Monday, 14th June 2021
India’s forex reserves
In News
India’s forex reserves cross record $600 billion-mark for first time.
About the News
- RBI’s Data on Forex:
- RBI data showed that India’s foreign exchange reserves crossed the USD 600 billion mark for the first time in the week ended June 4.
- Foreign currency assets (FCA): The reserves surged to a record USD 605.008 billion in the reporting week. Expressed in dollar terms, the FCAs include the effect of appreciation or depreciation of non-US units like the euro, pound and yen held in the foreign exchange reserves. Typically, the value of FCA for a said week is a function of currency depreciation and the intervention in the currency market by RBI.
- Gold reserves declined by USD 502 million to USD 37.604 billion. The special drawing rights (SDRs) with the International Monetary Fund (IMF) dipped USD 1 million to USD 1.513 billion.
- India’s reserve position with the IMF also dropped by USD 16 million to USD 5 billion in the reporting week.
- Significance of the Rise: The rise in forex reserves is typically a factor of increase or decrease of portfolio investments from offshore investors and a growth in the foreign direct investments (FDIs) during the period. Central banks purchase of gold reserves too affects the foreign exchange kitty.
- A strong reserve allows the central bank to timely intervene in forward and spot currency markets to arrest any slide in rupee devaluations.

What are Forex Reserves?
- Definition: The IMF defines reserves as external assets that are readily available to and controlled by monetary authorities for direct financing of external payments imbalances, for indirectly regulating the magnitudes of such imbalances through intervention in exchange markets to affect the currency exchange rate, and/or for other purposes.
- Form of Reserves: External assets are in the form of gold, SDRs (special drawing rights of the IMF) and foreign currency assets (capital inflows to the capital markets, FDI and external commercial borrowings) accumulated by India and controlled by the Reserve Bank of India.
- Role of RBI: The Reserve Bank functions as the custodian and manager of forex reserves, and operates within the overall policy framework agreed upon with Government of India. The RBI uses its forex kitty for the orderly movement of the rupee. It sells the dollar when the rupee weakens and buys the dollar when the rupee strengthens.
India Plastic Challenge -Hackathon 2021
In News: Considering the adverse impacts of littered single use plastic items on both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, the Ministry of Environment has launched India Plastic Challenge- Hackathon 2021.
What is India Plastic Challenge -Hackathon 2021?
- It is a unique competition calling upon start-ups /entrepreneurs and students of Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) to develop innovative solutions to mitigate plastic pollution and develop alternatives to single use plastics.

About single-use plastics
- Single-use plastics (disposable plastics) are items intended to be used only once before they are thrown away or recycled. Eg. grocery bags, food packaging, bottles, straws, containers, cups, and cutlery.
- According to the United Nations, most of the plastics produced today are designed to be thrown away after first use.
What are the possible repercussions of plastic use?
- Plastic bags can take up to thousands of years to decompose, contaminating soil and water, and thus pose significant ingestion, choking and entanglement hazards to wildlife on land and in the ocean.
- Plastic bags can choke waterways and exacerbate natural disasters.
- Styrofoam and plastic items contain toxic chemicals such as styrene and benzene that are considered carcinogenic and have effects on the nervous, respiratory, and reproductive systems.
- Illegal disposal practices such as open burning, accentuating the release of toxic gases.
- Blockages of sewage systems provide breeding grounds for mosquitoes that can cause vector-borne diseases such as malaria.
Measures taken by India:
- The Environment Ministry had notified Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016 with new provisions for effective and improved collection, segregation, processing, treatment and disposal of plastic waste.
- Notification of EPR: Extended Producer Responsibility(EPR) is a policy approach under which producers are given a significant financial and physical responsibility (with respect to segregation and collection of waste at the source) for the treatment or disposal of post-consumer products.
- Draft Plastic Waste Management (Amendment) Rules, 2021 that propose to ban the use of single-use plastic items in three stages.
Climate change and global food production
In News
The study published in the journal One Earth analysed how global food production will be affected if greenhouse gas emissions are left uncut.

Findings of the Study
- The research shows that rapid, out-of-control growth of greenhouse gas emissions may, by the end of the century, lead to more than a third of current global food production falling into conditions in which no food is produced today - that is, out of safe climatic space.
- Safe climatic space are those areas where 95% of crop production currently takes place, thanks to a combination of three climate factors- rainfall, temperature, and aridity.
- The good news is that only a fraction of food production would face as-of-yet unseen conditions if we collectively reduce emissions, so that warming would be limited to 1.5 to 2 degrees Celsius.
- The results show that threats affect countries and continents in different ways. The entire food production would remain in the safe climatic space in the future in Finland and most other European countries. Vulnerable countries such as Ghana will be hit hard if no changes are made.

