhipment port (TSP) at South Bay • Parallel-to-the-coast mass rapid transport system and • Free trade zone and warehousing complex on the southwestern coast. ● Andaman and Nicobar Islands Integrated Development Corporation (ANIIDCO) will be the nodal agency for the implementation of the Great Nicobar Development plan. |
What are concerns over the Great Nicobar Development Plan?
- Geological Volatility: Andaman & Nicobar Islands are located in seismic zone V. Further, the Andaman & Nicobar face frequent storms and cyclones which can easily destroy constructed structures. The 2004 Tsunami caused a 3-4 metre land subsidence.
- Impact on Biodiversity: The site selection for the plan has been done on the basis of technical and financial criteria, ignoring the environmental aspects. There is the need for independent study and evaluation to study the suitability of the proposed port site with specific focus on Leatherback Turtle, Nicobar Megapode and Dugong.
- Issues confronting Galathea Bay: More issues have been identified regarding the Galathea Bay which is the centrepiece of the NITI Aayog proposal. Galathea Bay is an iconic nesting site in India of the enigmatic Giant Leatherback, the world’s largest marine turtle—borne out by surveys done over three decades. Several new species like the Nicobar frog, Nicobar cat snake, etc have been found in the Galathea region.
- Tribal rights: The proposed project areas are important grounds for the hunter-gatherer nomadic community especially Shompen. Initiation of work would make large forest areas inaccessible and useless for the Shompen.
What are the recommendations of the Committee?
- Independent assessment: The Committee has recommended independent assessment of terrestrial and marine biodiversity, a study on the impact of dredging, reclamation and port operations, including oil spills (to be carried out by nationally recognised institutions such as the Wildlife Institute of India, IISc or the Salim Ali Centre for Ornithology and Natural History).
- Exploring alternative sites: The committee has also called for studies for alternatives sites for the port with a focus on environmental and ecological impact, especially on turtles, analysis of risk-handling capabilities.
- Disaster management plan: The committee has also highlighted the need for a seismic and tsunami hazard map, a disaster management plan, and a hydro-geological study to assess the impact on round and surface water regimes.
3rd Arctic Science Ministerial
In News
India participated in the 3rd Arctic Science Ministerial (ASM3) - the global platform for discussing research and cooperation in the Arctic region.
About the News
- Hosts: ASM3, jointly organised by Iceland and Japan, was the first Ministerial meeting being held in Asia. The theme for this year is ‘Knowledge for a Sustainable Arctic’.
- The first two meetings—ASM1 and ASM2—were held in the USA in 2016 and Germany in 2018, respectively
- Need for the Ministerial: Arctic warming and its ice melt are global concerns as they play a pivotal role in regulating climate, sea levels, and maintaining biodiversity.
- So, the meeting was designed to provide opportunities to various stakeholders to enhance collective understanding of the Arctic region, emphasize and engage in constant monitoring, and strengthen observations.
- India and ASM3: Since 2013, India enjoys ‘Observer’ status in the Arctic Council with twelve other countries (Japan, China, France, Germany, UK, Italy, Switzerland, Poland, Spain, Netherlands, Singapore, and South Korea).
- India shared its plans to contribute observing systems in the Arctic, both in-situ and by remote sensing. The country would deploy open ocean mooring in the Arctic for long-term monitoring of upper ocean variables and marine meteorological parameters.
- The launch of NISER (NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar) satellite mission, in collaboration with the USA, is underway. NISER aims to conduct global measurements of the cause and consequences of land surface changes using advanced radar imaging. India’s contributions to the Sustained Arctic Observational Network (SAON) would continue.
India in the Arctic
- India’s engagement with the Arctic dates back to 1920 with the signing of the Svalbard Treaty in Paris.
- Since July 2008, India has a permanent research station in the Arctic called Himadari at NyAlesund, Svalbard Area in Norway. It has also deployed a multi-sensor moored observatory called IndARC in the Kongsfjorden fjord since July 2014.
- The research in the Arctic region from India is coordinated, conducted, and promoted by the National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR), Goa, under the Ministry of Earth Sciences, Government of India.
