Monday, 31st May 2021
UGC’s Proposal for ‘Blended Teaching’
In News
UGC has recommended to adopt Blended Online, Offline Education and is seeking suggestions from people.
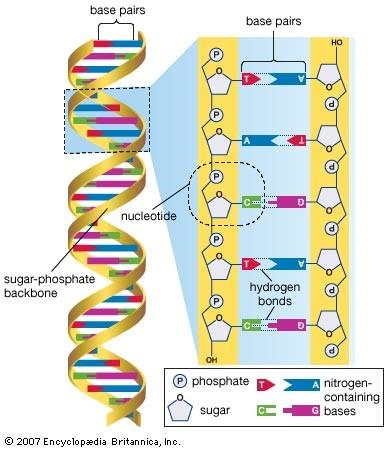
About the News
- Definition: Blended Learning (BL) is not a mere mix of online and face-to-face mode, but it refers to a well-planned combination of meaningful activities in both the modes.
- Through BL, UGC aims to achieve:
- Increased student engagement in learning and enhanced teacher and student interaction.
- Responsibility for learning, time management and flexibility
- Improved student learning outcomes and enhanced institutional reputation.
- More flexible teaching and learning environment amenable for self and continuous learning through better opportunities for experiential learning
- Evaluation pattern: Summative evaluation strategies including open book examination, group examinations even for conventional theory papers, spoken examinations, on-demand examinations have been recommended besides formative evaluation strategies like ePortfolio, creative products, classroom or online quizzes.
- Online Exams: UGC has suggested use of AI as technology for assessments like, attention levels, speed of learning, level of learning etc. Hence, new tools could be experimented with, for examinations and assessments.
Areas of concern that have been raised
- Increasing the Digital divide: Hundreds of students, especially those belonging to economically and socially backward communities are yet to get access to digital education in this pandemic period and blended learning will further divide the digital gap.
- Diminishing the role of Campus interactions: College campuses provide opportunity for dialogue. By interacting with students and colleagues, one learns to think as thinking does not happen in isolation. To reduce the role of the universities to merely enabling the transaction of a pre-cooked syllabi is to ignore their larger and more important purpose in all societies.
Sources: https://www.ugc.ac.in/pdfnews/6100340_Concept-Note-Blended-Mode-of-Teaching-and-Learning.pdf
https://indianexpress.com/article/opinion/columns/ugc-online-classes-blended-teaching-covid-7334748/
Semiconductor Chips Shortage in Vehicle Manufacturing
In News: A protracted shortage of semiconductor chips has made India-based car manufactures and premium bike makers curtail production across categories.
Why did the chip famine occur?
- Chip shortage is measured in chip lead time, which is the gap between when a chip is ordered and when it is delivered.
- The trigger point of the chip shortage was the beginning of the Covid-19 pandemicand the subsequent lockdowns across the world that forced shut crucial chip-making facilities in countries including Japan, South Korea, China, and the US.
- This was coupled with a 13% increase in global demand for PCs owing to some countries’ shift to a stay-at-home economy.
- The shortagein availability of key chips necessary for manufacturing of a broad range of electronics and the consequent cascading effects creating pent-up demand is the cause for the follow-up famine.
- Another reason for its shortage is the increased consumption. The number of transistorsmounted in IC chips has been doubling every two years. Electronic parts and components today account for 40% of the cost of a new internal combustion engine car, up from less than 20% two decades ago.
![]()
Impact of the chip famine:
- Reduced Supply: Consumers of semiconductor chips, which are mainly car manufacturers and consumer electronics manufactures, have not been receiving enough of this critical input to continue production.
- Reduced Production of Automobiles:With just-in-time deliveries, carmakers typically kept low inventory holdings and relied on an electronics industry supply chain to feed production lines as per demand.
- Delayed Supply and Reduced Features:It has caused delay in vehicle deliveries, with companies starting to discard features and high-end electronic capabilities on a temporary basis to deal with the chip shortage.
