Friday, 14th May 2021
India to launch low-cost charging devices for electric two, three wheelers
In News
The Indian government in collaboration with manufacturers of electric vehicles and charging devices has been able to develop a low-cost charging infrastructure for electric two and three wheelers which is expected to help push adoption of such vehicles in the coming years.
About the News
- Agencies involved: The Department of Science and Technology (DST), the Office of the Principal Scientific Advisor (PSA) to the Government of India, in close coordination with the NITI Aayog team have been working on this initiative.
- Ratification by BIS: The new standards for this new low-cost charging infrastructure will be ratified by the Bureau of Indian Standards.
- Affordable electric vehicle charging infrastructure: The government has set a target price of less than Rs. 3,500 for a smart AC charge point that can be operated with a smartphone for a global breakthrough in affordable electric vehicle charging infrastructure.
Significance of the low-cost charging devices
- Address the lack of charging infrastructure: India requires a widespread charging infrastructure to meet the growing adoption of EVs. In addition to more charging stations, the lack of space is also a challenge since people need a place to charge their EVs. The low-cost charging devices are an important step in this respect.
- Less expensive than charging stations: The emphasis on charging points rather than costly charging stations has led to the accelerated efforts for developing the Low-Cost AC Chargepoint (LAC) standard for the light electric vehicles segment.
- Advance government efforts for adoption of electric vehicles: The government has been urging vehicle manufacturers to develop and manufacture electric vehicles to reduce vehicular emission and curb oil imports. The union government has also been incentivizing purchase of such vehicles through the second phase of the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing Electric and Hybrid vehicle (FAME) scheme. The union government has been focusing on driving adoption of electric vehicles in the two and three-wheeler segment where the price gap has been narrowing.
- Easily Scalable: The LAC device is intended to be highly scalable and deployed in any place where a single-phase line is available – mainly targeting parking lots of metro and railway stations, shopping malls, hospitals, office complexes, apartments and even kirana and other shops. It can also be adopted for charging e-Scooters and e-Auto Rickshaws.
Sources:
BRICS nations keen on multilateral social security framework
In News
The representatives of BRICS nations have expressed willingness to have a multilateral social security framework in order to safeguard workers' rights.
About the News
- The member nations' representatives at the first BRICS Employment Working Group (EWG) meeting held on May 11 and 12, 2021 at New Delhi in a virtual format, discussed Promotion of Social Security Agreements amongst BRICS nations, formalization of labour markets, participation of women in the labour force and Gig and Platform workers' role in the labour market.
- On the issue of Social Security Agreement (SSA), the member nations resolved to enter into dialogue and discussion with each other and take it forward towards signing of the agreements, while the International Labour Organization (ILO) and International Social Security Agency (ISSA)
on their part, expressed willingness to provide technical support in facilitating conclusion of such agreements.
What is Social Security?
- The International Labour Organisation defines ‘social security’ as the protection which society provides for its members, through a series of public measures, against economic and social distress that otherwise would be caused by the stoppage or substantial reduction of earnings resulting from sickness, maternity, employment injury, unemployment, invalidity old-age and death; the provision of medical care; and the provision of subsidies for families with children.
- Social security legislations in India originate from the Directive Principles of State Policy as contained in the Constitution of India.
- The EPF Act is India’s most significant social security legislation. It has been enacted so as to provide for the institution of provident funds, pension fund and deposit-linked insurance fund for employees in factories and other establishments
What is Social Security Agreement (SSA)?
- Definition: An SSA (also known as Totalisation Agreement) is a bilateral instrument to protect the social security interests of workers posted in another country. Indian employees, who are posted to other countries by their Indian employers, without terminating the contract of employment, continue to make social security contribution in India as per Indian law.
- On account of the assignment undertaken in the other country, they may also be required to make social security contribution under the host country’s laws. Ordinarily, such employees do not derive any benefit from such contributions made outside India on account of restrictions on withdrawal and stipulations pertaining to duration of stay.
- India’s SSAs: As on date, India has signed SSAs with 18 countries. Being a reciprocal arrangement, an SSA is intended to provide for avoidance of double coveragee., coverage under the social security laws of both the home and host countries.
- Ordinarily, an SSA addresses 3 issues, i.e.:
- Detachment: An exemption, allowed to employees sent on an assignment to another country, from social security contribution in the host country, provided they are complying with the social security system of the home country.
- Exportability of Pension: A provision allowing employees sent on assignment to another country, and who are making social security contributions under such host country’s regime, to export the benefits to their home countries or to beneficiaries in a third country, on completion of their assignment or on retirement.
