Friday, 11th June 2021
Fast Tracking Freight in India
In News
NITI Aayog’s new report, Fast Tracking Freight in India: A Roadmap for Clean and Cost-Effective Goods Transport, presents key opportunities for India to reduce its logistics costs.
![]()
Findings of the Report
- Need for Fast Tracking Freight in India: As national freight activity grows about five-fold by 2050, India’s freight transport ecosystem has a critical role to play in supporting India’s ambitious priorities. Some of these include international competitiveness, job growth, urban and rural livelihoods, and clean air and environment. Today, the logistics sector represents five percent of India’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and employs 2.2 crore people.
- Energy Consumption: India’s cumulative energy consumption from freight transport between 2020 and 2050 under a business as usual (BAU) scenario will be around 5.8 billion tonnes of oil equivalent (TOE). However, India can reduce this energy consumption by 50 percent under an efficient scenario through three opportunity areas:
- Increasing the share of rail transport: To increase the mode share of rail transport, India can prioritise increase the rail network capacity and the share of intermodal transportation
- Optimising truck use: To optimise truck use, India can prioritise to improve transportation practices and warehousing practices.
- Promoting use of fuel-efficient vehicles and alternative fuels: To promote clean, fuel-efficient vehicle technologies such as EVs, India can prioritise to improve fuel economy and reduce ICE vehicles’ emissions and use EVs and cleaner fuels.
- Benefits of the Measures
- Reduced logistics costs: India has set a target of reducing the logistics costs as a share of GDP from 14 percent currently to 10 percent by 2022, which can save up to INR 10 lakh crore.
- Reduced carbon emissions and improved air quality: India can save 10 giga tonnes of CO2, 500 kilo tonnes of particulate matter (PM) and 15 million tonnes of nitrogen oxide (NOx) caused by freight transport by 2050.
- Less truck traffic on roads: Improved mode share and efficient logistics can reduce the vehicular-freight activity by 48 percent in 2050 over a BAU scenario.
Source: http://www.indiaenvironmentportal.org.in/files/file/fast%20tracking%20freight%20in%20%20India.pdf
QS World University Rankings 2022
In News: Three Indian universities in top 200, India’s tally remains unchanged in QS International University ranking for the fifth straight year.
About QS World University Rankings
- The ‘QS World University Rankings’ is anannual publication of university rankings which comprises the global overall and subject rankings.
- Six parametersand their weightage for the evaluation include academic reputation (40%), employer reputation (10%), faculty/student ratio (20%), citations per faculty (20%), international faculty ratio (5%), international student ratio (5%)

Indian Institutes and their Ranking
- Overall, there are22 Indian institutions in the top 1,000 list compared to 21 in the 2021 Rankings, with the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) in Guwahati, Kanpur, Kharagpur and Madras making major strides in rankings.
- Jawaharlal Nehru Universityhas entered the top 1,000 of the rankings for the first time, as its new undergraduate engineering program now makes it eligible for the rating.
- IIT Bombaymaintained its position as the top Indian institution for the fourth consecutive year, although it fell five places in the global rankings to the joint 177th
India’s Performance and its shortfalls
Indian universities have improved their performance on academic reputation metric and research impact but continue to struggle on the teaching capacity metric.
- No Indian university ranks among the top 250 for faculty-student ratio.
- Poor performance on teaching capacityis not because of any drop in hiring, but an increased student intake mandated by the government to implement reservations for economically weaker sections.
- The rankingsdo not accurately reflect the quality of education in India, as they are largely dependent on international perception factors. Half of the score comes from reputation indicators which are based on perception, rather than any objective methodology.
Global Rankings
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT)of the US is the top university for the 10th consecutive year.
- The University of Oxford (UK)has risen to second rank for the first time since 2006, while Stanford University (US) and the University of Cambridge (UK) share third spot.
- Singapore’sNational University of Singapore and Nanyang Technological University, and China’s Tsinghua University and Peking University, are the only Asian universities in the global top 20.
- Primary source: https://2thepoint.in/qs-world-subject-rankings-2021/
- https://indianexpress.com/article/education/three-in-top-200-india-tally-unchanged-in-international-university-ranks-7350182/
- https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/jnu-enters-top-1000-global-varsities-ranking/article34764068.ece
- https://www.oneindia.com/india/qs-world-university-rankings-iisc-bangalore-top-research-institute-in-world-3271333.html?story=3
- Picture source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/jnu-enters-top-1000-global-varsities-ranking/article34764068.ece
SAGE (Seniorcare Aging Growth Engine) initiative
In News: The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment has launched the SAGE initiative and SAGE portal for elderly persons.
 initiative.jpg)
What is SAGE Initiative?
