Wednesday, 12th May 2021
NITI Aayog and Mastercard Release Report on Connected Commerce: Creating a Roadmap for a Digitally Inclusive Bharat
In News
The NITI Aayog and Mastercard have recently released a report titled ‘Connected Commerce: Creating a Roadmap for a Digitally Inclusive Bharat’. The report has identified challenges in accelerating digital financial inclusion in India and provides recommendations for making digital services accessible to its 1.3 billion citizens.
What are challenges identified in digital financial inclusion?
- Demand side gap: One of the demand side gaps that has been identified includes the need to create user-friendly digital products and services that will help in bringing about behavioural transition from cash to digital. Government needs to incentivize small businesses, consumers, and merchants for the digitized last mile.
- Lack of success in Agri-Tech: Most agri-techs have not succeeded in digitizing financial transactions for farmers or enabling formal credit at lower rates of interest by leveraging transaction data.
- Gaps in MSME access to Formal Finance: Credit delivery to MSME’s has continued to remain a challenge despite the promotion of government schemes like MUDRA scheme, the 59-minute loan scheme and the Credit Guarantee Scheme. The data reveals that overall credit from scheduled commercial banks particularly that given to MSME’s continues to grow slowly.
- Security breaches in digital commerce: Trust is a critical factor for new users joining digital payment systems. Any data breaches and failures result in setbacks and users lose confidence in digital payments. Trust is a critical challenge as many citizens want to be assured that the money in their accounts is safe and that they are being offered an appropriate range of products.
- Digitally accessible transit systems: With the onset of the pandemic, there is an increasing need for transit systems to be further integrated with contactless payments in India. Globally, the trend is toward open-loop transit systems, with interoperable payment solutions allowing travellers to switch between different modes of transport with a connected payments network.
What are the recommendations regarding digital financial inclusion in the report?
- Strengthening the payment infrastructure to promote a level playing field for NBFCs and banks.
- Digitizing registration and compliance processes and diversifying credit sources to enable growth opportunities for MSMEs.
- Building information sharing systems, including a ‘fraud repository’, and ensuring that online digital commerce platforms carry warnings to alert consumers to the risk of frauds.
- Enabling agricultural NBFCs to access low-cost capital and deploy a ‘phygital’ (physical + digital) model for achieving better long-term digital outcomes.
- To make city transit smoothly accessible to all with minimal crowding and queues, and leveraging the use of existing smartphones and contactless cards
Sources
MNREGS registrations spike
In News
The number of MNREGS registrations have doubled from the year-ago period in the present second wave of covid-19.
About the News
- The first wave of the pandemic saw a spike in demand for jobs in MGNREGS due to reverse migration, touching record highs in May, June 2020. The number of registrations has doubled from the year-ago period in second wave.
- In view of the recent lockdowns, many rating agencies have revised Indian GDP forecasts. Nomura, for instance, rejigged the GDP for FY22 to 11.5% from 12.4%.
- A rising trend in demand for rural employment is an indicator of proportionate labour shortage in industrial units, both in organized and small-scale sectors.
About MGNREGS
- The Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act, 2005, guarantees 100 days of employment in a fiscal to adults in rural households willing to undertake unskilled labour.
- It is based on the principles of the Keynesian theory that during a downturn, governments can help generate employment and push demand by putting money in people’s hands.
- The scheme, which aims to generate employment and build infrastructure, ensures that productive economic activities are undertaken.
- The Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employee Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGA) has generated more rural employment than any other government scheme or private initiative in the history of independent India.
How does MGNREGS work as a shock absorber or buffer for the economy?
- Helped economy in times of crisis: The Indian economy is known to be domestic consumption-led, where 80% of the GDP relies upon the domestic market. With nearly 65% of people living in rural areas, increased and continuous demand among the rural population has boosted the economy in times of crisis.
- During the 2008-09 sub-prime crisis, the economy was insulated from the global financial crisis due to the rural purchasing power brought by the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme. Recovery from the first wave of the pandemic was faster than expected mainly due to a resilient rural economy.
- Agricultural productivity: The scheme has boosted agricultural productivity through development of wasteland/fallow land, and construction of post-harvest storage facilities and work sheds.
