Monday, 24th May 2021
WHO panel to investigate rise in zoonotic diseases
In News
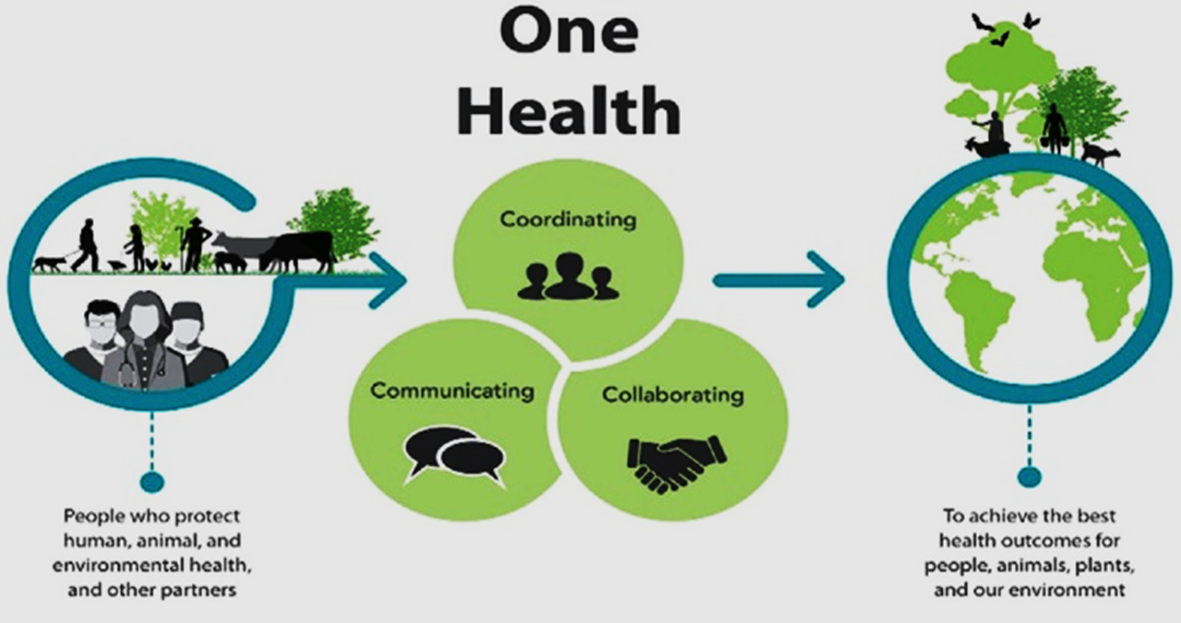
The World Health Organization (WHO) has formed a high-level expert panel ‘One Health’ to study the emergence and spread of zoonotic diseases like H5N1, avian influenza, MERS, Ebola, Zika and possibly the novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19).
About the WHO panel
- Recognizing the complex and multidisciplinary issues raised by the interface of human, animal and ecosystem health (“One Health”) that require enhanced coordination and collaboration among sectors and agencies, nationally and internationally, the partners have agreed to establish the One Health High-Level Expert Panel (OHHLEP) to assist them in their support to governments in the framework of the Partners’ One Health collaboration.
- The panel will advise global agencies such as the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), the World Health Organization (WHO), the World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE) and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) on how future outbreaks, especially due to zoonotic diseases, can be averted. It will also develop a surveillance framework and global action plan for the same.
Functions of the OHHLEP
- Scientific evidence: To provide advice on the analysis of scientific evidence on the links between human, animal and ecosystem health, and contribute to foresight on emerging threats to health.
- Impacts of Food systems: To provide advice on better understanding of the impacts of food systems (including agriculture, livestock farming and trade, wildlife hunting and trade, aquaculture, animal products processing, handling, distribution, and consumer practices) and ecological and environmental factors that may be contributing to zoonotic disease emergence/re-emergence and spillover events.
