Monday, 10th May 2021
Special long term repo operation (SLTRO)
In News
The Reserve Bank of (RBI) will be conducting one special long term repo operation (SLTRO) for small finance banks (SFB) for each month, totalling Rs 10,000 crore.
About the News
- To provide further support to small business units, micro and small industries, and other unorganised sector entities adversely affected during the current wave of the pandemic, the RBI has decided to conduct SLTRO of ₹10,000 crore at the repo rate for the SFBs, to be deployed for fresh lending of up to ₹10 lakh per borrower.
- The SLTRO will be valid for three years. All SFBs will be eligible to participate in the scheme.
- The SFBs will have to ensure that the amount borrowed from the RBI should at all times be let to the specified segments, namely small business units and other unorganised sectors impacted by the pandemic.
- SLTROs will be conducted on CBS (E-KUBER) platform. The operations would be conducted at a fixed rate. Banks would be required to place their requests for the amount sought under SLTRO during the window timing at the prevailing policy repo rate. Bids below or above policy rate will be rejected.
What is Long-Term Repo Operations (LTRO) and why is it important?
- The LTRO is a tool under which the central bank provides one-year to three-year money to banks at the prevailing repo rate, accepting government securities with matching or higher tenure as the collateral.
- While the RBI’s current windows of liquidity adjustment facility (LAF) and marginal standing facility (MSF) offer banks money for their immediate needs ranging from 1-28 days, the LTRO supplies them with liquidity for their 1- to 3-year needs.
- LTRO operations are intended to prevent short-term interest rates in the market from drifting a long way away from the policy rate, which is the repo rate.
- The RBI believes that offering banks durable longer-term liquidity at the repo rate can help them lower the rates they charge on retail and industrial loans, while maintaining their margins.
- The LTRO will also help bring down the yields for shorter-term securities (in the 1-3-year tenor) in the bond market.
- It is a measure that market participants expect will bring down short-term rates and also boost investment in corporate bonds.
Draft National Electricity Policy 2021
In News
Draft National Electricity Policy 2021 has been released by the Ministry of Power.
About the News
- Under Section 3 (3) of the Electricity Act, 2003, the Central Government may, from time to time, in consultation with the State Governments and the Central Electricity Authority, review or revise, the National Electricity Policy.
Some of the Major Provisions of the draft policy
- Thermal Generation: Coal-based generation capacity may still be required to be added in the country as it continues to be the cheapest source of generation.
- All future coal-based plants should only deploy so-called ultra-super critical less polluting technologies or other more efficient
- Renewable Energy Sources and Cogeneration: It recommends that a two-part tariff mechanism should be adopted for certain renewable sources of energy (such as wind and solar).
- Two-part tariff mechanism refers to tariffs having fixed and variable charge components. It may be helpful particularly in medium or long-term procurement of renewable energy for hybrid operations.
- Microgrids: Traditionally, microgrids with distributed generation, have been used to supply electricity in areas where it is not feasible or cost-effective to provide electricity to the consumers through the main grid.
- But with increasing used of microgrids in cities and towns, in urban centres, universities etc. having some local renewable energy generation for enhancing the reliability of power supply, such micro grids need to be strengthened.
- Transmission: The draft Policy recommends that the transmission projects must be classified into two categories: (i) the generator or drawing customer-specific projects (for catering to their specific needs), and (ii) system strengthening projects. The system strengthening projects may be used for supporting transmission of power from a region with high availability of power and low demand to a region with a high demand of power and low supply.
- Distribution: The Policy recommends that public-private partnership model (such as franchisee and sub-licensee) should be adopted in the distribution sector. This would be helpful in: (i) improving efficiency and customer satisfaction, and (iii) reduce financial losses of distribution companies.
- Use of automation and smart-metering can play a pivotal role in bringing the positive transformation in distribution.
- Power Markets: According to the draft, a new entity called aggregators may be created to aggregate demand, renewable power generation, demand response, micro-storage, and others, to help small consumers, prosumers, and producers reach the market. This would help promote open access, which is presently allowed for consumers with loads of 1 MW and above. Also, share of spot markets will be increased to about 25% during the year 2023-24.