- Totalisation of Benefits: The period of service rendered by an employee in a foreign country is counted for determining the eligibility for benefits, but the quantum of payment is restricted to the length of service, on pro-rata basis.
- Certificate of coverage (COC): A certificate of coverage or a detachment certificate is a document that must be obtained by an IW to avail the benefits under the applicable SSA. A COC is issued in the employee’s home country by the social security authority in accordance with the provisions of the relevant SSA. The COC acts as a proof of detachment, pursuant to which, exemptions from the applicable social security compliances at the host country are allowed.
- Benefits: SSAs broadly provide three benefits, including avoiding making of double social security contributions by the workers, easy remittance of benefits, and aggregating the contribution periods in two countries to prevent loss of benefits
Sources: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1718229
https://www.mea.gov.in/bilateral-documents.htm?dtl/26465/Social_Security_Agreements
Image of the Day -Corpse flower
This is the image of a titan arum, also called corpse flower, the biggest flower structure on Earth. Famous for its bad smell, the titan arum can grow up to 3m tall. It can take several years for a single flower to blossom. The plant is endemic to the steep hillsides of rainforests in western Sumatra but is cultivated in botanic gardens worldwide. The unusual short-lived flower structure is the largest unbranched inflorescence of any plant and smells of rotting flesh. Usually taking 4–10 years or more between flowerings, a titan arum is often a major tourist attraction when in bloom.
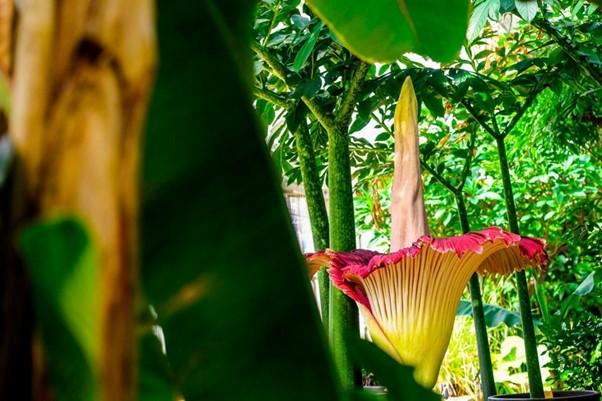

Sources: https://www.britannica.com/plant/Titan-arum
Image Source: https://www.bbc.com/news/in-pictures-52679694
Israel-Palestine Conflict continues
In News
Dozens of people have been killed in Gaza and Israel since violence escalated early this week. The current offensive is the heaviest between Israel and Hamas since a 2014 war in the Hamas-ruled region.
Background of the present conflict
Tensions have been building up in Jerusalem since the start of Ramzan in mid-April between Israeli forces and Palestinians.
- Recently, Israeli armed forces stormed Al-Aqsa Mosque in the Haram esh-Sharif in Jerusalem.
- In retaliation, Hamas, the Islamist militant group that administers Gaza, fired dozens of rockets targeting Israel.
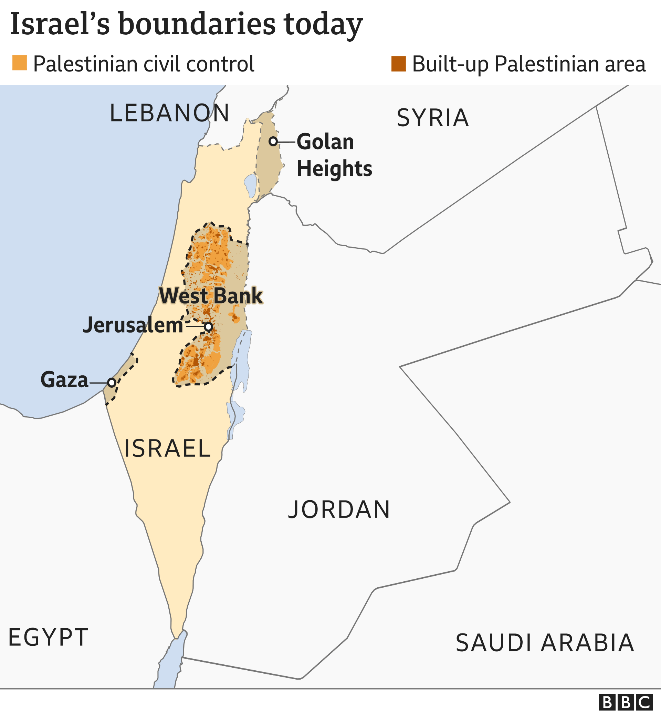
What are the areas where the conflict is presently concentrated?