- Research Agenda: To contribute to the One Health research agenda setting and propose, advise on and review approaches and specific studies relevant to the development of a global approach to reduce risk of zoonotic pandemics.
- Policy response: To provide advice by invitation on One Health policy response in relevant member countries.
- Highest concern issue: To provide recommendations on specific issues identified by the Partners in the areas of highest concern for attention and action, and future directions, in One Health.
The One Health approach
- With the increase in population, industrialization, and geopolitical problems, global changes are accelerating which damage the biodiversity, ecosystems, and migratory movements of both humankind and species in general. Rapid climate and environmental changes have led to the emergence and re-emergence of infectious and non-infectious diseases.
- The One Health Approach recognizes the links between the health of people, animals, and the environment and highlights the need for specialists in multiple sectors to address any health threats and prevent disruption to agri-food systems.
- The approach helps better understand the root causes of disease emergence and spread and informing decision-makers to prevent long-term public health risks.
Increased Subsidy on Di-Ammonium Phosphate (DAP) fertilizer
In News:
As international prices of phosphoric acid, ammonia etc. used in DAP have gone up by 60% to 70%, the government has increased the subsidy to 140% on Di-Ammonium Phosphate (DAP) fertilizer to retain the selling price for farmers at the current level.
What is DAP and why is it important for farmers?
- DAP stands for Di-Ammonium Phosphate and is the second most used fertilizer in India, next to urea. It contains 46% (P) and 18% nitrogen (N).
- Farmers normally apply this fertilizer just before or at the time of sowing because it is high in phosphorus (P) that stimulates root establishment and development without which plants cannot grow to their normal size or will take too long to mature.
- DAP is the farmer’s preferred choice as it is similar to urea and muriate of potash (MOP), which have very high (N) and potassium (K) content of 46% and 60%, respectively.
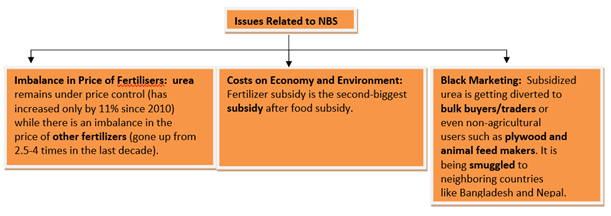
Subsidy Scheme for Fertilisers:
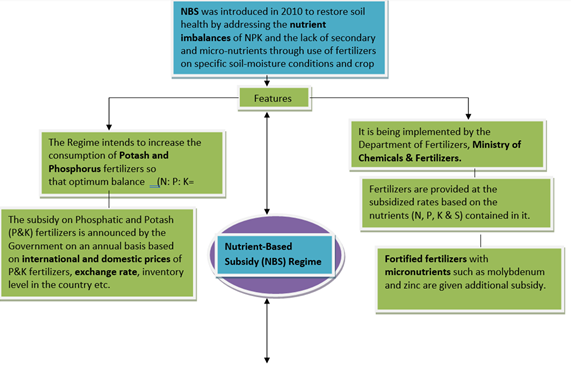
- Under the current scheme, the MRP of Urea is fixed (Rs 5,378 per tonne). Since companies have to sell at this controlled rate, the subsidy (the difference between the cost of manufacturing or import and the fixed MRP) is variable.
- The MRPs of all other fertilizers, by contrast, are decontrolled and decided by the companies themselves. The government only gives a fixed per-tonne subsidy. In other words, the subsidy is fixed, while the MRPs are variable.
- All Non-Urea based fertilizersare regulated under Nutrient Based Subsidy Scheme.
The case of DAP
- Most companies, until recently, were selling DAP fertilizer to farmers at around Rs 24,000 per tonne or Rs 1,200/bag provided international prices of both the final product and the imported raw materials such as rock phosphate, sulphur, phosphoric acid and ammonia were at reasonable levels.
