Thursday, 3rd June 2021
Mission Innovation CleanTech Exchange
In News
India launched the Mission Innovation CleanTech Exchange, at the Innovating to Net Zero Summit.
About the News
- As part of the Mission Innovation Platform, India launched the Mission Innovation CleanTech Exchange which will create a network of incubators across member countries.
- The network, launched virtually at the Innovating to Net Zero Summit hosted by Chile, will provide access to the expertise and market insights needed to support new technologies to access new markets globally.
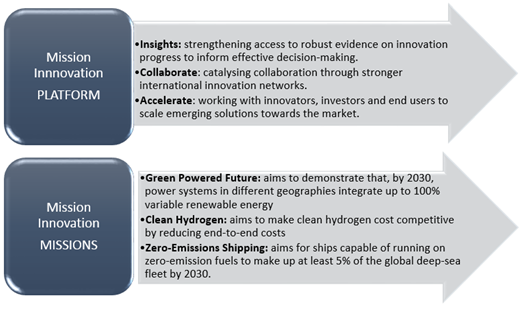
What is Mission Innovation 2.0?
- Mission Innovation 2.0 was officially launched at the Innovating to Net Zero Summit. It will spearhead a decade of innovation to catalyse increased investment in clean energy research, development, and demonstrations to deliver affordable clean energy solutions by 2030.
- Mission Innovation was launched alongside the Paris Agreement in 2015, to accelerate public and private investment, collaboration, and innovation to make clean energy widely affordable.
- Mission Innovation is the main intergovernmental platform addressing clean energy innovation through action-oriented cooperation.
- Member governments’ clean energy innovation investments are now USD$5.8bn per year higher than 2015, with a total USD$18bn of additional investments since 2015.
- Members have committed to sustained and strengthened cooperation across public-private sectors and key technologies to build momentum towards COP26 and accelerate innovation to meet the Paris goals.
Sources: http://mission-innovation.net/2021/06/02/decade-clean-energy-innovation-mi-6/
Revamping Competency of Bureaucracy
In News: The Government of India is looking to onboard a leading HR consultancy firm to help it revamp the competency of the country’s bureaucracy.
What would be the role of the Hired Consultant?
- To study the organizational structures and the work allocation documents of seven key ministries or departments of the Government of India.
- To design and develop an FRAC (Framework of Roles, Activities & Competencies) for the central government with a focus on molding a “fit-for-future civil service” that can deliver to larger social and economic mandates.
- Map the roles and activities corresponding to every government position with their desired competencies across behavioral attributes, functional skills, and domain knowledge.
- Set up and operationalize an FRAC Center of Excellence at the Institute of Secretariat Training & Management.
- Assessment of global practices, testing of hypothesis in the local context, focused group discussions, workshops with leaders and industry experts.
Competencies under FRAC:
- The FRAC will define three types of competencies:
- Behavioral competencies: that describe the values and strengths that help officials perform effectively, including attitudes like problem solving, decision making and networking.
- Functional competencies: involves application of skills and knowledge to perform effectively across domains and positions through project management, time management and communication.
- Domain competencies: like officials working at the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC) requiring competencies in indirect taxation, customs, and vigilance planning.
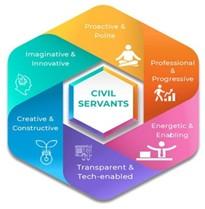
Intended Benefits:
- Accountability and Transparency in Governance
- Citizen-Centric Approach
- Preparing the Civil Servant for the future
- Bridging the gap between generalization and specialization
- Ensuring efficient service delivery
This exercise will be part of Mission Karmayogi- National Program for Civil Services Capacity Building (NPCCSCB) project.