- SAGE is a “one-stop access” for elderly care services and products by credible start-ups.
- It will aim to provide solutions for health, housing, care centers, apart from technological access linked to finances, food and wealth management, and legal guidance.
- The SAGE initiative promotes the idea of “silver economy” by developing residential and infrastructure facilities of different grades for seniors through public-private partnership for a dignified and safe ageing experience.
Silver Economy
- Silver economy is the system ofproduction, distribution and consumption of goods and services aimed at using the purchasing potential of elder and ageing people and satisfying their consumption, living and health needs.
- The silver economy isanalyzed in the field of social gerontology (study of aging) and gerontechnology not as an existing economic system but as an instrument of ageing policy.
Global Ageing scenario and the Need for such an initiative
- Both the share and size of elderly population has been increasing over time. From 5.6% in 1961 the proportion has increased to 8.6% in 2011.
- The share of elders, as a percentage of the total population in the country, is expected to increase from around 7.5% in 2001 to almost 12.5% by 2026 and surpass 5% by 2050.
- According to Population Census 2011, there are nearly 104 million elderly persons (aged 60 years or above) in India. A report released by the United Nations Population Fund and HelpAge India suggests that the number of elderly persons is expected to grow to 173 million by 2026.
- There is an urgent need to create a more robust eldercare ecosystem in India, especially in the post-COVID phase.
Primary source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1724425
Picture source: https://www.slideshare.net/ILC-UK/ilcuk-future-of-ageing-presentation-slides-09nov16
Impact Investing
Context of the News
India is being seen as an attractive destination for Impact Investing by various investors.
What is Impact Investing?
- Impact investments are investments made with the intention to generate positive, measurable social and environmental impact alongside a financial return.
- Impact investments can be made in both emerging and developed markets and target a range of returns from below market to market rate, depending on investors' strategic goals.
- As of 2017, McKinsey estimated that the cumulative investments in the social sector (impact investments) stood at $5.2 billion.
- Impact investments target financial returns that range from below market (sometimes called concessionary) to risk-adjusted market rate, and can be made across asset classes, including but not limited to cash equivalents, fixed income, venture capital, and private equity.
Why Impact Investing?
- Change in old investment mindset: Impact investing challenges the long-held views that social and environmental issues should be addressed only by philanthropic donations, and that market investments should focus exclusively on achieving financial returns.
- Increasing value of Sustainability: As the world has understood the value of sustainability, social impact investments are being aligned to the achievement of Sustainable Development Goals.
- The achievement the SDGs by the year 2030 demands developing nations to invest as much as USD 3.9 trillion annually. The impact investments are expected to fill the gap between the expected and actual investments for SDGs.
- Drawbacks of the market system: Market system of investments have contributed towards economic inequality, environmental degradation, the weakening of communities and fragile public systems, which is the root causes of many of the challenging social problems we encounter.
- The impact investing market offers diverse and viable opportunities for investors to advance social and environmental solutions through investments that also produce financial returns
Impact Investing in India
- Nascent Stage: Although Impact investments in India are relatively nascent, they are steadily gaining currency and appear to demonstrate bright prospects as well. The interplay between the scope for economic growth as well as social advancement on the one hand, and robust financial markets, on the other, has provided the impetus for growth of impact investments in India.
- Trends in India: The aggregate assets in impact investments between 2010 and 2016 in India were US$5.2 billion. In 2018, about 67 percent of impact investors invested their money in agriculture and education, followed by energy and microfinance.
- SEBI Report on Social Stock Exchange: The SEBI working group report on SSE offers NPOs and for-profit enterprises (FPEs) a platform to list themselves as social enterprises in a market that promotes social impact. The potential benefits include access to financial instruments and tax incentives.
Challenges in Impact Investing
- Universal Challenges to Impact Investing:
- Tricky Definition: Regulations rest on definitions, compliance and verification. But, structuring an enterprise on the market system and labelling it as “social" creates misunderstandings. So, there is need for sharper distinction to bring social enterprises under a distinct regulatory oversight.
- Less financially attractiveness: A social enterprises generally signals that the promoters shall not take anything out of the enterprise beyond the nominal value of investments and a one-time miniscule premium without consideration of the time value of money.
