Thursday, 29th April 2021
Satellite Internet
In News
The magnitude of satellites being launched by satellite internet project Starlink of SpaceX, owned by Elon Musk, has caused concerns among competitors regarding quality of the SpaceX satellites and safety of the latter.
What is Satellite or Space internet?
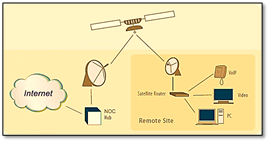
- Satellite Internet is the ability to transmit and receive data from a relatively small satellite dish on Earth and communicate with an orbiting geostationary satellite 22,300 miles above Earth's equator.
- Satellite internet is a wireless connection that involves 3 satellite dishes:
- One at the internet service providers hub
- One in space: The satellite in space is in the geostationary, medium earth orbit (MEO) or low earth orbit (LEO).
- One attached to the receiver’s router.
- Data is transmitted from the provider’s small satellite to the large satellite in space which transmits it to the receiver’s small satellite.
Benefits of Satellite Internet
- Satellite internet can provide internet connection in an area where other internet options such as cable or DSL isn’t available. So, it is an ideal internet access for users who live in rural areas, or live far away from cities or cable or phone offices.
- As it uses satellite dish for the two-way communication, does not need telephone cables or lines.
- Compared to other internet options, there is less or negligible network outages in case of satellite internet.
Starlink project
- SpaceX launched the Starlink project in 2015, wherein it aims to provide low cost and fast internet services all across the globe with very low latency rate (the time required for data to be transmitted from the provider to the receiver).
- India’s reaction to Starlink’s entry to the Indian market: With Starlink allowing Indian users to pre-order its services across several locations, Department of Telecommunications (DoT) will ask SpaceX to apply for relevant licenses before it can begin rolling out its much-anticipated Starlink satellite internet service across the country.
Centre bars use of liquid oxygen for non-medical purposes
In News
Invoking the Disaster Management Act, the Centre ordered States that all liquid oxygen shall be made available to the government and will be used for medical purposes only.
Medical Liquid Oxygen and its manufacture
- It (highly pure product) is supplied and stored as a liquid at very low temperatures, in vessels and storage tanks which in turn is converted to Medical Oxygen, a gas at normal temperatures, for the purpose of breathing.
- This converted Medical Oxygen is supplied via a medical gas pipeline system to hospitals which is used in the treatment of various illnesses that cause oxygen saturation levels in the body to drop.
- Oxygen saturationis the fraction of oxygen-saturated hemoglobin relative to total hemoglobin (unsaturated + saturated) in the blood. Normal arterial blood oxygen saturation level in humans is 95–100 percent.
- Unlike the air we breathe, which has 21% oxygen, medical grade oxygen is highly concentrated and can be obtained in several ways:
- Cryogenic distillation- oxygen is produced in air separation plants where the air is cooled, and the oxygen is distilled based on its boiling point.
- Oxygen concentrator- it is a self-contained, electrically powered medical device designed to concentrate oxygen from ambient air.
- Pressure Swing Absorption (PSA) plants: it employs a technology that absorbs nitrogen from ambient air to concentrate oxygen for supply to hospitals.
- Medical gases are regulated both by the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) and Petroleum and Explosives Safety Organization (PESO), Ministry of Commerce and Industry.

Why India is falling short of the life-saving gas?
- Officially, India’s daily oxygen production capacity is 7,127 MT and its medical oxygen requirement has increased by 76 per cent in few days’ time due to covid crisis and demand.
- Hoarding and price rise- the cost of cylinder and its refilling cost has risen 4-5 times in urban areas.
- Most Gas plants are located in Industrial Zones far from cities.
- There are fewer number of cylinders and cryogenic containers to ferry oxygen and there is considerable wastage due to poor storage infrastructure at hospitals.
Other steps taken
- Installation of Pressure Swing Adsorption Plants
- Encouraging Industrial Oxygen manufacturers to produce Medical Oxygen
- Increasing imports
Primary source: https://theprint.in/theprint-essential/how-medical-oxygen-is-supplied-to-hospitals-and-why-india-is-facing-an-acute-shortage/646443/
The role of health in foreign policy
In News
As India struggles to combat the second wave of the Covid-19 pandemic, many countries including the US, Germany, UK, Saudi Arabia, Russia, China have come forward assuring support in the form of medical equipment, vaccines and medicines for India. The pandemic has in many ways highlighted the role of health in foreign policy.
