Monday, 17th May 2021
India received $83 billion in remittances in 2020: World Bank report
According to the World Bank findings on global remittances, India received over USD 83 billion in remittances in 2020, a drop of just 0.2 per cent from the previous year, despite the Covid 19 pandemic.
Ranking of countries based on remittances
|
Country |
Remittance |
|
India |
83 billion |
|
China |
59.5 billion |
|
Mexico |
42.8 billion |
|
Philippines |
34.9 billion |
|
Egypt |
29.6 billion |
Global trends regarding remittances
- Regions that witnessed rise in remittances: Latin America and the Caribbean, South Asia and the Middle East and North Africa.
- Regions that witnessed decline in remittances: East Asia and Pacific, Europe, and Central Asia, and for Sub-Saharan Africa.
Factors that contributed to the steady remittance flow globally
- Fiscal stimulus: The main factor is the fiscal stimulus that was announced by several countries to relieve their economies from the Covid induced slowdown.
- Digital payments: shift in flows from cash to digital form. This has helped the economy to transition to more formal channels.
- Oil prices and currency exchange rates: The cyclical movements in oil prices and currency exchange rates are also responsible for aiding the steady remittance flow.
Significance of remittances during the pandemic
- Importance of remittances for households: Households in migrants’ origin countries use remittances for various purposes. Households use remittances to support income, purchase assets, and invest in businesses.
- Remittances act as insurance: specially when they are experiencing some sort of economic shock.
- Remittance and foreign exchange: International remittances often account for a large share of foreign exchange earnings and help countries that are facing foreign exchange shortages.
- Remittance and investment: Remittance helps to finance development and reduce macroeconomic volatility, thereby encouraging more investment. Remittances contribute to higher consumption spending and the accumulation of physical capital and productive capacity by reducing the cost of capital.
Sources:
Report of the Independent Panel for Pandemic Preparedness and Response
In News
An Independent Panel for Pandemic Preparedness and Response was formed by the WHO last year to examine the pandemic preparedness prior to Covid 19, the cause and circumstances leading to the Covid 19 outbreak and the response to the disease nationally, regionally, and globally. The panel has also analysed the wide-ranging impacts of the pandemic on health and health systems, and the social and economic crises that it has precipitated.
What are the problems in the global pandemic response as identified in the report?
- Disjointed and limited pandemic preparedness: Limited and disjointed health systems were easily overwhelmed when confronted by a fast-spreading virus. Closing the gap in preparedness not only requires sustained investment but also new kinds of leadership dimensions. The panel also pointed to the need for improved accountability globally through a system of universal periodic peer review of country preparedness.
- Absence of a fast response of the international alert system: International alert system does not operate with sufficient speed when faced with a fast-moving pathogen that does not obey national borders. The declaration of a Public Health Emergency of International Concern by the WHO in January 2020 did not lead to swift response by the countries.
- Uncoordinated approach in some countries: Countries where the response to the pandemic was poor were usually those that had an uncoordinated approach, that devalued science, denied the potential impact of the pandemic, delayed comprehensive action, and allowed distrust to undermine efforts. They had insufficient capacity to mobilise rapidly and coordinate between national and subnational responses.
- Pandemic response has not addressed the growing inequalities: COVID-19 has been a pandemic of inequality with the impact being particularly severe on people who are already marginalised and disadvantaged. Inequality has been a determining factor in explaining why the COVID-19 pandemic has had such differential impacts on peoples' lives and livelihoods. The unwillingness of the global community to tackle inequalities and an uncoordinated response system allowed the pandemic to create a socio-economic crisis.
What kind of practices need to be adopted to develop a robust pandemic response?
- Combining a spectrum of responses: The panel found that countries that performed well with respect to the pandemic, combined several responses including timely identification, contact tracing, designation of isolation facilities. These countries also combined responses across multiple levels of government sectors and engaged with community health workers, community leaders as well as the private sector.
- Open data and open science collaboration: The panel has recommended that open data and open science are central to the Covid 19 response system. For example, sharing of the genome sequence of the novel coronavirus on an open platform quickly led to the most rapid creation of diagnostic tests and helped in the development of vaccines.
What are the short-term measures that can be taken up globally to deal with the pandemic?
- High-income countries to ramp up their assistance efforts: They should, alongside their scale-up, commit to provide vaccines to low and middle-income countries.
- Technology transfer: Major vaccine-producing countries and manufacturers should convene, under the joint auspices of WHO and the World Trade Organization, to agree to voluntary licensing and technology transfer with intellectual property rights to be waived for a limited period for the benefit of low-income countries.
- Develop regional capacities: The panel also recommended the need to establish stronger regional capacities for manufacturing, regulation, and procurement of needed tools for equitable and effective access to vaccines, therapeutics, and essential supplies.
Conclusion
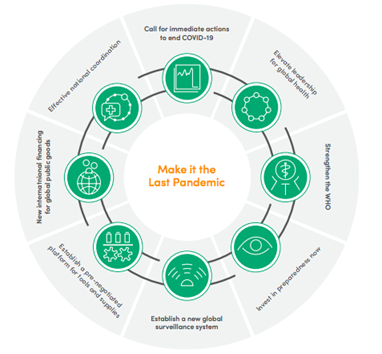
To prepare the world for a future disease outbreak, the panel called for a series of crucial reforms. These include coordinated leadership globally and nationally, WHO’s independence and better access to global public goods.
Question: Covid 19 has highlighted not only the uncoordinated global response to pandemics but also the role of poverty and inequality in determining health outcomes. Discuss.
Sources
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(21)01095-3/fulltext
Second World Ocean Assessment (WOA)
In News
The Second World Ocean Assessment (WOA - II) was released by the United Nations.
About the WOA - II
- WOA II is a comprehensive overview of the state of the ocean and the relationships between the ocean and humans, covering environmental, social, and economic aspects.
- It is the newest outcome of the only integrated assessments of the world’s ocean at the global level along all three pillars of sustainable development (economic viability, environmental protection and social equity).
- The assessment informs the critical work taking place during the UN Decade of Ocean Science for Sustainable Development (2021 to 2030) and the soon to be launched UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration (2021 to 2030) – both established to address the growing need for knowledge and capacity to safeguard the health of and improve people’s relationship with the natural environment.
- The first assessment (WOA-I), which was released in 2015, established a baseline for measuring the state of marine environment, including socioeconomic aspects. WOA II focuses on trends observed since the publication of WOA I and current gaps in knowledge and capacity.
Coastal and Marine Ecosystem
- The coastal and marine ecosystems of the world are composed of oceans and major seas which make up 8% of the Earth and cover an area of 362 million sq km., and span a coastline measuring 1.6 million km.
- The ocean forms 95% of the biosphere. Changes in the ocean drive weather systems that influence both land and marine ecosystems.
- The ocean and its ecosystems provide significant benefits to the global community, including climate regulation, coastal protection, food, employment, recreation, and cultural well-being.
- Those benefits depend, to a great extent, on the maintenance of ocean processes, marine biological diversity, and related ecosystem services.
Key Takeaways from WOA - II on the State of the Ocean
- The alarming pace of sea-level rise, combined with increasing storms and coastal urbanization, has led to coastal erosion and flooding in coastal cities.
- Rising carbon dioxide emissions have led to ocean acidification and together with warming and deoxygenation resulted in loss of biological diversity.
- The ocean heat content has more than doubled since the 1990s, severely affecting marine life and ecosystems.
- The number of “dead zones” or areas with reduced oxygen in the ocean has increased from more than 400 globally in 2008 to about 700 in 2019.
- Around 90% of mangrove, seagrass, and marsh plant species — as well as 31% of species of seabirds — are now threatened with extinction.
- Marine litter is present in all marine habitats, affecting the environment and marine organisms through entanglement, ingestion and rafting of invasive species.
- Overfishing is estimated to have led to an annual loss of $88.9 billion in net benefits.
- Human-mediated movements have introduced about 2,000 marine non-indigenous invasive species, some of which pose significant biosecurity and biodiversity hazards.
- Approximately 15% of all sandy beaches worldwide are seeing retreating shorelines at an average trend of 1 m/year or more over the last 33 years.