- Challenges in India:
- Conflicting laws: There are several conflicting laws that govern different forms of social enterprises in India, which creates numerous overlaps and eventually delays.
- Lack of legal recognition: As social enterprises are not recognised as separate legal entities, there is no standardised legal structure that oversees their functioning. This results in social enterprises incurring significant costs in terms of registration, compliance, seeking of approvals etc.
- No Tax Benefits: India does not distinguish between for-profits with a social mission as against those without such a mission, both entities are being taxed in the same manner.
- Funding Problems: The regulations around receiving philanthropic and foreign funds are unfavourable, which does not allow tax breaks on grants and donations made to for-profit social enterprises. Also, the for-profit enterprises are not eligible for Corporate Social Responsibility, which could have given them some tax relief.
What can be done to resolve the challenges?
- Measuring Practices, Setting Standards: The measurement of social impact is extremely expensive and notoriously difficult. This can be resolved by developing the mechanisms for capturing data and developing standards for the same.
- Standards for Social enterprises: Specifying a standard to be adhered would help organisations signal their values and commitment. These could include ownership patterns, caps on the share of profits distributed, remuneration ratios and rules for decision making.
- Avoiding Conflict of Interest: There is need to identify professionals who understand the social sector well enough to certify them and not reduce it to a site of profit mining.
- Need for Diversity: There is need for a more diverse and representative group to engage with local and global experiences of Social Business, B-Corps, Community Investment Companies, cooperatives and farmer producer organisations, and beyond the for-profit sector.
Conclusion
Impact investing has reached an inflection point, with the coronavirus pandemic highlighting deep social imbalances that have intensified the need for such forms of investments. So social enterprises need to set clear benchmarks rigorously and act as a catalyst to accelerate the growth.
Question: What is Impact Investing? Analyse its utility in Indian context.
Sources:
https://www.orfonline.org/expert-speak/impact-investments-in-india-66617/
This Day in History -Antonio Meucci
On June, 11, 2002, the United States Congress acknowledged Italian immigrant Antonio Meucci as the true inventor of the telephone. Alexander Graham Bell is often credited with being the inventor of the telephone since he was awarded the first successful patent. Antonio Meucci began developing the design of a talking telegraph or telephone in 1849. In 1871, he filed a caveat (an announcement of an invention) for his design of a talking telegraph. Due to hardships, Meucci could not renew his caveat. His role in the invention of the telephone was overlooked until the United States House of Representatives passed a Resolution, honoring Meucci’s contributions and work.

Sources: https://www.edn.com/meucci-acknowledged-as-telephone-inventor-june-11-2002/
https://www.loc.gov/everyday-mysteries/item/who-is-credited-with-inventing-the-telephone/
Image of the Day -TOI-1231 b
This image is of an artist’s rendering of TOI-1231 b, a Neptune-like planet about 90 light-years away from Earth. It is oddly reminiscent of our own Neptune, a gaseous world with a potentially rich atmosphere. TOI-1231 b orbits a red-dwarf star. But the planet stays relatively cool despite its close orbit because its star also is on the cooler side. Though not habitable due to its size, the planet could offer scientists one of their first chances to capture a “bar-code” type reading of the atmosphere of a temperate, Neptune-sized exoplanet, a planet orbiting another star. This will allow comparisons with similar worlds elsewhere in the galaxy, bringing potentially deep insights into the composition and formation of exoplanets and planetary systems, including our own.
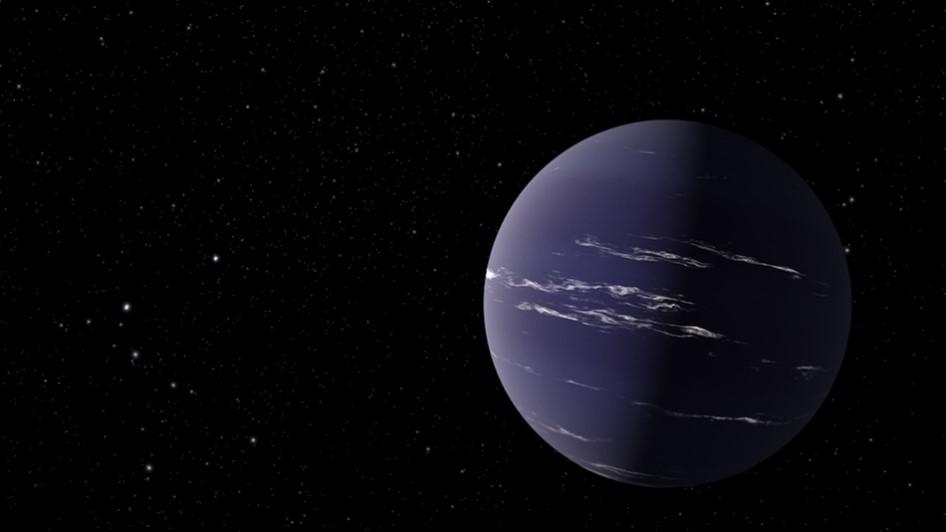

Source: https://exoplanets.nasa.gov/news/1685/discovery-alert-a-cool-planet-with-plenty-of-atmosphere/
Global Economic Prospects
- Context: The World Bank has released its June 2021 Global Economic Prospects.