- But global prices have surged over the past 6-7 months which has made it unviable for companies to sell at the old rates and this reflected in a steeply raised MRP.
- The Indian Farmers Fertilizer Cooperative (IFFCO) announced a hike in its MRP on DAP from Rs 1,200/bag to Rs 1,900/bag.
- Thus, in the light of international prices soaring, the government recently decided to more than double the subsidy on DAP from the existing Rs 10,231 to Rs 24,231 per tonne (a 137% increase).
- It will help the farmers in purchasing the DAP at reasonable prices during the kharif cropping season.
Primary source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-why-has-the-modi-government-increased-subsidy-on-dap-7323687/
Increased Child Marriages during Lockdown
In News: Recently, some activists and organisations of Karnataka have raised the issue of increased child marriages during lockdown with the Ministry of Women and Child Development.
Understanding Child Marriage:
- Prohibition of Child Marriage Act (PCMA), 2006 sets the minimum age of marriage at 18 years for females and at 21 for males.
- However, the act treats underage marriages as valid, but voidable.
- An underage marriage is treated valid when the minors involved in the marriage want it to remain valid and it is treated void when the marriage involves trafficking, enticement, fraud and deceit.
- PCMA also allows the minor party to repudiate the marriage or to have it nullified right up till two years of attaining minimum age.

What are the probable causes of Child Marriage?
- Major reasons for child marriage include poverty, insecurity, political and financial reasons, lack of education, patriarchy or gender inequalities and inadequate implementation of the law.
- As the Right to Education Act makes education free and compulsory only up to the age of 14, children above 14 years of age, especially girls, are seen as an economic burden and are considered unproductive till they are married off at 18.
Child Marriage in India and its status during the lockdown:
- UNICEF estimates suggest that each year, at least 1.5 million girls under 18 get married in India, which makes it home to the largest number of child brides in the world accounting for one third of the global total.
- The proportion of women aged 20 to 24 years who had been married when they were below the age of 18 years was 54% in 1992-93, 50% in 1998-99 and 47% in 2005-06.
- It fell impressively only in the last decade, between 2005 and 2015. Even so, roughly 1.5 crore young girls were married as children, in violation of the law.
- With lockdown in place, and weddings being restricted to houses due to tough guidelines, there has been a significant increase in child marriages which unfortunately go unnoticed.
- According to a report publishedby ChildLine India, the pandemic and the subsequent lockdown have proved to be new drivers of child marriages in rural Madhya Pradesh.
- This is because of lack of alert mechanisms (marriages at home are not alerted to the authorities) and pandemic induced pressure such as economic pressure as well as fear of violence against the girl child.
The possible impacts of Child Marriage:
- A girl, married as a child is more likely to be out of school and would not financially contribute to the community.
- She is more likely to experience domestic violence and forced sex.
- There are more chances of her dying due to complications during pregnancy and childbirth.
- It negatively influences children’s rights to education, health and protection.
- Child Marriage contributes to larger families and in turn, population growth. This delays the demographic dividend that would have come from reduced fertility and investment in education.
- Children married at a young age do not understand the responsibilities of marriage which leads to misunderstandings among family members. This disturbs the institution of the family.
- Prevention of Child Marriage is a part of SDG5which deals with gender equality and empowerment of all women and girls.
Arctic Council Approves First-Ever Strategic Plan
In News
Foreign ministers of the Arctic Council recently signed their first-ever strategic plan for the region, which will guide the body’s work for the next decade.
The Event- the 12th Arctic Council Ministerial
- The member countries’ Foreign Ministers of the Arctic Council signed the Reykjavik Declaration, reaffirming the Council’s commitment to maintain peace, stability and constructive cooperation in the Arctic region, emphasizing Arctic States’ unique position to promote responsible governance in the region.
- In recognition of the Council’s 25th anniversary, the Ministers adopted Council’s first ever Strategic Plan that reflects the shared values, goals and joint aspirations of the Arctic States and Indigenous Permanent Participants. It will guide the Council’s work for the next decade.