Climate change impacting crop production or agriculture
- Direct impacts of climate change on agriculture
- Changes in mean climate: An increase in the mean seasonal temperature can bring forward the harvest time of current varieties of crops and reduce final yield. In areas where temperatures are already close to the physiological maxima for crops, such as seasonally arid and tropical regions, higher temperatures may be more immediately detrimental, increasing the heat stress on crops and water loss by evaporation.
- Precipitation and irrigation demands: Water is vital to plant growth, so varying precipitation patterns have a significant impact on agriculture. As over 80 per cent of total agriculture is rain-fed, projections of future precipitation change often influence the magnitude and direction of climate impacts on crop production.
- Extreme Events:
- Drought: Extreme drought conditions, frequently occurring due to climate change, exacerbate the productivity of crops by causing nutrient immobilization and salt accumulation in soils making them dry, unhealthy, saline and finally infertile.
- Heavy rainfall and flooding: It can wipe out entire crops over wide areas, and excess water can also lead to other impacts including soil water logging, anaerobicity and reduced plant growth.
- Indirect impact of climate change
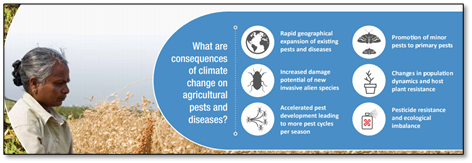
- Pests and diseases: Rising atmospheric CO2and climate change can indirectly impact crops through effects on pests and disease pests, which respond positively to elevated CO2. Evidence suggests that in sub-Saharan Africa migration patterns of locusts may be influenced by rainfall patterns. Impacts of warming or drought may decrease the resistance of crops to specific diseases and increase the pathogenicity of organisms by mutation.
- Mean sea-level rise: Increases in mean sea level threaten to inundate agricultural lands and salinize groundwater in coastal regions. It can also result in salinity of soils in coastal regions leading to stresses in crops such as decreased respiration, photosynthesis and transpiration, ultimately jeopardizing food availability and security in such regions.
Impact of agriculture on climate change
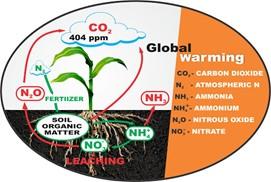
- Greenhouse Gases: The main direct agricultural GHG emissions are nitrous oxide emissions from soils, fertilisers, manure and urine from grazing animals; and methane production by ruminant animals and from paddy rice cultivation. Both of these gases have a significantly higher global warming potential than carbon dioxide.
- Intensive agricultural practices: The increasing demand of food due to ever growing population have resulted in intensive agricultural practices including unprecedented use of agro-chemicals, livestock generation (for meat and other source of income), exploitation of water resources, deforestation of grazing land and loss of valuable topsoil.
What can be done to reverse this phenomenon of mutual destruction?
- Climate smart agriculture: Climate smart agriculture system is in line with FAO’s vision of Sustainable Food and Agriculture goals. This includes:
- Developing resilient varieties of crops which can withstand abrupt stresses of temperature and precipitation.
- Implementing biotic and sustainable agricultural methods, for example, application of bioinoculants/biofertilizers, using tolerant plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) and other methods of organic farming to promote yield of crops in extreme environments in a holistic and a sustainable way.
- Use of biofertilizers and biopesticides will result in reduced emission of GHG and decrease in levels of soil, water, and air pollution.
- Also, change in crop cultivars, sowing time and cultivation techniques (such as mixed cropping systems) to provide greater durability to crops in extreme events can be considered.
- Restoration of Land: As per United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD) “restoring the soils of degraded ecosystems has the potential to store up to 3 billion tonnes of carbon annually”. Phyto or rhizoremediation of such soils increase the organic matter which results in enhanced CO2 fixation in the soil. By increasing the soil organic matter and subsequent enhancement in yield or planting of perennial crops or through planned agro-forestry can result in decreasing the levels of GHGs.
- Technological intervention: Extensive data collection and field trials to assess the impact of prevailing climatic conditions in different agro-ecological zones, remote sensing and satellite imaging can help in future predictions for the vulnerable agro-ecosystems, working out responses, preparedness, and planning of managing the agro-ecosystems for extreme events such as water scarcity, heat waves, foods and so on.
- Connecting and sensitizing farmers to sustainable technologies and activities is of utmost importance as they are the ones who can play a major role in implementation of the ecological goals.
Conclusion
Climate change and agriculture are strongly co-related. The fast pace of climate change will have far reaching impact on agro-ecosystems and their productivity. It is therefore paramount that we find ways to increase farming productivity in the future, whilst at the same time investigating ways of reducing the impact of agriculture on GHG emissions and the environment.
Question: Analyse how climate change and food production practices impact each other.
Primary Sources: https://www.aalto.fi/en/news/climate-change-threatens-one-third-of-global-food-production
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2935125/
https://www.pnas.org/content/108/50/20260
https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s42398-019-00078-w.pdf
Secondary Sources: https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2021/apr/01/climate-crisis-global-heating-food-farming-agriculture
https://blog.agrivi.com/post/climate-change-impacts-on-agriculture
Resolution 75/260 of UNGA
- Context: Union Minister for Health and Family Welfare addressed the 75thsession of the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) on prevention of HIV/AIDS.
- The Resolution 75/260 of UNGAdeals with the Implementation of the Declaration of Commitment on HIV/AIDS and the political declarations on HIV/AIDS.
- Key highlights of the address:
- HIV/AIDS Prevention Model: Social Contracting andTargeted Interventions Program with support from civil society. The program is aimed at behaviour change, communication, outreach, service delivery, counselling & testing and ensuring linkages to HIV care.
- Legal Framework, Free Treatment, National AIDS Control Program
- The target of Elimination of Mother to Child