Primary source: https://www.news18.com/news/india/centre-to-hire-leading-hr-firm-to-revamp-competency-of-bureaucracy-study-7-govt-depts-3793445.html
Picture source: https://www.quora.com/What-is-Mission-Karmayogi-How-will-it-reform-the-Indian-civil-services
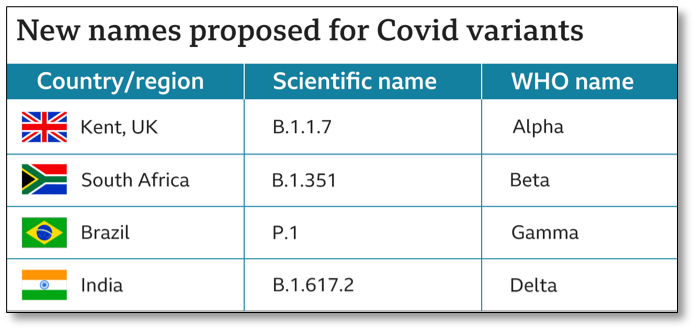
New naming system for variants of Covid-19
In News
The World Health Organization (WHO) has announced a new naming system for variants of Covid-19.
About the News
- WHO has assigned simple, easy to say and remember labels for key variants of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, using letters of the Greek alphabet. WHO will assign labels for those variants that are designated as Variants of Interest or Variants of Concern by WHO.
- These labels do not replace existing scientific names (e.g. those assigned by GISAID, Nextstrain and Pango), which convey important scientific information and will continue to be used in research.
- If more than 24 variants are officially identified, the system runs out of Greek letters, and a new naming programme will be announced.
- Significance: The scientific names can be difficult to speak and recall and are prone to misreporting. As a result, people often resort to calling variants by the places where they are detected, which is stigmatizing and discriminatory. To avoid this and to simplify public communications, WHO has encouraged national authorities, media outlets and others to adopt these new labels.
Naming Structure - SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern and Variants of Interest, as updated on 31 May 2021
- Variants of Concern
- Increase in transmissibility or detrimental change in COVID-19 epidemiology; or
- Increase in virulence or change in clinical disease presentation; or
- Decrease in effectiveness of public health and social measures or available diagnostics, vaccines, therapeutics.
- Variants of Interest
- Has been identified to cause community transmission/multiple COVID-19 cases/clusters, or has been detected in multiple countries, OR
- Is otherwise assessed to be a VOI by WHO in consultation with the WHO SARS-CoV-2 Virus Evolution Working Group.
Sources: https://www.who.int/en/activities/tracking-SARS-CoV-2-variants/
The Model Tenancy Act 2021
In News
The Union Cabinet has approved the Model Tenancy Act for circulation to all States / Union Territories for adaptation by way of enacting fresh legislation or amending existing rental laws suitably.
What is Model Tenancy Act (MTA)?
- The MTA aims to address factors like the need to have a formal rent agreement, how much security deposit should be paid, rate of rent increase, and grounds for eviction.
- This is called as ‘model act’, as land and urban development is a state subject and states will have the option to adopt or reject it.
- The Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs had floated the draft model tenancy law in July 2019.
Need of Model Tenancy Act
- Shortage of adequate housing: As per Census 2011, nearly 1.1 crore houses were lying vacant in the country and making these houses available on rent will complement the vision of ‘Housing for All’ by 2022.
- Trust deficit: Without a well-rounded rental policy and the proper implementation of rental contract, there is no sound mechanism to resolve tenant-landlord conflicts. Most owners do not want to give their property on rent, fearing that tenants will illegally occupy the property.
- Restricting nature of current rental laws: The existing rent control laws are restricting the growth of rental housing and discourage the owners from renting out their vacant houses.
- Unattractive rental yield: In India, the rental yield for residential property is quite low, even in bigger cities. It is in the range of 5% to 3% of the capital values. This has disincentivized people from investing in second or third homes which could be rented out.
- Poor Private participation in rental housing sector: There is need to promote private participation in rental housing as a business model for addressing the huge housing shortage.
- To address the migrant’s requirement of housing in urban space.
Salient features of the draft
- Rights and Obligations of Landlord and the tenant: MTA balances the interest and rights of both the owner and tenant in an accountable and transparent manner.