- Income to female-headed households: MGNREGA has been a critical source of income for female-headed households, providing as much as 15 percent of the household income in some states. It has also given a fillip to rural entrepreneurship, with households using the supplementary income to start a rural business.
- Multiplier effect: MGNREGA has also had a multiplier effect on the rural economy, with the additional purchasing power generated from it spent on items produced in the rural economy.
- Needs to be a buffer: But MGNREGS should continue only as a buffer. The need of the hour is for other stakeholders, especially manufacturing units, to build infrastructure that takes care of migrants during crises. Employers may expand their HR horizon by keeping migrant labourers gainfully employed, upskilling migrants and facilitating intrastate employment.
https://www.thehindu.com/sunday-anchor/is-the-mgnrega-being-set-up-for-failure/article7265266.ece
Union Agriculture Ministry allots funds for Horticulture Sector
In News: Keeping in view the huge potential and role of the horticulture sector in increasing farmer’s income and for the promotion of holistic growth of the sector in the country, the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare has provided an enhanced allocation of Rs. 2250 Crore for the year 2021-22 for Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH).
What is Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH):
- Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH) is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme for the holistic growth of the horticulture sector covering fruits, vegetables, root & tuber crops, mushrooms, spices, flowers, aromatic plans, coconut, cashew, cocoa and bamboo.
- The schemes under MIDH include National Horticulture Mission, Horticulture Mission for Northeast and Himalayan States (HMNEH), cluster development program, credit push through Agri Infra Fund, formation and promotion of FPOs.
- MIDH provides technical advice and administrative support to State Governments/State Horticulture Missions (SHMs) for the Saffron Mission and other horticulture related activities like Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY)/NMSA.
Achievements of MIDH:
- Area and production during the years 2014 – 15 to 2019 – 20 has increased by 9% and 14% respectively.
- The mission has boosted best practices followed in farms which have significantly improved the quality of produce and productivity of farmland.
- The initiative of MIDH has resulted in India’s self-sufficiency in the horticulture sector and contributed towards achieving sustainable development goals of zero hunger, good health and wellbeing, no poverty, gender equality etc.
How has the Government Intervention enhanced the sector?
- India’s estimated demand is around 650 Million MT of fruits and vegetables by the year 2050.
- Accordingly, the government’s intervention in the sector has led to increased horticulture production (India recorded its highest ever horticulture production of 320.77 million tonnes in 2019) that has surpassed the agriculture production in the country.
Significance of Horticulture:
- Horticultural crops constitute a significant portion of the total agricultural produce in India.
- They cover a wide cultivation area and contribute about 30% of agricultural GDP and account for 37 per cent of the total exports of agricultural commodities from India.
- It has played a vital role in generating employment as it is labor intensive and provides raw material to various food processing industries, pharmaceutical etc, and gives higher farm profitability due to higher production and export earnings from foreign exchange.
- Horticulture crops are a source of nutrients, vitamins, minerals, flavour, aroma, dietary fibres, which contain health benefiting compounds and medicines.
- The comparative production per unit area of horticultural crops is higher than field crops, e.g., paddy crop gives a maximum yield of 30 q/ha, while banana crop gives 300–450 q/ha and they also require low irrigation and input cost.
- These crops have aesthetic value and protect the environment.
Primary source:
India-EU Leaders Meeting
In News
The Indian Prime Minister recently participated in the India-EU Leaders’ Meeting with the leaders of all 27 member states of the European Union. India and EU agreed to relaunch the trade talks in a major push to boost ties during the video summit.
