Monday, 15th February 2021
First-Ever Voluntary Guidelines on Food Systems and Nutrition
In News
The first-ever voluntary guidelines on food systems and nutrition meant to end hunger and malnutrition were endorsed by members of the UN Committee on World Food Security (CFS).
Guidelines
These are structured around seven focus areas:
Significance of Guidelines
UN Committee on World Food Security (CFS)
Vigyan Jyoti programme
In News
The second phase of Vigyan Jyoti programme was commenced on the occasion of International Day of Women and Girls in Science on February 11, 2021.
About the Programme
- It is an initiative to encourage girls to take interest in science and build career, launched by the Department of Science & Technology (DST).
- It had been running successfully in 50 Jawahar Navodaya Vidyalayas (JNV) for a year and has now been expanded to 50 more JNVs for the year 2021-22 in second phase.
- Vigyan Jyoti activities include student-parent counselling, visit to labs and knowledge centres, partner’s role model interactions, science camps, academic support classes (online), resource material distribution and tinkering activities.
- The programme also has financial dimension. The girls will be given a modest financial incentive to cover their additional expense like travel to camps.
Under-representation of women in STEM
- Data compiled by the DST shows that females comprised 24 per cent of the total pas-out students in STEM subjects in engineering, 22 per cent at the post graduate level, 28 per cent at M Phil and 35 per cent at the PhD level.
- There are only 10 per cent of girls in the IITs and the number has remained static over the years.
Other initiatives to bring gender parity in Science & Technology (S&T)
- Women Scientists Scheme to help women with career-break.
- Indo-US Fellowship for Women in STEMM (WISTEMM) program where women scientists can work in research labs of USA.
- Consolidation of University Research for Innovation and Excellence in Women Universities (CURIE) programme for improving R&D infrastructure and establishing state-of-the-art research facilities in order to create excellence in S&T in women universities
- Gender Advancement for Transforming Institutions (GATI) program in pilot mode.
- SERB- POWER (Promoting Opportunities For Women in Exploratory Research) program was also launched recently.
First-Ever Voluntary Guidelines on Food Systems and Nutrition
In News
The first-ever voluntary guidelines on food systems and nutrition meant to end hunger and malnutrition were endorsed by members of the UN Committee on World Food Security (CFS).
Guidelines
These are structured around seven focus areas:
• Transparent, democratic and accountable governance
• Sustainable food supply chains
• Equal and equitable access
• Food safety across sustainable food systems
• People-centred nutrition knowledge, education and information
• Gender equality and women’s empowerment across food systems
• Resilient food systems in humanitarian contexts
Significance of Guidelines
· Support countries in their efforts to eradicate all forms of hunger and malnutrition by utilising a comprehensive food systems approach.
· The guidelines are intended to build upon and complement the work and mandate of other international bodies, for example the UN Decade of Action on Nutrition (2016-2025).
· They call for realisation of the right to adequate food in the context of national food security for all, particularly for the most vulnerable and affected groups.
UN Committee on World Food Security (CFS)
· It is an international and intergovernmental platform for stakeholders to work towards ensuring food security and nutrition for all.
· It is hosted and co-funded by the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization(FAO).
· The Committee reports to the UN General Assembly through the Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) and to FAO Conference.
· CFS develops and endorses policy recommendations and guidance on food security and nutrition topics that are developed starting from scientific and evidence-based reports.
Vigyan Jyoti programme
In News
The second phase of Vigyan Jyoti programme was commenced on the occasion of International Day of Women and Girls in Science on February 11, 2021.
About the Programme
· It is an initiative to encourage girls to take interest in science and build career, launched by the Department of Science & Technology (DST).
· It had been running successfully in 50 Jawahar NavodayaVidyalayas (JNV) for a year and has now been expanded to 50 more JNVs for the year 2021-22 in second phase.
· Vigyan Jyoti activities include student-parent counselling, visit to labs and knowledge centres, partner’s role model interactions, science camps, academic support classes (online), resource material distribution and tinkering activities.
· The programme also has financial dimension. The girls will be given a modest financial incentive to cover their additional expense like travel to camps.
Under-representation of women in STEM
· Data compiled by the DST shows that females comprised 24 per cent of the total pas-out students in STEM subjects in engineering, 22 per cent at the post graduate level, 28 per cent at M Phil and 35 per cent at the PhD level.
· There are only 10 per cent of girls in the IITs and the number has remained static over the years.
