Thursday, 6th May 2021
Eyeing rural coverage, IRDAI pitches for model insurance villages
In News
The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) has come out with the concept of model insurance villages to cover the entire population in selected areas, with the financial support of various institutions like NABARD and CSR funds.
About the implementation of the scheme
- The concept will be implemented in a minimum of 500 villages in different districts of the country in the first year and increased to 1,000 villages in the subsequent two years.
- Efforts in selected villages will be continued for a minimum of 3-5 years so as to ensure that the insurance benefits are visible to the community.
|
Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India · It is an autonomous and statutory body which is responsible for managing and regulating the insurance and reinsurance industry in India. · Key objectives of the IRDAI include promotion of competition so as to enhance customer satisfaction through increased consumer choice and fair premiums, while ensuring the financial security of the insurance market. Related concepts · Insurance penetration: Insurance penetration is calculated as the percentage of insurance premium to GDP. · Insurance density: Insurance density is the ratio of insurance premium to population |
Opportunities for Insurance Sector in Rural Areas
- Opportunities for growth: Creating awareness about insurance products and benefits will provide growth opportunities for public and private sector insurers.
- Existing low coverage in rural areas: Currently, only 8-10% rural households are covered under life insurance schemes. The remaining 90% can be targeted through new innovative insurance schemes that particularly cater to the needs of rural areas, for instance through insurance schemes for agriculture equipment.
Significance of the Model Insurance Villages
- Comprehensive insurance protection: The idea behind the model village concept is to offer comprehensive insurance protection to all the major insurable risks that villagers are exposed to and make available covers at affordable or subsidised cost.
- Demonstrating efficacy of insurance to rural population: In order to ensure the benefits of insurance to the rural population, there is a need to cover the entire population in the village and their property, farm machineries, vehicles. There is also a need to identify the insurance needs of the particular villages through targeted efforts.
- Making premium affordable: Financial support needs to be explored in order to ensure that the premium is affordable through NABARD, CSR funds, government support and support from reinsurance companies. This will help in ensuring that the insurance covers the property, crops and the entire village community.
Sources
IOC launches biodiesel from used cooking oil in Delhi
In News
Indian Oil Corporation has recently launched biodiesel made from used cooking oil (UCO) sourced from eateries. The Minister of Petroleum and Natural Gas remotely flagged off the first consignment under the ‘Randhan se indhan’ scheme.
|
Used Cooking Oil UCOs are oils and fats that have been used for cooking or frying in the food processing industry, restaurants, fast foods and at consumer level, in households. Biodiesel · Biodiesel is an alternative fuel similar to conventional or ‘fossil’ diesel. Biodiesel can be produced from straight vegetable oil, animal oil/fats, tallow and waste cooking oil. The process used to convert these oils to Biodiesel is called transesterification. ○ Transesterification process is the reaction of a triglyceride (fat/oil) with an alcohol to form esters and glycerol. |
Other initiative for converting cooking oil to biodiesel
- Procuring used cooking oil from 100 cities: State-run oil marketing companies Indian Oil, Bharat Petroleum and Hindustan Petroleum launched a programme to procure biodiesel made from used cooking oil in 100 cities.
- RUCO sticker and application: A Repurpose Used Cooking Oil (RUCO) sticker and a mobile phone application for collection of used cooking was launched to ensure that the oil does not come back to the ecosystem. The sticker would be affixed by the food joints, hotels and restaurants in their premises to show that they supply UCO for producing biodiesel.
- Exchange schemes by CSIR and another by FSSAI for used cooking oil: For instance, The Indian Institute of Petroleum (CSIR-IIP) launched a scheme to incentivise households and small-time restaurants to part with used cooking oil. They will be given either 5 litres of biodiesel or 1 litre of edible oil for every 10 litres of UCO.
Benefits of the use of UCO as Biodiesel
- Improvements in Health: It will remove reused or burnt cooking medium from the food. During frying, several properties of oil are altered, Total Polar Compounds (TPC) are formed on repeated frying. The toxicity of these compounds is associated with several diseases such as hypertension, atherosclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease, liver diseases.
- Cheap to procure: Sources of used cooking oil are plenty and they can be easily procured from hotels, restaurants and even households.
- Useful in number of diesel machines: Many of these machines will not need any re-calibration for them to use this fuel.
- Environmental benefits: Another benefit derived from used cooking oil as a biofuel, is the fact that it is environmentally friendly. Biofuels produced from used cooking oil can replace fossil fuel diesel. Biodiesel burns efficiently and has less harmful impact on the environment.
