Tuesday, 16th February 2021
Rules on geospatial data, maps liberalized
In News
The Department of Science and Technology has announced sweeping changes to India’s mapping policy, specifically for Indian companies.
Guidelines
· There shall be no requirement for prior approval, security clearance, license or any other restrictions on the collection, generation, preparation, dissemination, storage, publication, updating and/or digitization of Geospatial Data and Maps within the territory of India.
· Individuals, companies, organizations, and Government agencies, shall be free to process the acquired Geospatial Data, build applications and develop solutions in relation to such data and use such data products, applications, solutions, etc by way of selling, distributing, sharing, swapping, disseminating, publishing, deprecating and destructing.
· Self-certification will be used to convey adherence to these guidelines.
· There shall be a negative list of sensitive attributes that would require regulation before anyone can acquire and/or use such attribute data.
· This will be applicable to Indian Entities, whether in Government or outside. While Foreign companies and foreign owned or controlled Indian companies can license from Indian Entities.

Significance of the reforms
· India currently relies heavily on foreign resources for mapping technologies and services. It will significantly boost innovation in the country and greatly enhance the preparedness of the country for emergency response.
· Sectors spanning agriculture, finance, construction, mining and local enterprise; India’s farmers, small businesses, startups and corporations alike stand to gain tremendously from the application of innovative technologies based on modern geospatial data technologies.
· It would also help improve planning and management of resources.
· Emerging vibrant initiatives such as Digital India, Smart Cities, logistics and urban transport require a leap forward in mapping with greater depth, resolution and precision. Accurate geospatial data are crucial for national infrastructure projects such as linkages of rivers, creation of industrial corridors, and deployment of smart power systems.
10 biotech clusters unveiled to boost research ecosystem
In News
Centre on Monday announced setting up of 10 biotech URJIT (University Research Joint Industry Translational) clusters. Major cities having Universities, research institutions, start-up hubs and industries will get such clusters.
Purpose
· It seeks to establish India as a bio-manufacturing hub and create a strong research ecosystem in the country.
· To synergise resources between research labs and industries, forming umbrella structures for better coordination among R&D institutions.
· It will focus on identified national priority thrust areas under National Research Foundation (NRF).
· Each URJIT cluster will be established in a way that they will serve one of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) through frontier research.
· It will promote and ensure seamless translation of knowledge from “laboratory to market”.
About National Research Foundation (NRF)
· The NRF, will be governed by a board appointed by the PM, and consist of accomplished and eminent researchers and professionals.
· It will build on existing national strengths in research and innovation, and fill gaps in the current research and education ecosystem.
· The NRF as an autonomous body envisaged to support researchers working across several streams of science & technology with special focus on universities.
Government to set up digital intelligence unit to tackle pesky calls, financial frauds
In News
In order to ensure quick time-bound action in dealing with financial fraud-related complaints, a new nodal agency known as the Digital Intelligence Unit (DIU) is expected to be set up.
Rationale for setting up of the Digital Intelligence Unit
● Increase in incidents of financial fraud - Financial frauds by sending pesky messages and promising loans have increased. There have been increased incidents of mobile and internet subscribers being duped in the name of job portals, online shopping and digital marketing. Since the beginning of the lockdown with increased adoption of work from home there has been an increase in phishing attacks.
● Curbing fraudulent activities involving use of telecom resources - Special strategies are needed to block the telecom operations due to the rising concerns of increased fraudulent activities from areas like Jamtara and Mewat involving usage of telecom resources.
Main function of the Digital Intelligence Unit
● Coordination with various law enforcement agencies - The main function of the DIU will be to coordinate with various law enforcement agencies, financial institutions and telecom service providers in investigating any fraudulent activity involving telecom resources. In case of financial fraud-related complaints, quick time-bound action will help in reducing such menace.
● Fraud Management and Consumer Protection - A service area level, Telecom Analytics for Fraud Management and Consumer Protection (TAFCOP) system will also be created.
Special Series – Budget, Survey and Finance Commission
Topic 10 - Empowering Local Governments:Recommendations of Fifteenth Finance Commission
In News
The Finance Commission has granted Rs 4,36,361 crore from the central divisible tax pool to local governments, both rural and urban, for 2021-26.