- India’s Arctic Policy Roadmap for Sustainable Engagement draft rides on five pillars: science and research activities, economic and human development cooperation, transportation and connectivity, governance and international cooperation, and national capacity building.
- Though none of India’s territory directly falls in the Arctic region, it is a crucial area as the Arctic influences atmospheric, oceanographic, and biogeochemical cycles of the earth’s ecosystem.
- There is growing evidence of connection between the Arctic and the Indian Ocean (which modulates the Indian monsoon). Hence, improving the understanding of physical processes and quantifying the impact of Arctic ice melt on the Indian summer monsoon is very important.
Sources: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetailm.aspx?PRID=1717084
https://science.thewire.in/environment/india-draft-arctic-policy/
Over 200 endangered species threatened by conflict: IUCN
In News
Civil unrest and military exercises pose heightened risk to more than 200 threatened species, including elephant populations and the critically endangered eastern gorilla, finds IUCN Report. The theme of report is “Conflict and conservation” and comes timely as armed conflicts cause great economic and social harm, as well as environmental damage around the world.
Focus Area of the Report:
- This is the first report in the IUCN flagship report series Nature in a Globalized World, the purpose of which is to help bring the importance of nature conservation into mainstream political and economic decision-making.
- The Report examines the close interplay between the environment and armed conflict, warning that human violence and unrest are taking a devastating toll on nature.
- The report found that armed conflicts were particularly prevalent in some of the world's more bio-diverse regions, in less productive agricultural land available and where droughts are frequent while conflicts were less frequent within the boundaries of natural reserves and other protected areas.
Facts and findings:
- IUCN said that 219 endangered species were facing threats from war, civil unrest, and military exercises, including the direct killing of wildlife, degradation of ecosystems and the disruption of conservation efforts.
- While this is only a fraction of 30,000 animal and plant species listed as threatened on IUCN's Red List, the report stressed it included "iconic species".
- Among them is the critically endangered eastern gorilla, found in conflict-prone Democratic Republic of Congo, Rwanda and Uganda. One of the threats to the world's largest living primate was direct killing, sometimes for target practice and sometimes for food.
International Instances of Disruption:
- During the 1994 war in Rwanda, 90% of the large mammals in the Akagara National Park were killed for food or trade. The genocide during the war had thousands of people fleeing through protected areas, killing animals for food and clearing trees along the way.
- To meet the demand of ivory, the militia from Sudan were responsible for the deaths of some 2,000 elephants in the Central African Republic in 2007 alone.
- The report also said the Vietnam War "almost certainly accelerated the slide into extinction" of the Javan rhinoceros, as the Viet Cong shot them to supplement diet.
Recommendations of the Report to Curb the Destruction Menace:
- Conservation, restoration and sustainable management of natural resources can help reduce the pressures that drive conflict by improving the productivity of the landscape.
- Establishing safeguards for staff in protected areas and other conservationists.
- Sanctions against those who commit environmental war crimes.
- Coordinate law enforcement efforts across sectors and scales to strengthen prevention and mitigation.
Anti-Microbial Resistance - Edukemy Current Affairs
In News
The urgency to save lives in the pandemic is pushing doctors to prescribe a cocktail of over a dozen drugs, which may drive the world into the hidden pandemic of Anti-Microbial resistance.
About the News
- Doctors would ideally adhere to the clinical-management protocols, but the high flow of patients who may deteriorate and need hospital admissions, is compelling doctors to mount a pre-emptive attack against the virus.
- So, doctors are prescribing medicines like multivitamins, anti-allergens, asthma drugs, anti-hypertensives, anti-nausea drugs, and anti-cholesterol drugs. Even drugs which may not have gone through a robust approval process for use in Covid-19 treatment, also feature on the list.

But is this multiple drug therapy safe?
- May weaken the Immune system: A few of the anitbiotics or drugs, which are being prescribed prematurely, may potentially weaken the body’s immune system and backfire in the long run. With a fragile immune system, infections are easier to catch and some may be untreatable.
- Antibiotic or Antimicrobial resistance: Studies estimated that 55% to 98% of hospitalised Covid-19 patients around the world were treated with antibiotics, while only a fraction had a bacterial co-infection that would require their use. This has led to widespread concern about unnecessary antibiotic use during the pandemic.