Sources
Impacts of climate emergency on displacement
In News
A new data visualization by UNHCR shows how the climate emergency is converging with other threats to drive new displacement and increase the vulnerability of those already forced to flee.
About the News
- UNHCR recently released a new data visualization – ‘Displaced on the frontlines of the climate emergency’. It shows how our warming world is compounding risks for people already living with conflict and instability, driving further displacement, and often decreasing possibilities for return.
- Refugees, internally displaced people (IDPs) and stateless persons are on the frontlines of the climate emergency. Many are living in climate “hotspots” where they typically lack the resources to adapt to an increasingly inhospitable environment.
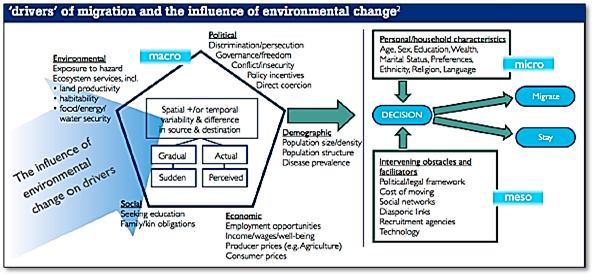
Who is a Climate Refugee or Migrant?
- The International Organization for Migration (IOM) proposes the following definition, “Environmental migrants are persons or groups of persons, who, for compelling reasons of sudden or progressive changes in the environment that adversely affect their lives or living conditions, are obliged to leave their habitual homes, or chose to do so, either temporarily or permanently, and who move either within their country or abroad”.
How is Climate change causing migration?
- Why do people migrate? People move their place of habitation because of a wide variety of social, political, economic and other environmental reasons which are all interconnected and it is difficult to delineate one from the other.
- Fundamental to the theory of climate-migration is that changes encourage individuals to leave their homes as environmental stresses make living in one place no longer feasible or desirable.
- Climatic events risk: Over the past decade, weather-related events triggered an average of 5 million new displacements each year – more than twice as many as displacements caused by conflict and violence. For instance,
- Soil degradation: It is linked to drought as well as unsustainable agricultural practices, and has also been tied to both increasing and decreasing rates of overall migration. An increased rate of short-term labor-related migration with increased soil degradation in Kenya, suggesting that migration is used as a common coping strategy to diversify income.
- Heat and Forest fires: Heat stress is associated with greater increase in long-term migration than flooding. This may be due to limited emergency relief after heat events compared with response to floods. Forest fires have also been linked to an increased intention to migrate.
What are the issues faced by these migrants or refugees?
- Lack of Recognition: On the diplomatic stage, international law does not recognize climate refugees under the 1951 Refugee Convention or the 1967 protocol, making them ineligible for any protection under national or international legal frameworks.
- Economic problems: Multiple disasters hit countries’ economies as well as individual household incomes, leaving communities with limited capacity or government assistance to recover. When combined with political and socioeconomic factors, they can push countries into a succession of crises and exacerbate instability and pre-existing vulnerabilities.
- Conflicts: Climate change does not in itself lead to conflict, but increases challenges to access to livelihoods and it puts pressure on education and health services. This is often compounded with pressures on governance and access to overall resources, and when you have challenges in relation to socio-political and religious grievances, or community structures, the combination of factors could be the spark to set everything off.
- Human trafficking concerns: Displacement or rise in migration due to disasters has raised concerns on increasing human trafficking. There have been clear evidence of linkage between disaster, migration and vulnerability to human trafficking. The UN Environment Programme estimates that trafficking goes up by 20-30 per cent during disasters.
- Food insecurity: As productive land and water become scarcer due to the impacts of climate change, decreasing crop yields and food production have major implications for food security. Prices tend to increase, making food unaffordable for many impoverished or displaced communities.
What is being done by the UNHCR in this regard?
UNHCR’s climate action agenda, which focuses on three main areas:
- Law and policy: Providing legal advice, guidance and support to the international community develop protection for refugees, IDPs and other people affected by the impacts of climate change.
- Operations: Reducing environmental degradation in places where people are already displaced and helping displaced people and host communities prepare for and adapt to the foreseeable effects of climate change. For example, in Bangladesh, UNHCR and partners have been helping Rohingya refugees reduce the risk of flooding and landslides.
- Another aspect of UNHCR’s work in this area involves helping countries with limited means and resources to better anticipate and respond to displacement caused by disasters.
- UNHCR’s environmental footprint: Improving UNHCR’s environmental sustainability by reducing our greenhouse gas emissions and minimizing negative impacts on the environment.