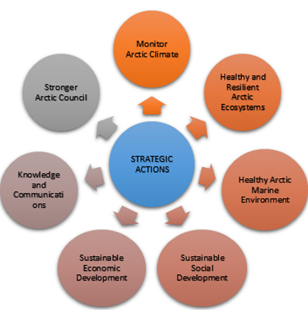
Arctic Council Strategic Plan 2021 To 2030
- Arctic Climate: Council will Monitor the climate considerations, promote enhanced actions to reduce greenhouse gases and short-lived climate pollutants, develop adaptation and resilience of Arctic communities. It will also promote clean energy solutions and technology.
- Healthy and Resilient Arctic Ecosystems: The Arctic Council will promote protection of the vulnerable Arctic ecosystems, action on issues that are critical to maintaining the health of Arctic ecosystems and support work on protection and restoration of wetlands and habitats.
- Healthy Arctic Marine Environment: The Arctic Council will support the implementation of the Agreement on Cooperation on Aeronautical and Maritime Search and Rescue in the Arctic (2011) and the Agreement on Cooperation on Marine Oil Pollution Preparedness and Response in the Arctic (2013), promote respect for international law, including as reflected in the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea.
- Sustainable Social Development: The Arctic Council will focus on the health, safety and long-term well-being of Arctic inhabitants by identifying, preventing and mitigating natural and human-induced disaster risks. It will enhance work on communicable diseases, epidemics and pandemics. It also aims to promote gender equality and non-discrimination in the Arctic.
- Sustainable Economic Development: The Arctic Council will enhance cooperation, provide guidance to decision-makers, support the transition towards sustainable and low-emission societies. This will be done through the use of clean technology, innovation and circular economy. The council will also address the issue of physical and digital connectivity.
- Knowledge and Communications: The Arctic Council will emphasize the importance of scientific assessments to improve knowledge and understanding of the Arctic to inform policy shaping and decision making and promote scientific and Arctic research cooperation.
- Stronger Arctic Council: The Arctic Council will maintain its commitment to peace, stability, and constructive cooperation in the Arctic, and continue to promote respect for the international legal framework that supports responsible governance relevant to the Arctic region.
Why is such a declaration and strategic Plan required and important?
- Accelerated global warming: As per a study, the warming Arctic tundra will make it harder for the world to curb climate change, as thawing permafrost and wildfires release greenhouse gases that are not fully accounted for in global emissions agreements. As temperatures rise and permafrost thaws, carbon dioxide and methane trapped within the long-frozen soil are released.
- Untapped resources and conflict: Varied estimates suggest that the Arctic holds a significant portion of the world’s undiscovered resources, both in terms of hydrocarbons and minerals.
- As the various countries scramble for a share of these resources, it could give rise to conflict and tensions, or worsen existing ones within the region and beyond. There is also the danger of these extraction activities triggering negative consequences such as oil spills.
- New maritime routes: The other area of potential disputes relates to the opening of new shipping routes owing to the melting Arctic ice. Canada, for one, holds the Northwest Passage to be falling within its territory of internal waters; the US, for its part, regards the passage as part of international waters. The stakes are significant as the new shipping routes will likely give economic returns with the shortening of journey time and the reduction of costs.
- Importance for India: Generally, India is seen to have taken the lead among Asian Observer states placing more weight on environmental and scientific rather than the economic potential of the region. The reason for this could be in the importance of agriculture to the Indian economy and its dependence on monsoons, along with its long coast-line with a high population make the country extremely vulnerable to climate change.
- So, such declarations and strategic plans are important for India. So India can also improve upon and put in place a more robust Arctic research programme to deal with these future threats.
Conclusion
The Arctic as a region for strategic competition has seized the world's attention, but it is also necessary to ensure the rule of law, so that it remains a region free of conflict where countries act responsibly. Through this declaration and plan, the council can act as an enabler to make the Arctic a region of peace, stability, and constructive cooperation.