Prominent Highlights of the Meeting
|
Free Trade Negotiations |
India and EU agreed to relaunch free trade negotiations by resuming talks that were suspended for the Bilateral Trade and Investment Agreement (BTIA). India and EU had launched talks for having a wide-ranging Free Trade Agreement (FTA), called broad-based BTIA, in 2007. The BTIA was proposed to encompass trade in goods, services, and investments. The talks stalled in 2013 over differences on market access and movement of professionals. |
|
Global Health Preparedness and Resilience |
The India-EU Leaders Meeting noted the intent to cooperate on resilient medical supply chains, vaccines, and Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, and on the application of good manufacturing standards to ensure high quality and safety of products. |
|
Green Growth |
The two sides reiterated their commitment to achieving the goals of the Paris Agreement and they agreed to strengthen joint efforts for mitigation, adaptation and resilience to the impacts of climate change, as well as providing means of implementation including finance in the context of Conference of the Parties (COP 26). India welcomed the EU’s decision to join the Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI). |
|
Fostering inclusive growth through trade, connectivity, and technology |
The High-Level Dialogue on Trade and Investment has been tasked to ensure market access and review the resilient value chains. The India-EU Aviation Summit will also help in enhancing air connectivity in a fair and equitable manner. India and EU are also looking to deepen their technological cooperation on Quantum and High-Performance Computing. A High-Level India-EU Digital Investment Forum would also be organized later this year. |
|
Indo Pacific |
The two sides noted their commitment to a free, open, inclusive and rules-based Indo-Pacific space, underpinned by respect for territorial integrity and sovereignty, democracy, and rule of law. |
Significance of the Summit
- Cooperation within Multilateral Framework: India and EU have shown commitment towards maintaining the multilateral framework fulfilling the goals set up in the Paris Agreement, 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, the UN Convention on Biological Diversity, International Labour Organisation conventions, etc. The India-EU Connectivity Partnership recognised India as a sustainable development partner towards jointly supporting resilient and sustainable connectivity in third countries and regions like Africa, Central Asia and the Indo-Pacific.
- Aligned India-EU approach in Indo Pacific: Over the past two years, the internationalisation of the Indo-Pacific construct has spurred extra-regional powers to emphasise cooperation with regional players like India. As pointed out in the India-EU Maritime Security Dialogue held earlier this year, both India and EU recognize the strategic relevance of the Northwest Indian Ocean and East Africa region in the wider Indo-Pacific.
- Focus of Digital Connectivity: The focus of the EU-India meet on digital connectivity is important for India as India has recently rolled out the 5G trials. New areas of cooperation like artificial intelligence and high-performance computing will be critical for the cooperation between India and Europe in the coming years.
- Health Cooperation: The Summit also comes at a time when India is fighting the second wave of the Covid-19 pandemic. The EU has announced emergency funding to support the WHO’s measures to help India deal with increasing cases of Covid-19.
Roadblocks in India-EU relations
- Pharmaceutical Sector: India is seeking European cooperation to reduce its dependence on Chinese Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients. India-EU pharmaceutical linkages have had their share of long-standing divergences over issues like exclusivity of clinical trial data.
- Economic Relations: India and EU had launched the negotiations on a Broad-based Trade and Investment Agreement in 2007. The negotiations stalled in 2013 and were not brought up during the 15th India-EU Summit last year. The bilateral trade has grown and has remained below potential.
- China’s Influence: The EU has close trade links with China and its dependence has been growing on the Chinese Markets. A significant portion of the trade value of the EU comes from supply chains in China.
- EU’s positions on India’s domestic politics: EU has often taken a strong position on issues that are related to India’s internal affairs. The abrogation of article 370 and 35A and the passing of Citizenship Amendment Act (CAA), 2019 received considerable attention from the EU, with many Members of European Parliament speaking out on possible human rights violations.
Way Forward
- Promoting Multilateralism: India and EU can make use of existing multilateral forums like the UN and G20 to promote rules-based order that ensures inclusive growth. They can develop joint initiatives to reform the WHO and the WTO.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Europe needs to address the supply chain vulnerabilities that arise from overdependence on China. India and EU can work on a mutually beneficial supply chain mechanism as it would create new synergies in terms of business and connectivity between India and the EU.
- Cooperation on Health Sector: The pandemic has revealed the urgency for cooperation on global health. India and the EU have called for a reform of the World Health Organisation. Therapeutics, disease management and preventive technologies can also be some of the areas of cooperation.
Conclusion
The India-EU Leaders Meeting will provide fresh direction for implementing the ambitious India-EU Roadmap 2025 that was adopted in the India-EU summit held last year. India and the EU can partner towards diversification of strategic value chains as well as creating opportunities for innovation and growth.
Mains Question:
The EU and India partnership has been slow-moving and fragmented, struggling to maintain momentum. Identify the challenges and opportunities in India-EU relationship.