Way Forward
- The need of the hour is a normative shift on the issue of climate-induced migration to ensure that those victimized by anthropogenic and natural climate change are met with a compassionate, coordinated global regime rather than strict national immigration policies, like those currently employed in India.
- An inevitable event like climate migration has to be addressed by legislative and policy measures like making sure that the refugees get their due rights of settlement and rehabilitation; also ensuring the rights of indigenous people over the land and resources so as to avoid future conflicts between the groups.
- Need for strong leadership and ambition from developed countries to cut emissions and support for developing countries to adapt to climate change and recover from climate disasters. A holistic approach that places the onus on rich countries to provide support and urges developing countries to scale up efforts to protect people from climate impacts is needed.
https://storymaps.arcgis.com/stories/065d18218b654c798ae9f360a626d903
https://en.unesco.org/news/new-unesco-working-paper-impact-climate-displacement-right-education
https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/13/4/443
https://thediplomat.com/2018/08/taking-indias-climate-migrants-seriously/
https://indianexpress.com/article/opinion/climate-refugees-and-assams-future-7165653/
This Day in History- POLARIS missile
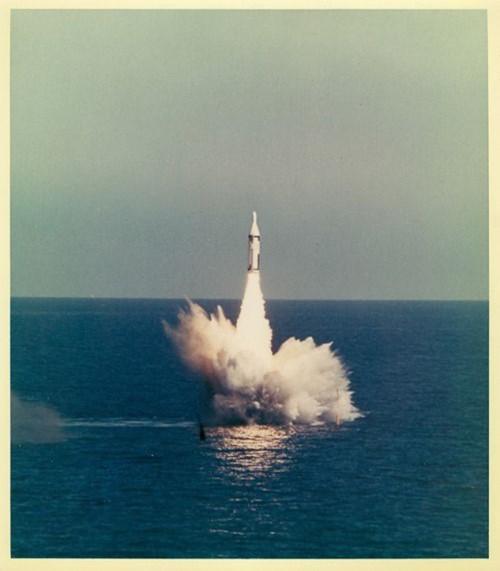

On 6 May, 1962 nuclear-armed POLARIS missile was launched from the USS Ethan Allen (SSBN-608) while being submerged in the Pacific, and its nuclear warhead was detonated over the South Pacific at the end of its programmed flight. To date, this is the only complete proof test of a U.S. strategic missile. With the ban on atmospheric testing, the chances of another similar test are remote. Polaris was a two-stage solid-fuelled submarine-launched nuclear missile. This was the first demonstration that Polaris submarines could launch missiles from the surface as well as from beneath the surface.
Image of the Day- Starship

This is image of the SpaceX prototype Starship rocket at its base. SpaceX managed to land the Starship rocket without blowing it up on 5 may, 2021. It is the first time that it has succeeded in doing so in five attempts. Eventually, SpaceX plans to combine the Starship spaceship with a Super Heavy rocket, creating a fully reusable system to explore deep into our solar system. This final version will stand 394 feet (120 meters) tall and will be able to carry 100 metric tonnes into Earth orbit -- the most powerful launch vehicle ever developed. SpaceX eventually wants to carry crew inside Starship for missions to Mars.
SUTRA Model
- Context: Scientists see flaws in Govt-backed model to forecast 2nd wave of the pandemic.
- Many scientists are blaming the government-backed model called SUTRA (Susceptible, Undetected, Tested(positive), and Removed Approach) for having a larger role in creating the perception that a second wave of Covid was unlikely in India.
- SUTRA first came into public attention when one of the expert members announced in October 2020 that India was “past its peak”.
- The model uses three main parametersto predict the course of the pandemic:
- Beta:Also called contact rate, it measures how many people an infected person infects per day.
- Reach:It is a measure of the exposure level of the population to the pandemic.
- Epsilon:It is the ratio of detected and undetected cases.
- Problems with SUTRA include:
- Variability- predictions of the SUTRA model are too variable to guide government policy.
- Lacked accounting for social or geographic heterogeneity and not stratifying the population by age
- Too Many Parameters
- Ignores Behavior of the Virus

Primary Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/government-backed-model-to-predict-pandemic-rise-and-ebb-lacks-foresight-scientists/article34479503.ece
Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI)
- Context: The IHS Markit India Manufacturing Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI)was at 55.5 in April 2021 (March- 55.4).
- It is an index of the prevailing direction of economic trends in the manufacturing and service sectors. It is a survey-based measure that asks the respondents about changes in their perception about key business variables as compared with the previous month.
