Wednesday, 26th May 2021
WHO launches global facility for pathogen storage, sharing and analysis
In News
The World Health Organization (WHO) and the Swiss Confederation signed a Memorandum of Understanding to launch the first WHO BioHub Facility as part of the WHO BioHub System.
About the News
- WHO BioHub Facility: The facility will serve as a centre for the safe receipt, sequencing, storage and preparation of biological materials for distribution to other laboratories, in order to inform risk assessments, and sustain global preparedness against these pathogens.
- This facility will enhance the rapid sharing of viruses and other pathogens between laboratories and partners globally.
- Switzerland will make available to the WHO the Spiez Biocontainment Laboratory External link as a repository for Sars-CoV-2 viruses or other pathogens with epidemic or pandemic potential.
- The BioHub System: In parallel, WHO will broaden its BioHub System for the use of biological materials by qualified entities, such as manufacturers, for the development of medical by-products for fair allocation to countries.
- Pilot project: WHO is currently running a pilot phase, using SARS-COV-2 and its variants, to test the feasibility and operational arrangements for sharing such materials with the facilities of the BioHub System.
- Following results from the pilot project, the BioHub will expand from SARS-COV-2 and its variants, to other pathogens, and connect partners with other repositories and laboratory networks in 2022.
Significance
- Currently, most pathogen sharing is done bilaterally between countries and on an ad hoc basis. This process can be slow, and leave some countries without access to the benefits and tools.
- The BioHub will enable Member States to share biological materials with and via the BioHub under pre-agreed conditions, including biosafety, biosecurity, and other applicable regulations. This will ensure timeliness and predictability in response activities.
- In the current times, close international collaboration to ensure the timely sharing of epidemiological and clinical data as well as biological materials is of utmost importance, as no country is capable of dealing with such a crisis alone.
- A system like BioHub can be a success only through continuous transparent sharing of data by countries. Only then knowledge of new diseases, their origins, their spread and cure can be derived. This is important in the backdrop of India’s leading scientists claiming that epidemiological data is not being systematically collected and released and also data collected by ICMR is inaccessible.
National Database for Unorganised Workers (NDUW)
In News
The Supreme Court has directed the Centre to file reply on position of National Database for Unorganised Workers (NDUW) in Suo Moto Migrant Workers Case.
About the News
- National database: The Supreme Court has asked the Centre and states to come out with a national database for unorganised workers to enable them to avail various benefits like dry ration, under the AtmaNirbhar scheme or any other scheme is found suitable by the States/Centre. The bench directed the Union, and state governments of Delhi, Haryana and UP, to provide income support, transportation and food rations without local ID cards.
- In the absence of such data the welfare measures do not percolate to them, especially during the present Covid-19 crisis.
- Monitoring mechanism: The court has also asked for a suitable mechanism to monitor and supervise whether the benefits of the welfare schemes reach the beneficiaries.
The National Database of Unorganised Workers’ (NDUW)
- The Ministry of Labour& Employment has proposed to develop National Database of Unorganized Workers (NDUW), which will be a comprehensive database of the unorganized workers and migrant workers, seeded with Aadhaar.
- It will have details of name, occupation, address, occupation type, educational qualification, skill types and family details etc. for optimum realization of their employability and extend the benefits of the social security schemes to them. Also, the movement of labour can be tracked in a situation like a Covid-induced lockdown.
- Workers will be encouraged to enrol on the website. Common Service Centre can be used in this process.
Why is the Database needed?
- The Code on Occupational Health, Safety and Working Conditions enables the provision for maintaining a database of migrant workers to help in targeting, skill mapping and utilising government schemes effectively. The Code ensures that migrant workers get journey allowance once a year from employers to visit their home towns.
- Migrant workers keep moving from one place to another place in search of work and such workforce also keeps shifting from one sector to another depending upon the opportunities (such as more wages, duration, and continuity of work), hence, it is not easy to keep record/data of migrant labour workforce.
Sources: https://thewire.in/labour/migrant-workers-covid-19-universal-pds-food-subsidies
https://www.hindustantimes.com/india-news
National Mission on use of biomass in thermal power plants
In News
Ministry of Power has decided to set up a National Mission on use of Biomass in coal based thermal power plants.
About the Mission
- The Mission would have a Steering Committee headed by Secretary (Power) comprising of all stakeholders including representatives from Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas (MoPNG), Ministry of New & Renewable Energy (MNRE) etc.
- It will have 5 subgroups to take care of various areas such as - research on properties/ characteristics of biomass, for resolving the issues of supply chain, testing of Agro-based biomass pellets and Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) pellets etc.
- NTPC will play a larger role in providing logistic and infrastructure support in the proposed National Mission.
- The duration of proposed National Mission would be a minimum 5 years.