- A mandatory written agreement to be signed and the original tenancy agreement to be retained by landlord and tenant.
- Cap on the amount of security deposit: A maximum of two months of rent in case of residential premises and six months in case of non-residential premises. Currently, this amount differs from one city to another.
- Responsibilities of landlord and tenant: Unless otherwise agreed in the tenancy agreement, landlord will be responsible to repair structural damages and undertake measures like whitewashing walls and painting doors and windows. Tenant will be responsible for drain cleaning, switches and socket repairs, kitchen fixtures repair etc.
- The Act states that a landowner cannot enter the rented premises without 24-hour prior notice to carry out repairs or replacement.
- Landlord or property manager shall not withhold any essential supply or service in the premises occupied by the tenant.
- Vacating the premises: If a landlord has fulfilled all the conditions stated in the rent agreement and tenant fails to vacate the premises on the expiration of the period of tenancy or termination of tenancy, the landlord is entitled to double the monthly rent for two months and four times after that.
- Coverage: It seeks to cover both urban as well as rural areas.
- Independent Rent Authority: MTA also seeks to establish an independent authority in every state and Union Territory for registration of tenancy agreements. Rent Authority will also determine the revised rent in case of dispute.
- Rent Court and Rent Tribunal: To ensure speedy redressal of disputes, the rent authority, rent court and rent tribunal would fast track resolution of disputes within 60 days.
Significance of MTA
- Encourage growth of Rental Housing: Features like cap on security deposits and clear responsibilities of both the tenants and the landlords etc. will help in making rental housing a preferred option for different segments including migrant workers, professionals, and students.
- Unlocking of vacant houses for rental housing purposes: There is no monetary ceiling under the law, which enables parties to negotiate and execute the agreement on mutually agreed terms. It will give confidence to landlords to let out their vacant premises.
- Addresses problem of housing shortages: Growth of rental housing and unlocked vacant houses for rent will fuel the rental housing supply pipeline, and more rental housing stock will help people to find urban accommodation, especially in Covid-19 like exigencies.
- Formalization of rental segment: The mandatory registration of rent agreement with Rent Authority will bring this sector under formal ambit. This will help better regulation of rents. This will also help enhance the property tax as well as income tax on rental earning.
- Boost Private sector participation: Formal agreements and better grievance redressal mechanism is expected to give a fillip to private participation in rental housing as a business model for addressing the huge housing shortage. Rental housing brings a lucrative proposition for real estate investment trusts (REITs) and FDI.
- According to Realtors' body NAREDCO, if implemented by all states, MTA will promote rental housing in a big way, and it expects builders to construct at least 50% of its total inventories for rent purpose in the next five years.
Challenges ahead
- The Act is not binding on the states as land and urban development remain state subjects. Like in the case with The Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act (RERA), the fear is that states may choose not to follow guidelines, diluting the essence of the Model Act.
- MTA is prospectively applicable and will not affect the existing tenancies. The repeal of rent control acts can be governed by political exigencies. This may be a complicated process in cities like Mumbai, where tenants have occupied prime residential properties for absurdly low rents.
- The cap on the security deposit may not find favour with many landlords especially in big cities like Bengaluru as a two-month deposit may be insufficient to cover any damage to the property or compensate for defaulted rent payments.
- In the present form, MTA lacks provisions which can mitigate long drawn landlord–tenant litigations.
Conclusion
MTA is expected to facilitate the creation of adequate rental housing stock for all the income groups thereby addressing the issue of homelessness. Moreover, the MTA would also help in overhauling the legal framework with respect to rental housing, thereby enabling the institutionalization of rental housing and gradually shifting it towards the formal market. However, the federal challenge must be overcome in accommodative manner to achieve the target of Housing for All.
Question: Discuss the features of the Model Tenancy Act. List down the challenges in its execution and suggest measures to overcome them.