- Jerusalem: Jerusalem has been a bone of contention in the Israel-Palestine Conflict. In 1947, the UN voted for Palestine to be split into separate Jewish and Arab states, with Jerusalem becoming an international city. That plan was accepted by Jewish leaders but rejected by the Arab side and never implemented. Following the 1967 war, Israel occupied East Jerusalem.
- Al-Aqsa Mosque: Al-Aqsa Mosque is one of the holiest structures in the Islamic faith. The mosque sits inside a 35-acre site known by Muslims as Haram al-Sharif, or the Noble Sanctuary, and by Jews as the Temple Mount. The site is part of the Old City of Jerusalem, sacred to Christians, Jews and Muslims.
- Sheikh Jarrah Issue: As Israel occupied East Jerusalem following the 1967 war, there have been forced evictions of Palestinian families from the area. Earlier this year, the Central Court in East Jerusalem upheld a decision to evict four Palestinian families from their homes in Sheikh Jarrah in favor of Jewish settlers. This issue has also potentially impacted the present tensions.
What are the reasons that have fuelled the present conflict?
- Citizenship issues: Since its annexation, Israel has expanded settlements in East Jerusalem, which is now home for some two lakh Jews. Jews born in East Jerusalem are Israeli citizens, while Palestinians in the city are given conditional residency permits.
- Control over the Al Aqsa mosque: Israeli security forces continue to maintain their presence in the Al-Aqsa mosque area. Jews and Christians are allowed to visit, but unlike Muslims, are prohibited from praying on the grounds under the status quo arrangement. The celebration of Jerusalem Day by Israel is also a question of provocation for Palestinians in the area.
- Conflict over Jerusalem: Israel exclusively claims Jerusalem and Israeli settlement building and expansion in and around East Jerusalem has resulted in the expulsion of Palestinians.
- Violations of International Law: The Israeli annexation of East Jerusalem and its ongoing settler activities in the West Bank contravene international humanitarian law. They are also not recognized by the vast majority of the international community. The continued Israeli occupation of these territories along with the appropriation of Palestinian land are among the primary causes of conflict between the two sides.
What is India’s stand on the Israel-Palestine Issue?
- Balancing act: India recognised Israel in 1950 but it is also the first non-Arab country to recognise Palestine Liberation Organisation (PLO) as the sole representative of the Palestinian. India had recognized the statehood of Palestine in 1988. India continues to maintain the image as a historical and moral supporter for the Palestinian self-determination and at the same time engage in the military, economic and strategic relations with Israel.
- Shifting stand of India on Israel’s human rights violations: In 2014, India favoured UNHRC’s resolution to probe Israel’s human rights violations in Gaza. Despite supporting the probe, India abstained from voting against Israel in UNHRC in 2015.
- De-hyphenated relationship with Israel and Palestine: India’s policies towards Israel and Palestine are shifting from mere symbolism to one driven by substantial outcomes for its interests on a global level. For instance, India went against the US in a vote at the UN to recognize Jerusalem as the capital of Israel but also voted in favour of a decision introduced by Israel in the UN Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) that objected to granting consultative status to a Palestinian non-governmental organization.
Conclusion
Given the complexity and the historical baggage of the Israel-Palestine issue, the conflict is not likely to cease anytime soon. The most recent peace plan, prepared by the United States, during the Presidency of Donald Trump- called "the deal of the century" by Israeli PM Benjamin Netanyahu - has been dismissed by the Palestinians as one-sided and never got off the ground. The Abraham Accords between Israel and the other regional powers like UAE, Bahrain is a step in the right direction.Any future peace deal will need both sides to agree to resolve complex issues.
Question: Jerusalem has been at the centre of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. Examine in light of the recent Israel-Palestine clashes.
Sources
Draft notification on utilisation of ash
In News
The Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) has released the draft notification on utilization of Fly ash.
About the notification
- Aim: The notification aims to implement these guidelines, based on the polluter pays principle (PPP), to ensure 100 % utilisation of fly ash by the coal or lignite based thermal power plants to conserve topsoil and natural resources, to protect the environment and prevent the dumping and disposal of fly ash discharged on land.