.gif)
Objectives of the Mission
- To increase the level of co-firing from present 5% to higher levels to have a larger share of carbon neutral power generation from the thermal power plants.
- To take up R&D activity in boiler design to handle the higher amount of silica, alkalis in the biomass pellets.
- To facilitate overcoming the constraints in supply chain of biomass pellets and agro- residue and its transport upto to the power plants.
- To consider regulatory issues in biomass co-firing.
Intended Significance of the Mission
- It will help to address the issue of air pollution due to farm stubble burning and to reduce carbon footprints of thermal power generation.
- This would further support the energy transition in the country and targets to move towards cleaner energy sources.
- The proposed National Mission will also contribute to the National Clean Air Programme (NCAP).
Other activities to promote biomass use in thermal power plants
- Ministry of Power has issued the "Policy for Biomass Utilization for Power Generation through Co-firing in Pulverized Coal Fired Boilers" wherein a target is set to use 5-10% blend of biomass pellets made, primarily of agro residue along with coal.
- In 2019, the MNRE has stated that the power generated from the co-firing of biomass in thermal power plants is renewable energy and is eligible for meeting the non-solar renewable purchase obligations.
|
Extra information · Biomass is renewable organic material that comes from plants and animals. Examples are wood, energy crops and waste from forests, yards, or farms. · According to the study by the International Energy Agency’s Clean Coal Centre (IEACCC), Coal-based thermal power stations with no pollution control technology are responsible for over half sulphur dioxide (SO2), 30% oxides of nitrogen (NOx), about 20% particulate matter (PM), among other man-made emissions in the country. |
Reference
Primary : https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1721473
Secondary
http://www.cercind.gov.in/2019/orders/12.pdf
Integrated Law Enforcement Centres
In News
The Bureau of Police Research and Development (BPRD) has recommended that India should have Integrated Law Enforcement Centres (ILECs) on all its borders to deal with cross-border crimes.
Cross-border and trans-national crimes on Indian borders
- The core threats include:
- Militancy/low intensity conflict – proxy war
- Trafficking in narcotics and Fake Indian Currency Notes (FICN)for funding covert operations
- Territorial disputes in J&K, Sir Creek and Arunachal Pradesh
- Frequent violation of ceasefire on Line of Control and other parts of J&K,
- Human trafficking, including illegal immigration
- Also, the nature of threats varies across different borders. For instance, cattle smuggling, smuggling of FICN and illegal infiltration are prominent crimes on India-Bangladesh borders whereas drug trafficking, sniper attacks and terrorist infiltration are common on India-Pakistan borders.
Issues with Current Border Security Mechanism
- There are different agencies (e.g., border guarding forces like BSF on Bangladesh border, ITBP on China border, Bureau of Immigration (BOI) to control illegal movement of people across the borders, Coast Guard and Navy on coastal borders) operating within the silos of their specific mandate with lesser degree of inter-agencies cooperation, coordination, and complementarity.
- Many a time, inter agencies competition leads to sub-optimal outcome at national level.
- There are instances of both gaps as well as overlapping in the role, jurisdiction and working of the agencies. E.g., BSF and Indian Army on some part of border with Pakistan.
- Law and Order being State Subject, local Police has a responsibility to investigate further after a crime is detected. Police often lack the expertise and personnel in such transnational crimes.
- In the matter of border management of India, security ambivalence and lack of strategic thinking is seen in:
- Absence of policy to check infiltration / illegal migration from eastern borders
- Inability to stop or contain cross-border terrorism; and
- Absence of an integrated approach to tackle, trafficking / smuggling in drugs, FICN, cattle, humans and other contrabands across international boundary.
Hence, there is a clear and urgent need for an institutional arrangement like Integrated Law Enforcement Centres (ILECs) under the Integrated Border Management approach, which has inter-disciplinary/ departmental jurisdiction and spans over the entire borders of the country dealing with trans-border related crimes.
About Integrated Law Enforcement Centres (ILECs)
BPRD recommends following with regard to ILECs -
- India should have ILECs on all its borders on the lines of the United States’ Department of Homeland Security and the European Union’s Frontex to deal with cross-border crimes including infiltration, terrorism, smuggling etc.
- The ILECs will be on the lines of police stations working inside the existing Integrated Check Posts (ICPs), will have the mandate to register, investigate and dispose of all types of cross-border crimes with jurisdiction clearly defined and coinciding with government regulations with respect to border guarding forces.
- ICPs are being set-up at major entry points on India’s land borders. These ICPs house all regulatory agencies like Immigration, Customs, border security, etc. together with support facilities like parking, warehousing, banking, hotels etc. in a single complex equipped with all modern facilities.
- ILECs will maintain a wealth of cross-border crime data and process it for short-, medium- and long-term trends. The data will be collated from different stakeholder agencies, mass-and-social-media, as well as cross-border sources.
