Tuesday, 18th May 2021
China's spacecraft lands on Mars
In News
A Chinese spacecraft has landed on Mars, making China only the second country after the U.S. to send a rover to the surface of the Red Planet.
About the News
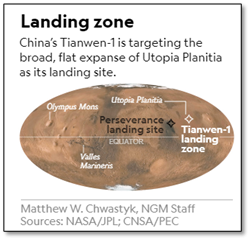
- News: A China National Space Administration (CNSA) lander from the Tianwen-1, which has been in orbit since February, touched down on Utopia Planitia, a large plain in the northern hemisphere of Mars on 15th May.
- Significance: The Tianwen-1 mission has achieved China’s first landing on another planet and is a milestone with great significance in China’s development of space and aviation.
- The Zhurong Mars rover is hoped to ignite the spark of China’s interplanetary exploration and guide humanity deep into the vast yet unknown outer space.
- If ‘Zhurong’ is deployed without a hitch, China will become the first country to successfully orbit, land and offload a rover during its maiden Mars mission.
- Landing on Mars is no easy feat: Utopia Planitia is one of the most difficult places in the solar system to land at. After orbiting around the Red Planet for about three months preparing for a safe landing attempt, the lander carrying the rover separated from the orbiter and descended towards the surface of Mars.
- Unlike the moon, Mars has an atmosphere, which makes it difficult to use rockets to decelerate. However, the Martian atmosphere is much thinner than Earth’s, making it harder to rely on parachutes. Touching down on Mars requires a huge deceleration in a very short time.
- The CNSA used the lander’s aerodynamic shape, parachute, and retrorocket to decelerate and buffer legs to touch down
- China’s Mars mission
- Launched by the China National Space Administration from southern China in July 2020, the Tianwent-1 mission consists of an orbiter, a lander and a golf cart-sized rover called ‘Zhurong’.
- Chinese scientists are hoping to explore Mars and study its geology for at least 90 days via the rover.
- Future plans of CNSA: China is also investing heavily in its manned space programme, as plans accelerate for its first space station, set to be functional by the end of next year and only the second space station after the International Space Station.
- In April 2021, a Long March-5B Y2 rocket carried out the first of three components for the space station, called the Tianhe or Heavenly Harmony The launch made news when debris from the re-entry of the rocket earlier this month fell into the waters of the Indian Ocean near the Maldives, with the uncontrolled re-entry criticised by NASA for failing to meet responsible standards.
Other countries who have managed to send rovers to Mars
- USA: Apart from China, only the United States has been able to deploy rovers to study the surface of the Red Planet. The first successful landing was made by NASA in July 1976, when the Viking 1 rover touched down on Mars. Shortly after that, Viking 2 arrived on Mars. Later, it successfully sent the Opportunity and Spirit rovers to explore Mars.
- Soviet Union: In 1971, the former Soviet Union managed to launch a Mars probe, however, communication was lost within seconds of it landing.
United Nations Global Road Safety Week (UNGRSW)
In News: The 6th UN Global Road Safety Week that highlights the benefits of low-speed streets at the heart of any community is being held from 17th-23rd May 2021.
About UN Global Road Safety Week and Its Objectives:
- Started in 2007, UNGRSW is a biennial global road safety campaign hosted by WHO.
- It raises awareness of road safety and make changes that will reduce the number of road deaths.
- The week aims to garner policy commitments at national and local levels to deliver 30km/h speed limits and zones in urban areas.
- It aims to build momentum towards the Global Plan for the decade of Action for Road Safety 2021-2030, adopted by UN General Assembly in August 2020 that sets the target of preventing at least 50% of road traffic deaths and injuries by 2030.
- The theme of the 6th UNGRSW is 30km/h on urban streets where people walk, live and play under the slogan: Streets for Life and hashtag #Love30.

Global Road safety scenario:
- Each year, approximately 1.3 million people die world over and over 54% of deaths are associated with motorcyclists, cyclists and pedestrians.
- It is also an interesting fact that Low Income Countries have 1% of the world’s vehicle but 13% of all deaths.
- On the contrary, High Income Countries have 40% of the world’s vehicles but 7% of all deaths.
Road Safety in India:
- According to the World Bank, India accounts for 11% of the total death in road accidents, the highest in the world, with only 1% of the world’s vehicles.
- About eighty thousand people are killed in road crashes every year and in most of the cases crashes occur either due to carelessness or due to lack of road safety awareness.
- The other causes include over speeding, drunk and drive, defect in road conditions, inadequate safety features in vehicles etc.
