Thursday, 13th May 2021
National Task Force for transparent oxygen allocation
In News
The Supreme Court has constituted a 12-member National Task Force to streamline and ensure the effective and transparent allocation of liquid medical oxygen on a scientific, rational and equitable basis to States and Union Territories fighting COVID-19.
About the News
- The Task force: The Supreme Court has put in place a 12-member National Task Force (NTF), including top experts and doctors from across the country, to facilitate a public health response to the pandemic based on scientific and specialised domain knowledge.
- The Court ordered the Task Force to commence work immediately, dealing with oxygen issues expeditiously within a week. Its term shall be six months initially, with its recommendations to be submitted to the government as well as the Court.
- The need for the Task Force: The SC expressed the need for an effective and transparent mechanism within the Union government for the purpose of allocating medical oxygen to all states and UTs for use during the Covid-19 pandemic.
- Background: The order came on a plea by the Centre challenging the contempt notice issued to it by the Delhi High Court over medical oxygen supply to Delhi.
- The apex court had expressed its dissatisfaction at the Centre’s earlier “oxygen-for-bed” As per the SC, the earlier arrangement was based on calculating the allotment of oxygen based on the number of ICU/non-ICU beds. But formula did not take into consideration the fact that many COVID-19 patients in dire need of oxygen do not get beds or were confined to home care.
- Also, different States may peak during different time and their needs for oxygen may vary.
- The SC clarified that till the NTF has submitted its recommendations, the Centre shall continue with the present practice of making allocations of oxygen (as modified by the orders of this Court or the orders of the High Courts as the case may be).
- Similar Working Group: Since April, a nine-member government committee under DPIIT Secretary has been functioning to ensure adequate availability of medical oxygen in the wake of COVID-19 Pandemic. An Empowered Group-II (EG-II) also coordinates medical logistics.
What will the Task Force do?
- The Task Force would undertake an oxygen audit for formulating a methodology for the scientific allocation of oxygen to states and UTs (Union Territories). The Union Cabinet Secretary or a nominee of the official will serve as Convenor of the NTF.
- Leading experts in the country to work with it both as members and resource persons.
- Public health institutions, government facilities and private hospitals have to cooperate with the Task Force. It could form sub-groups of experts on a regional basis in the specialised areas of Infectious Disease Modelling, Critical Care, Clinical Virology/Immunology and Epidemiology/Public health.
- While the government will be taking the final decision, the experts will suggest ways to ramp up the production of oxygen and streamline the issues faced by each state. The experts will advise the government to ensure that oxygen is equally distributed to states as well as hospitals.
- Apart from oxygen, the NTF will review availability of essential drugs and medicines, and plan for emergencies, facilitate the use of technology to ensure optimal utilisation of available manpower, suggest incentives for medical staff, promote research and help sharing of best practices across the country.
Significance:
- Addressing Future requirements: The task force will take into account the likely course of the pandemic so that future requirements could be scientifically mapped and modulated in the light of experiences gained. It will provide inputs on a transparent and professional
- Inputs for Decision makers: Establishment of this task force will enable the decision makers to have inputs, which go beyond finding ad-hoc solutions to the present problems.
GeM took several steps for easy procurement of critical health equipment: CEO
In News
Public procurement portal GeM has implemented several steps for easing the procurement of critical health equipment like onboarding sellers of oxygen cylinders and concentrators.
About the News
- Dedicated platform: GeM created a dedicated page on its platform for medical and protective equipment like thermal scanners, biohazard bags and disinfectants to help the government fight the pandemic.
- Special categories in the marketplace: GeM has taken several urgent and targeted measures to ease the procurement journey for Covid-19 related goods and services. This includes the creation of several Covid-19 specific categories in the marketplace.
|
What is Government E Marketplace? ● GeM is the National Public Procurement Portal for providing procurement of goods and services for Central and State Government Organizations. ● It is an online, end-to-end Marketplace for open, efficient and transparent procurement of goods and services. ● It provides the tools of e-bidding, reverse e-auction and demand aggregation to facilitate the government users achieve the best value. What is GeM 4.0? ● Unified Public Procurement System: The Unified Public Procurement System is a better, unified and inclusive system. ● Market Enhancement Feature: This includes Ease of Payment through integration with banks. The bidding module has been redesigned and item wise bidding is permitted. ● Adoption of TRedDS (Trade Receivable Discounting System): The TReDS platform will provide bill discounting and access to working capital for MSMEs. |
Significance of the measure:
- Easing availability and search: As the country is fighting the second wave of the pandemic, the availability of the critical medical equipment through the GeM portal will provide the concerned departments with quick access to search and access of these devices.