- Japanese carmaker Nissan is said to be leaving navigation systems out of its vehicles, while French company Renault has stopped offering a larger digital screen behind the steering wheel on several SUVs.
Way forward:
- The current slump in the automobile industry though temporary, can be fully addressed only by economic recovery.
- This is possible only when there is an active response in fighting the pandemicvia vaccination drives that will provide the necessary trigger to lift lockdowns and enhance economic growth.
Primary source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-the-semiconductor-chips-shortage-and-how-carmakers-are-coping-7327321/
NASA Joins Hands With ISRO To Develop Earth Observatory
In News
A new earth observatory system is being developed by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) aided by radar systems from the Indian Space & Research Organisation (ISRO).
More details
- NASA will design a new set of Earth-focused missions to provide key information to guide efforts related to climate change, disaster mitigation, fighting forest fires, and improving real-time agricultural processes.
- ISRO will provide two radar systems that can measure changes in Earth’s surface less than a half-inch. This capability will be utilized in one of the observatory’s first missions intended as a pathfinder, called NISAR (NASA-ISRO synthetic aperture radar).
- As part of the Earth System Observatory, each satellite will be designed uniquely to work together and create a 3D, holistic view of Earth, from bedrock to atmosphere.
Areas of focus for the observatory include
- Aerosols: Answering the critical question of how aerosols affect the global energy balance, a key source of uncertainty in predicting climate change.
- Cloud, Convection, and Precipitation: Tackling the largest sources of uncertainty in future projections of climate change, air quality forecasting, and prediction of severe weather.
- Mass Change: Providing drought assessment and forecasting, associated planning for water use for agriculture, as well as supporting natural hazard response.
- Surface Biology and Geology: Understanding climate changes that impact food and agriculture, habitation, and natural resources, by answering open questions about the fluxes of carbon, water, nutrients, and energy within and between ecosystems and the atmosphere, the ocean, and the Earth.
- Surface Deformation and Change: Quantifying models of sea-level and landscape change driven by climate change, hazard forecasts, and disaster impact assessments, including dynamics of earthquakes, volcanoes, landslides, glaciers, groundwater, and Earth’s interior.
Significance of the mission
- This mission will measure some of the planet’s most complex processes such as ice-sheet collapse and natural hazards such as earthquakes, volcanoes, and landslides.
- NISAR can assist planners and decision makers with managing both hazards and natural resources in the future.
Weaning Farmers Away From Paddy
In News
The Haryana government aims to wean farmers away from the water-guzzling paddy on two lakh acres this year.
About the News
- Under the ‘mera pani-meri virasat’ scheme the Haryana government aims to provide an incentive of Rs 7,000 per acre to farmers who opt for pulses, cotton, maize and horticulture crops in place of paddy.
- With the aim to make horticulture risk-free, the state government will also offer an insurance cover ranging from Rs 30,000 to Rs 40,000 per acre to farmers who choose to replace paddy with vegetables and fruits for a small premium. The government is also developing fruit clusters in different parts of the state to provide better marketing to the farmers.
- Farmers will also be encouraged to cultivate pulses such as moong, moth bean and urad considering the remunerative prices these items command in the market. To this end, the agriculture department will provide seeds at cheaper rates, especially to farmers of southern Haryana besides helping them in procurement of their produce.
Need for a policy like ‘mera pani-meri virasat’:
- Depleting Water levels: Paddy requires far more water than other crops and this leads to indiscriminate extraction of groundwater. Ideally, groundwater should be available at a depth of 50 ft to 60 ft, but in Punjab, its level has significantly dropped to 150ft to 200 ft in most places.
- Extraction is much more than the recharge of water table. The water table is depleting 0.33 meters every year.
- Deteriorating quality of groundwater: Due to an increased use of fertilisers and pesticides, around 50 per cent of the total geographical area of these states is severely affected with the problems of soil erosion, alkalinity, salinity and water logging.