Sources
- https://www.orfonline.org/expert-speak/india-eu-summit-aligning-brussels-and-new-delhis-propositions-for-the-indo-pacific
- https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/economy/foreign-trade/india-eu-announce-connectivity-partnership-to-checkmate-china/articleshow/82487420.cms
- https://www.reuters.com/world/europe/eu-india-re-launch-trade-talks-virtual-summit-2021-05-08/
- https://mea.gov.in/bilateral-documents.htm?dtl/33853/Joint_Statement_on_IndiaEU_Leaders_Meeting_May_08_2021
This Day in History- International Nurses and Midwives Day
The International Nurses and Midwives Day is celebrated every year on May 12 globally to appreciate the nurses' efforts. On this day in 1820, Florence Nightingale, the world's most famous nurse was born. She is considered to be the founder of modern nursing. The theme for this year's International Nurses Day is Nurses: A Voice to Lead - A Vision for Future Healthcare. Nurses are at the forefront of fighting the COVID-19 pandemic. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 9 million more nurses and midwives are required by 2030 so that all countries can attain Sustainable Development Goal (SDG)-3 on health and well-being.

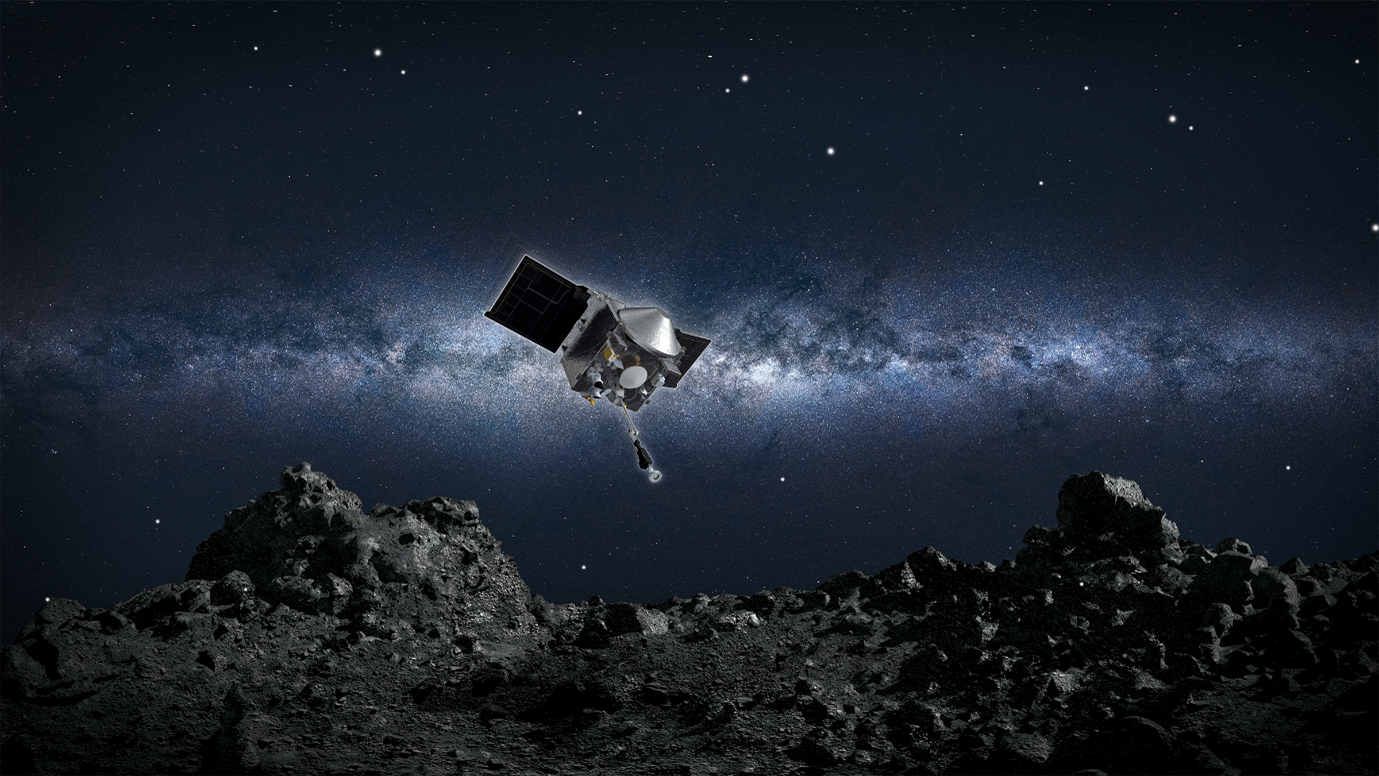
Image of the Day- Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security, Regolith Explorer (OSIRIS-REx) spacecraft
This is the image of NASA’s Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security, Regolith Explorer (OSIRIS-REx) spacecraft, which has departed from asteroid Bennu on May 11, 2021, and started its two-year long journey back to Earth. OSIRIS-REx is NASA’s first mission to visit a near-Earth asteroid, survey its surface and collect a sample from it. Bennu is considered to be an ancient asteroid that has not gone through a lot of composition-altering change through billions of years, which means that below its surface lie chemicals and rocks from the birth of the solar system.

