Tuesday, 2nd February 2021
Traditional Knowledge Digital Library
In News
CSIR celebrates 20 years of India’s Traditional Knowledge Digital Library, the first of its kind globally.
About
This initiative (started in 2001) was a follow up action to thwart misappropriation of India’s valuable traditional knowledge, based on learnings from the patent battles with international patent offices over the grant of intellectual property rights on turmeric, neem, basmati rice and other such ancient knowledge and practices of the country.
Achievements
· It has systematically and scientifically converted and structured the available contents of the ancient texts on Indian Systems of Medicines i.e. Ayurveda, Siddha, Unani and Sowa Rigpa as well as Yoga, into five international languages, namely, English, Japanese, French, German and Spanish, with the help of information technology tools and an innovative classification system - Traditional Knowledge Resource Classification (TKRC). 
· TKDL contains more than 3.9 lakh formulations/practices from the Indian systems of medicine.
· Significantly, 239 patent applications have either been set aside/ withdrawn/ amended, based on the prior art evidences present in the TKDL database till now.
Way Forward
· TKDL should aim to promote traditional knowledge and emerge as a global repository, apart from safeguarding the information from misappropriation.
· Going forward, the information from digitized and published manuscripts as well as oral knowledge is also proposed to be included in the TKDL database.
Strengthening Teaching-Learning and Results for States (STARS) project
In News
GoI, World back sign agreement under STARS project to develop educational outcomes
About
· STARS project would be implemented as a new Centrally Sponsored Scheme under Department of School Education and Literacy, Ministry of Education. (MOE)
· The overall focus and components of the STARS project are aligned with the objectives of National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 of Quality Based Learning Outcomes.
· STARS will draw on the existing structure under Samagra Shiksha.
The STARS Project has two major components
· National level:
o To strengthen MOE’s national data systems to capture robust and authentic data on retention and to establish a National Assessment Center (PARAKH).
o It includes a Contingency Emergency Response Component (CERC) under the National Component which would enable it to be more responsive to any natural, man-made and health disasters.
o India’s participation in the 2022 cycle of the Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA) survey will also be funded by this project.
· State level:
o It seeks to support the states in developing, implementing, evaluating and improving interventions with direct linkages to improved education outcomes and school to work transition strategies for improved labour market outcomes.
.
Highlights of Economic Survey Volume 2
Chapter 1 – State of the Economy
· Global economic output estimated to fall by 3.5% in 2020 (IMF January 2021 estimates)
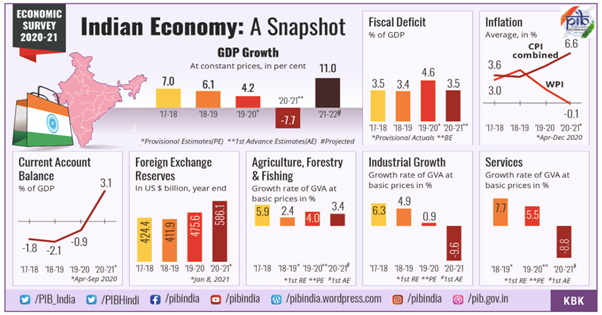
· India’s GDP is estimated to contract by 7.7 % in FY2020-21.
· India’s real GDP to record a 11.0% growth in FY2021-22 and nominal GDP to grow by 15.4% – the highest since independence.
· India adopted a four-pillar strategy of containment, fiscal, financial, and long-term structural reforms:
o Calibrated fiscal and monetary support was provided, cushioning the vulnerable during the lockdown and boosting consumption and investment while unlocking
o A favourable monetary policy ensured abundant liquidity and immediate relief to debtors while unclogging monetary policy transmission
· India’s mature policy response to the ‘once-in-a-century’ crisis provides important lessons for democracies to avoid myopic policy-making and demonstrates benefits of focusing on long-term gains.