- Problems with Monoculture: Decreased crop and genetic diversity leads to increase in vulnerability of crops to pest and disease attacks.
- Also, wheat and paddy cannot fix nitrogen from the atmosphere, unlike pulses and legumes. Their continuous cultivation sans any crop rotation, leading to depletion of soil nutrients and growing dependence on chemical fertilisers and pesticides.
- Water intensive crop in water deficit states: Paddy being a warm season crop is not very sensitive to high temperature stress. It can be grown in much of eastern, central and southern India, where water is sufficiently available. Probably half of the rice produce of Punjab can, instead, be procured from eastern Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal or Assam.
- Financially unviable future: The loss of growth momentum in the income from the agriculture sector, which has fallen to 1% in Haryana and 0.6% in Punjab after 2011-12. The prospects of further growth in agricultural income from rice and wheat are quite dim.
Reasons behind farmers still persisting with paddy:
- The Contract system: More than half of the land in Haryana is cultivated under contract system under which landless labourers or farmers with small parcels of land take more land on cultivation for an annual rent (theka) ranging from Rs 10,000 to Rs 70,000 for an acre depending on its location and irrigation facilities.
- So, the cultivator who takes the land on rent for only a year aims to squeeze the maximum profit out of it by cultivating crops like paddy and wheat.
- Other crops not as lucrative as wheat and paddy: Government agencies purchase rice and wheat (during rabi season) at the minimum support price (MSP), which assures the farmers of a remunerative return. But in the case of other crops, similar assurance is absent.
- Free electricity: Policy of providing free electricity to farmers along with the Central government’s favourable attitude towards paddy cultivation, are the key factors that have motivated farmers to persist with paddy.
- Ease of Established mechanisms: Farmers have enough equipment for cultivating wheat and paddy. It requires less effort now but horticulture, floriculture, and cultivation of vegetables, oil seeds, pulses require labour, which is scarce and quite costly in this region.
What further can be done to aid the farmers make this switch?
- Attractive procurement mechanism: As the switch to new systems is a difficult, adequate compensation becomes the key in this situation. A remunerative MSP and an assured marketing system for alternative crops such as maize, soya bean, cotton and sugarcane to give a fillip to the farm diversification programme in the state. Farmers’ groups and farmer producer organisations can play a significant role in the direct marketing of their produce.
- Differential incentive: This will act as a hand holding mechanism for these people, as switching crops makes them even more vulnerable for different farm categories, including small and marginal farmers, women farmers and those from weaker sections.
- Better management of electricity subsidies: New electric connections need to be restricted to the first-time applicants and small or marginal farmers and an undertaking can be introduced to grow paddy for certain length of time (5-10 years) only. This mechanism disincentivizes the indiscriminate use of pumps for water guzzling crops like paddy.
Conclusion
The traditional Green Revolution States of Punjab and Haryana may need to shed “business as usual” approach and embrace an innovative development strategy in agriculture and non-agriculture to secure and improve the future of farming and rural youth. The solution to the ecological and economic challenges facing agriculture in the traditional Green Revolution States lie in shifting to high value crops and in the promotion of non-farm activities.
Question: Analyze the reasons behind water crisis in farm sector in green revolution 1 states. Highlight the solutions for such emerging problems.
https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/punjab-farmer-protests-paddy-wheat-farm-laws-7106605/
https://ruralmarketing.in/stories/green-revolution-in-haryana-facing-fallout/
This Day in History - Ahilyabai Holkar
On May 31, 1725, Ahilyabai Holkar was born in the village of Chaundi, in the present-day Ahmednagar district in Maharashtra. Her father, Mankoji Rao Shinde, taught her to read and write, during the time in history when women did not go to school. Maharani Ahilyabai Holkar was the Holkar Queen of the Maratha Malwa kingdom, India. As a queen, she tried to protect her kingdom from plundering invaders and personally led armies into battle. Rani Ahilyabai was a great pioneer and builder of Hindu temples. She built hundreds of temples and dharmashalas throughout India. From a tiny village to a flourishing city, Indore prospered during her 30-year rule.