- Electric Vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure: It recommends that the tariff and rules of EV charging should be fixed by the concerned state electricity regulatory commission. Further, it recommended that distribution companies should proactively identify the part of the distribution network that needs strengthening for the implementation of EV charging.
Why was there a need for a New Electricity Policy?
- To address the Changes: The first NEP was formulated in 2005 and a lot of changes have taken place since then as far as the power sector is concerned.
- Between 2005 and 2021, generation capacity (inclusive of renewable capacity) has gone up by about 251 GW.
- Renewable generating capacity has gone up to 94 GW from almost nothing, leading to about 10% of generation from renewable sources
- An additional 2.5 lakh circuit-km of transmission lines (above 220 kV) has been added
- Per capita consumption has almost doubled from 630 units to approximately 1,200 units
- Peak and energy shortages have come down from double digit figures to about half a percentage point
- Rural electrification is almost complete with near 100% electricity access to households.
- To address the Issues in Power Sector:
|
Issues |
Description |
|
Peak deficit continues to persist |
The country continues to face a peak deficit of 2%. This deficit situation is more pronounced in certain regions and states. |
|
Capacity utilisation of thermal power plants has been declining |
Capacity utilisation of thermal power plants (also called Plant Load factor or PLF) has declined from 78% in 2009-10 to 61% in 2018-19. |
|
Renewable market is still developing |
Renewable energy sources are not evenly spread about the country. The NITI Aayog has observed that electricity buyers in renewable poor states are less willing to purchase renewable electricity due to higher costs. On the other hand, discoms in renewable rich states have indicated that they would support additional renewable deployment only if they are assured of sufficient buyers. |
|
NPAs in the sector have been increasing |
As per the RBI, public sector banks have the highest NPAs, most of which are in the power and the telecom sector. It also noted that the most severe shock to the power sector will cause the banking system NPAs to rise by about 68 bps. |
|
Environmental concerns of thermal generation |
With the push towards more domestic manufacturing and industrialisation, majority of the energy in India being generated from thermal sources, and increasing levels of consumption, environmental sustainability could become a much bigger concern. |
|
Transmission infrastructure issues affect power supply |
Bottlenecks in the transmission network cause issues with evacuation of power. Further, a poor transmission network also leads to underutilisation of generation capacity. |
|
Poor financial situation of the distribution utilities |
The discoms have accumulated outstanding of over `6 lakh crore and this seems to be going up year after year despite all government programmes aimed at improving distribution infrastructure and restructuring of loans. This makes it difficult for them to purchase power, and invest in the distribution network. This leads to a shortfall in power supply, and poor distribution infrastructure. |
Some Issues with the draft NEP, 2021
- Issue with the effectiveness of the policy: The draft policy has a lot to say on renewable generation but there is no guarantee that it would be followed. While the central government may fix targets on renewable generation capacity, the implementation will mainly be done by private enterprises.
- Now, private enterprises will move according to the investment climate as it exists in states. Unfortunately, some states completely shake off investor sentiments by reopening Power Purchase Agreements, or by not paying renewable generators. Such actions would ensure that the objectives of the policy remain unfulfilled.
- Issue of separate policy statements: Decision needs to be taken whether to have two separate policy statements, the NEP and the National Tariff Policy. Both these documents exist concurrently, but they practically run into each other’s domain.
- It is not really possible to segregate tariff-related issues from electricity policy in general since they are all interlinked. Thus, it would be appropriate to subsume the NTP into the NEP, and tariff would be one of the several issues which would be a matter of electricity policy.
Conclusion
As India has made significant progress in recent years in terms of capacity addition and increasing renewables in the power mix, the government is making yet another attempt to improve the state of the power sector and has come up with a new draft National Electricity Policy with objectives such as promoting clean energy, developing an efficient market for electricity distribution, and revitalising distribution companies.
Question: What are the problems being faced by the Power Sector? How can these issues be resolved with the help of a new electricity policy?
