Friday, 4th June 2021
NITI Aayog’s SDG India Index 2020-21
In News
NITI Aayog released the SDG Index 2020-21
Key takeaways of the SDG index 2020-21
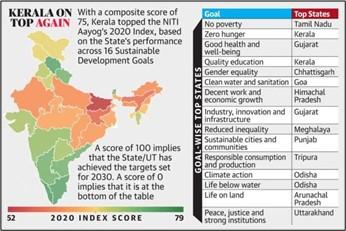
- Overall Score: India’s overall SDG score improved by 6 points, from 60 in 2019 to 66 in 2020-21.
- Improvement: Significant improvement is visible in the SDGs related to clean energy, urban development, health, eradication of poverty and hunger in 2020.
- Decline: India’s score on the SDG related to industry and infrastructure dropped 10 points to 55, while the scores on decent work dropped three points to 61. The Clean Water and Sanitation SDG also dropped.
- Top ranking states: Kerala retained its position at the top of the rankings in the third edition of the index, with a score of 75, followed by Tamil Nadu and Himachal Pradesh, both scoring 72.
- Union Territories: Chandigarh maintained its top spot among the union territories (UTs) with a score of 79, followed by Delhi (68).
- Worst Performers: At the other end of the scale, Bihar, Jharkhand, and Assam were the worst performing States. However, all States showed some improvement from last year’s scores, with Mizoram and Haryana seeing the biggest gains.
About the Index
- SDG India Index, which is developed in collaboration with the United Nations, tracks the progress of States and Union Territories on 115 indicators aligned with the Ministry of Statistics and Program Implementation (MOSPI)'s National Indicator Framework.
- Significance: The Index is useful to States/UTs to assess their progress against national targets, understand reasons for differential performance and devise better strategies to achieve the SDGs by 2030.
- Support States/UTs to identify priority areas in which they need to invest and improve by enabling them to measure incremental progress.
- Highlight data gaps related across SDGs for India to develop its statistical systems at the national and State levels.
https://niti.gov.in/sdg-india-index-dashboard-2019-20
World Employment and Social Outlook: Trends 2021
In News
The International Labour Organization (ILO) has published its flagship report World Employment and Social Outlook: Trends 2021.
About the Report
- This year’s report examines global and regional trends in employment, unemployment, labour force participation and productivity, as well as dimensions of job quality such as employment status, informal employment and working poverty.
- It also provides extensive analysis of the COVID crisis’s varied impact on enterprises and workers.
- It proposes a human-centred recovery strategy to avoid scarring of future global labour markets.
Key Observations
- Lost Working hours: In 2020, an estimated 8% of total working hours were lost – the equivalent of the hours worked in one year by 255 million full-time workers. Half the losses were due to outright job losses in COVID.
- Latin America and Caribbean, and Europe and Central Asia, are two worst-affected regions.
- Employment recovery, though strong, will be insufficient to close the gaps.
- Increased Poverty: Relative to 2019, an estimated additional 108 million workers are now extremely or moderately poor (living on less than US$3.20 per day in PPP terms).
- Five years of progress towards the eradication of working poverty have been undone, as working poverty rates have now reverted to those of 2015.
- Recovery: The recovery will be relatively faster in high-income countries. In low- and middle-income countries, the more limited access to vaccines and greater constraints on fiscal spending will dampen the employment recovery.
- Low quality jobs: Many of the newly created jobs are expected to be of low productivity and poor quality. The shift towards self-employment – which is disproportionately characterized by low-productivity, informal work – is yet another sign of deteriorating work quality.
- Highly uneven impact of the crisis: Workers whose labour market position was disadvantageous prior to the crisis – women, migrants, informal workers, and workers in lower-skilled occupations – suffered disproportionately.
- For instance, women’s employment declined by 5% in 2020 compared with 3.9% for men.
Way Forward
- Promote broad-based economic growth and the creation of productive employment through investment in sectors that can be a source of decent jobs and that support a just transition, gender equality and vibrant labour markets.
- Support household incomes and labour market transitions, particularly for those most affected by the crisis, through active labour market policies, public employment services and publicly provided, high-quality care services.
- Strengthen the institutional foundations of inclusive, sustainable, and resilient economic growth and development by enhancing social protection systems, promoting formalization, and protecting the rights of workers such as right to freedom of association and collective bargaining, minimum wages etc.