Health as an important component of foreign policy
-
Health has global ramifications: Health conditions impact beyond territorial boundaries and can have a defining effect on individual countries’ public health and may even pose a grave risk to the economy. From the HIV/AIDS epidemic in the 1990’s to the present Covid-19 pandemic, health has posed a formidable challenge to the leaders around the world.
-
Health is connected to international trade: Health has emerged as an arena of commercial interests of both governmental and non-governmental entities. Increasing collaboration can be seen between health and trade ministers within and among several countries. For instance, regional organizations like ASEAN have included the need to strengthen the national and collective capacity on issues of health implications of globalisation and trade liberalisation. The adoption of Sustainable Development Goals have further strengthened this linkage.
-
Linkage of Health and Security: The rise in the transborder spread of infections, non-communicable diseases and biological threats not only serve as a source of social and political unrest but also create diplomatic tensions between countries.
-
Health diplomacy is part of multilateral cooperation: Health diplomacy includes supply of vaccines, medical equipment and drugs. Health diplomacy is an integral part of multilateral cooperation through organizations like the WHO.
What are the challenges of including health as part of foreign policy?
-
Health issues have technical and scientific core: Health has been treated as a secondary matter in foreign policy, particularly due to the lack of awareness about the interconnectedness between health and areas of politics.
-
Health is considered a fundamental national responsibility: States still consider health issues as a fundamental national responsibility — despite their transnational character — and approach health-related challenges within nationalist frameworks.
-
Lack of coordination among agencies dealing with health: The collection of multilateral entities and bilateral agencies responsible for improving the health of the global population suffer from coordination issues and have failed to establish relationships conducive to collective action.
How has India promoted health as part of its foreign policy agenda?
-
Commitment to traditional health practices: India has made attempts to internationalise traditional health practices and ancient medical systems. AYUSH has become part of WHO’s Traditional Medicine Strategy 2014-2023 and member states of the WHO South East Regional Office signed the Delhi Declaration in 2014 to boost cooperation, collaboration in all fields of traditional medicine.
-
Robust pharma industry: The pharma manufacturing industry of India has helped it to emerge as a leader in the supply of generic medicines and vaccines. As part of the indigenous vaccine manufacturing effort, India became the first country in the region to develop the rotavirus vaccine through collaboration between academia, industry and international institutions. Indian pharma currently contributes around 20 percent of the worlds’ generics and 62 percent of the global vaccines.
-
Health as part of India’s Neighbourhood Policy: The vaccine development programme received fresh impetus under the government’s Neighbourhood First and Act East Policy. The Aysuhman Bharat also includes global components by way of extending affordable healthcare through telemedicine to other countries, especially developing ones.
-
Efforts during the Covid 19 pandemic: India has been prompt in its response to the UN Secretary General’s call for global solidarity against the pandemic. In the initial months following the outbreak, India ramped up the commercial supplies of essential drugs like hydroxychloroquine, paracetamol and azithromycin, and testing kits to around 90 countries. India has invested in producing affordable COVID-19 vaccines and has also pushed for its rapid and easy access by poor countries.
What are the ways in which health can be integrated in foreign policy in the future?
-
Public Health as an integrated public good: Promotion of health through foreing policy should be based on understanding public health as an integrated public good that benefits the state’s pursuit of security, economic well-being, development efforts and respect for human dignity.
-
Engage non state actors: Non-governmental organizations (NGOs), such as universities and schools of public health, could contribute to the pursuit of public health as an integrated public good by deepening understanding of the health–foreign policy dynamic and training prospective public health practitioners.
-
Looking beyond donor-recipient relationships: Inclusion of health as part of foreign policy should move beyond the traditional donor-recipient relationship to develop meaningful partnerships across developed and developing countries.