- Provide transparency and ease of buying: The procurement of medical equipment through the GeM portal will help in ensuring transparency and ease of buying these equipments and it will also simplify the purchase procedures.
- Seller friendly dashboard: The use of the GeM portal will not only be beneficial for the government departments who are the buyers but also for the sellers as it will help them to monitor the supplies and payments. Moreover, the portal also provides the sellers with the option of dynamic pricing based on the prevailing market conditions.
Global Methane Assessment
In News
The ‘Global Methane Assessment: Benefits and Costs of Mitigating Methane Emissions’ report has been released by the Climate & Clean Air Coalition (CCAC) together with the United Nations Environment Programme.
|
The Global Methane Initiative · The Global Methane Initiative (GMI) is a voluntary, multilateral partnership that aims to reduce global methane emissions and to advance e abatement, recovery, and use of methane as a clean energy source. · GMI achieves this goal by creating an international network of partner governments, private sector members, development banks, universities and nongovernmental organizations to conduct assessments, build capacity, create partnerships, and share information to facilitate project development for methane reduction in GMI Partner Countries. |
Why do we need to reduce methane?
- A potent greenhouse gas: Methane, a short-lived climate pollutant (SLCP) with an atmospheric lifetime of roughly a decade, is a potent greenhouse gas, tens of times more powerful than carbon dioxide at warming the atmosphere. Methane’s atmospheric concentration has more than doubled since pre-industrial times and is second only to carbon dioxide in driving climate change during the industrial era.
- Ground-level ozone: Methane contributes to the formation of ground-level ozone, a dangerous air pollutant. Ozone attributable to anthropogenic methane emissions causes approximately half a million premature deaths per year globally and harms ecosystems and crops by suppressing growth and diminishing production.
- Alarming rate of increase: The atmospheric concentration of methane is increasing faster now than at any time since the 1980s. Current concentrations are well above levels in the 2° C scenarios. The Paris Agreement’s 1.5° C target cannot be achieved at a reasonable cost without reducing methane emissions by 40–45 per cent by 2030.
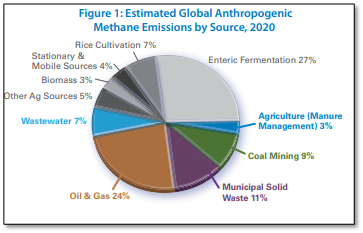
The Potential benefits of Methane reduction are:
- Save lives: Prevents approximately 1430 annual premature deaths due to ozone globally. Of those, 740 would have died from respiratory disease and 690 from cardiovascular disease.
- Increases crop production: Avoids losses of 145000 tonnes of wheat, soybeans, maize and rice ozone exposure every year. This is roughly equivalent to increased global yields of 55 000 tonnes of wheat, 17 000 tonnes of soybeans, 42 000 tonnes of maize, and 31 000 tonnes of rice annually for every million tonnes of methane reduced.
- Saves work hours: Avoids the annual loss of roughly 400 million hours of work, approximately 180 000 years, globally due to extreme heat. Employment within those sectors of the economy that are affected by heat exposure varies between genders, leading to disparities in the impacts for men and women that differ across countries.
- Monetary benefits: The global monetized benefits for all market and non-market impacts are approximately US$ 4 300 per tonne of methane reduced. When accounting for these benefits nearly 85 per cent of the targeted measures have benefits that outweigh the net costs.
- Accomplish SDGs: In addition to the benefits quantified here, methane reduction measures also contribute to multiple Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), including climate action (SDG13), zero hunger (SDG2), good health and wellbeing (SDG3). Additionally, they provide cost reductions and efficiency gains in the private sector, create jobs, and stimulate technological innovation.
