Friday, 19th February 2021
Govt plans new platform to flag online posts
In News
With a view of amending the Information Technology Act, 2000, the Centre is considering an alternative system for faster adjudication of cases related to cyberspace.
Purpose of creating a new platform
In the present scenario, complainants can either challenge the content they find offensive in the courts or report it to intermediaries, if any are involved, to address their concerns.
· Alternative forum to raise cyber issues - The idea is to provide people,who do not want to approach courts or the police regarding violative online content, with an alternative forum to raise these issues.
· Need to ensure time-bound action - There is a need for an urgent time frame for action in cases involving women’s safety and cyber frauds. The ideal time frame for action would be 48 hours so that the content can be contained.
· Need to revamp cyber-security infrastructure – Government has been receiving a far greater number of complaints in the recent years. There is a need for strengthening of cybersecurity, the provisions relating to intermediaries are also a data protection law. The new platform to flag online posts is a step in that direction.
|
Amendments to the Information Technology Act Context In December 2018, to crack down on spread of fake news and rumours circulated on online platforms, the central government has proposed stringent changes under the draft of Section 79 of the Information Technology (IT) that govern online content. The changes proposed by the central government are aimed at curbing fake news or rumours being spread on social media and check mob violence ahead. What are the new changes proposed? · Social media platforms will require to break end-to-end encryption in order to ascertain the origin of messages. · Social media platforms to deploy technology based automated tools or appropriate mechanisms, with appropriate controls to identify or disable access to unlawful information content. · Social media platforms will need to comply with the central government within 72 hours of a query. · There should be a ‘Nodal person of Contact for 24X7 coordination with law enforcement agencies and officers to ensure compliance. |
Government clears signing of India-Mauritius free trade pact
In News
The Union Cabinet has approved the Comprehensive Economic Cooperation and Partnership Agreement (CECPA) between India and Mauritius, the first such agreement with an African country.
About the CECPA
● The pact is a kind of a free trade agreement, that will cover 310 export items for India. Mauritius will benefit from preferential market access into India for 615 products.
● The pact also deals with issues related to trade in goods, liberalising norms to promote services trade, rules of origin, technical barriers to trade, sanitary and phytosanitary measures, etc.
|
Importance of Mauritius to India
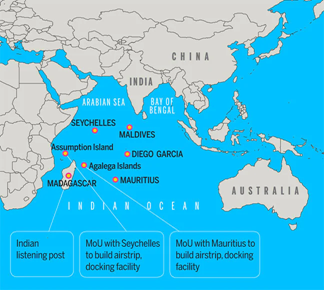
Strategic Significance ● Mauritius is part of India’s security grid including Coastal Surveillance Radar (CSR) station of Indian Navy’s National Command Control Communication Intelligence network. Economic Opportunities ● Mauritius was also the second largest source of foreign direct investment into India in 2019-20, accounting for around $8.24 billion (about Rs 57,785 crore) for the year. ● Mauritius can facilitate a number of Indian commercial activities in the southwestern Indian ocean — as a banking gateway, the hub for flights to and from Indian cities and tourism. Pivot of India’s Island Diplomacy ● The island nations of the Indian Ocean hold immense strategic value in shaping the geopolitical contours of the region and ensuring maritime security and order. ● The islands of Socotra (Yemen), Madagascar, Mauritius, and the Seychelles have gained strategic importance, standing at the crossroads of Europe, Africa, and South Asia. |
Draft “National Policy for India’s Blue Economy - 2020”
In News
Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) has invited suggestions on the Draft Blue Economy Policy for India.
India’s geographical benefits vis-à-vis Blue Economy
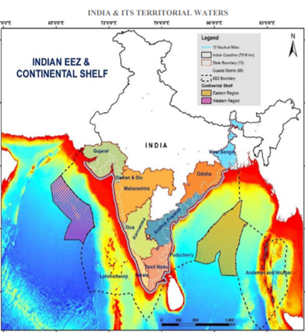
· India has a coastline of nearly 7500 kilometers with 9 coastal states and 1,382 islands.
· Nearly 199 ports, including 12 major ports handle nearly 1,400 million tons of cargo each year, as 95% of India’s trade by volume transits by sea.
· India’s Exclusive Economic Zone of over 2 million square kilometers has significant living and non-living recoverable resources such as crude oil and natural gas.
· Coastal economy sustains over 4 million fisherfolk and coastal communities.
India’s progress on harnessing Blue Economy
· India has launched Sagarmala for port led development.
· MoES has joined the United Nations on the “Clean Seas Programme” to fight marine pollution, which is also a part of SDG-14.
· MoES has also signed contracts with the International Seabed Authority for deep ocean exploration of minerals (Ploymetallic Nodules and Hydrothermal Sulphide) in Indian Ocean.