Sources: https://www.business-standard.com/article/opinion/power-play-121050300107_1.html
https://prsindia.org/policy/monthly-policy-review/april-2021
https://prsindia.org/billtrack/draft-electricity-amendment-bill-2020
https://static.mygov.in/rest/s3fs-public/mygov_162003108978977151.pdf
https://prsindia.org/policy/analytical-reports/overview-power-sector
https://powermin.gov.in/sites/default/files/uploads/NEP-Trans.pdf
DoT approves telcos' applications for 5G trials
In News
The Department of Telecom has approved applications of telecom companies for conducting 5G trials in India but none of them will be using technologies of Chinese entities.
|
What is 5G ? ● In telecommunications, 5G is the fifth-generation technology standard for broadband cellular networks, which cellular phone companies began deploying worldwide in 2019, and is the planned successor to the 4G networks which provide connectivity to most current cell phones. ● 5G or fifth generation is the latest upgrade in the long-term evolution of mobile broadband networks. 5G mainly works in 3 bands, namely low, mid and high-frequency spectrum. Benefits of 5 G ● 5G technology is expected to offer three times greater spectrum efficiency than 4G, and ultra-low latency. It can be applied in sectors such as agriculture, education, health, transport, traffic management, smart cities, smart homes, and multiple applications of IoT. |

About the 5G trials
- 5G trials for six months: The DOT has approved applications from 4 companies who have been allowed to conduct 5G trials for six months, including two months for procuring and setting up equipment.
- Non-commercial trials: The non-commercial trials in India will not be connected with the existing networks of operators and the data generated will have to be stored in India.
- Trials also in rural and semi-urban regions: The selected operators will have to conduct trials in rural and semi-urban regions in addition to urban areas so that the benefit of 5G technology is not only confined to cities.
- Trials before auctions: In the past, trials for new technologies happened after spectrum auctions. In the recent guidelines for experimental spectrum, the trails are being taken up before the auctions.
- Coordinating agency: As part of the policy, the National Cyber Security Coordinator will act as the designated authority for the trials.
Objectives of the trials
- Testing 5G spectrum in India
- Testing 5G phones and devices
- Evaluate chosen equipment and vendors
- Test indigenous technology and applications such as tele-medicine, tele-education, drone-based agricultural monitoring.
Why are the trials for 5G technology important for telecom companies?
- Means to increase revenue: Telecom companies in India have been incurring losses over the last few years. In order to increase their average revenue per user, it is pertinent for telcos to start offering the new 5G technology as soon as possible. It is also important for telecom companies to conduct trials in a variety of circumstances, including in semi-urban and rural areas, which remains an untapped market for them.
- Significant move for the government: It is also important that the government be ready to roll out the new technology as soon as possible. A standing committee of Lok Sabha on Information Technology has already pointed at the government delays in approvals, inadequate availability of spectrum and the low status of fiberisation among others.
- Geopolitical significance: Chinese telecom vendors have not been included as a part of the 5G Telecom trials. The move comes after the government has already taken steps to secure the mobile ecosystem by making amendments to the telecom licence rules. The absence of Chinese vendors can be attributed to the growing concerns around network security and prevailing tensions in diplomatic and military relations. The US had also earlier designated Chinese technology companies as posing a national security risk.
- Trials to involve India-specific applications: The 5G field trials would also include tests on India-specific applications in socially relevant sectors such as health, education, agriculture, traffic management and others.
What have been the hurdles in rolling out 5G technology in India?
- Affordability of Spectrum: India’s 5G ecosystem is underdeveloped and the cost of the spectrum will be high for the already debt ridden telecom operators.
- Last-mile connectivity: Catering to last-mile broadband connectivity in Tier II and Tier III cities and rural areas is challenging as India lacks optical fiber infrastructure.
- Affordability of 5G devices: Even if 5G network connectivity comes in, affordable 5 G devices are yet to take their place in the market. Mitigating existing 4G and 3G users to 5G networks will pose a challenge to the telecom industry.