Local Self-Government in India
· In 1992, the enactment of the 73rd and 74th Amendments to the Constitution led to emergence of formal decentralised governance in India with constitutional status to the Panchayats and urban local bodies.
· India had 262,771 elected rural local bodies and 4,657 urban local bodies in 2017. The rural bodies implement around 70% of India’s rural development programmes with an annual budget over Rs 2 lakh crore.
Role of Finance Commission (FC) in Empowering Local Bodies
· The FC is a constitutional body under Article 280 for centre-state financial relations. 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendments broadened the role of FC under Article 280.
· FC is mandated to recommend the measures needed to augment the Consolidated Fund of a State to supplement the resources of the panchayats and municipalities based on the recommendations of the SFC.
· It has been one of the biggest sources of funding for local bodies due to weak devolution of financial resources by the states and also due to weak mobilisation of their own resources. E.g., In 2017-18, Municipal own revenue stood at 0.43% of GDP, lowest since 2010-11.
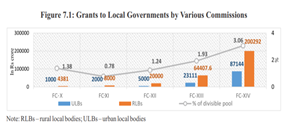
· Grants recommended by successive Finance Commissions in absolute terms have been growing (Figure 7.1). Except for the FC-XIII, all the previous Commissions recommended such grants in absolute terms and not as a proportion of the divisible pool.
o The divisible pool is that portion of gross tax revenue which is distributed between the Centre and the States. The divisible pool consists of all taxes, except surcharges and cess levied for specific purpose, net of collection charges.
Recommendations of Fifteenth Finance Commission
· Total grants to local bodies will be Rs 4.36 lakh crore (a portion of grants to be performance-linked) including: (i) Rs 2.4 lakh crore for rural local bodies, (ii) Rs 1.2 lakh crore for urban local bodies, and (iii) Rs 70,051 crore for health grants through local governments.
· The health grants for: (i) conversion of rural sub-centres and primary healthcare centres (PHCs) to health and wellness centres (HWCs), (ii) support for diagnostic infrastructure for primary healthcare activities, and (iii) support for urban HWCs, sub-centres, PHCs, and public health units at the block level.
· Grants to local bodies (other than health grants) will be distributed among states based on population and area, with 90% and 10% weightage, respectively.
· Conditions for availing these grants (except health grants): (i) publishing provisional and audited accounts in the public domain and (ii) additionally for ULBs, fixation of minimum floor rates for property taxes by states and improvement in the collection of property taxes.
· No grants will be released to local bodies of a state after March 2024 if the state does not constitute State Finance Commission and act upon its recommendations by then.
· Out of the total grants earmarked for Panchayati raj institutions (PRIs), 60% is earmarked for national priorities like drinking water supply and rainwater harvesting and sanitation, while 40% is untied and is to be utilised at the discretion of the PRIs for improving basic services.
· Differentiated approach in allocation of grants to ULBs.
o Urban local bodies have been categorised into two groups, based on population, and different norms have been used for flow of grants to each, based on their specific needs and aspirations.
o Basic grants are proposed only for cities/towns having a population of less than a million. For Million-Plus cities, 100 per cent of the grants are performance-linked through the Million-Plus Cities Challenge Fund (MCF).
o Further, grants have also been recommended for incubation of new cities.
Other noteworthy aspects of 15th FC recommendations
· Under the 14th FC, grants for local bodies included only the village Panchayat, excluding the block and district panchayats. It also excluded the village Panchayats in areas under the Fifth and Sixth Schedule of the Constitution. Similarly, for ULBs, it didn’t make any distinctions based on population and geographical sizes. The cantonment boards in urban areas were also excluded from grants.

o The 15th FC has included all levels of rural panchayats and also the panchayats in scheduled areas as mentioned above, besides cantonment boards.
· In view of the fast pace of urbanisation and future needs of the cities to act as engines of growth, the Fifteenth FC Recommendations will lead to the ratio of inter se distribution of the grants recommended for rural and urban local bodies gradually moves from 67.5:32.5 in 2020-21 to 65:35 in 2025-26.
Model Question – Highlight the role of Finance Commission (FC) in empowering local bodies. In this context, mention some of the important recommendations of 15th FC.
Topic 11 - Healthcare Sector Part 2
Context: Both Budget and 15th Finance Commission had given special emphasis on health sector this year as it has acquired urgency in the context of the Covid-19 pandemic.