Drivers of Changes in Ocean System
- Population growth and demographic changes: The extent to which an increasing global population places pressure on the marine environment varies, depending on a range of factors, including where and how people live, their consumption patterns and technologies used to produce energy, food, and materials, provide transport and manage waste.
- Economic activity: Many countries have developed, or are developing, strategies for growing ocean-based economies (the blue economy). However, an important constraint on the growth of ocean economies is the current declining health of the ocean and the pressures being placed on it.
- Technological advances: Advances in technology continue to increase efficiency, expand markets, and enhance economic growth. Innovations have enabled both positive outcomes (such as increasing efficiencies in energy generation) and negative (such as overcapacity in fisheries) outcomes for the marine environment.
- Changing governance structures and geopolitical instability: At both the international and national levels, improved methods of cooperation and implementation of effective policies across some regions have contributed to reducing some pressures on the ocean.
- However, in regions where there is conflict over access to resources and maritime boundaries, policies and agreements focused on sustainability can be undermined.
- Climate change: Rising anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions causing long-term climate changes, with widespread effects throughout the ocean that will persist for centuries and affect the ocean. The impacts of climate change have been recognized by the Paris Agreement of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change.
Conclusion
According to the WOA, analysis of the impacts of pressures and their cumulative effects remains limited, consequently leading to a general failure to understand, safeguard and put in place an integrated management of the ocean and coasts. Going forward, further advancing ocean science and technology, and ensuring a robust science-policy interface are critical to achieving sustainable ocean management.
Question: Analyse the changes in marine and coastal ecosystem which have happened as a result of anthropogenic interference.
Primary References:
https://www.un.org/regularprocess/sites/www.un.org.regularprocess/files/2011859-e-woa-ii-vol-i.pdf
https://environmentlive.unep.org/media/docs/assessments/WOA_screen.pdf
Secondary References
https://www.grida.no/resources/8130
https://www.un.org/regularprocess/sites/www.un.org.regularprocess/files/2011859-e-woa-ii-vol-ii.pdf
https://geographyandyou.com/coastal-marine-ecosystems-india/
https://uneplive.unep.org/media/docs/assessments/WOA_screen.pdf
https://www.futureearthcoasts.org/second-world-ocean-assessment/
http://eprints.cmfri.org.in/10406/1/01_KK_JOSHI_2.pdf
https://www.cbd.int/doc/meetings/mar/ebsaws-2015-02/other/ebsaws-2015-02-template-india-en.pdf
This Day in History - World Telecommunication Day
World Telecommunication Day is celebrated annually on 17 May since 1969, marking the founding of ITU and the signing of the first International Telegraph Convention in 1865. It was instituted by the Plenipotentiary Conference in Malaga-Torremolinos in 1973. The purpose of World Telecommunication and Information Society Day (WTISD) is to help raise awareness of the possibilities that the use of the Internet and other information and communication technologies (ICT) can bring to societies and economies, as well as of ways to bridge the digital divide. The theme of World Telecommunication Day 2021 is: Accelerating digital transformation in challenging times.