References
Primary
http://mohua.gov.in/upload/uploadfiles/files/Model-Tenancy-Act-English-02_06_2021.pdf
https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1723637
Secondary
This Day in History -Mountbatten Plan
On June 3, 1947, Lord Mountbatten, the last Viceroy of India, announced the Mountbatten Plan or June 3 plan or the Dickie Bird Plan. The June 3 plan announced that India would be splitting into two nations after its independence- India and Pakistan. The division came into effect on August 15, 1947. The plan included the principles of partition and gave autonomy and sovereignty to both India and Pakistan. It also gave the nations the right to form their own constitution. This plan was implemented through the Indian Independence Act 1947.

https://www.tribuneindia.com/news/archive/comment/plan-that-went-awry-416664
Image of the Day -Spacewalk
In this image, two Russian cosmonauts, members of the crew to the International Space Station (ISS), perform their first spacewalk to replace old batteries outside the International Space Station. Any time an astronaut gets out of a vehicle while in space, it is called a spacewalk. A spacewalk is also called an EVA. EVA stands for extravehicular activity. The first person to go on a spacewalk was Alexei Leonov, from Russia (1965). When astronauts go on spacewalks, they wear spacesuits to keep themselves safe. Astronauts put on their spacesuits several hours before a spacewalk. The suits are pressurized. This means that the suits are filled with oxygen. When on a spacewalk, astronauts use safety tethers to stay close to their spacecraft.

https://www.nasa.gov/audience/forstudents/k-4/stories/nasa-knows/what-is-a-spacewalk-k4.html
BIS SDO Recognition Scheme
- Context: Research Design & Standards Organization (RDSO)of Indian Railways has become the first institution to be declared a Standard Developing Organization (SDO) under One Nation One Standard mission of Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS).
- RDSO is the sole R&D Wing of the Ministry of Railways andis one of India’s leading standard formulating bodies undertaking standardization work for the railway sector.
- One Nation One Standard Mission- to make India a leader in setting global benchmarks, in bringing a national uniformity and standardization in all kinds of public procurement and tendering.
- To attain the One Nation One Standard vision of the Government of India, BIS launched a scheme which provides for Recognition of SDO.
- The recognition isvalid for 3 years and will require renewal after completion of the validity period.
Primary source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1723360
Variable Capital Company (VCC)
- Context: Krishnan panel on VCC submits report to International Financial Services Centres Authority.
- VCC is a new form of corporate structure for investment funds. It is an alternative to other ways of pooling funds through companies, unit trust and LLPs (Limited Liability Partnership). It can be set up as a standalone fund or an umbrella fund with multiple sub-funds.
- It helps in building the overall financial services ecosystem as it dispenses with some of the key limitations of the companies and Limited Liability Partnerships with higher regulatory standards. Thus, framework provides greater operational flexibility.
Primary source: https://www.ey.com/en_in/tax/india-tax-insights/variable-capital-companies-a-new-opportunity-for-asset-managers-and-lessons-for-india
International Nitrogen Initiative (INI)
- Context: Eighth Global Nitrogen Conference focuses on sustainable development goals.
- INI is an international program, set up in 2003 under sponsorship of the Scientific Committee on Problems of the Environment (SCOPE) and International Geosphere-Biosphere Program (IGBP).
- The key aims of INI are to:
- Optimize nitrogen’s beneficial role in sustainable food production
- Minimize nitrogen’s negative effects on human health and environment resulting from food and energy production.
- The program is currently a sustained partner of Future Earth.
Primary source: https://initrogen.org/content/about-ini#:~:text=The%20International%20Nitrogen%20Initiative%20(INI,%2DBiosphere%20Program%20(IGBP).
Public and Private Key in Public Key Infrastructure
Context: Security in tele-communication networks and authentication of users.
- Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is a technology for authenticating users and devices in the digital world. The idea is to have one or more trusted parties digitally sign documents certifying that a particular cryptographic key belongs to a particular user or device. The key can then be used as an identity for the user in digital networks.
- It is used to manage security through encryption using a pair of keys for this as:
- Public Key: This can be used by anyone as it is in open domain and seen as public pieces of data.