Primary source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=1726142
Picture source: https://www.who.int/news-room/events/detail/2020/09/15/default-calendar/who-at-the-high-level-session-of-the-75th-un-general-assembly-(unga)
Picture source: http://ddnews.gov.in/national/union-health-minister-addresses-75th-session-unga-prevention-hivaids
Koraput Turmeric
- Context: Increased remuneration for turmeric farmers in Odisha’s Koraput district.
- This turmeric contains 5.5%-6.66% of curcumin.
- The presence of curcumin increases medicinal value of the turmeric.
- Apart from Koraput, Odisha’s Kandhamal district is also famous for organic turmeric and has received the geographical indication (GI) tag.

Primary source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/other-states/new-market-brings-hope-to-odishas-turmeric-farmers/article34793384.ece
Picture source: https://dir.indiamart.com/koraput/turmeric.html
This Day in History- World Blood Donor Day
June 14 is observed as World Blood Donor Day, an initiative by the World Health Organization (WHO). This day is celebrated every year to spread awareness about the significance of blood donation and to recognise the contribution of voluntary unpaid blood donors. The first World Blood Donor Day was observed by WHO in 2004 and was declared as an annual global event in the 58th World Health Assembly in 2005. The day is celebrated on the birth anniversary of Austrian biologist and physician, Karl Landsteiner. He is the founder of modern blood transfusion. For 2021, the World Blood Donor Day slogan is 'Give blood and keep the world beating'.

Image of the Day- Floating Ambulance
This is the image of a floating ambulance on Dal lake, Srinagar. A houseboat owner has started a floating ambulance service that comes equipped with PPE kits, stretchers, wheelchair, and other healthcare amenities. The owner came up with the idea of the ambulance in the year 2020, when he tested positive for the Covid virus. The ambulance with sirens and speaker facilities makes announcements to make people aware regarding wearing masks and other important things. There will be a phone number on which people can call and the boat will rush for help.

Small Island Developing States (SIDS)
- Context: 2021 edition of UNCTAD’s “Development and Globalization” reports that small island states have faced thrice as much fall in GDP in 2020 as other developing countries mainly due to the impact of Covid 19 on the tourism sector.
- Small Island Developing States (SIDS) are a distinct group of 38 UN Member States and 20 Non-UN Members/Associate Members of United Nations regional commissions that face unique social, economic and environmental vulnerabilities.
- Factors like small population size, remoteness from international markets, high transportation costs, vulnerability to exogenous economic shocks and fragile land and marine ecosystems make SIDS particularly vulnerable to biodiversity loss and climate change because they lack economic alternatives.
- The geographical regions in which SIDS are located are: the Caribbean, the Pacific, and the Atlantic, Indian Ocean and South China Sea (AIS).
- The aggregate population of all the SIDS is 65 million which is less than 1% of the world’s population.
- Strong biodiversity in addition to the revenue also helps prevent the incurrence of additional costs that can result from climate change, soil erosion, pollution, floods, natural disasters, and other destructive phenomena.

Primary source: https://www.un.org/ohrlls/content/about-small-island-developing-states
Picture Source: https://medium.com/freeelio-studios/digital-energy-islands-657e8dada5b
Sub-Mission on Agricultural Mechanization (SMAM) Scheme
- Context: Government of India has released funds for various activities of farm mechanization under SMAM Scheme.
- The scheme aims at increasingthe reach of farm mechanization to small and marginal farmers and to the regions where farm power availability is low and was launched in 2014-15 by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- The main objectives of the scheme include:
- Promoting‘Custom Hiring Centres’ and ‘Hi-tech Hubs of High-Value Machines’ to offset the adverse economies of scale arising due to small and fragmented landholding and high cost of individual ownership.
- Creating awarenessamong stakeholders through demonstration and capacity building
- Ensuring performance, testing and certification of agricultural machinesat designated testing centres located all over the country.