Measures taken by the Government:
- The National Road Safety Policy outlines various policy initiatives to be framed/taken by the Government at all levels to improve the road safety activities in the country that include:
- Promoting awareness
- Establishing road safety information database
- Encouraging safer road infrastructure including the application of intelligent transport
- Enforcement of safety laws
- Road traffic Safety Education and training etc.
- Good Samaritan Guidelines to prevent the harassment of “Good Samaritans” who help the road accident victims.
- India signed the Brasilia Declarationand committed to reduction in fatalities.
- Motor Vehicles (Amendment) Bill was passed to strengthen rules governing road safety.
- The first ever National Road Safety Month was inaugurated in January 2021 to build awareness with respect to road safety.
Primary source: https://nation.com.pk/18-May-2021/6th-global-road-safety-week-being-observed-from-may-17-23
Cabinet approves Production Linked Incentive scheme “National Programme on Advanced Chemistry Cell Battery Storage”
In News
The Cabinet has recently approved the proposal of the Department of Heavy Industry for the implementation of the Production Linked Incentive Scheme for Advanced Chemistry Cell known as the National Programme on Advanced Chemistry Cell (ACC) Battery Storage.
About the Production Linked Incentive Scheme
- The Scheme aims to provide companies incentives on incremental sales from products manufactured in domestic units.
- Foreign companies will also be encouraged to set up units in India although the primary goal is to encourage local companies to set up or expand existing manufacturing units.
- The PLI Scheme has also been approved for sectors such as automobiles, pharmaceuticals, IT hardware including laptops, mobile phones & telecom equipment, white goods, chemical cells, and textiles, etc.
|
Advanced Chemistry Cell ACCs are the new generation of advanced storage technologies that can store electric energy either as electrochemical or as chemical energy and convert it back to electric energy as and when required. |
Benefits and outcomes expected from the scheme
- Development of manufacturing facilities in India under the Programme
- Facilitate demand creation for battery storage in India
- The manufacturing of ACCs will facilitate demand for electric vehicles, which are proven to be significantly less polluting.
- As India pursues an ambitious renewable energy agenda, the ACC program will be a key contributing factor to reduce India's Green House Gas (GHG) emissions which will be in line with India's commitment to combat climate change.
- Import substitution to the tune of Rs.20,000 crore every year.
- Impetus to Research & Development to achieve higher specific energy density and cycles in ACC.
Source
Cyclone Tauktae
In News
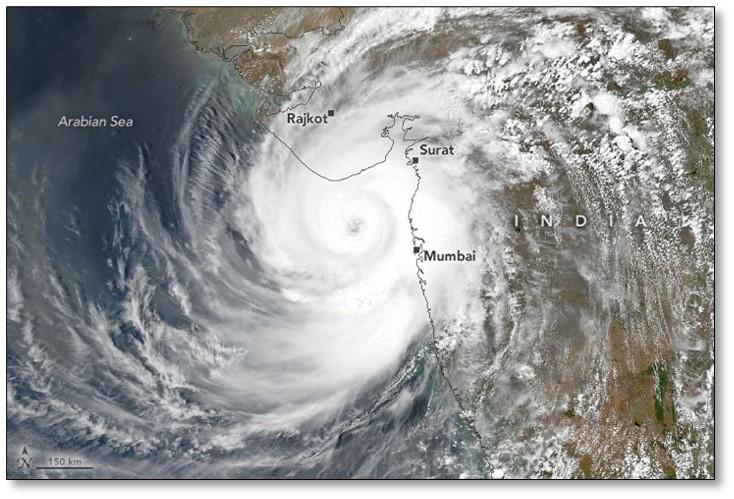
Cyclone Tauktae, the biggest to hit the western coast in decades, made landfall in Gujarat on 17th May, packing winds with speeds of 155-165 kilometres per hour, gusting to 190 km/hour.
About the Cyclone Tauktae
- Category: The India Meteorological Department (IMD) rated Tauktae an “extremely severe cyclonic storm” with peak winds of 115 mph (three-minute average), and a central pressure of 950 mb.
- Name: Cyclone Tauktae has been named by meteorologists from Myanmar. The word ‘Tauktae’ (pronounced as Tau’te) means a particular type of gecko or a distinctively vocal lizard, in the Burmese language.
- Impact: Perhaps the biggest threat from Tauktae is its storm surge. Heavy rains causing flashing flooding and river flooding will also be a major concern all across northwestern India. The Gulf of Khambhat, to the east of Tauktae’s landfall location, is a funnel-shaped bay, ideal for concentrating storm surge water.