- High negligence: Overwhelmed by the flow of patients and high-transmission risks, some doctors are not checking for medical history of comorbidities like hypertension or diabetes.
What are Superbugs and Anti-Microbial resistance?
- Definition: Superbugs are strains of bacteria, viruses, parasites and fungi that are resistant to most of the antibiotics and other medications commonly used to treat the infections they cause. This is called Drug resistance or Antimicrobial resistance (AMR).
- Mechanism: Whenever microbes are exposed to a condition that inhibits growth, such as antibiotics, they are pressured to make changes that will help them survive. Microbes that acquire resistance can multiply rapidly and spread the resistance to other microbes, resulting in exponential spread of resistance.
- Reasons for their development: There are many reasons behind the development of AMR, ranging from microbial causes to human aspects such as overuse and over-prescription of antimicrobials, agricultural and commercial application of antimicrobials in the animal sector, and human behavioural factors.
How the response to Covid-19 is Shaping Antibiotic Resistance or AMR?
- Increased standard antibiotic usage:
- Precautionary measure: Several studies estimate that 70-97% of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 receive antibiotic therapy. Early and precautionary antibiotic treatment is a standard of care that is often beneficial in the case of true bacterial or fungal infections. However, during the COVID-19 pandemic, the number of patients presenting with these symptoms and thus receiving this standard antibiotic therapy has drastically increased.
- Misguided antibiotic usage: Early in the pandemic, in the absence of well-defined treatments for the novel disease, doctors tried to use drugs that were already clinically approved for use in patients.
- Tele-health services: The increase in Tele-health appointments during the pandemic has also increased antibiotic prescriptions. The higher frequency of antibiotic prescriptions during virtual healthcare was well-documented prior to the pandemic.
Why is antibiotic resistance a problem?
- Challenging: Antibiotic resistance makes it more challenging and expensive to treat infections. Our ability to treat common pathogens becomes challenging because of AMR, resulting in increased duration of illness, costs, number of complications, and deaths. Resistant infections require testing to determine what drugs are suitable for treating the infection.
- Multi-drug resistance: Additionally, microbes resistant to one antibiotic may also be resistant to others, a phenomenon known as multi-drug resistance that further exacerbates challenges in treating resistant infections.
- Increasing numbers:8 million people contract antibiotic-resistant infections every year, resulting in 700,000 deaths. While these numbers may seem small in comparison to the devastating impact of COVID-19 in 2020, antibiotic-resistant infections occur year after year, leading to a sustained impact on healthcare and the economy.
- Furthermore, trends of increasing antibiotic resistance suggest that the annual death toll from antibiotic resistant infections will be greater than 10 million by 2050.
Steps that have been taken to prevent or reduce AMR
- Initiatives by WHO:
- World Antimicrobial Awareness Week: Held annually since 2015, WAAW is a global campaign that aims to increase awareness of antimicrobial resistance worldwide and to encourage best practices among the general public, health workers and policy makers to avoid the further emergence and spread of drug-resistant infections.
- The Global Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System (GLASS): The WHO-supported system supports a standardized approach to the collection, analysis and sharing of data related to antimicrobial resistance at a global level to inform decision-making, drive local, national and regional action.
- Global Antibiotic Research and Development Partnership (GARDP): A joint initiative of WHO and Drugs for Neglected Diseases initiative (DNDi), GARDP encourages research and development through public-private partnerships. By 2023, the partnership aims to develop and deliver up to four new treatments, through improvement of existing antibiotics and acceleration of the entry of new antibiotic drugs.
- Interagency Coordination Group on Antimicrobial Resistance (IACG): The United Nations Secretary-General has established IACG to improve coordination between international organizations and to ensure effective global action against this threat to health security.
- National Action Plan on AMR: India announced its National Action Plan on AMR and has since established surveillance systems for tracking AMR.
Conclusion
Indiscriminate and premature use of broad-spectrum antibiotics to treat Covid-19 patients may be pushing the world into the hidden pandemic of bacterial infections, as there is no proven efficacy of this practice. Further research to determine relevant indications for antibiotic use in Covid-19 patients is critical in view of the significant mortality associated with secondary infections in these patients, and the rising antimicrobial resistance.