Facts related to Indian healthcare sector
1. Health Outcomes:
· According to the National Health Profile 2018-19:
o The estimated birth rate declined from 25.8(2000) to 20.4 (2016) per 1,000 population while the death rate declined from 8.5 to 6.4 per 1,000 population over the same period.
o The natural growth rate declined from 17.3 (2000) to 14 per 1,000 population in 2016.
o The long-prevailing urban-rural divide in institutional births has largely been bridged with 75 per cent of rural births now supervised as compared to 89 per cent in urban areas.
o Life expectancy at birth has increased to 68.7 years in 2012-16.
· Health indicators from NFHS-5 (2019-20) shows that,
o Total Fertility Rate (TFR) has reduced sharply from 3.6 in 1991 to 2.2 in 2018.
o Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR) was 113 per 1,00,000 live births for the period 2016- 2018.
o Under Five Mortality Rate (U5MR) was 36 per 1000 live births in 2018.
· Poor Nutritional status: Childhood stunting rates of 38 per cent are among the highest in the world while 35.8 per cent of children are underweight and 58.6 per cent are anaemic as well.
· There are large inter-State variations in health outcomes like life expectancy, MMR, TFR, IMR, the rate of institutional deliveries as well as in nutritional outcomes as highlighted in the Health Index contained in NITI Aayog’s, ‘Healthy States, Progressive India’ report.
· Less focus on non-communicable diseases:
o 71 per cent of global deaths and about 65 per cent of deaths in India are caused by non-communicable diseases (NCDs) according to the report “Global Burden of Diseases 2019”.
o Between 1990 and 2016, the contribution of NCDs increased 37 per cent to 61 per cent of all deaths (National Health Portal).
2. Health Infrastructure:
· India is estimated to have roughly 1.4 beds per 1,000 populations much lower than in China (4 per 1,000); Sri Lanka, UK and the USA (3 per 1,000).
· PHCs and CHCs in rural areas have significant shortfalls, ranging from 23 per cent for sub centres to 28 per cent for PHCs to 37 per cent for CHCs.
· The doctor to population ratio in India is 1:1,511 against the WHO norm of 1:1,000 and the nurse to population ratio is 1:670 against the norm of 1:300, as per the MoHFW.
3. Public Health Spending:
· In India the combined public expenditure on health is only 1% of GDP.
· In 2018-19, States' spending on the health sector on an average, was only 5.18% against goal of at least 8% of their respective budgets by 2020 in The National Health Policy 2017.
· Expenditure on primary health is only 53 per cent against target of 2/3rd by 2020 in NHP 2017.
Recent Steps taken by 15th FC and Union Budget
· 15th FC recommends unconditional grants-in-aid support to the health sector of about 0.1 per cent of GDP to be provided which will cover health grants to the local governments for urban HWCs, PHCs, CHCs, grant for critical care hospitals and grant for States for building public health laboratories, for training of the allied healthcare workforce.
· Union Budget 2021-22 has announced –
o Supplementary Nutrition Programme and the Poshan Abhiyan will be merged to form a new Mission Poshan 2.0, which shall adopt an intensified strategy to improve nutritional outcomes across 112 Aspirational Districts.
o The Pneumococcal Vaccine, a Made in India product, is presently limited to only 5 states will be rolled out across the country. This will avert more than 50,000 child deaths annually.
o PM AtmanirbharSwasth Bharat Yojana to strengthen health systems will be launched. It will develop the capacities of primary, secondary and tertiary care health systems, strengthen existing institutions and create institutions to cater to detection and cure of emerging diseases.
Steps needed to improve Healthcare system
· Health spending by States should be increased to more than 8 per cent of their budget by 2022.
· Primary health expenditure should be increased to two-thirds of the total health expenditure of the state by 2022.
· Public health expenditure of Union and States together should be increased to reach 2.5 per cent of GDP by 2025.
· Finance commission further recommends that:
o Union Government should shift the focus of CSS and transfers towards outcomes.
o To eliminate the inter-State disparity, Union government should constitute an All India Medical and Health Service.
o A certain degree of specialisation in MBBS course should be included in the curriculum and encourage AYUSH as an elective subject for medicine undergraduates.
o Measures should be taken to assign a larger role for nursing professionals.
Hope Mission
· It is the first Arab interplanetary mission.
· The objective of the mission is to collect data on Martian climate dynamics and help scientists understand why Mars' atmosphere is decaying into space.