- Engage in social dialogue to develop and ensure effective implementation of human-centred recovery strategies.
https://www.ilo.org/global/research/global-reports/weso/2021/WCMS_795453/lang--en/index.htm
BRICS joint statement on reform of global institutions
In News
The BRICS foreign ministers recently met to discuss the Covid challenge and reforms in multilateral institutions.
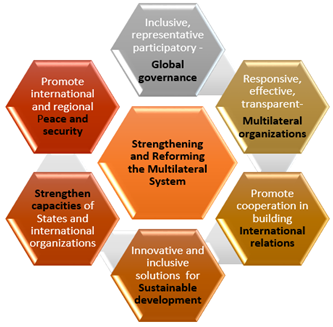
Key issue and resolutions at the meeting
- BRICS Joint Ministerial Statement on Strengthening and Reforming of the Multilateral System: The BRICs ministers stressed on the urgent need for strengthening and reforming of the entire multilateral architecture, including the United Nations and its principal organs.
- Global Financial Safety Net: with a quota-based and adequately resourced IMF at its center and broadening and strengthening the participation of emerging markets and developing countries (EMDCs) in the international economic decision-making and norm-setting processes.
- TRIPS Waiver: BRICS countries agreed to support India and South Africa on issue of TRIPS waiver for Covid-19 vaccines.
- Vaccine Cooperation: Hold a BRICS Symposium on Vaccine Cooperation, operationalization of the BRICS Vaccine Research and Development Centre and stressed the need for further work on the proposal for BRICS Integrated Early Warning System for Preventing Mass Infectious Diseases Risk
- UNSC: Stressed on need for consolidation and strengthening of the working methods of the UN Security Council Sanctions Committees to ensure their effectiveness, responsiveness, and transparency. This is significant in sanctioning of terror masterminds in the Af-Pak region.
- Comprehensive Convention on International Terrorism (CCIT): BRICS members resolved to step up joint efforts in building support for the adoption of the Comprehensive Convention on International Terrorism (CCIT).
Precision Farming
In News
Many countries such as China, Japan, the ASEAN nations, USA and Brazil are making rapid strides in adopting precision farming for use in agriculture.
Why does India need to adopt new technology in farming or agriculture?
- India has one of the highest arable lands globally with over 155 million hectares and is one of the key agricultural producers. In 2019, the agricultural sector contributed 18 per cent of India’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and employs more than half of India’s population.
- However, there are structural challenges plaguing the sector including low productivity, uneconomic landholding size, sub-optimal input use efficiency, high biotic losses, and a low level of mechanisation.
- For India to double its farmer incomes, there is an immediate need for the agricultural sector to adopt leading-edge digital and precision agriculture technologies to improve farm productivity and democratize access to market information for all farmers.
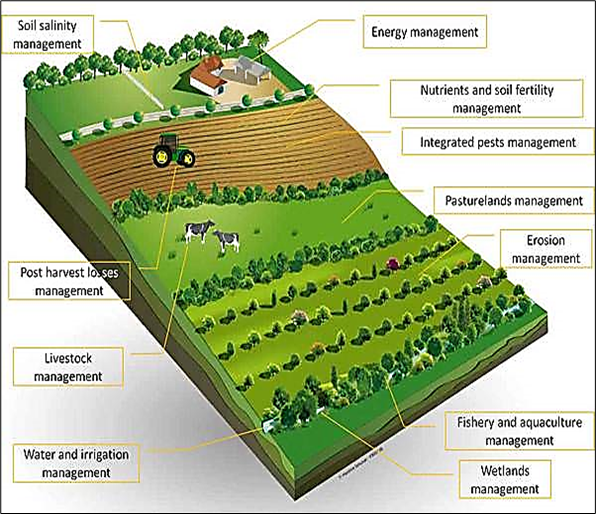
What is Precision Farming (PF)?
- Precision Agriculture (PA), Satellite Farming or Site-Specific Crop Management (SSCM) is defined as ‘a technology-enabled approach to farming management that observes, measures, and analyses the needs of individual fields and crops’.
- According to McKinsey, the development of precision agriculture is shaped by two trends: “Big Data and Advanced Analytics Capabilities, and Robotics — aerial imagery, sensors, sophisticated local weather forecasts”. In simple words farming that collects and uses data of plots for managing and optimizing the production of crops is known as Precision farming.