· India is connecting island territories to submarine optical fiber cables to ensure high-speed broadband connectivity there.
o In this context, Seychelles-Singapore-Samoa (SSS) axis becomesan important emerging economic and strategic axis that spreads from the East Coast of Africa to the Western Pacific Ocean. This axis should form the basis of a robust Blue Economy Policy for India.
Priorities for Blue Economy Policy
· A framework for proper measurement of Blue Economy activities and their contribution to the national income
· Spatially oriented planning along with scientific assessment of Ocean resources and their - sustainable use
· Investment in financial capital, physical capital, natural capital and human capital to harness the potential of the Blue Economy and optimize GDP and employment growth.
· Ensuring welfare, safety and livelihood of fishermen in the coastal areas
· Innovation to ensure zero waste, low carbon technologies that yield economic dividend for large sections of the population.
· Ocean security measures and balanced international engagements.

Key Features of Draft Policy
· Draft defines Blue economy. India’s Blue Economy can be defined as a subset of the national economy comprising of the entire system of ocean resources and man-made economic infrastructure in marine, maritime and the onshore coastal zones within India’s legal jurisdiction, which aid in the production of goods and services and have clear linkages with economic growth, environmental sustainability, and national security.
· It is in line with the Vision of New India by 2030 which highlighted blue economy as one of the ten core dimensions for national growth.
· It recognizes seven thematic areas (refer to infographic).
· National Blue Economy Council (NBEC):Apex body to integrate planning process between various stakeholders.
· National Blue Economy Fund (NBEF) to implement various initiatives under NBEC would be set up.
· Expand the approach and implementation of Swachh Bharat to the concept of ‘Swachh Prithvi, Swachh Sagar’ to fight marine pollution. Plastic Elimination and National Marine Litter Policy can be developed.
|
Evolution of the Concept of Blue Economy- Extra Information · The economic philosophy of the Blue Economy was first introduced in 1994 by Professor Gunter Pauli at the United Nations University. The concept was based on developing more sustainable models of development including concepts of engineering based on “no waste and no emissions”. · Third Earth Summit Conference - Rio+20 in 2012- It focused on expanding the concept of Green Economy to include Blue Economy. · United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goal 14 sought to “conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources for sustainable development” as a guiding principle for global governance and use of ocean resources. · Countries like Australia, Brazil, U.K., U.S., Russia, and Norway have developed dedicated national ocean policies. Also, Canada and Australia have enacted legislation and established hierarchal institutions regarding Blue Economy targets. · India’s SAGAR vision: In 2015, India unveiled its strategic vision for the Indian Ocean i.e., Security and Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR). |
Model Question -Given India’s geography and location, the proposed roadmap for evolving a Blue Economy Policy would be a crucial step towards unlocking the potential of economic growth and welfare. Elaborate.