Question: What is Anti- Microbial Resistance (AMR)? Analyze the effects of Covid-19 on AMR.
https://sitn.hms.harvard.edu/flash/2021/how-covid-19-is-shaping-antibiotic-resistance/
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antibiotic-resistance
This Day in History- National Technology Day
May 11 is observed as National Technology Day every year to mark the anniversary of the Pokhran nuclear tests of 1998. The day also commemorates the achievements of engineers and scientists in the field of science and technology. Pokhran nuclear tests were a series of five nuclear bomb test explosions that were conducted at the Indian Army's Pokhran Test Range. The test was headed by an aerospace engineer and former President Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam. The National Technology Day 2021 theme is 'Science and Technology for a sustainable future'.
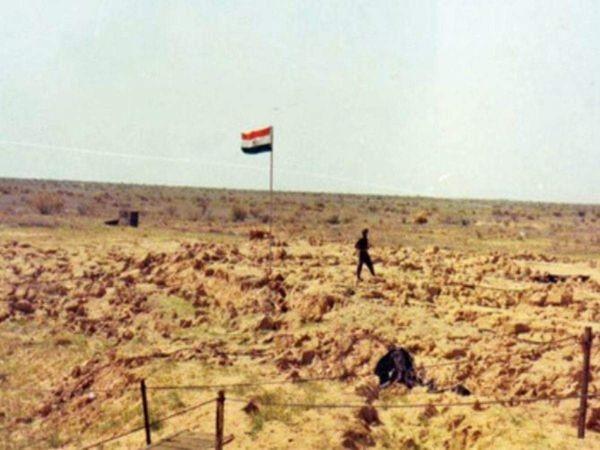

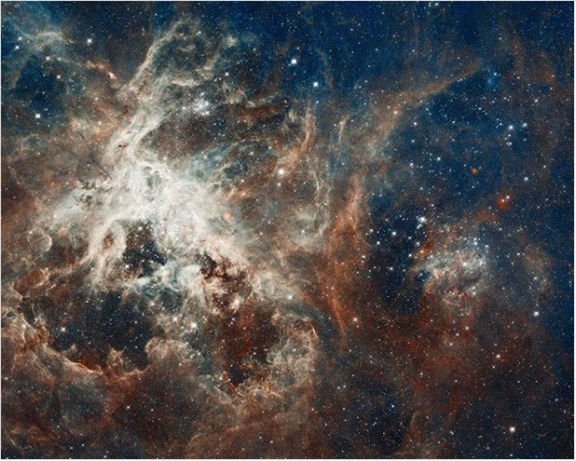
Image of the Day- 30 Doradus
This is an image of a star-birth region called 30 Doradus, which has apparently “raised millions of young stars”. NASA’s Hubble Telescope shared an image of a sparking region of star birth on the occasion of Mother’s Day. According to Hubble, the region lies around 170,000 light-years away from earth, in the heart of Tarantula Nebula and is reportedly the largest visible star-forming site in a neighbouring galaxy.

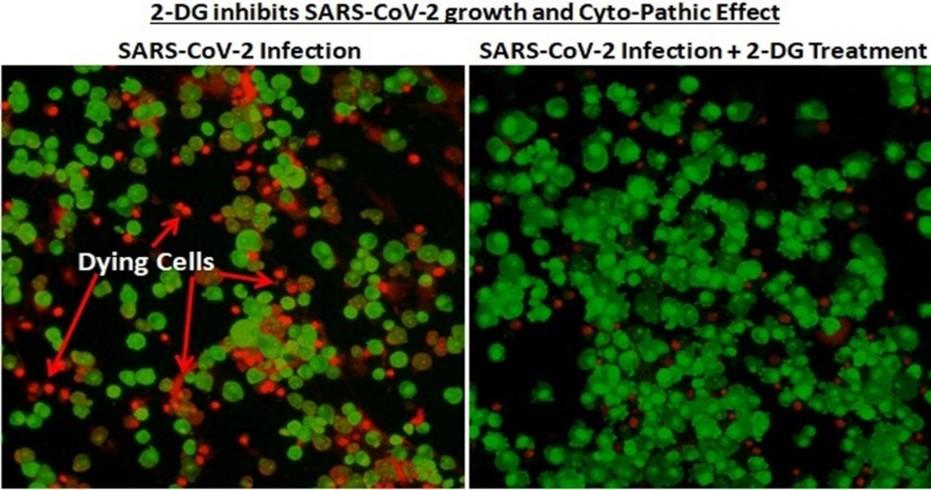
2-DG of DRDO
- Context: DCGI approves 2DG (anti-COVID drug) developed by DRDO for emergency use.