Other initiatives to bring gender parity in Science & Technology (S&T)
· Women Scientists Scheme to help women with career-break.
· Indo-US Fellowship for Women in STEMM (WISTEMM) program where women scientists can work in research labs of USA.
· Consolidation of University Research for Innovation and Excellence in Women Universities (CURIE) programme for improving R&D infrastructure and establishing state-of-the-art research facilities in order to create excellence in S&T in women universities
· Gender Advancement for Transforming Institutions (GATI) program in pilot mode.
· SERB - POWER (Promoting Opportunities For Women in Exploratory Research) program was also launched recently.
Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB)
· It is a statutory body mandated to support basic research in emerging areas of Science & Engineering.
· It has both financial and administrative powers that would enable quicker decisions on research issues.
· The Board also gives special attention to young scientists below the age of 35 years to undertake independent research in newly emerging and frontier areas of science and engineering.
· High priority areas are supported through the “Intensification of Research in High Priority Area “(IRHPA) Program.
· The Board offers Fellowships such as RAMANUJANFellowship for brilliant scientists and engineers from all over the world to take up scientific research positions in India, especially those scientists who want to return to India from abroad.
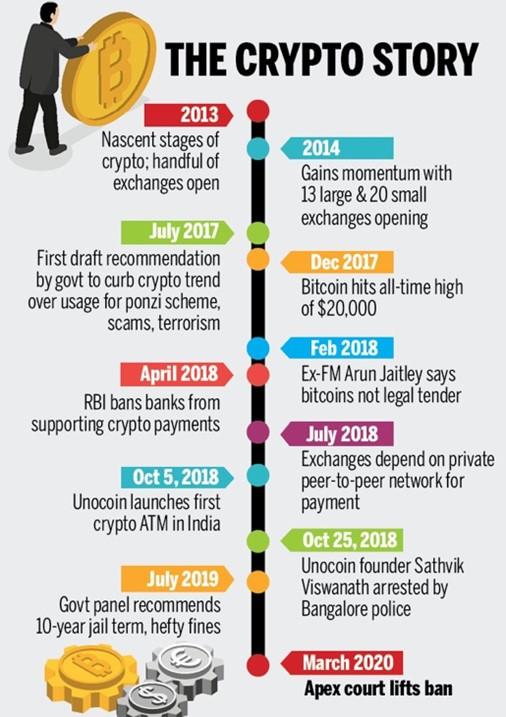
Digital Currency and Regulating Cryptocurrency
In News
The government is likely to introduce Cryptocurrency and Regulation of Official Digital Currency Bill 2021 in the ongoing Budget Session of the Parliament.
Contours of the proposed bill
- It will create a facilitative framework for creation of the official digital currency to be issued by the RBI.
- It will put a complete ban on investment in cryptocurrencies and people, traders, exchanges, and other financial systems' participants will not be permitted to deal in cryptocurrencies.
- Cryptocurrency investors will be given a transition period of three-to-six months after the implementation of the new law to liquidate their investments.
- It will allow for certain exceptions to promote the underlying technology of cryptocurrency and its uses.
Need for such a bill
- As per the official estimates, around 7 million Indians hold cryptocurrencies worth more than $1 billion. This is vast unregulated financial sector till now.
- Without own official virtual currency, private coins or another country’s virtual cash might fill the vacuum leading to loss of monetary sovereignty.
- If private digital currencies are allowed to dominate the ecosystem, there is more than a slight chance that these could eventually replace the legal tender cash. This is usually deemed detrimental to consumer interest.
Opportunities with formal digital currency
- It holds promise as there are efficiency gains to be had in terms of tapping unexplored commerce and investment avenues.
- Monetary and financial transactions could be boosted by the ease of access and the sheer resilience of the technology.
- A general-purpose digital currency being legal tender can contribute to diversity and innovation in the payment market.
- Self-executing contracts programmed into virtual tokens can help fractionalize and democratize finance by automating trade settlement, making it both quicker and less expensive.
- Central banks could perhaps target monetary stimulus better as individual beneficiaries and vulnerable sections could be identified quickly and assisted during times of economic stress.
Risks with Digital Currency
- Virtual cash is seen as a double-edged swordmainly because of its fundamentally transnational character.
- There are issues like financial data security, tax evasion and money laundering, and the likelihood of disturbances in money supply and exchange rates.