Sources
Immunization Agenda 2030: A Global Strategy to Leave No One Behind
In News
The Immunization Agenda 2030 titled as a ‘Global Strategy to Leave No One Behind’ was launched by WHO, UNICEF, GAVI and other partners with an ambitious new global strategy to maximize the lifesaving impact of vaccines through stronger immunization systems.
Importance of immunization
- Saving lives and protecting the health of populations - Immunization has reduced the number of deaths from infectious diseases dramatically. Vaccines also prevent disability, which can impair children’s growth and cognitive development. Between 2010 and 2017, the mortality rate of children under 5 years of age decreased by 24%, due in large part to immunization.
- Improving countries’ productivity and resilience - Preventing infections reduces the burden on health systems, and a healthier population is a more productive one. Children protected against infectious diseases have better educational attainment and contribute more to national development and prosperity.
- Ensuring a safer, healthier, more prosperous world - Vaccines are a critical component of the battle against emerging and re-emerging infections. Pathogens are not bound by national borders, and local and international movement of people can rapidly spread infections. Increasing urbanization results in large, dense populations, raising the likelihood of infectious disease transmission and outbreaks. In addition, climate change exposes new populations to vector-borne diseases and may alter the patterns and intensity of seasonal diseases.
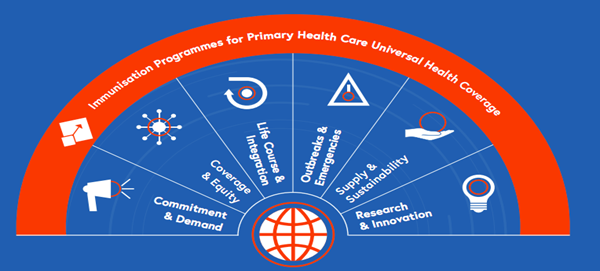
Core Principles of Immunization Agenda 2030
- Responding to population needs: The design, management and delivery of immunization services should be shaped by and responsive to the needs of individuals and communities, including addressing barriers to access to immunization services due to age, location, social and cultural norms and gender-related factors.
- Partnerships to increase efficiency: Immunization partners should align and coordinate their actions to increase efficiency, build on complementarity and involve sectors beyond immunization for mutual benefit.
- Bottom up process: Countries should establish targets that represent the local context and should be held accountable for achieving them.
- Promoting evidence-based decision-making: High-quality, “fit-for-purpose” data will be used to track progress, improve programme performance and form the basis of decision making at all levels.
Challenges in immunization
- Sustaining trust in vaccines: Uptake of vaccination depends on many factors, from the convenience and quality of facilities and services to the spread of misinformation about the safety and effectiveness of vaccines. These considerations must be addressed to enhance and sustain trust in vaccines and immunization services in communities, to increase health literacy with a focus on vaccination at all levels, and to build resilience against misinformation and vaccine hesitancy.
- Inequity: The benefits of immunization are not spread equally, either among or within countries. In 2018, 70% of unvaccinated children lived in middle-income countries.
- Population movements: Migration and cross-border population movements can result in large communities of unprotected individuals at risk of infection. There is a lack of accountability among public authorities with respect to vaccinating migrant populations.
- Climate change and natural disasters: The world’s changing climate will have significant implications for the prevalence of infectious diseases. New populations will be exposed to vector-borne diseases such as malaria and dengue, and more flooding will increase the spread of waterborne diseases such as cholera.
- Conflict and political instability: Civil conflict can rapidly lead to loss of health service infrastructure and shortages of trained health workers, often for extended periods, thereby disrupting delivery of immunization services. The affected populations are also frequently at higher risk of infectious diseases because of the breakdown of national infrastructure and mass displacement into temporary settlements.
Sources
https://www.who.int/teams/immunization-vaccines-and-biologicals/strategies/ia2030
This day in History- Construction of Delhi's Red fort had commenced by laying the Foundation Stone by Shah Jahan

On 29 April 1639, Construction of Delhi's Red fort had commenced by laying the Foundation Stone by Shah Jahan. This fort was completed on May 13, 1646. The first monument built in the new capital, after Shah Jahan shifted capital from Agra to Delhi the Red Fort. It was also known by the names of Qila-e-Mubarak (The Fortunate Citadel),Qila Shahjahanabad or Qila-e-Mualla (The Exalted Fort). The fort was central to the plan for the new capital. The Red Fort took nine years to build, and when it was done it really was a city within a city. It held palaces, barracks, marketplaces, assembly halls and public areas.