Jal Jeevan Mission
- Context: Puducherry has achieved the target of 100% piped water connection in rural areas under Jal Jeevan Mission.
- Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM) is the mission to supply water infrastructure so that every rural household has Functional Tap Connection (FHTC) by 2024 and water in adequate quantity of prescribed quality made available on regular basis. It operates under the Ministry of Jal Shakti.
- The Mission is based on a community approachand focuses on integrated demand and supply-side management of water at the local level.
- Jal Jeevan Mission (Urban) was announced under the Housing and Urban Affairs Ministry in the 2021-22 Budgetto provide universal coverage of water supply to all households through functional taps in all statutory towns in accordance with SDG-6 (clean water and sanitation).

Primary source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1694420
https://www.medicircle.in/sensorbased-system-monitoring-jal-jeevan-mission
H-1B Visa - Edukemy Current Affairs
- Context: ending the lottery-based system of allocating H-1B visas will make it tough for international students to get a work permit in the US.
- The H-1B visa is a work permit that allows foreign workers to go to the United States and work for American companies.
- The foreigner must specifically work in a field that requires specialized knowledge, for which the employer cannot find a US-based worker.

Primary source: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/nri/visa-and-immigration/what-is-an-h-1b-visa-heres-everything-you-need-to-know/articleshow/76683083.cms
Super Cycle of Commodities
- Context: Rise in global commodity prices.
- A commodity super cycle is a sustained long period in which commodities trade above their long-term price trend.
- Steel,other metals including base and precious metals, sugar, corn, coffee, soybean oil, palm oil have risen sharply in the the commodity market.
- The new commodity super cycle is the result of-
- recovery in global demand
- supply-side constraints
- expansionary monetary policy
- investment in asset creation
- The super cycle will have an impact on the overall inflation, economic recovery and policy making.
Primary Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/business/commodities-in-super-cycle-hit-highs-but-cast-cloud-over-recovery-inflation-7309966/
Gopal Krishna Gokhale
- Context: his birth anniversary.
- Protégé of MG Ranade, he worked towards realizing constitutional ideals in India in liberal ways and abjured the use of reactionary or revolutionary ways. Gandhi regarded Gokhale as his political mentor.
- As a member of Bombay Legislative Council, Gokhale opposed the British land revenue policies, advocated free and compulsory primary education, and asked for the creation of equal opportunities to fight against untouchability.
- He joined the Indian National Congress emerging as one of its moderate leaders and became its president at INC Banaras session in 1905.

Primary source: https://indianexpress.com/article/who-is/who-was-gopal-krishna-gokhale-liberal-nationalist-mahatma-gandhi-6403225/
National Financial Reporting Authority (NFRA)
- Context: NFRAis in the process of creating a verified and accurate database of companies and auditors that come under its regulatory ambit.
- Set up in 2018 under the Companies Act, NFRA is a regulatory body to oversee compliance with accounting and auditing standards of companies that can be described asPublic Interest Entities (PIEs). This group includes all listed companies, and large unlisted companies.
- The organization works in public interest and consists of a chairperson, who shall be a person of eminence and having expertise in accountancy, auditing, finance, or law, appointed by the Central Government and such other members not exceeding 15.

Primary source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=1522343
Why India must not say ‘no’ to NATO
Essence: NATO is not offering membership to India; nor is Delhi interested. At issue is the question of exploring potential common ground.