- Network Security and privacy: Data collection is a major concern for 5G users, as all mobile applications demand user’s personal information during or before installation. It will be difficult for 5G operators to safeguard user data in the cloud environment.
What is the global progress on 5G?
- Lead taken by telecom companies: More than governments, global telecom companies have started building 5G networks and rolling it out to their customers on a trial basis. In countries like the US private companies have taken the lead in rolling out 5G to users.
- Commercial services: In countries like China, some of the telcos such as China Unicom had started 5G trials in 2018 and have now begun the commercial services for users.
- Early entrants: South Korean Company Samsung had started researching on 5G technology in 2011 and has taken the lead in building hardware for 5G networks for several companies.
Conclusion
India’s National Digital Communications Policy 2018 highlighted the importance of 5G and stated that the convergence of a cluster of revolutionary technologies including 5G, the cloud, Internet of Things (IoT) and data analytics, promised to accelerate and deepen the digital engagement. India can also learn from some of the best practices developed in other countries that have rolled out 5G networks like the US and South Korea.
Question: Analyse the utility of 5G technology in Indian scenario. Highlighting the various challenges in the implementation of 5G technology in India, suggest measures to overcome them.
This Day in History: India's First War of Independence

On May 10, 1857 India's First War of Independence, better known as the Indian Rebellion of 1857, began. Begun in Meerut by Indian troops (sepoys) in the service of the British East India Company, it spread to Delhi, Agra, Kanpur, and Lucknow. The first martyr of the revolt was Mangal Pandey, and the war was the result of accumulation of many factors over time. The rebellion of 1857 is considered the first blow that came to shatter the British rule in India. Some of the other rebellions and leaders included Rani Lakshmibai, Kunwar Singh, Bahadur Shah, Nana Saheb, Tatia Tope and Begum Hazrat Mahal.
Image of the Day- Bonnethead Shark

This is the image of a Bonnethead Shark, the species used in the new study, swims in the New England Aquarium in Boston. A new study found the first solid evidence that sharks use Earth’s magnetic fields for their long-distance travel. Sharks undergo precise, long-distance migrations and make roundtrips of over 20,000 kilometres. Several birds and animals have also been known to use magnetoreception or the special sense to detect Earth’s magnetic field to perceive the location and track the direction during migration.
https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/homing-sharks/article34515943.ece
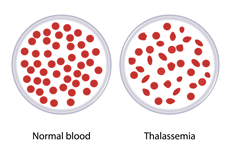
World Thalassemia Day
- Context: Myths regarding Thalassemia busted.
- Thalassemia syndrome is an inherited blood disorder that causes the body to have less hemoglobin than normal.
- The disorder results in excessive destruction of red blood cells, which leads to anemia.
- Various myths around thalassemia:
- Thalassemia isn't detectable and can’t be cured
- Thalassemia carriers should not get married to each other
- If two thalassemia carriers marry each other, they will always have a thalassemia major child
- TheMoHFW had launched “Thalassemia Bal Sewa Yojna” for the underprivileged Thalassemic patients in 2017 under the Coal India CSR funded Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HSCT) program in which it aims to provide a one-time cure opportunity for Haemoglobinopathy patients who have a matched family donor.
Kabasura Kudineer & AYUSH 64
- Context: Ayush Ministry launches nationwide campaign to distribute the drugs AYUSH 64 & Kabasura Kudineer.
- Kabasura Kudineer is a Siddha medicine which was subjected to clinical trials to study efficacy in Covid19 patients by Central Council for Research in Siddha (CCRS) under Ministry of Ayush.
- Through multi-centre clinical trials, it has been found useful in the treatment of mild to moderate Covid19 infection.
- AYUSH-64 is an Ayurvedic formulation developed by the Central Council for Research in Ayurvedic Sciences (CCRAS) and has been a recommended drug in National Clinical Management Protocol for COVID-19 patients in home isolation.

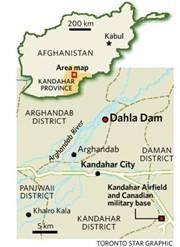
Dahla Dam
- Context: the Taliban has recently captured Afghanistan’s second-biggest dam-Dahla Dam.