Methane emissions reduction potential of different sectors
- Oil, gas and coal: The fossil fuel sector has the greatest potential for targeted mitigation. Readily available targeted measures could reduce emissions from the oil and gas sector by 29–57 Mt/yr and from the coal sector by 12–25 Mt/yr. Up to 80 per cent of oil and gas measures and up to 98 per cent of coal measures could be implemented at negative or low cost.
- Waste: Existing targeted measures could reduce methane emissions from the waste sector by 29–36 Mt/yr by 2030. The greatest potential is in improved treatment and disposal of solid waste.
- Agriculture: Existing targeted measures could reduce methane emissions from the agricultural sector by around 30 Mt/yr by 2030. Methane emissions from rice cultivation could be reduced by 6–9 Mt/yr. The targeted mitigation potentials from livestock are less consistent, ranging from 4–42 Mt/yr.
Measures to mitigate methane emissions
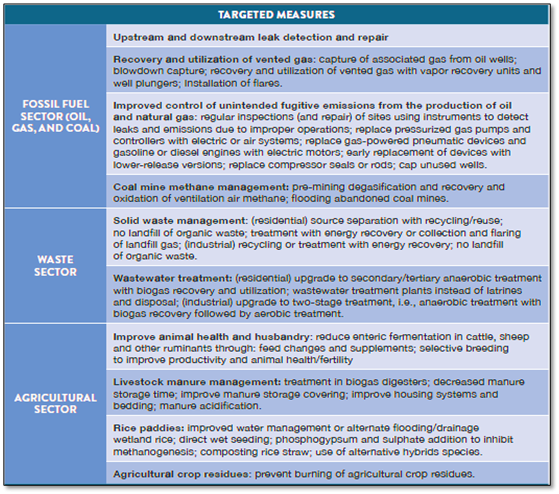
Conclusion
Urgent steps must be taken to reduce methane emissions this decade. Given the wide range of impacts from methane, the societal, economic, and environmental benefits of acting are numerous and far outweigh the costs. The existence of readily available, low-cost, targeted measures, and methane’s short-lived atmospheric lifetime means significant climate and clean air benefits can be achieved by 2030. To keep warming to 1.5° C, focused strategies specifically targeting methane emissions need to be implemented alongside substantial and simultaneous mitigation of all other climate pollutants including carbon dioxide and short-lived climate pollutants.
https://www.globalmethane.org/documents/gmi-mitigation-factsheet.pdf
Question: How does methane contribute to global warming? What measures that can be taken to reduce or mitigate methane emissions?
This Day in History - Rajya Sabha held its first session
On May 13, 1952, the upper house of the Parliament, Rajya Sabha held its first session. The creation of a Second Chamber was also in sync with the ideals of bicameralism. Today, the Rajya Sabha is an important part of the Indian Parliament, which provides the necessary deliberations on important matters of the nation along with the Lok Sabha. The first sitting of the Council of States had begun by the President's address for both the Upper and Lower House. This tradition still continues every year and after every general election.

Sources: https://rstv.nic.in/role-upper-house-parliament.html
https://www.indiatoday.in/education-today/gk-current-affairs/story/rajya-sabha-323350-2016-05-13
Image of the Day- Anole
This is image of a water anole present underwater. It has a partially formed bubble on its snout. These animals can re-breathe oxygen in these bubbles to extend their time underwater. Scientists have found tropical lizards that also “breathe” underwater this way, a first-of-its kind discovery. Some species of Caribbean and Latin American anoles, a type of lizard, can exhale air to create large, oxygen-filled bubbles that cling to their head. Several types of insects can carry air bubbles with them underwater. Some insects can survive indefinitely underwater by breathing through these bubbles. However, compared with lizards these insects have significantly lower metabolic rates, need less oxygen, and are smaller.