Question: What is the Reykjavik Declaration and what are its goals? Why is this declaration important for the Arctic region and India?
Primary Sources: https://www.statecraft.co.in/article/arctic-council-approves-first-ever-strategic-plan
Secondary Sources: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/arctic-fires-thawing-permafrost-pose-growing-threat-to-climate-study/article34584285.ece
https://www.orfonline.org/research/indias-arctic-potential-48263/
This Day in History-Father of modern astronomy, Copernicus died
On May 24, 1543 the father of modern astronomy, Copernicus died in Prussia. He was the first astronomer who popularised the heliocentric theory that entails that all planets revolve around the Sun. In 1514, Copernicus proposed that the sun is the centre of the universe and earth lay close to it. He even accounted Earth’s rotation for the rise and setting of the sun, the movement of the stars, and the change of seasons. In 1532, Copernicus laid out his model of the solar system and the path of the planets in his book ‘On the Revolutions of the Heavenly Spheres’ which he published two months before he died in the year 1543. The Church eventually banned the book in 1616.

Image of the Day -Zero Shadow Day
Odisha’s Bhubaneswar witnessed Zero Shadow Day on May 21, 2021. It is a rare celestial phenomenon during which no shadow of an object or a being is observed. The phenomenon occurs twice a year when the sun is at its highest point in the sky at all the regions between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn. Due to the sun being exactly overhead, the shadow of all beings or objects disappears, resulting in Zero Shadow Day. The event takes place when the rotation axis of the Earth is tilted at an angle of 23.5° to the axis of revolution around the sun. During the sun’s apparent North to South and South to North movement, there are two days in a calendar year when the sun’s declination and the latitude of a place within the tropics align briefly, making shadows disappear for a short while.

Personal Guarantors Liable for Corporate Debt
- Context: The Supreme Court of India has upheld theCentral Government 2019 notification that allows lenders to initiate insolvency proceedings against personal guarantors.
- A personal guarantor is a person or an entity that promises payment of another person’s debt, in case the latter fails to pay it off.
- Until now, the IBC code only covered insolvency resolution and liquidation of corporate debtors. According to the Supreme Court verdict, there was an “intrinsic connection” between personal guarantors and their corporate debtors and that the adjudicating authority for personal guarantors will be the NCLT if a parallel resolution process is pending in respect of a corporate debtor for whom the guarantee is given.

White Fungus
- Context: An infection called white fungus (Candidiasis)
- Caused by a yeast(Candida) which normally lives on the skin and inside the body (mouth, throat, gut, and vagina, etc), without causing any problems, infections happens if it grows out of control or if it enters deep into the body (Eg. bloodstream or internal organs like kidney, heart, lungs, brain, etc).
- Main cause of infection being low immunity, pre-existing medical condition, recent operation, or being in contact withwhite fungus moulds (eg. Water), people experience symptoms similar to Covid if it reaches the lungs, despite testing negative for the virus.
- Proper sanitation and special caution of moulds in water that can lead to infection is important to prevent the infection.

Primary source: https://indianexpress.com/article/lifestyle/health/white-fungus-covid-doctor-explains-why-more-dangerous-than-black-fungus-7323224/
Magnetospheric Multiscale (MMS) Mission
- Context: Indian Scientists have developed a theory that helps understand the complicated nature of Sun-Earth interactions happening in the magnetosphere.
- MMS Mission is a NASA robotic space mission initiated in 2015 to study the Earth’s magnetosphere using four identical spacecraft flying in a tetrahedral formation.
- The mission is designed to gather information about the microphysics of magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence.
- Indian researchers have developed a theory that solves uncertainty regarding the conflict between the observations from MMS Mission.
- This has led to the unravelling of mystery around plasma.