- A fully functional CBDC has never been implemented anywhere, partly because of technological handicaps. Given the absence of empirical data, it is difficult to estimate the true costs associated with such a transition.
- Extensive powers with the central bank may spark privacy concerns, which can be uses to keep track of all transactions and exercise more control over the public.
- There is an additional concern that if the public is allowed to convert their deposits into their digital currency accounts, commercial banks may be deprived of their primary funding source.
- Efficacy of monetary policy under such conditions is unclear.
Conclusion
But besides these vexing challenges, digital fiat opens up a world of welfare-enhancing possibilities. While Central banks could cherish new flexibilities in policy, user preferences will undoubtedly be a crucial factor in determining the macroeconomic effects of digital currencies.
Special Series – Budget, Survey and Finance Commission
Topic 9 - Healthcare takes centre stage, finally!
Context
The recent COVID-19 pandemic has emphasised the importance of the healthcare sector and its inter-linkages with other key sector of the economy. The ongoing pandemic has showcased how a healthcare crisis can get transformed into an economic and social crisis.
Indian Healthcare Currently
· On quality and access of healthcare, India was ranked 145th out of 180 countries as per the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016.
· Poor health outcomes: Despite improvements in MMR and IMR, India still needs to improve significantly on these metrics. Countries such as China, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Cambodia, etc. have improved much more on these metrics than India.
· Low access and Utilisation: As per theOECD,at 3-4 per cent, the hospitalisation rates in India are among the lowest in the world; which reflect lower access and utilisation of healthcare in India.
· High out-of-pocket health expenditures: At 58.7% the out of pocket expenditure (OoPE) as a percentage of total health expenditure, India has one of the highest levels of OOPE in the world as per the National Health Accounts (NHA) 2016-17.
· Low budget allocations for healthcare: India ranks 179 out of 189 countries in prioritization accorded to health in its government budgets (consolidated union & state government) as per the World Bank.
· Low human resources for health: Although aggregate human resources for health density in India is close to the lower threshold of 23 per 10,000 populations (optimal 44.5 as per WHO), the distribution of health workforce across states is lop-sided. Also, the skill mix (doctor/nurse-midwives ratio) is far from adequate.
Characteristics of Indian healthcare system leading to underperformance
· Uncertainty/Variability of demand:The need for health care is driven often by factors that cannot be controlled or predicted. This is also coupled with the nature of demand, which is inelastic especially for emergency care.
· Information asymmetry: In healthcare markets, patients rarely know the value of the information until after it is purchased and sometimes never at all. Therefore, rely on the reputation of the hospital/doctor as a proxy for the quality. Reimbursement rates pre-negotiated with insurance companies, advertising, etc. can exacerbate the conflict of interest.
· Hyperbolic tendencies: People tend to indulge in risky behaviour likesmoking, eating unhealthy food, which are, not only be sub- optimal for the individual but also create negative externalities for the entire healthcare system.
· Issue of unregulated Private Enterprise: With information asymmetries in the healthcare sector, unregulated private enterprise can create significant negative effects.
Policy Implications
· Indian healthcare policy must not become beholden to “saliency bias”, where policy over-weights a recent phenomenon.
· Telemedicine needs to be harnessed to the fullest by especially investing in internet connectivity and health infrastructure.
· The National Health mission (NHM) has played a critical role in mitigating inequity as the access of the institutional deliveries. Therefore, in conjunction with Ayushman Bharat, the emphasis on NHM should continue.
· An increase in public spend from 1 per cent to 2.5-3 per cent of GDP can decrease the Out-Of-Pocket Expenditures from 65 per cent to 30 per cent of overall healthcare spend.
· It is critical for policymakers to design policies that mitigate information asymmetry in healthcare, which renders unregulated private healthcare sub-optimal. Therefore, information utilities that help mitigate the information asymmetry can be very useful in enhancing overall welfare.
· Healthcare standards on the lines of Quality and Outcomes Framework (QOF) introduced by the National Health Service (NHS) in the United Kingdom in 2004 should be designed.
· A sectoral regulator to undertake regulation and supervision of the healthcare sector must be considered given the market failures stemming from information asymmetry.
Model Question - Indian healthcare system needs overhaul. Examine the various aspects and characteristics of the Indian healthcare system in context of poor outcomes of healthcare system in India over the years.
Digital Currency and Regulating Cryptocurrency
In News
The government is likely to introduce Cryptocurrency and Regulation of Official Digital Currency Bill 2021 in the ongoing Budget Session of the Parliament.