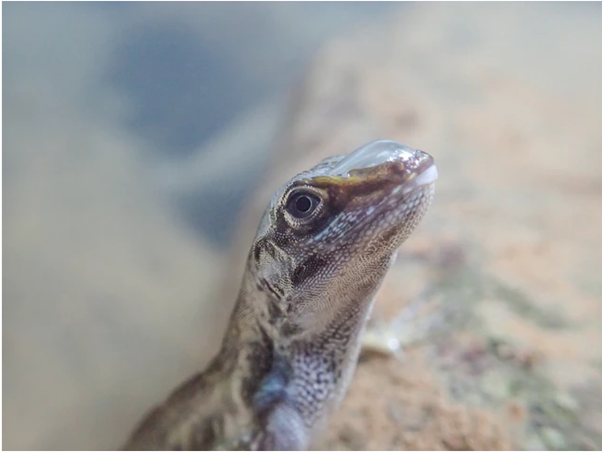

Source: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/animals/article/lizards-breathe-underwater-bubbles-anoles
Beema Bamboo
- Context: The Tamil Nadu Agricultural University (TNAU) has designed an ‘oxygen park’ with Beema Bamboo within its premises at Coimbatore.
- Oxygen Park is a unique public space designed for health and wellbeing in an environment.
- Beema or Bheema Bamboois a superior cloned variety of Bambusa balcooa, a higher biomass yielding bamboo species. It was developed by the conventional breeding method, devoid of scientific genetic modifications. It is thorn-less and sterile and thus, does not produce any seed.
- This species is one of the fastest-growing plants that grows about 1.5 feet/ dayunder tropical conditions. It does not die for several hundred years and hence can assure a permanent green cover.
- This bamboo’s calorific value is equal to that of coal. Cement industries use this bamboo species for their boilers and its fibres find use in the making of fabric and garments by the textile industries.
- It is a great carbon sink.

https://www.agriculture.com.ph/2019/05/15/beema-bamboo-health-enhancer-and-clean-energy-producer/
Moorhen Yoga Mat
- Context: A biodegradable and compostable yoga mat (Moorhen Yoga Mat) has been developed from water hyacinth in Assam.
- It is a hand-woven 100% biodegradable and 100% compostable mat developed from water hyacinth.
- The mat could improve the aquatic ecosystem of the wetland (Deepor Beel) through removal of water hyacinth and generate livelihood for indigenous communities.
- The ‘Moorhen Yoga mat’ is named after Kam Sorai(Purple moorhen, a resident bird of Deepor Beel Wildlife sanctuary).
- The initiative was supported by North East Centre for Technology Application and Reach (NECTAR), an autonomous body under Department of Science & Technology(DST), Govt. of India.
|
Water Hyacinth: · Water hyacinth is a type of invasive floating plant found in water bodies across the world. · These species block the sunlight and reduces the oxygen level in water systems, resulting in a disturbed ecosystem. · It has adverse impacts on irrigation, hydroelectricity generation, and navigation. Deepor Beel: · Deepor Beel (Beel means wetland in Assamese), located near Guwahati city, is considered one of the largest and the most important riverine wetlands in the Brahmaputra Valley of lower Assam. · It is one of the staging sites for migratory birds in India. It is an Important Bird Area (IBA) site (Birdlife International) and Ramsar site as well. |

Primary source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetailm.aspx?PRID=1715872
https://www.prakati.in/moorhen-yoga-mat-biodegradable-yoga-mat-made-by-6-young-girls-from-assam/
Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency Ltd (IREDA)
- Context: IREDA has been conferred with Green Urja Award.
- IREDA receives this award for being the leading public institution in financing institution for renewable energy this year by Indian Chamber of Commerce (ICC).
- It is a Mini Ratna Government of India enterprise under Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) engaged in extending financial assistance for setting up projects relating to new and renewable sources of energy and energy efficiency. Its motto is 'ENERGY FOR EVER'.

Primary source: https://www.psuconnect.in/company/indian-renewable-energy-development-agency-ltd/132
4th India-Swiss Financial Dialogue
- Context: The 4thIndia-Swiss Financial Dialogue was held virtually through video conferencing.
- The Dialogue covered collaboration on various financial aspects including investments, International Financial Services Centre Authority (IFSCA), National Investment and Infrastructure Fund (NIIF), FinTech and cross border financial services.