 Mission.png)
Primary source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=1720408
https://study.com/academy/lesson/magnetosphere-definition-facts.html
DIPCOVAN
- Context: DRDO develops antibody detection-based kit “DIPCOVAN”.
- The Kit will be very useful for understanding COVID-19 epidemiology, sero-surveillance and assessing an individual’s previous SARS-CoV-2 exposure.
- It would be available at about 75 rupees per test, and it requires 75 min to conduct the test.
Primary source: http://newsonair.com/Main-News-Details.aspx?id=417525
The many benefits of an eco-tax
Essence- Despite of pandemic related stimulus package, sustained health financing in Indian remains a challenge in this pandemic. Various reports show the increase in out-of-pocket payments on health, with higher rate in the rural areas. This outlines why alternate sources of health financing in India need to be stressed. The COVID-19 pandemic has also forced the world to rethink climate change and the need for preservation of the environment. It has become important to bring Fiscal reforms for managing the environment, where India has great potential for revenue generation. The success of an eco-tax in India would depend on its planning and design for which it needs to be credible, transparent and predictable. In environmental tax reforms in developing countries like India, the revenue can be used to a greater extent for the provision of environmental public goods and addressing environmental health issues. In India, eco taxes can target several areas which will have three broad benefits: fiscal, environmental and poverty reduction.
Why you should read this article?
- To get an overview of health financing in India and different regions of the health.
- To understand the major issues with India’s health financing and what possible steps should be taken to address the same.
- How environment tax is a good way to address both, environmental public goods and addressing environmental health issues.
- What are the three complimentary activities which environmental tax have and what major areas which eco-tax can target to get a maximum benefit.
Article Link: https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/op-ed/the-many-benefits-of-an-eco-tax/article34629283.ece
Afghanistan 2.0: What continued US engagement means for the region
Essence: The US has announced that the Afghan War will end by September 11, having seized the Doha agreement as an opportunity. While its withdrawal will exacerbate chaos and violence in Afghanistan and impact the wider region, there are enough indicators of a “re-engagement” by the US and NATO in the country (Afghanistan 2.0), implying that a shadow presence will remain. Current geopolitical compulsions, including the US-China competition, have made Afghanistan strategically important. It is certain that the Taliban-ISKP-Pakistan combine will unleash much more violence. Groups like ISKP and al-Qaeda in Indian Subcontinent (AQIS) and their variants will be used for high-profile attacks in Afghanistan and in the region, including against Western targets, to deter deeper re-engagement in Afghanistan. The chaos would create more ungoverned spaces strengthening the terror infrastructure. Hence, the developments in Afghanistan will continue to raise security concerns, far beyond South Asia.
Why you should read this article ?
- To learn more about the global counter-terrorism (CT) campaign led by the United States.
- To comprehend the distinction between US involvement in Iraq and US involvement in Afghanistan.
- To be aware of potential challenges to regional security following the withdrawal of US forces.
- To understand about the meaning & necessity of Afghanistan 2.0.
Article Link: https://indianexpress.com/article/opinion/columns/us-withdraws-troops-from-afghanistan-taliban-7327211/
Good Corporate Practice: Example from Tata Steel
About Corporate Practises followed in Tata steel:
- Fairness and Transparency: Tata Steel embeds the highest standards of governance in its operations and strive to manage its affairs in a fair and transparent manner
- Welfare of all: It aims to create long-term value for all stakeholders and not just the shareholders
- High Benchmark: It not only follows corporate governance guidelines given by government of India but also global best practices as well.
- Ethical Governance Framework: Tata Code of Conduct ensures that business is conducted ethically and responsibly
- Values the environment: It aims to reduce their environmental footprint and contribute towards the creation of a circular economy.
Where can we use this case study: Example for Codes of Conduct, Work Culture,
Quality of Service Delivery, Good Corporate Practise.
Things to ponder: Definition of work culture, code of ethics, Good Corporate Practise etc
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.