How can it aid the farming sector in India?
- Soil and field planning: Precision Farming can be used for soil and field analysis for irrigation, fertilisation and planting activities including checking nutrient levels, moisture concentrations, and erosion. Instruments like sensors and drones can be used in this operation.
- Crop monitoring: Drones can be used to perform continuous and consistent crop surveillance that can trigger actions to mitigate the effect of various biotic and abiotic stresses on crops. The data generated through such surveillance can help site-specific agronomy to optimise the use of inputs and promote sustainable farming.
- Crop protection from weeds, pests, and diseases: Precision Farming instruments are capable of spraying precise amounts of insect, weed and disease control products in a way that can ensure correct dosage, minimise accidental exposure to applicators and improve the overall effectiveness of the products and therefore outcomes of growers.
- Productivity: Farmers receive the feedback in real time and then deliver water, pesticide, or fertilizer in calibrated doses to only the areas that need it. The technology can also help farmers decide when to plant and harvest This can significantly alleviate labour pressure on agricultural operations like applying pesticides or fertilisers, while enhancing the crop coverage area per day.
- Climate-smart agriculture: Remote Sensor and GIS technology ensures the effective field management strategies for chemical application, cultivation, and harvest, based on local crop and site-specific conditions. Excess usage of fertilizers, pesticides can damage ecological balance. This information can be used to calculate how much carbon is being sequestered by what plants, or how it is being trapped in soil.
- Yield Monitor: Through Yield monitors, crop yield information is recorded on grid basis during harvest. Yield differences are analysed with fine tuning the variable rate of application of agriculture inputs to various grids. GPS and GIS provides information land fertility, weather condition, information of yield monitor help in effective planning of all agriculture activity further enhancing the agriculture productivity.
Challenges to Precision Farming in India
- Resistance in adopting new technology: High illiteracy among Indian farmers holds them back from adopting technology in agriculture practices. Various initiatives taken by public and private sector towards ICT adoptability in agriculture has not generated desired result in terms of awareness, and adoptability.
- Economic Challenges: Higher initial cost-Precision farming includes many expensive machines and tools which are beyond the economic reach of small and marginal farmers. Operational cost of machine and tools under precision agriculture are the fear factor for its adoption. Financial credit to farmers can help to stimulate agriculture technology adoption
- Social and behavioural factors- The lack of awareness and absence of dedicated education of precision agriculture among farming communities is major obstacle for its adoption. Indian farming is predominated by age old farming practices. The same agriculture practices are being carried out from generation. Resistance and rigidity are two major hurdles in adoption of precision farming.
Conclusion
Precision farming has great potential to transform Indian agriculture by helping farmers to manage their fields and resources in a better and more sustainable way. Some initiatives in this direction have been taken like the TATA Kisan Kendra (TKK) which has introduced precision farming in rural India and the Tamil Nadu Precision Farming Project, which has been widely accepted by farmers and increased yields 12 times higher than normal. Thus, precision farming can be scaled up by creating of multidisciplinary teams to study precision agriculture, providing complete technical backup support to the farmers to develop pilots or models, which can be replicated on a large scale and creating awareness among farmers.
Question: What is Precision Farming? Enumerate the various benefits and challenges to precision farming in India.
https://www.unoosa.org/documents/pdf/psa/activities/2008/colombia/presentations/3-1.pdf
This Day in History - Tiananmen Square protests
On 4 June, 1989, the Tiananmen Square protests ended violently in Beijing with People's Liberation Army killing 241 protesters. Tiananmen Square incident, also called June Fourth incident or 6/4, series of protests and demonstrations arose in China in the spring of 1989. The protests were student-led demonstrations calling for democracy, free speech, and a free press in China. In the aftermath of the crackdown, the United States instituted economic and diplomatic sanctions for a time, and many other foreign governments criticized China’s handling of the protesters.