- Uniqueness of Tauktae:
- Third cyclone in last four years in the Arabian sea in pre-monsoon season that has attained 100 knots windspeed.
- Most severe intensification by a cyclone in the month of May in the Arabian sea since 1999.
- Intensified from category 1 (Minimal damage capacity) to category 4 (extreme damage capacity) cyclone in just 24 hours.
What is a cyclone and how is it formed?
- Definition: A cyclone is a system of winds rotating counterclockwise in the northern hemisphere around a low pressure center. In southern hemisphere, the cyclone winds rotate clockwise. The swirling air rises and cools, creating clouds and precipitation. Cyclones can be the most intense storms on Earth.
- Classification: Cyclones are classified as: Extra tropical cyclones (also called temperate cyclones) and Tropical cyclones.
- Various names: Cyclones are known as typhoons in the China Sea and Pacific Ocean; hurricanes in the West Indian islands in the Caribbean Sea and Atlantic Ocean; tornados in the Guinea lands of West Africa and southern USA; willy-willies in north-western Australia and tropical cyclones in the Indian Ocean.
How are cyclones named and categorized?
|
Category name |
Wind Speed |
|
Depression |
20–31 mph (31–49 km/h) |
|
Deep Depression |
32–38 mph (50–61 km/h) |
|
Cyclonic storm |
39–54 mph (62–88 km/h) |
|
Severe Cyclonic Storm |
55–72 mph (89–117 km/h) |
|
Very Severe Cyclonic Storm |
73–102 mph (118–166 km/h) |
|
Extremely Severe Cyclonic Storm |
166–221 km/h (104–137 mph) |
|
Super Cyclonic Storm |
Above 138 mph (222 km/h) |
- There is a global panel, the World Meteorological Organisation/United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Panel on Tropical Cyclones, including the regional specialised meteorological centres as well as Tropical Cyclone Warning Centres that prepare the names of the cyclones/storms around the world.
- India along with 12 other nations, Bangladesh, Maldives, Myanmar, Oman, Iran, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Qatar, Thailand, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates and Yemen are members of this panel. India’s IMD suggests names of future cyclones and issues guidelines in case of a cyclone.
- Cyclones are categorized on the basis of the wind speed:
Effect of climate change on intensity of cyclones
- Scientists and meteorologists have attributed the growing number of cyclones including the latest one, Tauktae, to climate change more so because of the intensity with which they have now started hitting the Arabian Sea.
- The Bay of Bengal is usually warmer than Arabian Sea and therefore hosts more tropical storms. However, the scenario is now changing, the Sea Surface Temperature (SSTs) has been increasing rapidly in the last century. As a result, SSTs in the Arabian Sea are over the threshold values which leads to active convection, torrential rainfall, and intense cyclones. Climate projections indicate that the Arabian Sea will continue warming due to increasing carbon emissions, resulting in more intense cyclones in the future.
- Recent cyclones like Ockhi, Fani, and Amphan have confirmed the trend as they have intensified from a weak cyclonic storm to an extremely severe cyclone in less than 24 hours due to exceptionally warm SSTs.
- According to the US weather agency, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), if global temperatures increase by 2 degrees Celsius, the global warming temperature limit set by the Paris agreement, the intensity of cyclones could still worsen by as much as 10%.
Cyclone Preparedness in India
- National Cyclone Risk Mitigation Project: The Government of India initiated the National Cyclone Risk Mitigation Project (NCRMP), with financial assistance from the World Bank with a view to address cyclone risks in the country. The overall objective of the Project is to undertake suitable structural and non-structural measures to mitigate the effects of cyclones in the coastal states and UTs of India. The project is implemented by the National Disaster Management Authority under the ministry of home affairs in coordination with the state governments.
- National Guidelines of Management of Cyclones: The NDMA formed its National Guidelines of Management of Cyclones in 2008. The basic premise of these guidelines is for multi-sectoral mitigation through Early warning systems, Aircraft Probing of Cyclone (APC) facility, National Disaster Communication Infrastructure (NDCI) and Expanding the warning dissemination outreach.
Conclusion
In order to brace for the frequency of storms like Cyclone Taukae, India needs to start by building more climate resilient coastal infrastructure. The country needs to accept that pre-monsoon cyclones are going to get more common, rather than have a knee jerk reaction to such incidents. Considering that both cyclones and floods due to heavy rains are increasing across the west coast along with a gradual rise in sea level, we need to be prepared and have a special task force to tackle such natural disasters in the long term.