- Key features of the draft notification
|
Responsibilities of Thermal Power Plants (TPPs) to dispose fly ash and bottom ash: |
1. Every coal or lignite based thermal power plant (including captive and / or co-generating stations) shall be primarily responsible to ensure 100% utilisation of ash (fly ash, and bottom ash) generated by it for eco-friendly purposes like · Manufacturing: Manufacturing of brick /blocks/tiles, Cement manufacturing, ready mix concrete; Manufacturing of sintered/ cold bonded ash aggregate · Construction: Construction of road and fly over embankment, Ash and Geo-polymer-based construction material; Construction of dam; Construction of shoreline protection structures in coastal districts · Filling: Filling up of low-lying area; Filling of mine voids · Agriculture in a controlled manner based on soil testing · Export of ash to other countries; Any other eco-friendly purpose as notified from time to time. 2. A Committee will be constituted to examine, review, and recommend eco-friendly ways for ash utilisation. |
|
For the purpose of utilisation of ash, the given paras shall apply: |
1. All agencies (Government, Semi Government and Private) engaged in construction activities within 300 km from the lignite/coal based TPPs shall mandatorily utilise ash in these activities, 2. Manufacturing of ash-based products and use of ash in such products shall be in accordance with specifications and guidelines laid down by the Bureau of Indian Standards, Indian Road Congress, and Central Pollution Control Board. |
|
Fines for non-compliance: |
If the concerned power plants are unable to utilise at least 80% ash in the first two years of the three-year cycle period, they will have to pay a fine. Further, the notification specifies penalty for underutilisation of legacy ash. |
|
Enforcement, Monitoring, Audit and Reporting: |
The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) and the concerned State Pollution Control Board (SPCB)/ Pollution Control Committee (PCC) shall be the enforcing and monitoring authority for ensuring compliance of the provision. |
What is Fly ash?
- Fly ash is a naturally-cementitious coal combustion by-product. It is the finely divided residue that results from the combustion of pulverized coal and is transported from the combustion chamber by exhaust gases. It is extracted by the precipitators in the smokestacks of coal-burning power plants to reduce pollution.
- Fly ash consists of a complex mixture of organic (1–9%) and inorganic(90–99%) constituents of which about 30–84 % is amorphous and17–63% is crystalline
- The quality of flyash depends on coal, coal particle fineness, percentage of ash in coal, combustion technique used, air/fuel ratio, burners used, and type of boiler.
Why do we need to capture Fly Ash?
Harmful Effects:
- High production levels: In India, unlike in most of the developed countries, ash content in the coal used for power generation is 30–40%. India ranks fourth in the world in the production of coal ash as by-product waste after USSR, USA and China, in that order.
- Some of the fly ash from coal-fired power plants escapes into the atmosphere. Air pollution in the vicinity of a coal fired thermal power station affects soil, water, vegetation, the whole ecosystem and human health.
- Bad Impact on Human health: The fine particles of fly ash reach the pulmonary region of the lungs and remain there for long periods of time; they behave like cumulative poisons. The residual particles being silica (40–73%) cause silicosis. All the heavy metals (Ni, Cd, Sb, As, Cr, Pb, etc.) generally found in fly ash are toxic in nature.
- Disposal problems: Fly ash can be disposed-off in a dry or wet state. Studies show that wet disposal of this waste does not protect the environment from migration of metal into the soil. Heavy metals cannot be degraded biologically into harmless like other organic waste.
- Studies also show that coal ash satisfies the criteria for landfill disposal. According the hazardous waste management and handling rule of 1989, fly ash is considered as non-hazardous. Thus, Fly ash can be treated as a by-product rather than waste.
Fly Ash can be utilized in innovative and eco-friendly ways like:
- Cement Industry: It saves both precious lime stone and coal. The utilization of fly ash in manufacturing of cement has value-added use
- Development of Fly Ash Based Polymer Composites: Fly ash-based composites have been developed using fly ash as filler and jute cloth as reinforcement. The developed components / materials are stronger, more durable, and resistant to corrosion and above all cost effective as compared to the conventional material i.e. wood.
- Fly Ash- Sand-Lime-(Gypsum /Cement) Bricks /Blocks: Fly ash is being used in manufacturing of fly ash based building products like bricks, blocks, tiles etc which results in saving of fertile top soil. Fly ash based bricks/blocks/tiles are as good as clay based conventional building products.
- Back Filling/Stowing of Mines: Fly ash is being used for backfilling of open cast mines and stowing of underground mines which results in saving of top fertile soil and precious river sand. It is also being used in construction of roads/embankments/flyovers and the raising of ash dykes which results in saving of top fertile soil.