· The overall life of UAE’s Mars mission is around one Martian year, which is about 687 days on Earth.
· With this, UAE becomes the fifth entity to reach the Red Planet, joining NASA, the Soviet Union, the European Space Agency and India.
Arjun Main Battle Tank
· Arjun Main Battle Tank (AMBT)is an indigenously designed, developed and manufactured in India as a part of the multi-laboratory programme of DRDO.
· The project to manufacture was initiated by DRDO in 1972.
· The first batch was first inducted into the Indian Army in 2004.
· The upgraded MK 1A version has 54.3 %indeginous content against the 41 % in the earlier model.
Bridge the geopolitical distance with Russia – Hindustan Times
Essence- Foreign secretary’s forthcoming visit to Moscow is a good occasion to examine the relevance of Indo-Russian ties in a world of changing geopolitical equations, greatly accelerated by the Covid-19 pandemic. The year 2020 saw several trends that impacted both India and Russia. Against this backdrop, this article identifies steps to intensify contacts and diversify areas of cooperation with Russia and suggests active engagement of Russia in the Indo-Pacific to ensure a multi-polar Euro-Asian supercontinent.
Why you should read this article?
• Identify recent geopolitical trends such as the sharpening rivalry between United States (US) and China, the India-China border tussle, the continuing decline in ties between the West and Russia, and the change of guard in Washington and their consequent impacts.
• Learn about traditional areas of cooperation between India and Russia such as weapons, hydrocarbons, nuclear energy and diamonds as well as new sectors of economic engagement like mining, agro-industrial, and high technology, including robotics, nanotech and biotech, connectivity projects, etc.
• Know about cooperation between India and Russia on regional and global issues such as closing the gap on Afghanistan, early finalisation of the Comprehensive Convention on International Terrorism and Russia’s supports for India’s candidacy for permanent membership of a reformed United Nations Security Council and of the Nuclear Suppliers Group.
Policy must heed climate resilience: Embracing climate adaptation & resilience – Financial Express
Essence - Recent disasters like COVID 19, drought, severe heat/cold wave, flash floods and most recent 2021 glacial burst or avalanche in Uttarakhand all are pointing to prolonged climate change effect. Such disruptions are expected when nature’s own balance repeatedly gets disrupted. The Climate Risk Index (2020) tagged India as the fifth-most vulnerable country in the world. Several national & international agreements are made to operationalise & implement adaptation projects. But several challenges continue to beset the progress to build resilience & risk reduction. Article suggests some policy pointers to combat climate vulnerability & associated risk but it says, achieving a state of ‘coherence’, characterised by reduces stress & increased resilience, is the key to better tomorrow.
Why you should read this editorial?
· To get an idea about the impact of disruption in nature’s own balance.
· To understand how vulnerable India is to climate change & what steps have been taken by the government.
· To know what steps have been taken at international level.
· To understand what policies should contain to combat climate vulnerability & associated risks.
Democracies must modernise their laws to protect freedoms in the era of technological transformation – Indian Express
Essence - Editorial is analysing the need of world’s democracies coming together to discuss global digital governance.
Why you should read this editorial?
• To know challenges tech behemoths poses in domestic and international sphere like concentration of economic power, disinformation, the rise of digital geopolitics.
• To know steps taken by countries like China, Australia for finding right path to digital salvation.
• To understand the political clout & thereby influence of big tech giants from elections to legislative processes.
• To understand the need of tackling the overarching position of these big companies & preserve liberal domestic & world order for giving space to innovation.
Dilli Annashree Yojna: Food Security for the vulnerable in Delhi
• National Capital Territory of Delhi has many vulnerable households due to a large migratory population who are not able to avail benefits under existing food security schemes like Targeted Public Distribution System (TPDS), Annapoorna Yojana or Antyodaya Anna Yojana.
• DilliAnnashreeYojna (DAY) is using Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) mechanism to provide food security to households in Delhi which were left uncovered by existing food security schemes.
• The eldest woman of a vulnerable household is made the beneficiary, thus providing this scheme a gender-sensitive edge.
• Since its implementation, the scheme has covered more than 1,00,000 families in Delhi.
• Women beneficiaries felt that cash served the dual purpose of food security along with social security in case of illness, especially in occupationally vulnerable families.
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.