- Both the countries emphasized the importance of coordinated bilateral action on clean and resilient post-COVID world.
|
India-Switzerland Relations: · India’s policy of non-alignment and Switzerland’s traditional policy of neutrality has led to a close understanding between the two countries. · India-Switzerland Bilateral Investment Treaty (BIT) and India-EFTA (European Free Trade Association) Trade and Economic Partnership Agreement are under negotiation. · The Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC) is supporting the implementation of the CapaCITIES(Capacity Building for Low Carbon and Climate Resilient City Development) project in Indian cities. |

Primary source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1717793
Black marketing during the pandemic comes from longstanding, systemic flaws
Essence: Courts have passed strictures against hoarders and black marketeers. Across the country, there have been arrests for diversion, hoarding and black-marketing of remdesivir, oximeters and oxygen cylinders. This article while highlighting the instances of fake drugs and black marketing, points out to the legal provisions to counter them and their lack of enforcement.
Why you should read this article?
- Briefly know about the problems of fake and sub-standard drugs, hoarding and black marketing.
- Learn about the legal provisions under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act (DCA) and the powers of CDSCO (Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation) to tackle these problems.
- Understand the issues of inaction and lack of enforcement mechanism.
The best path towards doubling farmers’ income
Essence: There are three-pronged principle in doubling farmers’ income i.e., when yields rise, cost of production falls and when they receive remunerative prices. But a three-year action research project, it was found that farmers’ income goes up when site specific farm models are evolved and executed through participatory methods. Agricultural universities and the agriculture departments were co-opted for providing technical inputs, backstopping and capacity building. The underpinning of the project was ‘convergence’ with the existing government programs and involving banks for providing loans but convergence happened to some extent only. Because each agency is used to working in silos and there are no empowered agencies to converge, integrate and run missions. Farmers face several risks and availability of comprehensive farmers’ data at one place is an issue. Primary grading, primary processing and creation of storage facilities help. This is where the role of banks, NBFCs and FPOs (farmer producer organizations) kicks in. There are many companies that are involved in manufacturing and marketing of agricultural inputs. Requisitioning them to design and implement projects that will help double farmers’ income under their CSR (corporate social responsibility) initiatives will be a game changer.
Why you should read this article?
- To understand why convergence of project with existing government programs and involving banks happened to some extent only.
- To understand the issues faced by farmers and how banks and companies can help.
Article Link: https://www.thehindubusinessline.com/opinion/the-key-to-doubling-farmers-income/article34544434.ece
Agriculture Reforms: Innovative ways via which Israel is feeding the world
Present Situation:
- Food security is a critical concern as the global population expands and natural resources dwindle.
- So, smart solutions for more efficient farming like the hardier crops, alternative sources of nutrition, and safer food packaging and storage are essential.
- Israel is leading the way and has contributed the breakthroughs and converted ways to green their own desert
Best Practises adopted by Israel:
- Drip Irrigation: Israel has revolutionized the idea by promoting the technology of Tipa (Drop) by using a kit that enables gravity to irrigate when there is no water pressure in rural areas. The kit has been provided to famers in rural areas of Senegal, Kenya, South Africa etc.
- Getting more grain to market: About one-third of the food produced for human consumption globally is lost or wasted each year. Israel has invented the bag that keep both water and air out to reduce the food loss. They’re used in about 100 countries including in Africa, Latin America and the Middle and Far East.
- Precision Agriculture: Israel uses advanced level data for precision agriculture like accurate tests of plant tissue, soil and water in the field, nutrient requirements of crops. This help in dealing with the scare resources.
- Squeezing every drop of water from the air by Tal-Ya Water Technology that makes use of plastic tray to collect dew from the air, reducing the water needed by crops or trees by up to 50 percent.
- Hardier seeds for better crops by seed breeding by making seeds more nutritious, high-yield and resistant to drought.
Outcome:
- More crops despite scarcity of resources in desert like condition like scarce water, scare fertile land etc
- Climate Smart Agriculture is being practised by using technological based intervention like drought prone resistant seeds
- Reducing the wastage of food which can be utilised the hungry population
Where can we use this case study:
- As an example of use of technology in food production, example to conserve water, fertilizers, pesticide etc, creating climate smart agriculture like drought prone resistance seeds, hardy crops etc
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.