Image of the Day- Eden Project
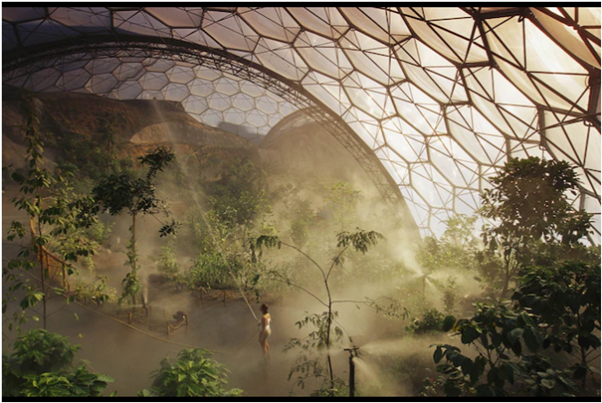

This is picture of the Eden Project in Cornwall, England, where the morning mist covers 4,500 different plant species. Opened in the year 2001, its tropical biome is the largest indoor rainforest in the world. The dome houses tropical plants including sugar cane, banana trees and coffee trees, as well as a waterfall and reproduction homesteads. Visitors can also see birds and insects but no larger animals. The main goal of the Eden Project is to educate the public about the natural world.
Joint logistics node (JLN)
- Context: The Chief of Defense Staff General Bipin Rawathas operationalized the third Joint Logistics Node (JLN) in Mumbai (others being Guwahati and Port Blair).
- The JLNs will provide integrated logistics support to the armed forces for their arms ammunition, rations, fuel, transport, and engineering support to synergize their operational efforts.
- The initiative would save manpower, economize utilization of resources, strengthening cohesion and create avenues for financial savings.
- It is the precursor to the joint logistics commandwhich will lead to setting up of integrated theatre commands for the best use of military resources to fight future battles.
|
About Integrated Theatre Command · An integrated theatre command envisages a unified command of the three Services (Army, Air Force and Navy) under a single commander, for geographical theatres (areas) that are of strategic and security concern. · The commander of such a force will have all resources at his disposal from all the three services with seamless efficacy. |
Primary Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/cds-rawat-launches-joint-logistics-facility-in-mumbai/article34216887.ece
Advanced Chaff Technology
- Context: The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has developed an Advanced Chaff Technology tosafeguard the naval ships against enemy missile attack.
- Chaff is a passive expendable electronic countermeasure technology used to protect naval ships from enemy’s radar and Radio Frequency (RF) missile seekers.
- The chaff rockets deployed in the airappear as multiple targets for the missile guidance systems and deflect adversary missiles, thus protecting their own assets.

Primary source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1709617
Supreme Court panel red-flags Goa rail project
- Context: Raising serious environmental concerns, the Supreme Court’s Central Empowerment Committee (CEC) has red-flagged a key rail expansion project in Goa and suggested changes in power and road plans.
- These projects cut through the Bhagwan Mahaveer Wildlife Sanctuary (BMWS) and the Mollem National Park (MNP) in South Goa.
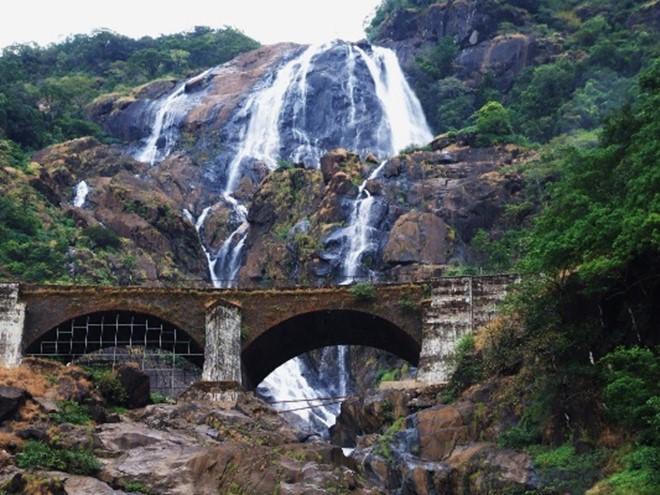

Bhagwan Mahaveer Wildlife Sanctuary and Mollem National Park
- The Bhagwan Mahavir Wildlife Sanctuary is located in the Goan town of Mollem and contains within it Molem National Park
- The region locates geographical milestones like the Devil's Canyon and the Dudhsagar Waterfalls.