- Agriculture: Fly ash is being used as manure in agricultural sector as it has many micronutrients. Fly ash provides the uptake of vital nutrients/minerals (Ca, Mg, Fe, Zn, Mo, S and Se) by crops and vegetation, and can be considered as a potential growth improver.
Possible Benefits
- Helps in CO2 capture: Due to its silica, alumina, and un-burned carbon content it is useful as a precursor for the synthesis of porous materials such as, silica, zeolite or activated carbon which could be used as cheap CO2 adsorbents.
- FBC fly ashes are waste materials that, due to the high content of free CaO, can be used to reduce CO2 emissions by mineral carbonation.
- Longer life of Concrete: Delays the heat of hydration which helps in reduction of thermal cracks in concrete; improves the workability of concrete and enhances the life of structures and buildings among others.
- For instance, Ghatghar Dam in India is a classic example which is constructed using fly ash and the tallest building in the world - Burj Khalifa in Dubai is another structure constructed using fly ash.
- Green building material: In addition, fly ash has been proven to be the green building material due to environmental benefits that it offers. Hence, the global fly ash market is anticipated to experience high demand in the market.
- Agriculture: It improves permeability status of soil, fertility status of soil (soil health) / crop yield, improves soil texture, reduces bulk density of soil, improves water holding capacity / porosity, optimizes pH value, improves soil aeration, reduces crust formation, provides micro and macro nutrients and works as a part substitute of gypsum for reclamation of saline alkali soil and lime.
Conclusion: The generation of coal fly ash is anticipated to increase in coming years, as a result of the world's increasing reliance on coal-fired power generation. So, despite the current utilization, there are some limitations which need to be considered for further development in fly-ash utilization:
- Areas having large prospective of fly ash utilization needs to be discovered for increasing the overall utilization of fly ash in India.
- Technological advancement is required for collection, storage and disposal facilities of fly ash so that fly ash in dry form could be made available to its users.
- The states and districts where TPPs are located needs to promote fly ash utilization; construction of building/highways/roads/flyovers and other infrastructure projects.
- Utilization of fly ash in agriculture is below expectation because of presence of heavy metal and radioactive elements in fly ash. Theses apprehensions are mandatory to be addressed for increasing fly ash utilization.
Question: Discuss the various uses of Fly ash and their benefits. What are limitations in utilization of fly ash?
This Day in History - First Smallpox Vaccination
On May 14, 1796, the British physician Edward Jenner successfully inoculated an 8-year-old with the first smallpox vaccination. Smallpox was widespread in the 18th century, and occasional outbreaks of special intensity resulted in a very high death rate. Edward Jenner used cowpox material to create immunity to smallpox. It was the first vaccine to be developed against a contagious disease. Mortality during outbreaks was as high as 35% before the vaccine. From 1958 to 1977, the World Health Organization conducted a global vaccination campaign that eradicated smallpox. Although the vaccine is no longer given to the public, the vaccine is kept on hand to guard against bioterrorism and biological warfare.
Source: https://www.timeanddate.com/on-this-day/may/14
https://www.ktnv.com/news/coronavirus/a-brief-history-of-vaccines-from-smallpox-to-covid-19
Iron Dome Air Defence System
- Context: Israelused its Iron Dome air defence system in recent violent clashes over Jerusalem.
- It is a short-range, ground-to-air, air defence systemthat includes a radar and Tamir interceptor missiles that track and neutralize any airborne threat aimed at Israeli targets.
- Iron Dome has three main systems that work togetherto provide a shield over the area where it is deployed: radar to spot any incoming threats, Battle Management and Weapon Control System (BMC) and Missile Fire Unit.
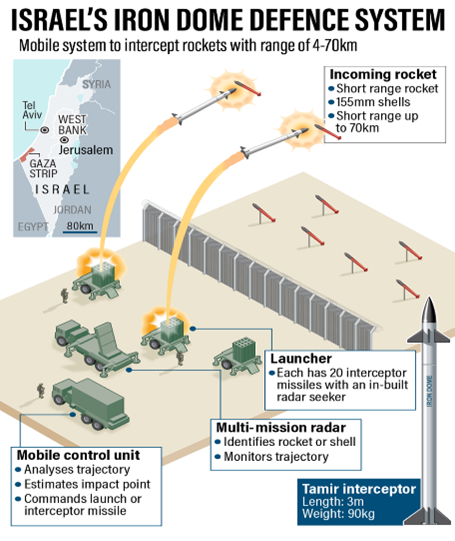
Primary source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-how-israels-iron-dome-intercepts-rockets-7312743/
Sovereign Gold Bond Scheme - Edukemy Current Affairs
- Context: The Government of India, in consultation with RBI, has decided to issue gold bonds.