Question - What are the recent changes being observed in pattern of occurrence of cyclones in the Arabian sea? What are the reasons behind such changes?
http://www.ndma.gov.in/Natural-Hazards/Cyclone
http://www.rsmcnewdelhi.imd.gov.in/images/pdf/faq.pdf
https://www.indiatoday.in/information/story/how-is-a-cyclone-formed-1744025-2020-11-26
https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/images/148325/cyclone-tauktae-strikes-india
https://sites.google.com/site/disasterportal/stroms_cyclones/cyclone-formation
This Day in History -First Atomic Bomb
On this day, May 18, 1974, India successfully conducted its first atomic bomb test at the army base at Pokhran in Rajasthan. The operation ‘Pokhran-I’ was undertaken by the code name ‘Smiling Buddha’ and was carried out under the supervision of several key Indian Army generals. The device tested was a fission device and there was no release of radioactivity in the atmosphere. With the Smiling Buddha, India became the world's sixth nuclear power after the United States, Soviet Union, Britain, France and China to successfully test out a nuclear bomb.

Image of the Day - Blue jets
The International Space Station's Atmosphere-Space Interactions Monitor- ASIM observatory spotted an exotic type of upside-down lightning called as blue jet zipping up from a thundercloud into the stratosphere. Blue jets are a burst of electrical lightning which travel upwards from the clouds into the Earth's atmosphere. The blue jets occur when some positively charged upper part of any cloud interacts with a negatively charged layer present immediately above it. This then briefly equalizes both opposing charges which result in a bright blue discharge of static electricity. This is called blue lighting. Understanding Blue Jet Lightning is important because such events could affect the theories of how radio waves travel through the air. This can potentially impact communication technologies.
Sources: https://www.sciencenews.org/article/space-station-detectors-found-source-weird-blue-jet-lightning
Zeolites
- Context: Air India has begun the first of its “zeolite cargo flights”
- Zeolites are crystalline solid structures made of silicon, aluminium and oxygen and find applications in industry and medicine. They find application as sorbents, in detergents, as catalyst in industrial process and in oil refining.
- Air India has initiated the “zeolite cargo flights” to import zeolites to use them in medical oxygen plants. The medical oxygen plant technology being developed by the DRDO uses the pressure swing adsorption process and molecular sieve zeolite in oxygen generation.
- The technology is expected to be remote and rural settings with on-site generation of medical oxygen in a cost-effective manner.

Primary source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/air-india-begins-zeolite-cargo-flight-service/article34565547.ece
Covid 19 management in rural areas
Context: Centre issues guidelines on Covid-19 management in rural, peri-urban areas.
- The health infrastructure planned shall be aligned to 3-tier structure – Covid Care Centre (CCC) to manage mild or asymptomatic cases, Dedicated COVID Health Centre (DCHC) to manage moderate cases and Dedicated Covid Hospital (DCH) to manage severe cases.
- Covid care centres should have a Basic Life Support Ambulance (BLSA) networked among such CCCs equipped with sufficient oxygen support on 24×7 basis
- Symptomatic cases can be triaged at village level by tele-consultation and cases with comorbidity or low oxygen saturation should be sent to higher centers.
- Providing pulse oximeters and thermometers on loan to families with a confirmed covid cases through ASHA/Anganwadi workers.
- Provision of home isolation kit shall to those under home quarantine- Paracetamol 500 mg, cough syrup, multivitamins, a detailed pamphlet indicating precautions to be taken, etc.

Primary source: https://indianexpress.com/article/india/centre-issues-guidelines-on-covid-management-in-rural-peri-urban-areas-7317350/
Mission Covid Suraksha
- Context: Government augments capacity of indigenous production of Covaxin under Mission Covid Suraksha.
- Mission COVID Suraksha is India’s targeted effort to enable the development of indigenous, affordable and accessible vaccinesfor the country and will complement the ongoing mission of Atmanirbhar Bharat.
- The Mission isled by DBT and implemented by Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC).
- The objectives of the mission include accelerating pre-clinical and clinical development, licensing of vaccine candidates, establishing clinical trial sites, developing protocols, training, data management systems, regulatory submissions, quality management systems and accreditations and developing suitabletarget product profile so that vaccines being introduced through the mission have preferred characteristics applicable to India.
Primary source: https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1676998
National Crisis Management Committee (NCMC)
Context: NCMC meets to take stock of cyclone preparations.
- It is a committee set up by Government of India for effective coordination and implementation of relief measures and operations during a natural calamity.
- As an integral part of Natural Disaster Management System, it is country’s apex body to handle any emergency and functions under the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- The committee comprises of Cabinet Secretary as Chairman, Secretary to Prime Minister, Secretary (MHA) and other secretaries of concerned Ministries/Departments & agencies as members.