- Besides personnel from border guarding forces of the area, there will be officials from different stakeholder agencies, such as Customs, NCB, NIA, Local Police, Anti-Trafficking (Human) Cells, IB etc.
Advantages of ILECs
- Synergy of efforts: For example, the powers of interception and electronic surveillance available with IB/RAW etc. can be complemented with the expertise available with NCB, the reach and manpower availability of BSF, the investigative skills and experience of the local police (all available under one roof).
- Optimum utilization of resources: ILECs envisage pooling of resources of different agencies and mutual sharing by them. This ensures optimal utilization of resources and overall cost cutting and increased efficiency in governance with regards to law enforcement on borders.
- Enhanced efficiency and desirable outcome: Almost all aspects of different crimes are likely to be entertained and disposed of at a single place through structural and functional integration of different stakeholder agencies. This results in speedy disposal with lesser resources and optimum outcome.
- Minimum Augmentation of Infrastructure: The need for having separate infrastructure and human resource for each agency like NCB, NIA, DRI, RAW and IB etc. gets avoided in ILECs which function on the dictum of pooling of resources, including infrastructure and would operate from within the premises of already sanctioned ICPs.
- The structure and function of ILECs is ‘Federal in nature and unitary in spirit’. It ensures that, while providing resources and expertise of the Central agencies to the states, it doesn’t encroach upon the authority and jurisdiction of the states.
Conclusion
Law and Order is a ‘State subject’. Given the federal balance of power between the Centre and States, an overarching institutional arrangement would require strong political will at the Central level as well as accommodation by the states. However, a workable and politically feasible solution has to be necessarily found in the interest of national security.
Model Question – Highlight the need and significance of recently proposed Integrated Law Enforcement Centres (ILECs) for dealing with cross-border crimes.
This Day in History Benjamin Peary Pal
On May 26, 1906, the first Director of Indian Council of Agricultural Research, Benjamin Peary Pal was born. Dr Pal is well known for his contributions to crop improvement, particularly the breeding of superior disease-resistant wheat. As the first Director-General of the reorganized ICAR, he was largely responsible for the first phase of India’s Green Revolution. He is known as the Father of Roses and harbinger of green revolution. Pal was the architect of All India Coordinated Research Projects on crops, animals and fisheries. He was honoured with the awards like Padma Shri, Padma Bhushan and Padma Vibhushan.

Sources: https://www.insaindia.res.in/detail.php?id=N46-0536
http://indiangalaxies.blogspot.com/2014/03/benjamin-peary-pal-1906-1989-ad.html
Image of the Day -Clyde’s Spot
The Juno Spacecraft, which is hovering over Jupiter, captured the intriguing evolution of a feature in the giant planet’s atmosphere known as “Clyde’s Spot.” The spot is named after astronomer Clyde Foster of Centurion, South Africa, who discovered it in 2020 using his own 14-inch telescope. The feature is a plume of cloud material erupting above the upper cloud layers of the Jovian atmosphere. The cloud material erupting above the top layers of the atmosphere is southeast of Jupiter’s Great Red Spot, which is currently about 1.3 times as wide as Earth.

Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI)
- Context: the appointment committee (chaired by the Prime Minister) met to select the new CBI director.
- Deriving power to investigate from the Delhi Special Police Establishment Act, 1946, CBI is the premier police investigation agency in India to investigate serious crimes related to defense of India, corruption in high places, serious fraud, etc. CBI also picks up investigations in conventional crimes like assassinations, kidnappings, hijackings, crimes committed by extremists, etc. It coordinates investigations in India on behalf of Interpol Member countries.
- It functions under the Department of Personnel, Ministry of Personnel, Pension & Public Grievances. However, for investigations of offences under the Prevention of Corruption Act, its superintendence vests with the Central Vigilance Commission.
- CBI is exempted from the provisions of the Right to Information Act.
- It is headed by a Director, an IPS officer with a rank of Director General of Police with a term of two years.
- The Appointment Committee consists of:
- Prime Minister – Chairperson
- Leader of Opposition of Lok Sabha
- Chief Justice of India
.png)
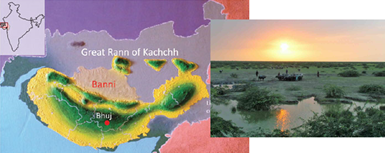
Banni Grasslands - Edukemy Current Affairs
- Context: The National Green Tribunal has ordered all encroachments to be removed from Gujarat's Banni grasslandswithin six months.
- Banni is the largest grassland of Asia located near the Great Rann of Kutch in Gujarat.
- Wetland and Grassland ecosystemsare mixed side by side in Banni. Vegetation in Banni is sparse and highly dependent on rainfall. It is dominated by low-growing plants, halophiles (salt tolerant), scattered tree cover and scrub.