- Global Economic Prospects is a World Bank Group flagship report published biannually that examines global economic developments and prospects, with a special focus on emerging market and developing economies.
- Highlights of the June 2021 Report:
- India's economy is expected to growat 8.3% for Fiscal Year 2021-22, 7.5% for 2022-23 and5% for 2023-24.
- The world economy is expected to expand6%,the fastest post-recession growth rate in eighty years.
- However, global output will still be 2% below pre-pandemic projectionsby year-end.

- Primary source: https://thewire.in/economy/world-bank-slashes-india-growth-forecast-8-3-fy22
- https://www.thehindu.com/business/Economy/india-expected-to-grow-at-83-says-world-bank/article34762989.ece
- Picture source: https://www.financialexpress.com/economy/indian-economy-estimated-to-contract-by-9-6-in-2020-grow-at-7-3-in-2021-un/2178984/
Sardar Sarovar Dam
- Context: The Sardar Sarovar Dam is providing irrigation water in summer for the first time in history.
- The Sardar Sarovar Narmada Dam is a terminal dam built on the Narmada River at Kevadia in Gujarat’s Narmada district.
- Called the ‘lifeline of Gujarat’, it usually has no water for irrigation during summers.
- It is a concrete gravity dam and four Indian states, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra and Rajasthan, receive water and electricity supply from the dam.
- The project took form in 1979 as part of a development scheme funded by the World Bank to increase irrigation and produce hydroelectricity.
- The construction for dam begun in 1987, but the project was stalled by the Supreme Court of India in 1995 due to Narmada Bachao Andolan over concerns of displacement of people.
- In 2000 the project was revived but with a lower height of the dam.
Primary source: https://artsandculture.google.com/entity/m02xsn9?hl=it
Turbidity Current
- Context: A vast underwater avalanche (aka turbidity current) has sent mud and sand more than 1,000km out into the ocean rupturing submarine cables and disrupting internet traffic on Africa’s western coast.
- A turbidity current is a rapid, downhill flow of watercaused by increased density due to high amounts of sediment.
- Turbidity currents can be caused by earthquakes, collapsing slopes, and other geological disturbances. The turbid water then rushes downward like an avalanche, picking up sediment and increasing in speed as it flows.
- Turbidity currents can change the physical shape of the seafloor by eroding large areas and creating underwater canyons. These currents also deposit huge amounts of sediment wherever they flow.
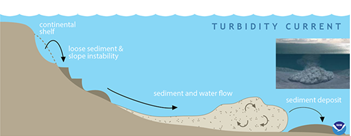
Primary source: https://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/turbidity.html
Picture source: https://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/turbidity.html
Bitcoins
- Context: El Salvador has become the first in the world to make Bitcoin legal.
- Bitcoin is a digital or virtual currency created in 2009 by a Japanese entrepreneur named Satoshi Nakamoto. It uses peer-to-peer technology to operate with no central authority or banks, to facilitate instant payments.
- It offers the promise of lower transaction fees than traditional online payment mechanisms and, unlike government-issued currencies, it is operated by a decentralized authority.
- Bitcoin is open-source, its design is public and nobody owns or controls it. All the transactions ever made are contained in apublicly available, open ledger, although in an anonymous and an encrypted form called a
- One can mine a new Bitcoinif they have the computing capacity, purchase them via exchanges, or acquire them in over-the-counter, person-to-person transactions.