Source: https://www.un.org/en/observances/telecommunication-day
Image of the Day-Subdoluseps nilgiriensis
This is the image of new species of skink found from Western Ghats. Named Subdoluseps nilgiriensis, after the Nilgiris, the reptile has a slender body of just about 7 cm and is sandy brown in colour. The new species was found in a dry deciduous area, unlike high biodiversity areas in the wet and evergreen forests. Most skinks are diurnal and are usually secretive in their habits. Because of their elusiveness, not much is known about their natural and evolutionary history. Most of the species are placed under the data-deficient category. Subdoluseps nilgiriensis is currently considered a vulnerable species as there are potential threats from seasonal forest fires, housing constructions and brick kiln industries in the area.

Basava Jayanti
- Context: Jagadguru Basaveshwara’s 890th birth anniversary.
- Lord Basaveshwara was a Lingayat saintand social reformer during the 12th century AD from Bijapur, Karnataka. He is known for the establishment of a Parliament type edifice - the Anubhava Mantapa, to create an egalitarian society.
- Basavanna, like Gautama Buddha,taught people how to live happily in a rational social order which later came to be known as the Sharana movement. He believed that man becomes great not by his birth but by his conduct in the society. He fought against the inhuman practice of the caste system. He taught the dignity of manual labor by insisting on work as worship.

Primary source: https://khened.blogspot.com/2020/04/basava-jayanti-birth-anniversary-of.html
SWAMIH Fund
- Context: Ministry of Finance’s Special Window for Affordable and Mid-Income Housing (SWAMIH) fund has completed its first residential project.
- The SWAMIH fund was set up in 2019, to provide priority debt financing for the completion of stalled housing projects that are in the Affordable and Middle-Income Housing sector.
- It will be managed by SBICAP Ventures Limited (SVL).
- All affordable and middle-income housing projectsthat are:
- Net worth positive
- Registered with the Real Estate Regulatory Authority (RERA)
- That have not been deemed liquidation-worthy and
- Stuck projects classified as Non-Performing Assets and those undergoing resolution under the National Company Law Tribunal will be eligible for funding.
- The fund bridges the gap between homebuyers and developers by completing construction without depending on any other source of finance.

Primary source: https://pib.gov.in/Pressreleaseshare.aspx?PRID=1590799
https://realtyplusmag.com/swamih-to-provide-funding-at-12-irr/
Red Eared Slider Turtle
- Context: Native Indian turtles face threat from invasive Red Eared Slider Turtles in North-East India.
- Red Eared Slider Turtle derives its name from red stripes around the part where its ears would be and from its ability to slide quickly off any surface into the water.
- Native to U.S. and northern Mexico, this turtle is a popular pet due to its small size, easy maintenance, and relatively low cost.
- Since it is an invasive species, it grows fast and leaves nothing for the native species to eat, thus having a negative impact on the areas they invade.
- The Northeast region of India is home to more than 72% of the turtle and tortoise species in the country and the invasive red-eared slider could become a major threat to the biodiversity of water bodies in this region. They can impact human health as these species may accumulate toxins in their tissues which pass on with the food chain to humans.