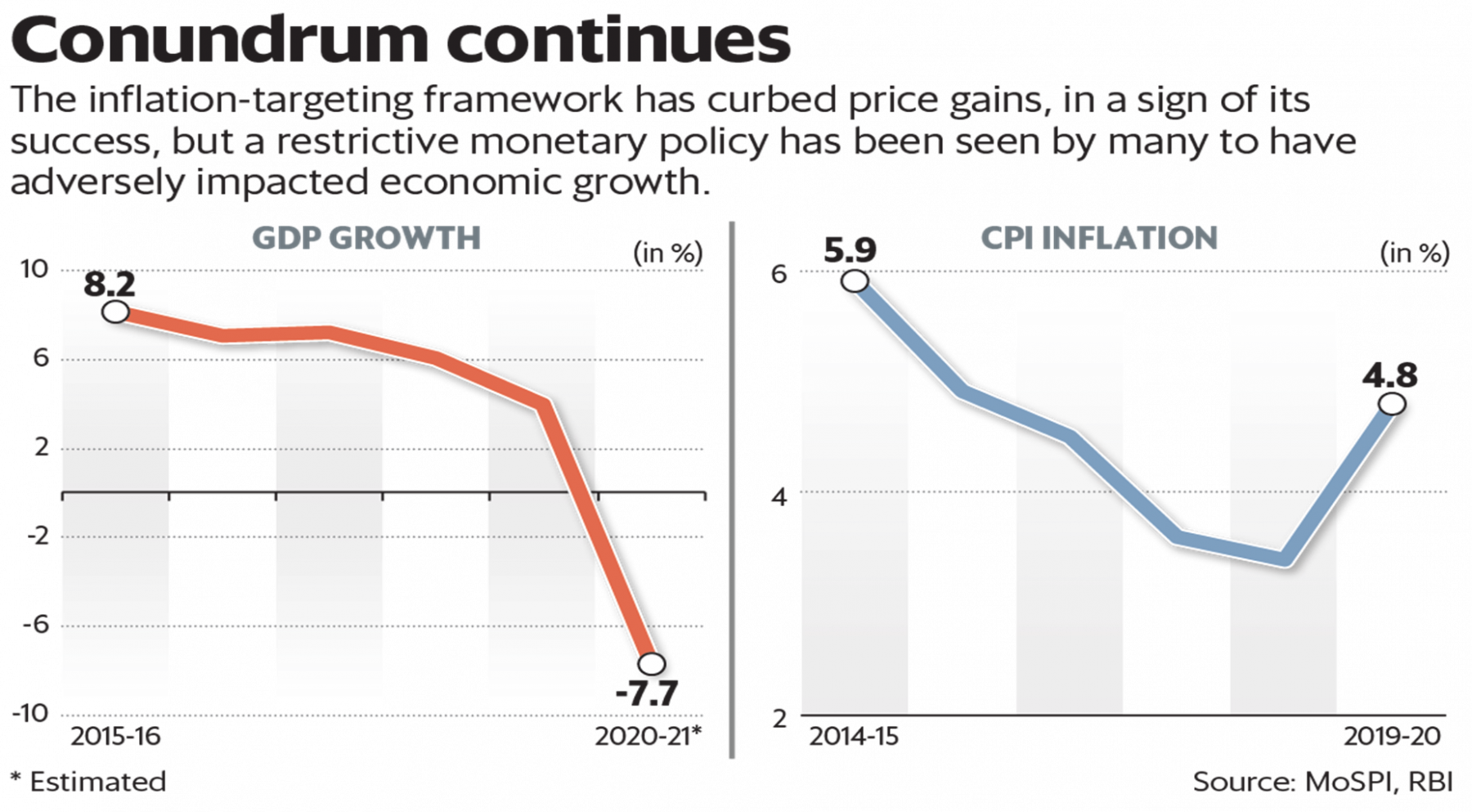
India's inflation target band up for review
Context
The amendment of the Reserve Bank of India Act in 2016 allows the government to set the inflation target, in consultation with RBI, once in every five years. This is up for review for the first time. The law provides for only a review of the inflation target, and not the framework itself.
Past Mechanism
· Earlier RBI governor was the sole decision maker with regards to monetary policy decisions. He was mandated to decide repo rates and use monetary policy instruments keeping in mind the various macroeconomic factors like inflation, exchange rate, growth and employment in the country.
· In India, the consideration of inflation-targeting was necessitated by six years of high inflation between 2008 and 2013.
Flexible Inflation Targeting
· In 2015, the Centre and RBI signed a monetary policy framework, setting out an explicit, but flexible, inflation target for the central bank which was given legal basis later.
· RBI was tasked with bringing consumer price inflation(CPI) within a band of 2%-6% with 4% as the mid-point for 2016-17 and subsequent years.
· This provided for a six-member Monetary Policy Committee, chaired by the RBI governor only policy tool of repo rate to hold inflation within the target. MPC has a review meeting every two months. Its mandate is to bring ‘price stability keeping in mind growth’. The decision of the Monetary Policy Committee is binding on the RBI.
Need for wider inflation target band
· The intent behind proposing a wider band is that the RBI should also focus on reviving growth. RBI can’t be saddled with a rigid inflation target at a time when pushing growth is a priority due to Covid induced economic recession.
· Inflation in India have been driven by factors beyond the central bank’s control: costlier food items, broken supply chains due to a strict lockdown, and rising retail fuel prices. (CPI inflation, has weightage of around 46 per cent for food inflation).
Need for status quo in the inflation target band
· Anchoring inflation expectations is the RBI’s primary task. A wider inflation target band will be meaningless as it will dilute RBI’s effectiveness in setting monetary policy.
· Expansionary policies instituted following the 2008-09 crisis fuelled runaway inflation later which suggests RBI to be cautious with allowing higher repo rate. A long five-year fiscal consolidation path to 4.5 per cent fiscal deficit by 2025-26 will already create inflationary pressure.
· The deterioration in India's financials due to Covid, could result in a rating downgrade, which has the potential to trigger FII outflows from the country. This could depress the currency value, which means imported inflation.
· A 4% inflation target for the Indian Monetary Policy Committee is just ideal as it matches with the average trend inflation measured since 2014, as per the RBI’s research paper.
Way forward
Price stability is the foundation on which the economy can strive to reach its potential in a virtuous cycle of higher financial savings and investment; reduced uncertainties for firms in investment and wage decisions; and increased external competitiveness.
A review of the inflation target should be empirically sound and should take into account the global inflation outlook. While there is no consensus on a threshold level of inflation beyond which it turns adverse for growth prospects, the reasons for modifying the target must be documented and fully assessed.