During the Cold War, India’s refusal to talk with NATO was premised on its non-alignment. That argument had little justification once the Cold War ended during 1989-91. Since then, NATO has built partnerships with many neutral and non-aligned states. NATO has regular consultations with both Russia and China, despite the gathering tensions with them in recent years.
Delhi knows that no single power can produce stability and security in the Indo-Pacific. India’s enthusiasm for the Quad is a recognition of the need to build coalitions. A sustained dialogue between India and NATO could facilitate productive exchanges in a range of areas, including terrorism, changing geopolitics; the evolving nature of military conflict, the role of emerging military technologies, and new military doctrines. Would Russia be upset with India’s engagement with NATO? Russia has not made a secret of its allergy to the Quad and Delhi’s dalliance with Washington. Putting NATO into that mix is unlikely to make much difference. Delhi, in turn, can’t be happy with the deepening ties between Moscow and Beijing. As mature states, India and Russia know they have to insulate their bilateral relationship from the larger structural trends buffeting the world today.
Why you should read this article?
- To comprehend the course of Delhi's interaction with European powers, as well as the underlying reasons for it.
- To gain an understanding of the pre-independence power struggle in the Indian peninsula between European powers, as well as how this has influenced India's foreign policy.
- To learn about the opportunities that NATO offers India in terms of strategic outreach.
Editorial Link: https://indianexpress.com/article/opinion/columns/why-india-must-not-say-no-to-nato-7260435/
Energy democracy needs more than laws
Essence: Despite having Electricity (Rights of Consumers) Rules, inefficient process of harnessing, transmitting, and distributing energy is preventing the equitable access to energy and are resulted in soaring debt. To ensure energy democracy and consumer empowerment we need distributed energy resources, reliable smart grids, robust utilities, efficient power markets and enabling regulations. While large grids and concentrated high-capacity generation units are ingredients of energy security for the country, energy democracy needs focus on distributed energy resources (DERs) (called harbinger of equitable and inclusive source of energy access). On the other hand, solar roof top requires the enabling regulations and a robust grid to handle variability of energy generation and capability of balancing the grids. India’s power utilities have been facing systemic efficiency issues over last many years now. Moving away from monopolistic distribution markets and increasing billing and collection efficiencies are the critical ingredients to correct the trajectory. Smart metering program of government seeking utilities to install smart pre-paid meters based on Build, Own, Operate and Transfer (BOOT) model is poised to be the next big move towards consumer empowerment and building efficient utilities. The success of democratised energy systems will require the convergence of technological innovations, conducive policy reforms and a shift in consumption patterns and behaviour.
Why you should read this article?
- To understand the meaning of energy democracy and consumer empowerment and why are they important.
- To understand why energy needs focus on distributed energy resources (DERs) and what are their current contribution in energy generation.
- To know the possible steps India could take towards consumer empowerment.
Editorial Link: https://www.thehindubusinessline.com/opinion/energy-democracy-needs-more-than-laws/article34537090.ece
Vision of Better sanitation for rural India: SCOPE
Background:
- Padma Awardee Marachi Subburaman’s NGO, Society for Community Organisation and Peoples Education (SCOPE) has focused on improving sanitation in rural India from 1986.
- SCOPE was initially started with an intention to help young widows and women which aimed at providing training women in tailoring, mat weaving.
Turnaround in vision:
- Few years later, when detailed study was conducted on how the income was being used, it was realised that a lot of their income went in hospital expenditure due to infections caused by contaminated drinking water and improper sanitation.
- Then, the focus got shifted to sanitation and drinking water.
- To provide safe sanitation practises without overconsuming the water, NGO created ECOSAN toilets (Ecological sanitation), which are dry toilets, with no flushes and septic tanks.
- The excreta becomes compost, which is excellent for the soil.
Outcome:
- Nature-based sanitation solutions help treat human waste before it returns to the environment.
- Health Benefits as it has reduced infections, diarrhoea-related diseases in children.
- Improved the nutritional status of children as avoidable infections could be avoided due to better sanitation practises
Where can this case study be used:
- It can be used to highlight the contribution of NGOs in solving the problems in rural areas, to understand the importance of toilet (Use it an example under Swachh Bharat Abhiyan), how to use waste for effective purpose: Excreta to compost use the example of ECOSAN toilets.
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.