Contours of the proposed bill
· It will create a facilitative framework for creation of the official digital currency to be issued by the RBI.
· It will put a complete ban on investment in cryptocurrencies and people, traders, exchanges, and other financial systems' participants will not be permitted to deal in cryptocurrencies.
· Cryptocurrency investors will be given a transition period of three-to-six months after the implementation of the new law to liquidate their investments.
It will allow for certain exceptions to promote the underlying technology of cryptocurrency and its uses.
Need for such a bill
· As per the official estimates, around 7 million Indians hold cryptocurrencies worth more than $1 billion. This is vast unregulated financial sector till now.
· Without own official virtual currency, private coins or another country’s virtual cash might fill the vacuum leading to loss of monetary sovereignty.
· If private digital currencies are allowed to dominate the ecosystem, there is more than a slight chance that these could eventually replace the legal tender cash. This is usually deemed detrimental to consumer interest.
Opportunities with formal digital currency
· It holds promise as there are efficiency gains to be had in terms of tapping unexplored commerce and investment avenues.
· Monetary and financial transactions could be boosted by the ease of access and the sheer resilience of the technology.
· A general-purpose digital currency being legal tender can contribute to diversity and innovation in the payment market.
· Self-executing contracts programmed into virtual tokens can help fractionalize and democratize finance by automating trade settlement, making it both quicker and less expensive.
· Central banks could perhaps target monetary stimulus better as individual beneficiaries and vulnerable sections could be identified quickly and assisted during times of economic stress.
Risks with Digital Currency
· Virtual cash is seen as a double-edged sword mainly because of its fundamentally transnational character.
· There are issues like financial data security, tax evasion and money laundering, and the likelihood of disturbances in money supply and exchange rates.
· A fully functional CBDC has never been implemented anywhere, partly because of technological handicaps. Given the absence of empirical data, it is difficult to estimate the true costs associated with such a transition.
· Extensive powers with the central bank may spark privacy concerns, which can be uses to keep track of all transactions and exercise more control over the public.
· There is an additional concern that if the public is allowed to convert their deposits into their digital currency accounts, commercial banks may be deprived of their primary funding source.
· Efficacy of monetary policy under such conditions is unclear.
Conclusion
But besides these vexing challenges, digital fiat opens up a world of welfare-enhancing possibilities. While Central banks could cherish new flexibilities in policy, user preferences will undoubtedly be a crucial factor in determining the macroeconomic effects of digital currencies.
Special Series – Budget, Survey and Finance Commission
In News
The Finance Commission has granted Rs 4,36,361 crore from the central divisible tax pool to local governments, both rural and urban, for 2021-26.
Local Self-Government in India
· In 1992, the enactment of the 73rd and 74th Amendments to the Constitution led to emergence of formal decentralised governance in India with constitutional status to the Panchayats and urban local bodies.
· India had 262,771 elected rural local bodies and 4,657 urban local bodies in 2017. The rural bodies implement around 70% of India’s rural development programmes with an annual budget over Rs 2 lakh crore.
Role of Finance Commission (FC) in Empowering Local Bodies
· The FC is a constitutional body under Article 280 for centre-state financial relations. 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendments broadened the role of FC under Article 280.
· FC is mandated to recommend the measures needed to augment the Consolidated Fund of a State to supplement the resources of the panchayats and municipalities based on the recommendations of the SFC.
· It has been one of the biggest sources of funding for local bodies due to weak devolution of financial resources by the states and also due to weak mobilisation of their own resources. E.g., In 2017-18, Municipal own revenue stood at 0.43% of GDP, lowest since 2010-11.
· Grants recommended by successive Finance Commissions in absolute terms have been growing (Figure 7.1). Except for the FC-XIII, all the previous Commissions recommended such grants in absolute terms and not as a proportion of the divisible pool.
o The divisible pool is that portion of gross tax revenue which is distributed between the Centre and the States. The divisible pool consists of all taxes, except surcharges and cess levied for specific purpose, net of collection charges.
Recommendations of Fifteenth Finance Commission
· Total grants to local bodies will be Rs 4.36 lakh crore (a portion of grants to be performance-linked) including: (i) Rs 2.4 lakh crore for rural local bodies, (ii) Rs 1.2 lakh crore for urban local bodies, and (iii) Rs 70,051 crore for health grants through local governments.