- Private Key: It is also known as the secret key which is used for digitally signing documents. Throughout the key lifecycle, secret keys must remain secret. It is commonly used in issuance and management of digital certificates.
Primary source: https://www.tutorialspoint.com/cryptography/public_key_infrastructure.htm
A far-reaching tax measure- TH
Essence: Editorial is presenting analysis on the proposal for a global minimum corporate tax, avenues for India & scope of international disagreements.
The U.S. has sought to impose a global minimum tax on foreign income earned by U.S. corporations. The proposal is perhaps intended to disincentivise American companies from inverting their structures due to the increase in the U.S. corporate tax rate. The proposal is similar to Pillar Two which was the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development’s (OECD) plan to plug the remaining Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS) issues. This caused pushback from countries such as Ireland, which made a case for fiscal autonomy for smaller jurisdictions to compete with larger economies. India has been part of the Pillar Two discussions and has not objected in principle to the proposal. The proposal, along with the increased tax bill for U.S. companies, may benefit the Indian revenue department.
Why you should read this article?
- To understand the purpose of global minimum corporate tax & how it can help in plugging the Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS) issues.
- To know the difference between US proposal & that of Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development’s (OECD).
- To understand possible benefits for India from global minimum corporate tax regime.
Article Link: https://www.thehindu.com/todays-paper/tp-opinion/a-far-reaching-tax-measure/article34712359.ece
Food safety during Pandemic- HBL
Essence- To enhance the benefit of package in response to COVID-19, the government has announced several schemes to maintain supply of food grains to states and union territories for distribution under the National Food Security Act (NFSA) and Targeted Public Distribution System (TPDS). In spite of instrumental role of TPDS more than 10 crore people have not been covered by the food safety net. So, the States/ UTs need to develop an inclusive NFSA/TPDS in association with the Central Government. To improve the NFSA coverage ratio and infuse inclusivity in TPDS we can integrated management of PDS through automation of operational fair price shops (FPS) or Aadhaar-seeding of ration cards helps deepen the portability of One Nation One Ration Card (ONORC) to reduce targeting (inclusion/exclusion) errors and improve other benefits. To mitigate deprivation of the poor and migrant labourers during the pandemic following measures can be taken, one: The Food and Civil Supplies Department should keep a vigil on the functioning of FPSs; second, data governance should be put in place to increase transparency and accountability of TPDS; third, States and UTs should allocate food grains to those who are excluded from the TPDS by means of food coupons, etc.; fourth the community kitchen concept, etc.
Why you should read this article?
- To get an overview of efficacy of NFSA and TPDS during this time of pandemic.
- To understand the issues related and what could be the possible solution to cover more people under food safety net.
Article Link: https://www.thehindubusinessline.com/opinion/food-safety-during-pandemic/article34683498.ece
Vermicomposting brings better yield and returns- A small farmer shows the way
Background:
- This is the case of a small farmer who chose to be different from the typical resource-poor farmers struggling to make a living in the degraded drylands.
- ‘Nursery Chandranna’ and ‘Vermicompost Chandranna’ is the new tag with the farmers in Karnataka named after the Chandranna, a young farmer.
- The farmers now earn more than Rs. 1 lakhs from the sale of vermicompost and earthworms in three years far exceeding the average income of small farmer
Brief Background of his village:
- Village has 15% dryland and 3.5% is under bore well irrigation.
- 5% is common land that includes wasteland, common grazing land and the ‘reserve forest’ where only shrubs and bushes are seen.
- The terrain, in general, has shallow red sandy soils. With boulders scattered all over, it is not an ideal village for remunerative farming.
The triggering point:
- In 2000, Chandranna raised a nursery of 15,000 seedlings.
- His nursery was rated the best in the watershed project in 2003
- Chandranna became popular as ‘Nursery Chandranna’. The project has become a source of hope for small famers to increase their income in drylands
Where can we use this case study:
- Importance of SHG and vision of change agent, how to improve agricultural income for small and marginalised farmers, innovative practices under agriculture, vermicompost, conservation agriculture.
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.