- It is usually released at the beginning of every month and is thus a good leading indicator of economic activity. As the official data on industrial output, manufacturing, and Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth comes much later, PMI helps to make informed decisions at an earlier stage.
- The PMI is a number from 0 to 100: A print above 50 means expansion, while a score below that denotes contraction and a reading at 50indicates no change.
- It is different from Index of Industrial Production in a way that IIP covers the broader industrial sector compared to PMI. PMI is more dynamic compared to a standard industrial production index.
Primary Source: https://www.thehindu.com/business/Economy/factory-orders-production-rise-at-slowest-rates-in-8-months-in-april-in-india-pmi/article34471383.ece
Karen National Union (KNU)
- Context: Recently Karen rebels seized army base near Thailand border.
- KNU is Myanmar’s oldest rebel group representing ethnic minority Karen communities in Karen, or Kayin State bordering Thailand. Karen National Liberation Army, its armed wing has been battling against the Myanmar government since 1949.
- Nationalists from Myanmar's Karen ethnic minority ultimately seek equality, democracy, self-determination, human rights and their own independent state, with federal system of government.

The MSME sector needs help. First, smoothen financial flows - HT
Essence - The aim of this editorial is to highlight the importance of the MSME sector in our economy, as well as the challenges it faces and the government's efforts to address them. India’s 63 million micro, small and medium enterprises (MSMEs) contributed to 30% of the GDP. MSMEs also employ more than 100 million workers. Major problems include — the absence of viable credit providers, absence of credit products, schemes such as micro-insurance that help enterprises tide over episodic downturns, and delayed payments leading to a persistent crunch in working capital. The average number of days it takes for enterprises to receive cash for the credit sale are 176, 112 and 81 days for micro, small and medium enterprises, respectively. A recent report calculates that unlocking this delayed amount as working capital is equal to an increase in the GDP by 0.42%. While the government has taken steps such as setting up the online Receivables Discounting System (TReDS) and MSME Samadhan, they have not been very effective. Easing the cash flow woes of small businesses is vital not just for their growth but their survival.
Why you should read this article?
- To comprehend the MSME sector's contribution to India's jobs and GDP.
- It provides data on key factors that are causing financial difficulties in the MSME market.
- To learn about the government's efforts to improve efficiency and resource mobilisation.
In India’s Covid war, the role of the fauj - HT
Essence - The Covid-19 tsunami is expected to continue in India till at least the end of May, and remain an issue of concern for the rest of the year. In this context, this article suggest how Indian political and defence leadership can maximise the institutional capacity of the military in the war against Covid-19, without diluting its primary operational orientation, in the backdrop of a resource crunch.
Why you should read this article?
- Have a background knowledge about How the Indian military has been providing “aid to civil power”, since the beginning of Pandemic.
- Learn about different initiatives through which Indian policymakers can maximise the institutional capacity of the military in the war against Covid-19
Link - https://www.hindustantimes.com/opinion/in-india-s-covid-war-the-role-of-the-fauj-101620131297517.html
SAFAR: System of Air quality Forecasting And Research in metropolitan cities like Delhi
Situation before SAFAR was introduced
- Systems to scientifically assess the quality of air for the general public had not been adequately developed in India.
- Private institutes, research organisations has developed techniques in a sporadic manner for monitoring air quality.
- So the awareness about air quality, the level of air pollution and the emission levels is generally low.
- It has a direct impact on the life of the common man, primarily in the form of health so SAFAR was introduced to know the status of air quality in a period of 48-72 hours.
About SAFAR
- Ministry of Earth Sciences, Government of India, has introduced the System of Air Quality Forecasting and Research to provide location-specific information on air quality in near real time
- The system can forecast the air quality in 1-3 days in advance in major metropolitan cities such as Delhi and Pune.
- The World Meteorological Organization has recognised SAFAR as a prototype due to high quality control and standards given by it.
Outcome
- Awareness among public: It increased the awareness on climate- related events and also help in forecasting adverse environment effects.
- Health Benefits: Hospitals and medical colleges due to SAFAR stations get the data identify the rise of ailments like bronchitis cases in the area.
- Timely intimation of impending disaster extremities which help authorities to tackle the disaster.
- Input for studies on environment studies to tackle the problems of pollution
- Improvement of crop yields as the effects of pollutants on ozone, sulphur dioxide and particulate matter on vegetation can be studied.
Where can we use this case study
Data based decision making, data to tackle the pollution, nudge effect so that the citizen is sensitised to the problem of pollution.
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.