- An anti-COVID-19 therapeutic drug 2-deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG) has been developed by DRDO lab, in collaboration with Dr Reddy’s Laboratories.
- Clinical trial results have shown that this molecule helps in faster recovery of hospitalised patients and reduces supplemental oxygen dependence as it works effectively against SARS-CoV-2 virus and inhibits the viral growth.
- Being a generic molecule and analogue of glucose, it can be easily produced and made available in plenty in the country.
- The drug comes in powder form in sachet, which is taken orally by dissolving it in water. It accumulates in the virus infected cells and prevents virus growth by stopping viral synthesis and energy production. Its selective accumulation in virally infected cells makes this drug unique.
Primary source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1717007
Animal Corridor
- Context: probing cases of clearance of forest land and construction activities on animal corridors within the eco-sensitive zone of the Kaziranga National Park.
- Wildlife or animal corridorsare meant to ensure safe passage for animals between two isolated habitats. Wildlife corridors are mainly of two types- functional and structural:
- Functional corridorsare defined in terms of functionality from the perspective of the animal (areas where there have been recorded movement of wildlife).
- Structural corridorsare contiguous strips of forested areas and structurally connect the otherwise fragmented blocks of the landscape.
- When structural corridors are affected by human anthropogenic activities, functional corridors automatically widen because of animal use.

Significance of Animal Corridors:
- These corridors are crucial for the rhinos, elephants, tigers, deer and other animals that escape the flooded Kaziranga during the monsoonmonths for their safety on the hills of Karbi Anglong region.
Black Fungus
- Context: Rise in fungal infection during the second covid wave
- Cases of mucormycosis, a fungal infection, are rising among COVID-19 survivors, causing blindness or serious illness and even death in some cases.
- It is caused by a fungus named mucor (black fungus), which is found on wet surfaces and is prevalent among people who have diabetes.
- This disease is not new, but it is on rise among COVID-19 patients because of the use of steroids (elevates sugar level) and medicines that suppress the immunity of the patients.
- Symptoms of mucormycosis include headache, fever, pain under the eyes, nasal or sinus congestion and partial loss of vision.
Primary Source: https://www.livemint.com/news/india/fungal-infection-cases-rising-in-second-covid-wave-warn-maharashtra-gujarat-doctors/amp-11620483979583.html
Hakki Pikki Tribe
- Context: A Hakki-Pikki tribal lady from Karnataka recovers and wins battle against the Covid 19 virus.
- The Hakki Pikki are a semi-nomadic tribe who have migrated from Northern India and settled in Karnataka and other Southern States.
- They are known as Bird Catcher (Hakki means Bird and Pikki means Catcher in Kannada Language) which is their traditional occupation.
- They are known for their various indigenous herbal products specially the herbal oil.
- Scholars named their mother tongue as ‘Vaagri’ (an Indo-aryan language). The UNESCO has listed Hakki pikki as one of the endangered languages.

Primary source: https://sppel.org/hakkipikkidoc.aspx
Maharana Pratap
- Context: Birth anniversary celebrations
- Hailing from Sisodia clan of Rajputs, Rana Pratap Singh was born at Mewar, Rajasthan in the year 1540.
- He was the 13thKing of Mewar and eldest son of Udai Singh II, founder of the city of Udaipur (Rajasthan).
- Rana Pratap Singh resisted efforts of the Mughal emperor Akbar to conquer his capital Chittor and is honored as a hero in Rajasthan.
- He was defeated in June 1576 by Mughal forces at Haldighat and fled to the hills.