Money Bill
● For a Bill to be considered as a Money Bill, it must only contain provisions related to taxation, borrowing of money by the government, expenditure from or receipt to the Consolidated Fund of India, and matters that are incidental to such taxation, expenditure and related subjects. For example, the Finance Bill, which only contains provisions related to tax proposals, would be a Money Bill.
● In the event a proposed legislation contains other features, ones that are not merely incidental to the items specifically outlined, such a draft law cannot be classified as a money bill.
● Article 110 further clarifies that in cases where a dispute arises over whether a bill is a money bill or not, the Lok Sabha Speaker’s decision on the issue shall be considered final.
Delimitation Commission
· Also known as Boundary Commission, the Delimitation Commission is appointed by the President and works in collaboration with the Election Commission of India.
· Delimitation Commissions have been constituted 4 times– in 1952, 1963, 1973, and in 2002 under the Delimitation Act.
· It determines the number and boundaries of constituencies to make population of all constituencies nearly equal and also identifies seats reserved for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes, wherever their population is significant.
· It is a high-power body whose orders have the force of law and cannot be called in question before any court.
· These orders come into force on a date specified by the President which are laid before the House of the People and the State Legislative Assembly concerned, but no modifications are permissible therein by them.
COVAX
· COVAX global vaccines facility is a plan designed to pool funds from wealthier countriesand non-profits to develop a Covid-19 vaccine and distribute it equitably around the world.
· Its aim is to deliver 2 billion doses of effective, approved Covid-19 vaccines by the end of 2021.
· The plan is led by the WHO, along with the Gavi vaccine alliance, and the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI).
· COVAX is part of Access to Covid-19 Tools (ACT) Accelerator, that works to ensure that vaccines, treatments, diagnostic tests and other healthcare resources are broadly available to combat the coronavirus pandemic.
Building from below – Indian Express
Essence - The Fifteenth Finance Commission(FFC) has recommended grants of Rs. 4,36,361 crore from union government to local governments for 2021-26, which is a 52 % rise from previous grant (2015-20). Since local governments are closest to people at grassroots level & provide critical civic amenities, it becomes more important to provide measures of effective resource mobilisation, which remain a critical challenge until now. Recommendations of FFC took into consideration the rapid urbanisation& allocations are directed towards incubation of new cities, institutional & technological innovation, shared municipal services model, performance-based allocation, etc.
Why you should read this article?
· To understand the underlying reasons for inadequate allocations to local governments until now.
· To know prioritisation of FFC among various heads like plugging gaps in primary health care, sanitisation, innovation in urban governance.
· To know about the criterion used for allocation of grants among states.
· Editorial is providing insights into innovative Million-plus challenge fund, a 100% outcome based grant.
Budget is not lacking in green signals – Hindu BusinessLine
Essence - Union Budget is an important document in the sense that it gives an insight into the working priorities of the government. In this context, this article provides an insight of the environmental perspective in the Union Budget.
Why you should read this editorial?
· To know what announcements have been made in the Union Budget regarding environment.
· It has identified certain areas where we need to focus upon going forward so that the targets identified are fulfilled - capital, R&D, regulation etc.
· Finally, in brief, it talks about the role of the private sector as well.
Large hydro projects risk Himalayan communities – Hindustan Times
Essence- Recent tragedy in Uttarakhand has started a debate on Himalayan dams & other developmental projects and associated risks on environment & people of the region. Article mentions how status of Renewable energy (by Central government) to all hydropower projects signals a grave risk for all Himalayan communities whose sole aim is to attract investment in this ecologically sensitive region. Article also discussed anticipated developmental benefits of energy transition & why public sector is still dominating in hydro sector.
Why you should read this article?
· To understand how status of Renewable Energy to all hydro power projects are grave risks to Himalayan Community.
· To know what are developmental benefits of energy transition & what are co-benefits.
· Article argues how government is more focused on reducing the financial risk instead of examining the reasons of ‘geological surprises’.
Integrated Basin Development and Livelihood Promotion Program: Fostering a spirit of entrepreneurship in Meghalaya
· Meghalaya is rich in important minerals such as coal, limestone, clay and sillimanite. However, despite such natural abundance, almost half the population of the state lives below poverty line.
· In order to reduce poverty, government provided various goods and services free of cost to target beneficiaries. However, this approach made beneficiaries become dependent on government
· The paradoxical existence of such high poverty amidst plenty led the Meghalaya government to rethink its development strategy
· Government came up with Integrated Basin Development and Livelihood Promotion Programme
· The programme also seeks to promote Knowledge-Centric Development through capacity building, particularly in natural resource management and entrepreneurship.
· Government used concept of Mobile Multi-Facility Centre to create awareness of the programme.
· The programme has facilitated holistic development via Inclusive Growth, Livelihood Promotion and Environmental Conservation.
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.