· The health grants for: (i) conversion of rural sub-centres and primary healthcare centres (PHCs) to health and wellness centres (HWCs), (ii) support for diagnostic infrastructure for primary healthcare activities, and (iii) support for urban HWCs, sub-centres, PHCs, and public health units at the block level.
· Grants to local bodies (other than health grants) will be distributed among states based on population and area, with 90% and 10% weightage, respectively.
· Conditions for availing these grants (except health grants): (i) publishing provisional and audited accounts in the public domain and (ii) additionally for ULBs, fixation of minimum floor rates for property taxes by states and improvement in the collection of property taxes.
· No grants will be released to local bodies of a state after March 2024 if the state does not constitute State Finance Commission and act upon its recommendations by then.
Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB)
- It is a statutory body mandated to support basic research in emerging areas of Science & Engineering.
- It has both financial and administrative powers that would enable quicker decisions on research issues.
- The Board also gives special attention to young scientists below the age of 35 years to undertake independent research in newly emerging and frontier areas of science and engineering.
- High priority areas are supported through the “Intensification of Research in High Priority Area “(IRHPA) Program.
- The Board offers Fellowships such as RAMANUJAN Fellowship for brilliant scientists and engineers from all over the world to take up scientific research positions in India, especially those scientists who want to return to India from abroad.
SANKALP
- It is an outcome-oriented centrally sponsored programme of Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship (MSDE) with a special focus on decentralised planning and quality improvement.
- Assisted by World Bank, it aims to implement the mandate of the National Skill Development Mission (NSDM).
- Four key result areas have been identified-
- Institutional Strengthening (at National, State & District level).
- Quality Assurance Quality Assurance of skill development programs
- Inclusion of marginalised population in skill development
- Expanding Skills through Public Private Partnerships (PPPs).
SANKALP
• It is an outcome-oriented centrally sponsored programme of Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship (MSDE) with a special focus on decentralised planning and quality improvement.
• Assisted by World Bank, it aims to implement the mandate of the National Skill Development Mission (NSDM).
• Four key result areas have been identified-
o Institutional Strengthening (at National, State & District level).
o Quality Assurance Quality Assurance of skill development programs
o Inclusion of marginalised population in skill development
o Expanding Skills through Public Private Partnerships (PPPs).
Triggering growth: Are free trade agreements the answer? – Financial Express
Essence
The signing of the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) agreement and the launch of the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) have revived the narrative on free trade agreements (FTA). Today, the spaghetti bowl of FTAs includes about 500 arrangements with linkages and overlaps. The article analyses Indian experience with FTAs in brief.
Why you read this editorial?
- Understand the basics of FTAs and what role they play in international trade.
- Provides a brief background on India’s history with FTAs.
- Highlights the approach India should follow going forward. It identifies actors whom India should partner with – EU, UK, Africa etc and also whom it should avoid – China, US.
Link
https://www.financialexpress.com/opinion/triggering-growth-are-free-trade-agreements-the-answer/2194845/Commission on Air Quality Management — A general without foot soldiers - ORF
Essence
Air pollution being recognized as one of the major public policy challenges that India is facing today. Delhi, Faridabad & Gurugram are recognized amongst the world most polluted cities. A Commission on Air Quality Management in National Capital Region & Adjoining Area (formed after removal of EPCA) was setup to monitor the status of air pollution, enforcement of laws & providing solution to curb the same. But the inefficient outcome of EPCA in past raises questions on future of this commission in eradication of air pollution in India. Article also suggested some institutional reforms.
Why you read this editorial?
- To understand the issues associated with present mechanism & regulatory system & how its compromising the efficiency of established Commission to tackle air pollution in India.
- To understand the issues associated recently established Commission on Air Quality Management.
- To know what could be done to make commission more efficient & powerful.
Link
https://www.orfonline.org/expert-speak/commission-on-air-quality-management-a-general-without-foot-soldiers/Effective regulation is key to banking reforms
Essence
Finance minister (FM) announcements on the policy for privatisation in banking, insurance and financial services indicate that there will be bare minimum presence of public sector enterprises. The privatisation of a general insurance company and two State-owned banks are to be “taken up” in the year 2021-22. The FM has also proposed to set up an asset reconstruction and management company. Here, it is important to consider how these will be implemented in the context of the existing regulatory framework. This article discusses the key elements of Regulatory governance which involves standard-setting, supervision and monitoring, and enforcement.