- Sovereign Gold Bonds are government securities denominated in grams of gold. They are substitutes for holding physical gold.
- The scheme was launched in 2015with an objective to reduce the demand and import for physical gold.
- The minimum permissible investmentis 1 gram of gold. A fixed rate of 5% per annum is applicable on the scheme. The bond comes with a maturity period of eight years, with an option to exit the investment after the first five years.
- Bonds can also be used as collateral for loans.
Primary source: https://www.livemint.com/topic/sovereign-gold-bonds
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)
- Context: OECD has asked the revenue starved countries to revisit inheritance tax.
- OECD was established in 1961 with an aim to stimulate economic progress and world trade.
- It is an intergovernmental economic organization with 37 member countries and headquarters at Paris, France.
- Most OECD countries are regarded as developed countries with high Human Development Index (HDI).
Primary source: https://www.oecd.org/india/
Rural India is being devastated by Covid. Urgent action is needed
Essence: It is important that the government executes and implements the delivery of vaccines and healthcare services on a war footing in the backdrop of Covid-19 crisis. This article emphasises on urgent need for active coordination not just between the Union and state governments but right down to the last level of governance, the panchayats.
Why you should read this article?
- Learn about the needs to build a robust healthcare system in the rural areas.
- Know about the urgent steps required to combat pandemic such as furnishing of accurate and timely data, Oxygen availability and allocation, building additional capacity, decentralisation in decision making among others.
Article Link: https://indianexpress.com/article/opinion/columns/covid-19-virus-spread-rural-areas-india-second-wave-7314173/
India and the elusive demographic dividend
Essence- India’s demographic dividend window began in 2018 which is expected to last for 37 years until 2055. But the concern is, will India manage to gain through this bulging working population? According to Malthus, the human population and economic growth were tied in a zero-sum game limited by the availability of food. But the recent history has proved Malthus wrong, as rapid technological progress in the post-Malthusian world has made population an asset rather than a burden. For example, many Asian countries were able to benefit from the rise in their working population due to fall in fertility rates through contraceptive usage and increase in life expectancy which enabled sustained periods of high growth so the same expectations are from India. But mere existence of technology is not sufficient to overcome Malthusian trap and we need two prerequisites i.e., ample availability of productive employment and the capability to make use of available technologies and India is lacking on both fronts. Even before the Covid-19 pandemic hit, unemployment levels in India had hit a 45-year high and the troubled scenario of education and skills is evident from the Pratham surveys. Recently, the pandemic has worsened the situation and the possibility of India falling into a ‘middle-income trap’ are higher than the chances of reaping a demographic dividend. Hence, India’s chances of levering upon its demographic dividend are soon becoming obscure.
Why you should read this article?
- To understand the concept of demographic dividend and the current status of India?
- To understand how India’s chances of levering upon its demographic dividend will become obscure and how COVID-19 will impact present working generation.
- To understand the concept of ‘middle income trap’ and how India is falling in this trap?
Waste-Water Treatment: Seechewal Model
Present Situation:
- Nearly 70% of India's sewage is untreated and is dumped in rivers, seas, lakes and wells, polluting three-fourths of the country's water bodies.
- This causes lot of health issue like rise of water borne disease like typhoid, jaundice etc
About Seechewal Model:
- The method has been devised by one of the state’s leading environmentalist, Sant Balbir Singh Seechewal to treat, recycle and reuse wastewater.
- The water from the sewerage system is collected in a pond. A filter-mash is used to remove objects floating on the surface of water. Then the polluted water is taken into three separate wells.
- In the first well the silt from the sewerage is removed. In the second, fats, oil and ghee are taken away. The third well transfer the cleaned water into the main pond. The water collected in the pond is cleaned with sun rays. A motor pump is installed to lift the treated water to send it to fields for irrigation.
Outcome:
- It has solved the problem of sewage disposal and also provided a pond of treated water for fishing, vegetable cultivation
- It has helped in recharging of groundwater and saves expenditure of farmers and brings more profit to them
- It promotes organic farming and can save the natural resources and ecology of earth if adopted honestly.
- It has evolved community sustained processes for water management and strengthened community collectives.
Where can this case study be used:
- Innovative method to treat wastewater, case study for recharging of ground water, save the precious water resource.
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.