- Banni grasslands, traditionally, were managed following a system of rotational grazing.
- The court also said theMaldharis (Pastoralists) will continue to hold the right to conserve the community forests in the area according to Forest Rights Act, 2006. Maldharis are a tribal herdsmen community inhabiting Banni.
Primary source: https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/environment/ngt-upholds-rights-of-pastoralists-in-banni-grasslands-wants-encroachments-removed-77075
https://www.downtoearth.org.in/coverage/forests/grasping-at-grass-40906
India-Israel Agreement on Agriculture Cooperation
- Context: India and Israel have signed“a three-year work program agreement” for development in agriculture cooperation.
- Indo-Israeli Agricultural Cooperation Projectstarted in 2008 with Centres of Excellence (CoE) focussing on dairy, farming technology and micro-irrigation.
- CoE offer free training sessions for farmers on efficient agricultural techniques. Vertical farming, drip irrigation and soil solarization are taught at the centres.
- INDO-ISRAEL Villages of Excellence (IIVOE) is a new concept aimed at creating a model ecosystem in agriculture- modern agriculture infrastructure, capacity building and market linkage.

Primary source: https://indianexpress.com/article/india/india-israel-sign-agreement-on-agriculture-cooperation-7328840/
https://mfa.gov.il/MFA/mashav/Latest_News/Pages/New-Center-of-Excellence-in-India.aspx
Recycling Carbon Technology
- Context: startupawarded Technology Development Board (TDB) National Award 2021.
- The startup has been awarded for developing a commercial solutionfor conversion of carbon dioxide (CO2) to chemicals and fuels.
- It has led to improvisation of process engineeringto enhance the production of chemicals and fuels from anthropogenic CO2 generated from various sources including coal and natural gas power generation sectors, steel industry, cement industry, and chemical industries.
- It has integrated multiple components involved in the CCUS (Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Sequestration)to develop a complete solution for the environmental issues due to global warming.
- CCUS is a process that captures carbon dioxide emissions from sources like coal-fired power plants.

Why community efforts are essential for real change
Essence- Pandemic has identified the significant ‘role of civil society’ which emerged as a resilient entity and enabled society to overcome the failure of the state and market. But issues like information asymmetry, lack of clarity over the ever-changing rules and regulations, etc are posing challenge to them. The possible way to overcome these challenges could be, one, NITI should engage government with a new framework to attract more community participation. Second, we should leverage advanced technologies for bridging demand-supply gaps. Third, NITI should partner with willing states to promote cross-learning and experience-sharing to overcome the asymmetric flow of information. Four, NITI Ayog’s portal DARPAN should facilitates the entry of new actors. Several micro-models are coming up with initiatives like: Breathe India and HelpNow, etc but with little connection with each other. We should once again call for a lost idea of community participation which is the necessity of present situation.
Why you should read this article?
- To understand and appreciate the importance of civil society in providing solutions to social problem.
- To know the current challenge faced by civil society in dealing with this pandemic and what could be the possible solution.
- To understand the importance of micro-models and why we need to scale them up.
The pandemic has worsened inequality between countries and within them
Essence: More than a year after the Covid-19 pandemic struck, the virus has not only affected 190 countries, leading to a 4.3 per cent contraction of the world economy, but has also perpetuated inequalities on three interconnected fronts: Inequalities in access to and availability of vaccines; loss of livelihood and standards of living, with millions pushed back into poverty in low and middle-income countries (LMICs); and gender inequality across sectors.
Why you should read this editorial?
- Understand the disparities in access to and distribution of vaccines across countries.
- Know about the impact of pandemic on poverty levels and job losses with the help of data.
- Learn about the economic impacts of the pandemic and how they have affected certain groups and sectors more than others.
Visit the World's Only Carbon-Negative Country
About the World's Only Carbon-Negative Country
- Bhutanis the world’s happiest and greenest country. That is no coincidence.
- Bhutan developed Gross National Happinessindex based on four pillars: sustainable development, environmental protection, cultural preservation, and good governance.
- This Himalayan kingdom is carbon negative despite increasing tourism.
How did Bhutan do this?
- Bhutan has built sustainability into its national identity.
- Leaders have tried to develop Bhutan by balancing economic growth carefully with social development, environmental sustainability, and cultural preservation, all within the framework of good governance
- The Constitutionitself mandates that 60 percent of its landmass be maintained and protected as forest.
- Tourists have to pay daily sustainable development fee of $65 which is utilised towards environment conservation, funding education, healthcare, and poverty alleviation. So, tourism itself is promoting sustainability
Lessons to be learnt:
- How to promote sustainability as economic growth, Importance of vision of leadership, innovative policies
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.