The advent of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, often referred to as the Digital Revolution, has ushered in a transformative era marked by unprecedented technological advancements. Within this landscape, e-Governance has emerged as an integral and indispensable component of government operations. This paradigm shift is characterized by the extensive integration of digital technologies, data analytics, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT) into the traditional frameworks of governance. Governments worldwide are increasingly leveraging these technological tools to streamline processes, enhance service delivery, and promote transparency. The digitalization of governance not only facilitates more efficient administration but also fosters citizen engagement and participation. By embracing e-Governance, authorities can harness the power of information technology to optimize decision-making processes, bridge the gap between the government and the public, and create a more responsive and citizen-centric model of governance for the challenges of the 21st century. The evolution towards e-Governance underscores the imperative for governments to adapt to the dynamic digital landscape and harness the potential of technology for the betterment of society.
UPSC Mains General Studies Paper – 2 Mains 2020
Important aspects of governance, transparency and accountability, e-governance applications, models, successes, limitations, and potential; citizens charters, transparency & accountability and institutional and other measures
UPSC Mains Civil Services IAS Exam Question Paper – 2020
Contents
- 1 Structure of the Question
- 2 Answer
- 3 Conclusion
- 4 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 4.1 1. What is the Fourth Industrial Revolution, and how has it contributed to the emergence of e-Governance?
- 4.2 2. How does e-Governance differ from traditional governance, and what benefits does it offer in the context of the Fourth Industrial Revolution?
- 4.3 3. What technologies are driving the integration of e-Governance in the Fourth Industrial Revolution?
- 4.4 4. How does e-Governance enhance citizen engagement and participation in the Fourth Industrial Revolution?
- 4.5 5. What challenges does the integration of e-Governance face in the era of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, and how can they be addressed?
Structure of the Question
- In Introduction,
- Discuss the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
- In Body,
- Impact of Fourth Industrial Revolution on Governance.
- e-Governance and its examples.
- In Conclusion,
- Importance of the Fourth Industrial Revolution in strengthening governance.
Answer
Introduction
Millions of algorithms and codes are there around humans to understand their commands and perform human-like tasks. The First Industrial Revolution used water and steam power to mechanize production. The Second Industrial Revolution used electric power to create mass production. The Third Industrial Revolution used electronics and information technology to automate production. Now the Fourth Industrial Revolution is characterized by a fusion of technologies in AI (Artificial Intelligence), IoT(Internet of Things), quantum computing, and others.
Fourth Industrial Revolution and its impact on governance
Better Policy measures
Newer technologies such as Big Data, Data Analytics, Data Mining etc., have the ability for better identification of important aspects from a large dataset. This could be helpful for policymakers to make clear distinctions for the usefulness of data and ensure better policy measures.
Faster Resolution of Grievances
Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies have helped in bringing new grievance resolution techniques to the table, such as bots. This has led to increased efficiency in reducing public issues.
Transparency
Technology growth has created new opportunities for ensuring transparency in governance. This includes monitoring misgovernance issues such as corruption or favoritism.
Efficiency and better delivery of services
Initiatives like PM Gatishakti National Master Plan, which aims at developing our infrastructure smarter, Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC), which aims at democratizing E-commerce, and GeM which has made a significant impact on government procurement – all these are leveraging AI to bring efficiency and better delivery of services.
Logistics ecosystem Improvement
The government is using AI to redefine the way it works such as the Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP), which is leveraging AI to improve the entire logistics ecosystem of the country.
e-Governance
e-Governance can be defined as the application of information and communication technology (ICT) for providing government services, exchange of information, transactions, and integration of previously existing services and information portals. Mumbai Declaration on e-Governance has a ten-fold goal to take forward the roadmap for e-Governance defined in the Shillong Declaration of 2019, which focuses on improving public service delivery, and exhausting digital platforms, particularly concerning health, agriculture, education, and land.