https://www.myindiamyglory.com/2017/05/31/ahilyabai-holkar-warrior-renovator-temples/
Image of the Day - Suryakiran
This is the image of the Suryakiran aerobatic display team of the Indian Air Force (IAF). The word Suryakiran means ‘rays of the sun’ in Sanskrit. This team was raised in May 27, 1996, at the IAF air base in Bidar, Karnataka, with six Kiran MkII trainer aircraft. It is one of the few aircraft display teams in the world and the only one in Asia. The team has carried out over 600 displays across the country and south- east Asia. All the pilots of the Suryakiran team are qualified flying instructors and belong to the fighter stream of the IAF, selected through a rigorous selection process at a ratio usually around 1:10. The Suryakiran team conducts its display to motivate young students to take up a career in the armed forces and to reassure the citizens of the superior flying skills and discipline of the nation’s air warriors.

Anti-Dumping
- Context: The Finance Ministry has extended by six months, the validity of existing anti-dumping duty on inert gas R-134a imports from China.
- R-134a (tetrafluoroethane) is a hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) which is primarily used as a high temperature refrigerant in domestic refrigeration and automobile industry.
- Anti- Dumping duty is a protectionist tariff that the domestic government imposes on imports manufactured in foreign countries that are priced below the fair market value of similar goods in exporting country’s domestic market.
- Dumping is a process wherein a company exports a product at a price that is significantly lower than the price it normally charges in its home (domestic) market.
- While the intention of anti-dumping duties is to save domestic manufacturing and employment, these tariffs can lead to higher prices for domestic consumers.
- And, in the long-term, anti-dumping duties can reduce the international competition of domestic companies producing similar goods.

Primary source: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/a/anti-dumping-duty.
Picture source: https://www.agc-chemicals.com/jp/en/products/detail/index.html?pCode=JP-EN-G006
Vinayak Damodar Savarkar
- Context: his birth anniversary.
- Also known as Swatantryaveer Savarkar, Veer Savarkar was born in 1883 in Bhagur, Nasik, Maharashtra.
- He was an Indian independence activist, politician, lawyer, writer, and leading figure in the Hindu Mahasabha who formulated the Hindu nationalist philosophy of Hindutva.
- He founded Abhinav Bharat secret society in 1904 and was later arrested in 1909on charges of plotting an armed revolt against the Morley-Minto reform and in 1910 for his connections with the revolutionary group India House. The 50-years’ imprisonment (Kala Pani) led him to Cellular Jail in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands in 1911 for detention for life.
- He died in 1966 afterrenouncing medicines, food, and water which he termed as atmaarpan (fast until death).

Primary source: https://www.britannica.com/biography/Vinayak-Damodar-Savarkar
Picture source: https://www.telegraphindia.com/india/hindutva-is-not-the-same-as-hinduism-said-savarkar/cid/1699550
National AI Portal
- Context: https://indiaai.gov.in- first anniversary.
- It serves as a central hub for AI related news, learning, articles, events, and activities etc., in India and beyond. The website aims to be the trusted content powerhouse in the backdrop of India’s journey to global prominence in Artificial Intelligence.
- The portal focuses on creating and nurturing a unified AI ecosystem for driving excellence and leadership in India’s AI journey, to foster economic growth and improve lives through it.
- The portal intends to showcase AI initiatives from the public sector and constantly strive to remain as the top choice for AI-related knowledge repository amongst the AI community.
- The National AI Portalis a joint initiative by Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY), National e-Governance Division (NeGD) and NASSCOM.