Chapter 2 –Fiscal Developments
· Expenditure policy in 2020-21 initially aimed at supporting the vulnerable sections but was re-oriented to boost overall demand and capital spending, once the lockdown was unwound
· Central Government has also taken consistent steps to impart support to the States in the challenging times of the pandemic
· Monthly GST collections have crossed the Rs. 1 lakh crore mark consecutively for the last 3 months, reaching its highest levels in December 2020 ever since the introduction of GST.
Chapter 3 – External Sector
· India’s forex reserves at an all-time high of US$ 586.1 billion as on January 08, 2021, covering about 18-months worth of imports.
· India to end with an Annual Current Account Surplus after a period of 17 years.
· Improvement in debt vulnerability indicators like Ratio of forex reserves to total and short-term debt (original and residual) etc.
· Trade balance with China and the US improved as imports slowed.
· Parameters in April-December 2020 compared to same period last year.
o India’s merchandise trade deficit was lower.
o Net services receipts remained stable.
· RBI’s interventions in forex markets ensured financial stability and orderly conditions, controlling the volatility and one-sided appreciation of the Rupee.
Chapter 4 - Money Management and Financial Intermediation
· Systemic liquidity in FY2020-21 has remained in surplus so far. RBI undertook various conventional and unconventional measures like:
o Open Market Operations
o Long Term Repo Operations
o Targeted Long Term Repo Operations
· Gross Non-Performing Assets ratio of Scheduled Commercial Banks decreased
· The monetary transmission of lower policy rates to deposit and lending rates improved.
Chapter 5 – Prices and Inflation
· Headline CPI inflation: Averaged 6.6% during April-December, 2020 and stood at 4.6% in December, 2020, mainly driven by rise in food inflation.
· Rural-urban difference in CPI inflation saw a decline in 2020.
· Steps taken to stabilize prices of food items: Banning of export of onions, Imposition of stock limit on onions, Easing of restriction on imports of pulses.
· Consistency in import policy warrants attention - Imports impacting production and prices of domestic edible oil market, coupled with frequent changes in import policy of pulses and edible oils, add to confusion among farmers/producers and delay imports.
· Gold Prices: They saw a sharp spike as investors turned to gold as a safe haven investment amid COVID-19 induced economic uncertainties.
Chapter 6 - Sustainable Development and Climate Change
· India has taken several proactive steps to mainstream the SDGs into the policies, schemes and programmes.
o Localisation of SDGs: Several States/UTs have created institutional structures for implementation of SDGs within every department and at the district levels for better coordination and convergence.
· The goal of jointly mobilizing US$ 100 billion a year by 2020 for climate financing by the developed countries has remained elusive.
· International Solar Alliance (ISA) launched two new initiatives – ‘World Solar Bank’ and ‘One Sun One World One Grid Initiative’.
Chapter 7 - Agriculture and Food Management
· Agriculture set to cushion the shock of the COVID-19 pandemic on the Indian economy in FY21 with a growth of 3.4% with both Industry and Services Sectors witnessing contraction.
· Total food grain production in the country in the agriculture year 2019-20, is 11.44 million tonnes more than during 2018-19. Fish production reached an all-time high.
· Food Processing Industries (FPI) sector growing at an Average Annual Growth Rate (AAGR) of around 9.99 % as compared to around 3.12 % in Agriculture and 8.25 % in Manufacturing at 2011-12 prices during the last 5 years ending 2018-19
· Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana: 80.96 crore beneficiaries were provided foodgrains.
· AatmaNirbhar Bharat Package: 5 kg per person per month for four months (May to August) to approximately 8 crores migrants (excluded under NFSA or state ration card) entailing subsidy of Rs. 3109 crores approximately.
Chapter 8 - Industry and Infrastructure
· India’s rank in the Ease of Doing Business (EoDB) Index for 2019 has moved upwards to the 63rd position in 2020 from 77th in 2018.
· FDI equity inflows increased with the bulk of them in the non-manufacturing sector.
· Government has announced a Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme in the 10 key sectors under the aegis of AatmaNirbhar Bharat for enhancing India’s manufacturing capabilities and exports.