- Primary source: https://bitcoin.org/en/
India’s PACK challenge requires a political response
Essence: Editorial is presenting analysis on India’s engagement with neighbours like Pakistan, Afghanis & China amid rapid changes observed in last 1.5 year. Territorial disputes, political instability, religious radicalism, popular aspirations and great power dynamics are key issues in this region. Things have started moving between India & Pakistan, as latter is speaking a new language of geoeconomics and a trade-fronted regional policy. For Afghanistan, India has articulated its preference for a constitutional and democratic regime that protects the rights of women and minorities. When it comes to Kashmir, New Delhi considers a new and sustainable Kashmiri equilibrium, one where all Kashmiris feel included, within the larger PACK matrix. On the China policy, the core problem remains unaddressed — the collapse of bilateral political understanding forged at the highest level in Ahmedabad, Wuhan and Mamallapuram. PM needs to set out his government’s efforts at securing India’s national interest vis-à-vis China.
Why you should read this article?
- To gain understanding on recent changes observed in Pakistan’s regional policy.
- To know about the importance of political approach to resolve long standing bilateral issues.
- To know about India’s outreach in Afghanistan, amid Taliban getting closer to decide future of Kabul.
- To gain insights on Kashmiri equilibrium and how it’s linked to PACK matrix.
Article Link: https://www.hindustantimes.com/opinion/indias-pack-challenge-requires-a-political-response-101623320356358.html
Big spender: What Centre must do to meet the economic challenges following Covid second wave
Essence: On May 31, important updates regarding India’s GDP growth and the Centre’s fiscal performance for 2020-21 became available. In this context, the article discusses the numbers related to GDP, Inflation, tax revenue, non-tax revenues and non-debt capital receipts, planned priority expenditure and estimated fiscal deficit. The article, against the background of an unprecedented borrowing programme by the Centre, suggests to monitor the implications that liquidity expansion will have for inflation.
Why you should read this article?
- Know about the estimated numbers related to GDP, Inflation, tax revenue, non-tax revenues and non-debt capital receipts, planned priority expenditure and estimated fiscal deficit following Covid second wave.
- Have a brief understanding of the borrowings of government and how RBI is supporting it through indirect monetisation of debt.
- Understand the reasons for low money multiplier and why it is necessary to keep in mind the implications that liquidity expansion will have for inflation.
The promise and perils of digital justice delivery
Essence: This article is written in the backdrop of how use of technology within the constitutional framework can revolutionise the India’s courts and solve the issues associated with delays in delivery of justice. Recently, the e-committee of the supreme court (SC) has released its draft vision document for phase III e-courts project with the objective of providing 360-degree approach with an ‘ecosystem approach’ to justice delivery. Which further suggests a ‘seamless exchange’ of information between various branches of states through ‘interoperable criminal justice system’ (ICJS) with a concern of exacerbating existing class and caste inequalities because of involvement of large-scale data sharing and gathering. SC must take care not to violate the privacy standards and provide anonymous, aggregated, and statistical information about issues without identifying the individuals. So that objectives like streamlining of judicial processes, reducing pendency and help litigants may achieve by moving towards localization of data, instead of centralization.
Why you should read this article?
- To understand how technology can revolutionise the India’s judicial system.
- To know the objective of phase III e-courts project and why seamless exchange of data should be prevented.
- To understand how ICJS can exacerbate the existing class and caste inequalities.
- To understand possible steps that should be taken to tackle these existing challenges.
Article Link: https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/lead/the-promise-and-perils-of-digital-justice-delivery/article34773168.ece
Art Of Healing Among India’s Poorest: A Remarkable Story of SEARCH
About SEARCH (Society for Education, Action and Research in Community Health)
- It is a non-profit organization working in the vulnerable, semi-tribal district of Gadchiroli in Maharashtra.
- It was founded by Padma Shri Dr. Abhay Bang and Dr. Rani Bang
- Its vision is to achieve 'Aarogya Swaraj' which aims at empowering individuals to take charge of their own health to achieve freedom from disease and dependence.
- It has done pioneering work in maternal and child health, tribal health, reduction of alcohol & tobacco, and non-communicable diseases
Methodology adopted by SEARCH
- It follows a participatory model, whereby the community's health needs are considered while working on the intervention areas.
- The community members are empowered to work as health messengers and workers (Aarogya Doot) to educate the larger community on health topics and provide preventive and curative care.
Outcome
- The methodology has reduced the infant mortality rate in this tribal area to 12-30 % per 1,000.
- Oorganisations world-wide have accepted the new approach by SEARCH as an effective way to reduce child mortality.
Values upheld by the organisation:
- Gandhian Talisman, Compassion, Selflessness
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.