Primary source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/other-states/native-indian-turtles-face-us-slider-threat-across-northeast/article34555420.ece
https://www.redearedslider.net/indoor-aquarium-compatible-tankmates/
https://www.petful.com/other-pets/how-care-for-aquatic-turtles/
Global COVAX Alliance
- Context: Punjab Cabinet decides to join the Global COVAX Alliance as the first India State to do so.
- Abbreviated as COVAX, the COVID-19 Vaccines Global Access is a worldwide initiative aimed at providing equitable access to anti-Covid vaccines.
- COVAX is co-led by the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI), Gavi and the World Health Organization (WHO), alongside key delivery partner UNICEF.
- It aims at accelerating the development and manufacture of COVID-19 vaccines and to guarantee fair and equitable access for every country in the world.

Primary source: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/india/punjab-to-join-global-covax-alliance-to-procure-anti-covid-vaccines/articleshow/82606084.cms
Restructuring the tribunals system
Essence: The Tribunals Reforms (Rationalisation and Conditions of Service) Ordinance 2021, which abolished several appellate tribunals and authorities and transferred their jurisdiction to other existing judicial bodies, has been challenged in the Supreme Court. This article highlights the major criticism of the ordinance and emphasise on establishing a National Tribunals Commission (NTC).
Why you should read this article?
- Learn about the major criticism of the ordinance such as bypassing the usual legislative process, disregard for stakeholder consultation, absence of any judicial impact assessment, and no reference to a National Tribunals Commission (NTC), among others.
- Understand the need for establishing a NTC vide a constitutional amendment or backed by a statute that guarantees it functional, operational, and financial independence.
- Identify the major functions which the NTC could perform, and its advantages.
The road from Ladakh is paved with disruptions
Essence: In the context of the ongoing pandemic, the editorial discusses India-China relations and the threats to India's overall geopolitical strategy, as well as how the situation on the LAC is far from normal. With the PLA troops denying India access to territories it controlled by patrolling, the government’s avowed aim of restoring the status quo ante as of April 2020 remains unfulfilled.
Due to ongoing crises at home, Indian government has backtracked from existing commitments to supply vaccines to its friendly neighbours. Countries such as Bangladesh and Sri Lanka have started procuring vaccines from China, further casting doubts on India’s reliability as a partner and raising questions about its ability to act as a counter to China. Sensing the opportunity, Beijing also moved in quickly, organising a meeting with all South Asian countries except India, ostensibly to deal with the pandemic. A weaker India is not only less attractive as a partner globally, it makes New Delhi more dependent on the United States to deal with China. With the imminent American military withdrawal from Afghanistan and a win for the Taliban, the signs are ominous.
Why you should read this?
- To gain a better understanding of the problems that India faces on India China border in Ladakh, as well as the steps taken in this regard over the past year.
- To learn about the specifics of significant hotspots of conflict between India and China on the LAC, as well as their current status.
- To comprehend the effect of the Covid crisis on India's regional power status.
Article Link: https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/lead/the-road-from-ladakh-is-paved-with-disruptions/article34574297.ece
Baba Amte: Example of Compassion
About Baba Amte
- He was a social activist who devoted his life to India’s poorest and least powerful
- He took utmost care of those individuals who suffered from
- For his work he received, 1988 UN Human Rights Prize and 1999 Gandhi Peace Prize.
Story Behind the scenes: Change of heart
- Baba Amte abandoned his legal career in the 1940s and settled in Gandhi’s ashram in Sewagram, Maharashtra, India, working among the downtrodden.
- After an encounter with a man suffering from advanced leprosy, Amte’s attention turned to that disease
- In 1949 Baba Amte founded Anandwan, an ashram dedicated to the treatment, rehabilitation, and empowerment of leprosy patients.
- The centre came to encompassprograms in health care, agriculture, small-scale industry, and conservation and to serve people with disabilities over time.
Value showcased by Baba Amte:
- Compassion, Empathy, Antodaya
Where can this case study be used:
- Lessons learnt from the leaders, Ethical value upheld by Baba Amte, as an example of compassion, empathy
Thinks to ponder: How will you as a civil servant inculcate such values.
https://www.beaninspirer.com/murlidhar-devidas-amte-indian-social-activist-angel-leprosy-survivors/
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.