Primary source: http://goatourismtravels.com/sight-seeing/wildlife/bhagwan-mahavir-wildlife-sanctuary/#.YIpz_5AzbIU
Digitalising education will also democratise it - IE
Essence - With public schools being completely shut for an entire year now, the majority of our kids have had no access to any form of education for over 12 months. Due to obvious problems like lack of smart devices and access to the internet, these kids have missed an entire year of schooling. Most of them have probably also forgotten what they already knew. In this context, the article calls for creative solutions to the mammoth education crisis while suggesting possible short term measures.
Why you should read this article?
- Learn about the creative ways to solve gaping education crisis in short term such as restarting schools at outdoor locations and in smaller groups, expanding the definition of teachers, disseminating free standardised content through existing widespread mediums.
- Understand how democratisation of education through its digitalisation can be a boon in the long term to ensure quality education.
Making social welfare universal - TH
Essence- Article discusses how in the absence of social capital, economic capital is insufficient in accessing healthcare facilities as seen in case of COVID-19 where India despite being one of the largest welfare states in the world witnessing multiple crises. To manage such crisis we need to, one, leverage our existing schemes & can provide universal social security on the lines of Pulse Polio Universal Immunisation Programme. Second, we need a universal system for social security schemes or welfare provisions like- education, maternity benefits, disability benefits etc. That would improve the ease of application by consolidating the data of all eligible beneficiaries under one database. It can also reduce exclusion errors & also would ensure a better standard of living for the people. For implementation of any of these ideas is only possible through a focus on data digitisation, data-driven decision-making and collaboration across government departments.
Why you should read this article?
- To understand the importance of social capital and how its absence makes economic capital insufficient.
- To understand the importance of universal system for providing social security or welfare provisions.
- To know what possible steps India can take to manage such crisis in future.
Link - https://www.thehindu.com/todays-paper/tp-opinion/making-social-welfare-universal/article34434985.ece
How An IAS Officer Cut Nandurbar’s Single-Day COVID-19 Spike By 75%
Situation in the country
While India’s healthcare infrastructure finds itself overwhelmed by the surge in cases
Nandurbhar District presents a different example
- District has 150 vacant beds and two oxygen plants with combined capacity of 2,400 litres/ minute.
- Due to sufficient resources, robust health infrastructure, people from neighbouring like Madhya Pradesh & Gujarat have been admitting themselves in Nandurbar.
- With the additional admissions too, district has managed to slash the positivity rate by 30%.
- The daily active cases have decreased from 1,200 to 300.
- Nandurbar District Collector Dr Rajendra Bharud, the administration staff, doctors and volunteers, are to be credited for this feat.
People friendly infrastructure
- After the steady decline in cases, many other cities dismantled the temporary COVID-19 facilities. However, Nandurbhar district did not let the guard down rather they ramped up the infrastructure.
- For monetary purpose, a combination of resources, like district planning fund, development funds, state disaster relief funds, CSR were used to meet expenses.
- For patients the oxygen pipes were given as soon as saturation levels started dropping, instead of waiting for the critical stage. So the patients use only 30% of oxygen, as against 90% in the latter situation
- Schools, Community halls were converted into COVID-19 centres. Website and control room were created to systematically guide the citizens. This would also ensure that people were not running from pillar to post in search of beds.
Outcome
District has been afloat even amid the second wave of coronavirus, with adequate oxygen supply, beds due to a well-planned vaccination drive and systematic preparation beforehand
Where can we use this case study?
Innovative steps to tackle covid crises, steps to take pre-emptive steps to tackle a disaster, how to improve health infrastructure locally, Covid Best Practices.
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.