- He was succeeded by his son Amar Singh, who submitted in 1614 to Emperor Jahangir, son of Akbar.

Primary source: https://www.britannica.com/biography/Rana-Pratap-Singh
Assessing Tatmadaw’s intention & capabilities: What is next for North east insurgencies?
Essence: Editorial is uncovering the security issues at India’s North eastern border, in light of ongoing crises in Myanmar. India and Myanmar have had several on-and-off cooperation partnerships against North-East (NE) insurgents operating from the territory of the latter. However, despite this cooperation, over 2000-3000 Naga, Manipuri, and Assamese militants continue to use Myanmar as a terror launchpad against India. Since 1993, Tatmadaw (Myanmar Army) started coordinating or acting against the North-east (NE) insurgents. China continues to use the NE insurgencies to off-balance India, limit its growth, earn profits through black arms markets, and also widen mistrust between India and Myanmar. This supply of arms has empowered several insurgent organisations, which now poses a threat to India’s Kaladan Project. India’s intelligence and arms supply to Myanmar has led to an increase in security cooperation. This has forced several militants to surrender or return to India—contributing to India’s increasing securitisation. However, the ongoing civil strife in Myanmar has raised new opportunities for revival for the NE insurgencies.
Why you should read this article?
- It’s an important article for internal security module.
- To understand the security challenges in India’s North east & information about the various insurgent groups involved.
- To know about journey of security cooperation between India & Myanmar Army (Tatmadaw).
- To understand the implications of ongoing civil strife on cross border security cooperation & thereby risk of insurgents gaining ground again
Article Link: https://www.orfonline.org/expert-speak/assessing-tatmadaws-intention-and-capabilities/
A TRIPS waiver is useful but not a magic pill
Essence: The United States has finally relented and declared its support for a temporary waiver of the Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) agreement for COVID-19 vaccines at the World Trade Organisation (WTO). In this context, the article analyses the challenges and impediments in its successful implementation.
Why you should read this article?
- Briefly know about the sections of TRIPS related to the prevention, containment, or treatment of COVID-19 and the conditions for waiver as mentioned in Article IX of WTO agreement.
- Learn about the experience of 2003 WTO waiver in the aftermath of the HIV/AIDS crisis in Africa in the 1990s.
- Understand the key obstacles in operationalisation of such waiver and the measures required to overcome these.
Article Link: https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/lead/a-trips-waiver-is-useful-but-not-a-magic-pill/article34522578.ece
Mumbai Oxygen model during 2nd Wave of Covid 19
- Amid the second Covid-19, worst surge in infection wave was triggered by oxygen shortage across the country but this was not the case with Mumbai.
- Mumbai made effective use of Oxygen tanks installed at 6 hospitals. Tanks helped meet the daily demand for medical oxygen despite the increasing demand from 210 metric tonnes to 270 metric tonnes.
- Management was so effective that the Supreme Court prompted Centre to examine “Mumbai model” of optimal utilisation of oxygen.
Mumbai Model:
- Infrastructure: LMO Tanks and piping and the other requisite infrastructure was created to deal with the second wave.
- Governance: Brihanmumbai Municipal Corporation appointed officials for coordination between oxygen suppliers, assistant municipal commissioners of the 24 civic wards, and the Food and Drug Administration with the responsibility for maintaining the existing oxygen supplies and ensuring they are used when necessary.
- Inventory: All hospitals were mandated to keep cylinders as a backup. Resource inventory of oxygen use and infrastructure at hospitals proved helpful. Oxygen was also supplied to suburbs such as Navi Mumbai and Thane.
- Crisis Handling: When Mumbai faced a shortfall of 15 to 20MT oxygen, it was managed by moving surplus stock from one place to another and seeking oxygen from Gujarat.
Outcome:
- Effective in dealing with the COVID crises with proper management of demand and supply of oxygen cylinders.
- Pre-emptive dealing of the crisis had helped in saving of lives
Where can we use this case study:
- As a way forward in the answers to deal with a disaster by taking pre-emptive steps, to tell in answers how can data help to make effective policy, to be used as a suggestion for the other states like Delhi where hospitals are struggling to get oxygen.
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.