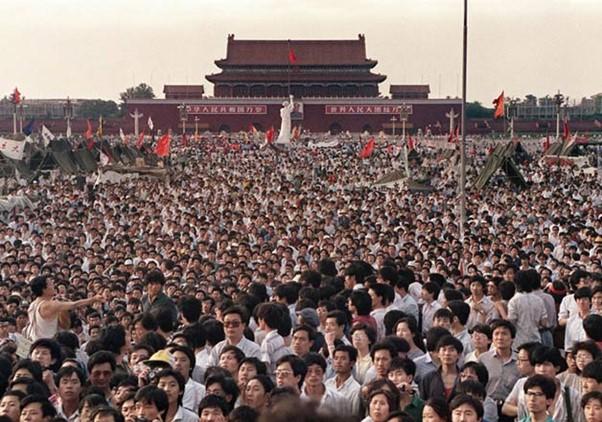

Sources: https://www.history.com/this-day-in-history/tiananmen-square-massacre-takes-place
https://www.indiatvnews.com/buzz/who-cares/5-historic-events-of-4th-june-135.html
Image of the Day- Baekdudaegan National Arboretum Seed Vault Centre
This is the image of the Baekdudaegan National Arboretum Seed Vault Centre, South Korea. Protected against climate change, natural disaster and even war, about 5,000 wild plant species are kept safely in a hidden mountain tunnel in South Korea. It is one of two such facilities in the world, the other being the biggest seed vault in the world located on Svalbard, Norway about a thousand kilometers from the North Pole. South Korea has allowed other countries to store their samples and withdraw as they need. The Centre can withstand a 6.9 magnitude earthquake and an atomic bomb blast.

NASA’s New Mission to Venus
- Context: NASA picks Venus for two new robotic missions.
- These two sister missions aim to understand how Venus became an inferno-like world capable of melting lead at the surface.
- DaVinci Plus Mission will analyse the thick, cloudy Venusian atmosphere to determine whether the planet ever had an ocean or was habitable.
- Veritas Mission will seek the geologic history by mapping the rocky planet’s surface.
- Previous Missions to Venus include US: NASA’s Mariner 2 flyby in 1962, PioneerVenus 1/2 and Magellan, Russia: Venera 7, Vegas ½, Japan: Akatsuki in 2015, Europe: Venus Express in 2005, India: launch a new orbiter Shukrayaan to Venus in 2024.

Primary source: https://indianexpress.com/article/technology/science/nasa-picks-venus-as-hot-spot-for-two-new-robotic-missions-7341904/
H10N3 bird flu
- Context: China reports first human case of H10N3 bird flu.
- H10N3 is a subtype of the Influenza A virus which is commonly known as the bird flu virus.
- The bird flu/avial flu is caused by influenza virus that spreads between birds but rarely in humans.
- H10N3 is a low pathogenic or relatively less severe strain of the avian flu in poultry and its risk of spreading on a large scale is very low (as compared to H05 and H07).
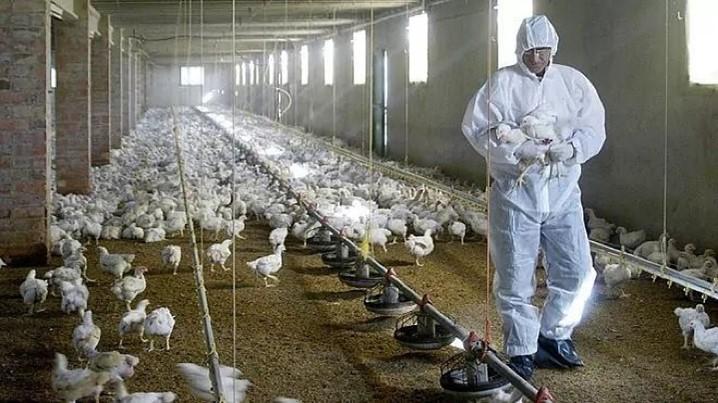

Primary source: https://www.republicworld.com/lifestyle/health/what-is-h10n3-strain-of-avian-influenza-is-it-dangerous-to-humans-here-are-the-details.html
Picture source: https://www.marca.com/en/lifestyle/2021/06/02/60b794c7e2704e6c888b45a9.html
Section 51 of the Disaster Management (DM) Act, 2005
- Context: Centre serves show cause notice to former Bengal Chief Secretary under Disaster Management Act, 2005.
- Section 51 (b) of the DM Act prescribes “punishment for obstruction” for refusal to comply with any direction given by or on behalf of the central government or the state government or the national/state executive committee/district authority under the Act.
- Anyone refusing to comply with orders is liable for punishment with imprisonment up to one year, or fine, or both. In case this refusal leads to death of people, the person liable shall be punished with imprisonment up to two years.
- Section 51 of the Act has two important reservations.