- Also known as Arghandab Dam, it islocated in the Shah Wali Kot District of Kandahar Province, Afghanistan.
- Dahla was built by the United States nearly 70 years ago on the Arghandab River to provide water for irrigating land in Kandahar region.
- The Dam provides irrigation to farmers via a network of canals as well as drinking water for the provincial capital.
Primary Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/international/taliban-captures-key-afghan-dam-as-fighting-rages/article34501522.ece
The Quad’s economic imperative: Participating nations should cooperate and benefit beyond the security framework- ToI
Essence: The editorial explores how broadening the Quad's current strategic orientation to improve economic links could result in a win-win situation for all parties concerned. A paper published in the Journal of Economic Structures analysed the likely impact of tariff reduction and trade facilitation in a scenario of Indo-Pacific regional integration on various macroeconomic and trade variables. It showed that if Quad countries were to sign a trade agreement where bilateral tariffs are scrapped, it could boost India’s real GDP and exports. Sectors where India’s exports are competitive such as clothing, textiles, and light manufacturing would benefit the most. If other nations or groupings like ASEAN were to join such an FTA and engage in reducing non-tariff barriers, the benefits for member countries could be exponentially higher. To emerge stronger from the covid 19 induced crisis, there is a compelling case for India and its Quad allies to embrace even greater trade, investment, and economic cooperation.
Why you should read this article?
- To learn about the QUAD grouping's key areas of collaboration & how its strategic alignment can rope in economic ties.
- It is providing possible outcomes of trade facilitation among member countries.
- To learn about high-priority areas in India's bilateral ties with the United States, Japan, and Australia.
How diaspora pushed US to help India’s Covid efforts- IE
Essence: On April 30, Super Galaxy, a huge US military plane, landed in Delhi, bringing oxygen cylinders, hospital equipment and Covid test kits. More flights with aid material are on the way to India. In this context, the article lists several elements of the package of assistance and their immediate impact while discussing the role of Indian diaspora in it.
Why you should read this article?
- Learn about the various ways through which the US government is offering assistance to India in times of her need.
- Know about the immediate impact of US assistance which is the robust engagement of corporate, mostly Big Tech, America.
- Briefly know about the role of Indian Diaspora in America’s turn around to assist India.
Sustainable Plastic Waste Management Plan: Defending the fragile ecosystem of Himachal Pradesh
Issue of Plastic Pollution:
- While indiscriminate use of plastics and plastic littering is harmful for the environment and its impact can be even more devastating for the fragile ecosystem of the Himalayas.
- To solve the issue pf plastic menace, Government of Himachal Pradesh enacted the Himachal Pradesh Non-Biodegradable Garbage (Control) Act, 1995.
- Act embodied scientific disposal of plastic waste, imposed a ban on plastic carry bags.
- However, the act only addressed these issues partially and plastic littering continued to be a challenge.
- Environmental problems like pollution of water bodies, lowering of soil quality, choking of drains and rivers continued with the adverse impact on the health of people.
- So, the Government of Himachal Pradesh introduced the Sustainable Plastic Waste Management Plan in 2009
Sustainable Plastic Waste Management Plan, 2009
- Plan focusses on controlling the use of plastic by a systematic disposal mechanism.
- Use of plastic cups and plates were prohibited for use in 2011.
- Continuous Information, Education and Communication was undertaken to generate awareness and encourage the citizens to stop using plastic products.
Outcome:
- Himachal Pradesh developed a successful system of disposing off plastic in construction of roads thus making state of Himachal Pradesh free from plastic.
- Nudge effect helped in creating awareness and secured people’s cooperation
- Created responsible citizens who took the responsibility of cleaning their state and creating a plastic-free world.
- Vision of Clean Himachal and Healthy Himachal has been reached.
Where can we use this case study?
- Innovative example for scientific disposal of plastic to be implemented across the state and at level of centre, nudge effect and importance of Continuous Information, Education and Communication in bringing change in the behaviour of people.
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.