Primary source: https://journalsofindia.com/national-crisis-management-committee/
Re-imagining PSU bank privatisation- HBL
Essence: Although the sudden surge in the pandemic has caused an apparent loss of momentum in the government’s privatisation exercise, it remains very much on the table. Plenty of behind-the-scene activity has transpired post the public sector bank (PSB) sale announcement in the Budget. In this context, while highlighting the steps taken by government, the article suggests a ‘nuanced creep-up investment’ solution rather than an ‘upfront majority stake-sale’ approach, for road to privatisation.
Why you should read this article?
- Have a brief background on recent steps taken to sustain PSB privatisation momentum.
- Know about the pros and cons of an upfront stake sale of close to 50 per cent through a ‘Swiss challenge’ method.
- Learn about the blueprint of proposed ‘nuanced creep-up investment’ strategy and how it can be deliver a workable win-win outcome for all.
Article Link: https://www.thehindubusinessline.com/opinion/reshaping-the-psb-privatisation-exercise/article34580949.ece
Design of a new health system could emerge from the Covid crucible, for universal health coverage- IE
Essence- Though big cities are showing early sign of recovery from second wave but, spread of Covid in small towns and villages especially in central and North India is becoming a cause of concern due to weak health infrastructure. During first wave, because of- prevalence of strict travel restrictions even after lockdown, lower population density, lower co-morbidities, etc., rural health services were not severely challenged. But this time due to lack of anticipation of second wave and assumption of countrywide herd immunity, etc. virus has evaded rural boundaries too. To tackle present situation, we need to follow standard operating procedures (sop) released by Ministry of Health and Family Welfare; ensure engagement of primary healthcare teams and local community; availability of emergency transport system, restricting rural-urban movement, Vaccination on preference basis and assisting registration of those who do not have access to smart phones, etc., Decentralized planning, delivery and monitoring are needed at the district level with the district collector and the district health officer mobilising resources and coordinating operations.
Why you should read this article?
- To get an overview of health care system of rural India especially of central and north India.
- To understand the difference between first and second wave of Covid and how second wave may challenge rural health care system this time.
- To know what possible steps should be taken to tackle present situation.
Article Link: https://indianexpress.com/article/opinion/columns/virus-in-the-village-7319228/
Sukumar Sen: The Civil Servant Who Helped Set Up India’s Extraordinary Electoral System
Topic of syllabus: Public/Civil Service Values and Ethics in Public Administration; Concept of Public Service
Background Story:
- There was the general euphoria that followed the birth of India. As Prime Minister Nehru aptly said, “The soul of a nation, long suppressed, [found] utterance.”
- On the other hand, there was a complicated responsibility of building a nation, setting up a functional system of governance.
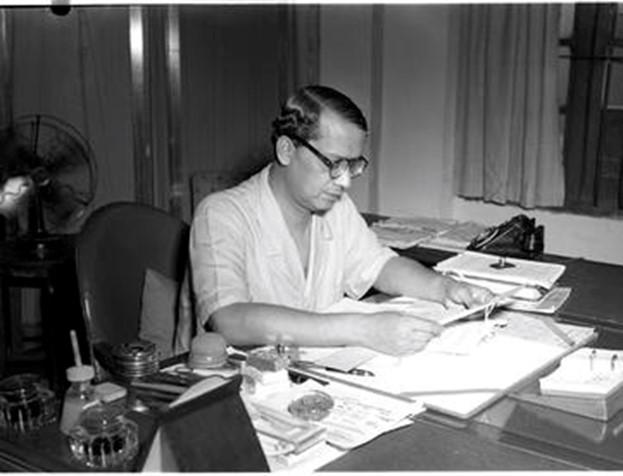

Contribution of Sukumar Sen:
- He is one of the most prominent personalities in setting up India’s electoral system as it is today.
- He was India’s first Chief Election Commissioner with responsibility for designing an electoral system for the largest democracy in the world.
- His task was to get 176 million Indians, who were 21 years of age or above, to vote in India’s first-ever general elections in 1951-52.
- The Election Commission under Sukumar undertook the mammoth task of approaching every adult in India to register their name and to convince them to vote in the 1951-1952 elections.
- The obstacles like sheer ignorance, social norms and taboo were attacked by the tool of social persuasion and perseverance
Value showcased by Sukumar Sen:
- Dedication to duty, Perseverance, Probity etc
Where can we use this case study:
- As an example of contribution of civil servant for public service delivery, values in public service etc
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.