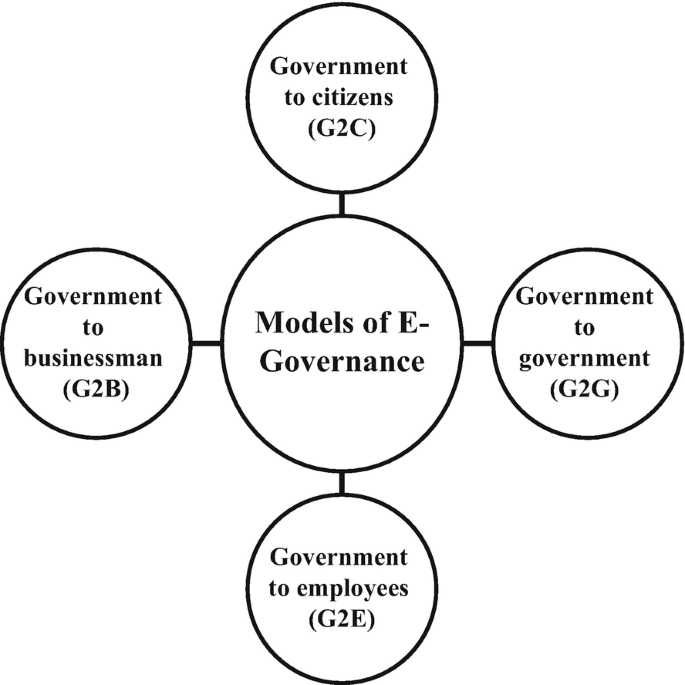
Examples of harnessing e-Governance
Digital India
Through technological improvement and the Digital Revolution, easier access to government services has been ensured. Technologies such as cloud computing have improved connectivity which has been helpful in dealing with connectivity issues of digital governance.
UMANG (Unified Mobile Application for New-age Governance)
It is developed by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) and the National e-Governance Division (NeGD) to drive Mobile Governance in India. It provides a single platform for Citizens to access pan India e-Gov services ranging from Central to Local Government bodies.
DBT(Direct Benefit Transfer)
Under this initiative, the scholarships and subsidies are directly credited in the bank account of the beneficiary which helps to ensure targeted delivery of benefits and also reduces the instances of corruption in the system.
BharatNet
This initiative facilitates the delivery of e-governance, e-health, e-education, e-banking, Internet, and other services to rural India. The aim is to connect all the 2,50,000 Gram panchayats in the country and provide 100 Mbps connectivity to all gram panchayats. To achieve this target, the existing unused fibers (dark fiber) of public sector undertakings (PSUs) (BSNL, RailTel and Power Grid) have been taken advantage of and incremental fiber has been laid to connect to the Gram Panchayats wherever necessary.

Conclusion
The fourth industrial revolution has a lot of potential to harness the converging technologies to create an inclusive, human-centered future. It presents the opportunity to help everyone including the people and the government policy makers. Initiatives like PM Gatishakti National Master Plan, which aims at developing our infrastructure smarter, Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC), which aims at democratizing E-commerce, and GeM which has made a significant impact on government procurement – all these are leveraging AI to bring efficiency and better delivery of services.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the Fourth Industrial Revolution, and how has it contributed to the emergence of e-Governance?
The Fourth Industrial Revolution, characterized by the integration of digital technologies into various aspects of society, has played a pivotal role in the rise of e-Governance. This FAQ explores the key features of the Fourth Industrial Revolution and its influence on transforming traditional government processes into digital counterparts.
2. How does e-Governance differ from traditional governance, and what benefits does it offer in the context of the Fourth Industrial Revolution?
This question delves into the distinctions between conventional governance methods and e-Governance, highlighting the advantages that the latter brings in the era of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. It touches upon efficiency, accessibility, and transparency as some of the key benefits associated with the digital transformation of governmental functions.
3. What technologies are driving the integration of e-Governance in the Fourth Industrial Revolution?
Here, the focus is on the technological enablers that have propelled the adoption of e-Governance in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. Topics may include artificial intelligence, blockchain, Internet of Things (IoT), and data analytics, shedding light on how these technologies are reshaping the landscape of governance.
4. How does e-Governance enhance citizen engagement and participation in the Fourth Industrial Revolution?
This question explores the impact of e-Governance on citizen involvement in decision-making processes. It discusses how digital platforms and tools facilitate greater interaction between the government and citizens, fostering a more participatory and responsive governance model in the context of the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
5. What challenges does the integration of e-Governance face in the era of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, and how can they be addressed?
Addressing the potential obstacles and challenges is crucial for understanding the comprehensive implications of e-Governance in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. This FAQ explores issues such as cybersecurity concerns, digital literacy gaps, and the need for robust infrastructure, while also providing insights into strategies for overcoming these challenges.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here
Visit our YouTube Channel – here