Primary source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1726205
Picture source: https://journalsofindia.com/sub-mission-on-agriculture-mechanization/
The world is hardly wired for cyber resilience-TH
Essence:
Editorial is discussing range of cyber security issues not just for critical government digital infrastructure but to civilian sector too. Motivation for cyberattacks vary: for (some) nation states, the motivation is geopolitical transformation; for cybercriminals, it is increased profits; for terror groups, the motivation remains much the same, but the risk factor may be lower.
What is especially worrisome at this time, when a pandemic is raging, is the number of cyberattacks on health-care systems. Cybersecurity essentially hinges on data protection. Nations that are adequately prepared — conceptually and technologically — and have made rapid progress in artificial intelligence and quantum computing and the like will have a clear advantage over states that lag behind in these fields. In the end, it might be appropriate to quote IBM Chairman, Arvind Krishna, that cybersecurity will be “the pressing issue of this decade” and that “value lies in the data and people are going to come after that data”.
Why you should read this article ?
- To know how cyber-attacks are emerging as weapon of new age warfare.
- Article is giving insights into the type of cyber-attacks posed in recent past & their damage capabilities.
- To gain understanding of importance of data & need for leverage emerging technologies.
- To learn about some ways to build robust digital infrastructure.
Article Link: https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/lead/the-world-is-hardly-wired-for-cyber-resilience/article34807136.ece
The pandemic must lead to a reset of capitalism-HT
Essence: World War I paved the way for the departure of monarchies. World War II sparked the Cold War of communism versus capitalism. The fall of the Berlin Wall in the late 1980s paved the way for the collapse of the communist system. In this context the article discusses the impact of coronavirus pandemic on the economy and the challenges it poses to the current face of capitalism.
Why you should read this article?
- Briefly know about the prevalent inequality in the country and the unfeasibility of dream of Gram Swaraj.
- Understand the impact of pandemic on the economy, job market and the condition of women.
- Know about ineffectiveness of various ideologies with the help of examples and need for fundamental restructuring of the world in post pandemic era.
How India can tackle its formidable nutrition challenge- IE
Essence- COVID-19 has silently amplified the issue of malnutrition, as income, food consumption and essential services all come under pressure. Though government has prioritised addressing malnutrition through the Prime Minister’s Overarching Scheme for Holistic Nourishment (POSHAN) Abhiyan with recently updated POSHAN 2.0 guidelines (Prioritising women and girls). Which sets accountability among district collectors, focusing on data driven approach to plan and manage delivery of nutrition services. Where ‘Poshan Tracker’ was deployed to monitor and improve such interventions by ensuring real-time updates and enhancing transparency. POSHAN 2.0 will provide multiple levers required for an evidence-based, integrated, outcome-focused approach to address India’s nutrition challenge.
Why you should read this article?
- To get an overview of issue of malnutrition in India and governments efforts to tackle the same.
- To understand the aim of POSHAN 2.0 and how it will help in tackling the issue of identification and tracking of coverage and quality of nutrition interventions in real time, (remained a key challenge)
Article Link: https://indianexpress.com/article/opinion/columns/how-india-can-tackle-its-formidable-nutrition-challenge-7353391/
The man who built a forest: Jadav Payeng
How did the journey begin
- Almost 3 decades ago, Jadav Payeng noticed deaths of a large number of reptiles due to a lack of a tree cover. So, he started planting bamboo in a particular area.
- Today, that same land hosts 1,360 acres of Jungle called Molai Forest, named after Jadav “Molai” Payeng.
Contribution of Jadav Payeng
- Jadav Payeng is known as ‘The Forest Man of India’
- Through his journey of grit, he saw a desert turning into a forest.
- The forest now attracts 80% of the world’s migratory bird.
His ideas on how education should promote environmental sensitivity
- A child should be taught to plant a sapling or a seed when he is initiated in school and as he grows up, he or she is taught to take care of it and be responsible for it.
His idea of Happiness
- He mentions that his friends have become engineers and are living in the city. However, jungle is his home now.
- The recognition and awards that he has received are his wealth and that makes him the happiest man in the world.
Where can this case study be used:
- Environmental ethics, How should the education be structured for creation of environmental sensitivity, idea of happiness, story of grit and perseverance.
Quote:
“One person can make a difference, and everyone should try.”: John F. Kennedy
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.