Primary source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1722559
Picture source: https://thenfapost.com/2021/05/29/meity-owned-national-ai-portal-indiaai-celebrates-first-anniversary/
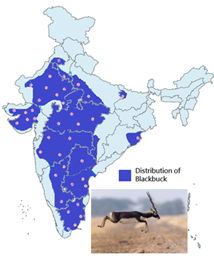
Blackbuck - Edukemy Current Affairs
- Context: Odisha's blackbuck population has doubledin the last six years.
- The Blackbuck (Antilope cervicapra), or the Indian Antelope, is a species of antelope native to India and Nepal. It has been declared as the state animalof Punjab, Haryana, and Andhra Pradesh.
- It is found in grasslands and is one of the fastest land animals after Cheetah.
- Its skin and horns are regarded as sacred
- It is protected under Schedule I of Wildlife Protection Act and Appendix III of CITES. It is categorized as Least Concern in the IUCN Red List. Habitat fragmentation, deforestation, natural calamities, illegal hunting are the threats faced by the antelope.
Primary source: https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/wildlife-biodiversity/odisha-s-blackbucks-double-in-6-years-reveals-census-77138
The priority sector lending India needs- HT
Essence: The origins of priority sector (PS) lending can be traced back to 1966 when Morarji Desai saw a need for increasing credit to agriculture and small industries. The PS definition grew over time, and was not just limited to important lobby groups, but extended to cover important neglected sectors of the economy. But despite the tweaks, the classification retains a heavy focus on agriculture and small industries (defined as micro, small and medium enterprises or MSME) till today. In this context, the article analyses the need to revisit priority sector lending formulations.
Why you should read this article?
- Identify the priority sectors and the limits for lending therein.
- Understand why the norms and sectors under priority sectors lending need to be revised
- Assess whether priority sector lending is the right form of intervention for some of its targeted categories.
Article Link: https://www.hindustantimes.com/opinion/the-priority-sector-lending-india-needs-101622376883593.html
India’s dairy sector is in crisis. Government must do more to help- IE
Essence- Out of India’s farm-dependent population, 70 million are those who are involved in dairying and livestock which alone contributed 28% in Gross Value Added (GVA) from agriculture (2019-20). This sector provides a great support to farmers, especially during crop failures. But Indian milk producers are highly susceptible to even minor shocks as seen in the second wave of COVID-19 pandemic. Reason being, sector is unorganised and there is no official and periodical estimate of the cost of production and Minimum Support Price for milk. During the pandemic, farmers were forced to sell the entire produce to dairy cooperatives at a much lower price causing livelihood crisis to milk producers. Following steps could help the dairy sector: a stable market and remunerative price; uninterrupted supply of fodder and cattle feed at a reasonable price; and regular supply of veterinary services and medicines.
Why you should read this article?
- To get an overview of India’s dairy sector and why dairy cooperatives are less preferred by the milk producers.
- What possible steps should be taken to further improve the condition of dairy sector and dairy farmers as well.
Article Link: https://indianexpress.com/article/opinion/columns/indias-dairy-sector-is-in-crisis-government-must-do-more-to-help-7333340/
Tribal Traditions in India: The Siddi Tribe of Gujarat
...the lost gems of ancient Africa, hidden away in India.

About the Siddi Tribe:
- They live deep in Gujarat, hidden in the quaint Sirvan village and are known as one of the most unusual tribal communities in India.
- Their origins can be traced back to Africa.
- Some legends mention that this community was brought to India as slaves by the Portuguese for the Nawab of Junagadh.
- In present day, siddis do not retain much of their African heritage, neither language nor history.
- However, they perform Dhamal dance.
- Siddis are guardians of a rich and unique musical tradition that is a truly hidden jewel of Indian indigenous culture.
What can we learn from this case study?
- Respecting the tribal traditions, knowledge of the tribal traditions.
- Know the tribe and the state
Where can we use this case study?
- While answer rich tribal traditions, origin of the tribe, tribal art questions
Source: https://www.soulveda.com/conversations/siddis-the-story-of-a-lost-tribe/
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.


.gif)