 Act, 2005.jpg)
Primary source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/centre-serves-show-cause-notice-on-former-bengal-chief-secretary-under-dm-act/article34696329.ece
https://www.taxscan.in/itat-deletes-penalty-for-failure-to-issue-notice-read-order/106095/
SWASTIIK Technology for disinfecting Water
- Context: Modern technology and Indian traditional knowledge combine to bring safe & healthy drinking water.
- SWASTIIK (Safe Water and Sustainable Technology Initiative from Indian Knowledge Base) is a novel hybrid technology that combines modern technology and Indian traditional knowledge of Ayurveda to disinfect water completely and offer possible health benefits of natural oils.
- SWASTIIK involves boiling of a liquid because of pressure reduction(cavitation) and uses natural oils having antimicrobial properties. It can eliminate harmful bacteria, including antimicrobial-resistant bacteria.
- It was observed that disinfection using oil can drastically reduce the time of operation and cost.
Primary source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1723594
Picture source: http://ibgnews.com/2021/06/02/modern-technology-and-indian-traditional-knowledge-combine-to-bring-safe-healthy-drinking-water/amp/
Developing the sister islands of Indian Ocean
Essence: Editorial is presenting insights on issues faced by Island nations in the Indian Ocean like - sustainable development, illegal fishing, disaster management, the climate crisis and other aspects of the blue economy. Andaman and Nicobar Islands not only provide Delhi with a key maritime space but also carry significant potential in shaping the strategic and military dynamics of the Indian Ocean region. They need to be developed sustainably for maximising its potential — given its economic, ecological, and environmental constraints as well as the laws to protect the indigenous tribes on the islands.
Reunion island is an excellent case study to develop strategic islands in a sustainable manner. The similarities between Reunion and Andamans are manifold, from strategic location and military bases to strict conservation and environmental laws as well as governing bodies, climate, and marine ecosystems. While the concept of sister cities is quite common, this could be extended to a framework of “sister islands” addressing specific concerns and challenges
Why you should read this article?
- To get a better grasp of the strategic significance of Indian Ocean islands.
- To learn about the major challenges that islands in the Indian Ocean confront.
- Gain insight into India's efforts to shape the strategic and military dynamics of the Indian Ocean region.
- To comprehend the Indian Ocean Commission's role.
Article Link: https://www.hindustantimes.com/opinion/developing-the-sister-islands-of-indian-ocean-101622720051095.html
Rethinking water’s value
Essence- Article is written in the backdrop of value of water and its effective management when 2.2 billion people around the world are struggling to get clean water. Valuing water begins at its source, distribution & usage and finally its treatment and reusage. There are several initiatives at international level like Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) which stress on ensuring availability and sustainable management of water. India being the most populous country needs to manage water crisis through its active efforts Jal Shakti Abhiyan along with collaborating with international initiatives. Apart from this, depleting water table and overall water loss through distribution networks in urban areas are another major concern. This problem can be tackled by restoring water bodies like lakes, ponds. For this to happen, government, civil society and corporate must come together to managing water efficiently.
Why you should read this article?
- To get an overview of issues related to water availability around the world.
- To understand what valuing water stands for and why water management is important for India.
- To know the possible solution to tackle this issue of water crisis.
Article Link: https://www.thehindubusinessline.com/opinion/rethinking-waters-value/article34720293.ece
Students’ Educational and Cultural Movement of Ladakh (SECMOL)
Background:
- In 1998, 95% of Ladakhi students failed the state 10th class exams because of which it was necessary to change the educational system.
- In 1994, SECMOL launched the Operation New Hope movement to improve education in collaboration with the education department, local government, and the village community members.
.png)
Problems with the education system in Ladakh in 1990s:
- The language used in books and exams was non-Ladakhi language up to class 8 and English for classes 9 and 10.
- All the textbooks came from Delhi with examples of unfamiliar environments like ships, oceans, coconut trees and monsoon rains. Alien examples in alien languages only confused Ladakhi children.
- Most of the teachers had no training at all. They mainly taught through rote memorisation without comprehension.
- Community participation was minimal.
Operation New Hope:
- It was launched with an aim to overhaul the primary education system in Ladakh.
- The movement had three arms working together: the government, the non-governmental organizations, and the village communities.
How did they bring a turn around:
- They created Village Education Committee to raise a sense of community ownership of the government schools and to insure accountability.
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.