Why you should read this editorial?
- Understanding what principles to be followed while setting legislative standards.
- An analysis of supervision and monitoring functions of regulator for implementing reforms.
- A robust enforcement mechanism especially with regard to individual accountability for regulatory non-compliance.
Link
https://www.hindustantimes.com/opinion/effective-regulation-is-key-to-banking-reforms-101613141969425.html
- Understanding what principles to be followed while setting legislative standards.
- An analysis of supervision and monitoring functions of regulator for implementing reforms.
- A robust enforcement mechanism especially with regard to individual accountability for regulatory non-compliance.
Link
https://www.hindustantimes.com/opinion/effective-regulation-is-key-to-banking-reforms-101613141969425.htmlTriggering growth: Are free trade agreements the answer? – Financial Express
Essence - The signing of the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) agreement and the launch of the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) have revived the narrative on free trade agreements (FTA). Today, the spaghetti bowl of FTAs includes about 500 arrangements with linkages and overlaps. The article analyses Indian experience with FTAs in brief.
Why you read this editorial?
· Understand the basics of FTAs and what role they play in international trade.
· Provides a brief background on India’s history with FTAs.
· Highlights the approach India should follow going forward. It identifies actors whom India should partner with – EU, UK, Africa etc and also whom it should avoid – China, US.
Commission on Air Quality Management — A general without foot soldiers - ORF
Essence – Air pollution being recognized as one of the major public policy challenges that India is facing today. Delhi, Faridabad & Gurugram are recognized amongst the world most polluted cities. A Commission on Air Quality Management in National Capital Region & Adjoining Area (formed after removal of EPCA) was setup to monitor the status of air pollution, enforcement of laws & providing solution to curb the same. But the inefficient outcome of EPCA in past raises questions on future of this commission in eradication of air pollution in India. Article also suggested some institutional reforms.
Why you read this editorial?
· To understand the issues associated with present mechanism & regulatory system & how its compromising the efficiency of established Commission to tackle air pollution in India.
· To understand the issues associated recently established Commission on Air Quality Management.
· To know what could be done to make commission more efficient & powerful.
Effective regulation is key to banking reforms
Essence- Finance minister (FM) announcements on the policy for privatisation in banking, insurance and financial services indicate that there will be bare minimum presence of public sector enterprises. The privatisation of a general insurance company and two State-owned banks are to be “taken up” in the year 2021-22. The FM has also proposed to set up an asset reconstruction and management company. Here, it is important to consider how these will be implemented in the context of the existing regulatory framework. This article discusses the key elements of Regulatory governance which involves standard-setting, supervision and monitoring, and enforcement.
Why you should read this editorial?
· Understanding what principles to be followed while setting legislative standards.
· An analysis of supervision and monitoring functions of regulator for implementing reforms.
· A robust enforcement mechanism especially with regard to individual accountability for regulatory non-compliance.
Link - https://www.hindustantimes.com/opinion/effective-regulation-is-key-to-banking-reforms-101613141969425.html
e-Uparjan: Re-inventing the procurement system through digitisation in Madhya Pradesh
- In a local Mandi in Madhya Pradesh, a common site is long queues of farmers, overcrowded Mandi Centre leading to transport bottlenecks and Law and Order issue
- The e-Uparjan Initiative uses versatile technology for the speedy and transparent transfer of Minimum Support Price (MSP) dues into the accounts of farmers directly
- The process is shown:
- The Initiative strengthens Procurement Operations, develops a near Real-Time Reporting Mechanism and a Decision Support System for enhancing the Forecasting, Monitoring and Tracking Capabilities
- Now, many farmers are willing to sell their produce at the procurement centres created by the government.
e-Uparjan: Re-inventing the procurement system through digitisation in Madhya Pradesh
· In a local Mandi in Madhya Pradesh, a common site is long queues of farmers, overcrowded Mandi Centre leading to transport bottlenecks and Law and Order issue
· The e-Uparjan Initiative uses versatile technology for the speedy and transparent transfer of Minimum Support Price (MSP) dues into the accounts of farmers directly
· The process is shown:
· The Initiative strengthens Procurement Operations, develops a near Real-Time Reporting Mechanism and a Decision Support System for enhancing the Forecasting, Monitoring and Tracking Capabilities
· Now, many farmers are willing to sell their produce at the procurement centres created by the government.
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.