Chapter 9 – Services Sector
· Owing to its contact-intensive nature, India’s services sector contracted by nearly 16 % during H1: FY2020-21.
· The services sector accounts for over 54 % of India’s GVA and nearly four-fifths of total FDI inflow into India.
· Services sector accounts for 48% of total exports, outperforming goods exports in the recent years.
· India’s space sector has grown exponentially in the past six decades.
· Indian start-up ecosystem has been progressing well amidst the COVID-19 pandemic, being home to 38 unicorns - adding a record number of 12 start-ups to the unicorn list last year.
Chapter 10 - Social Infrastructure, Employment and Human Development
· Expenditure on social services (education, health and other social sectors) by Centre and States combined as a proportion of GDP increased from 6.2 to 8.8 per cent during the period 2014-15 to 2020-21 (BE).
· Limit of collateral free lending increased from Rs. 10 lakhs to Rs. 20 lakhs for 63 lakh women SHGs which would support 6.85 crore households.
· Wages under Mahatma Gandhi NREGA increased.
· Government’s incentive to boost employment through AatmaNirbhar Bharat Rozgar Yojana and rationalization and simplification of existing labour codes into 4 codes
· Low level of female LFPR in India:
o Females spending disproportionately more time on unpaid domestic and care giving services to household members as compared to their male counterparts
o Need to promote non-discriminatory practices at the workplace like pay and career progression, improve work incentives, including other medical and social security benefits for female workers.
· NFHS-5 (Phase-I), results show improvement in immunization coverage for children, institutional birth, infant mortality rate and under-five mortality rate in most of the selected States.
Towards a ‘healthy’ India-Africa partnership
Essence - Editorial is examining how India can build partnerships around the process of Covid pandemic recovery, especially with countries in Africa.This is a crucial juncture as economic shock has rolled back a decade of progress with 49 million Africans likely to be pushed into poverty. India-Africa health cooperation will be critical in the short, medium, and long term.
Why you should read this article?
· To know about various steps already taken in the India-Africa partnership in the field of technology sharing, vaccine supply, health care ecosystem building, boosting e-initiatives, etc.
· To understand why Africa's growth is aligned to India's aspirations.
· To know about initiatives which are already in place in Africa.
How PFMS is ensuring transformation via digital inclusion
Essence - Indian government envisioned Public Financial Management System (PFMS) with an objective of bringing in transformational accountability and transparency and to further promote good governance. The article throws light on how this system has evolved over the period of time.
Why you should read this article?
· Gives information about the mandate of PFMS.
· As the government looks to use it in other areas, the article identifies areas on what areas to focus upon going forward.
Contemporising Data Protection Legislation
Essence:
The 30-member Joint Parliamentary Committee (JPC) reviewing the Personal Data Protection (PDP) Bill 2019 has proposed 89 amendments, an additional clause and amendments in the schedule. In this context, this article analyses the issues and suggest a possible framework to ensure a well-rounded data protection law which will help bridge gaps, instil user confidence, power trusted innovation, fuel economic progress and could serve as a reference model for other countries looking to advance digitisation and their data protection journey.
You should read this article to identify and understand-
· The quagmire of data ecosystem and the need for Data protection legislation along with its objectives.
· Certain challenges and issues related to important sections of the PDP Bill 2019 such as exemption to government agencies, personal data of foreigners, Cross Border Data Flows & Data Localisation and privacy invasive technologies.
· Principles which can guide the framing of model PDP Bill 2019 such as limiting unreasonable processing, ensuring the individual’s right to appeal and to remedy privacy violations, jurisdiction based on individual citizenship, Reciprocal Adequacy.
· Some open-ended questions that bill should address.
Link - https://www.orfonline.org/expert-speak/contemporising-data-protection-legislation/
Jitender Singh Shunty – Story of Compassion
· The MLA from Delhi turned a hero during the pandemic.
· Through his organisation, Shaheed Bhagat Singh Sewa Dal (SBSSD), he conducted 900+ cremations. 
· He has also arranged ambulances for more than 1300+ COVID positive patients.
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.


